Intraoperative Details Of Turbt
In most cases, general or regional anesthesia must be used to establish nerve paralysis, to minimize risk of obturator nerve reflex and subsequently, bladder perforation.
Complete eradication of tumor is the first step in TURBT. Most tumors are papillary and are easily removed by endoscopically transecting their narrow stalk or base. Following this, biopsy of the base or deeper resection is performed to ensure complete removal and the absence of invasion. The goal is that muscle tissue must is present in the base biopsy specimen to ensure accurate staging.
Medium and large tumors are resected in a controlled serial fashion prior to transection of the stalk. This ensures that large segments do not remain that might be too large to evacuate through the resectoscope.
Smaller and more friable tumors may be removed at least partially by knocking off fragments with the cutting loop of the resectoscope without the electricity turned on. This sometimes allows partial removal with less risk of bladder perforation.
Pulling the cutting loop away from the tumor is generally much safer than pushing it toward the tumor. Lifting the tumor away from the surrounding normal bladder tissue using the cutting loop is also advisable.
Transurethral resection syndrome, which results from absorption of electrolyte-free irrigating fluid, has become uncommon since the advent of bipolar resectoscopes, which utilize normal saline irrigation.
Treatment Of Stage Iv Bladder Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage IV bladder cancer that has not spread to other parts of the body may include the following:
- Urinary diversion or cystectomy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
Treatment of stage IV bladder cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, such as the lung, bone, or liver, may include the following:
- External radiation therapy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Urinary diversion or cystectomy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- A clinical trial of new anticancer drugs.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Cancer May Spread From Where It Began To Other Parts Of The Body
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if bladder cancer spreads to the bone, the cancer cells in the bone are actually bladder cancer cells. The disease is metastatic bladder cancer, not bone cancer.
Recommended Reading: Botox Dose For Overactive Bladder
Transurethral Resection Of Bladder Tumour
This information is designed to help you, your family and friends prepare for your surgery. It will also help you plan how to take care of yourself in the weeks following discharge from hospital.
The bladder sits low within the pelvis and stores urine. It has two ureters that join to it from above, that transport urine from the kidneys. The urethra exits from the bottom of the bladder and through this, urine is passed to empty the bladder.
The Urologist has determined from the various tests you have had that it is likely that you have a bladder tumour and that surgical removal of the cancer is required.
Types Of Surgical Techniques
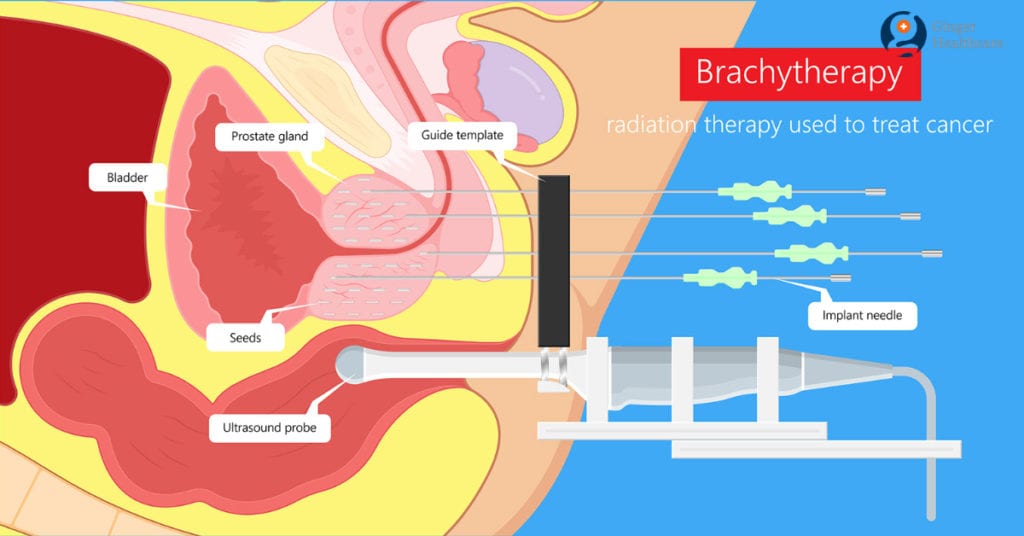
- Endoscopic surgery: A thin, flexible tube equipped with a camera and surgical tools is inserted into a natural opening so no incision is made in the skin.
- Keyhole surgery: This minimally invasive procedure involves several small incisions in the skin to access the bladder, and the cancer is removed through these holes using special instruments.
- Robotic surgery: Similar to keyhole surgery, robotic surgery differs in that the actual surgery is done via mechanized instruments instead of a surgeon’s hands controlling the instruments.
- Open surgery: With an open approach, a traditional large incision is made in the abdomen to access the bladder.
You May Like: How Do Males Get Bladder Infections
Trans Urethral Removal Of Bladder Tumour
A trans urethral resection of bladder tumour is usually the first treatment you have for early bladder cancer.
Your surgeon removes the tumour in your bladder through the urethra. The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of your body.
You might have TURBT to remove early bladder cancer:
- during a cystoscopy test if your specialist sees a tumour
- after having tests that have shown a bladder tumour
You usually have it under general anaesthetic, which means you are asleep. In some hospitals, you may have a spinal anaesthetic instead of a general anaesthetic. This is an injection into your spine so you cant feel anything from below your waist.
This treatment takes between 15 to 90 minutes.
What Is A Continent Cutaneous Pouch
An internal storage container for urine. Using a combination of small and large intestine, the urologist reconstructs the tubular shape of the intestine and creates a sphere or pouch. This pouch is connected to the skin on the abdomen by a small stoma creating a type of continent urinary reservoir no external bag is necessary. The patient drains the pouch periodically by inserting a catheter through the small stoma and then removing the catheter and, in some cases, covering the stoma with a bandage.
Read Also: Can Stress Cause Overactive Bladder
Patients May Want To Think About Taking Part In A Clinical Trial
For some patients, taking part in a clinical trial may be the best treatment choice. Clinical trials are part of the cancer research process. Clinical trials are done to find out if new cancer treatments are safe and effective or better than the standard treatment.
Many of today’s standard treatments for cancer are based on earlier clinical trials. Patients who take part in a clinical trial may receive the standard treatment or be among the first to receive a new treatment.
Patients who take part in clinical trials also help improve the way cancer will be treated in the future. Even when clinical trials do not lead to effective new treatments, they often answer important questions and help move research forward.
How Turbt Is Done
This surgery is done using an instrument put in through your urethra, so it there’s no cutting into the abdomen . You’ll get either general anesthesia or regional anesthesia .
A type of thin, rigid cystoscope called a resectoscopeis put into your bladder through your urethra. The resectoscope has a wire loop at the end that’s used to remove any abnormal tissues or tumors. The removed tissue is sent to a lab for testing.
After the tumor is removed, more steps may be taken to try to ensure that the cancer has been completely destroyed. For instance, the tissue in the area where the tumor was may be burned while looking at it with the resectoscope. This is called fulguration. Cancer cells can also be destroyed using a high-energy laser through the resectoscope.
Don’t Miss: How To Control Bladder Leakage
How Is Bladder Tumor Biopsy And Resection Performed
You may have general anesthesia for this procedure, which means youll be asleep for it. Some providers might use regional anesthesia, which means youll be awake. However, you wont feel any pain.
Bladder tumor biopsy and resection is performed when a doctor inserts a rigid instrument called a resectoscope into the bladder through the urethra. Inserting the resectoscope in this way means that no incisions are necessary.
Your provider will use the resectoscope to remove the tumor, which will be sent to a pathology lab for testing. Once the tumor is removed, your doctor will attempt to destroy any remaining cancer cells by burning the area using electric current by a process called fulguration or cauterization.
Your provider may decide to insert some type of chemotherapy medicine into the bladder using the scope. This is called intravesical chemotherapy. Your provider might suggest that you have maintenance intravesical chemotherapy for a period of time, meaning that you’ll have regular treatments.
Remission And The Chance Of Recurrence
A remission is when cancer cannot be detected in the body and there are no symptoms. This may also be called having no evidence of disease or NED.
A remission may be temporary or permanent. This uncertainty causes many people to worry that the cancer will come back. While many remissions are permanent, it is important to talk with your doctor about the possibility of the cancer returning. Understanding your risk of recurrence and the treatment options may help you feel more prepared if the cancer does return. Learn more about coping with the fear of recurrence.
If the cancer returns after the original treatment, it is called recurrent cancer. It may come back in the same place , nearby , or in another place .
When this occurs, a new cycle of testing will begin again to learn as much as possible about the recurrence. After this testing is done, you and your doctor will talk about the treatment options.
People with recurrent cancer often experience emotions such as disbelief or fear. You are encouraged to talk with the health care team about these feelings and ask about support services to help you cope. Learn more about dealing with cancer recurrence.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Calm An Overactive Bladder
Palliative Or Supportive Care
If your cancer is at an advanced stage and can’t be cured, your medical team should discuss how the cancer will progress and which treatments are available to ease the symptoms.
You can be referred to a palliative care team, who can provide support and practical help, including pain relief.
Page last reviewed: 01 July 2021 Next review due: 01 July 2024
Urinary Diversion Surgery Options
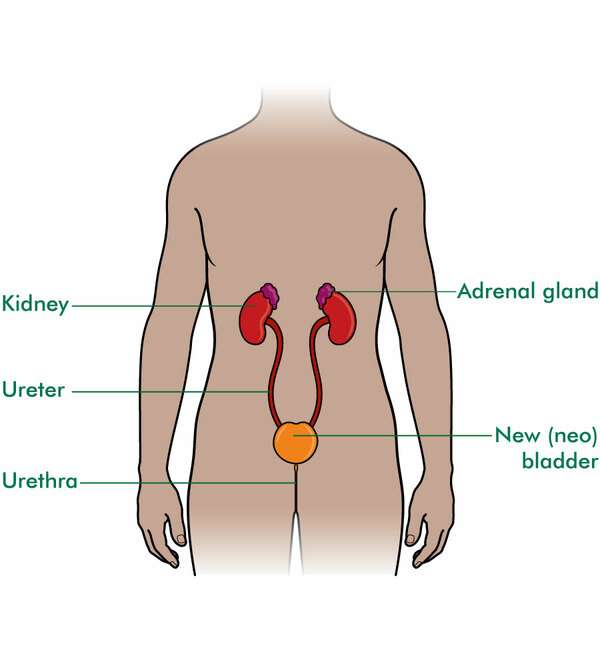
When the entire bladder is removed, an alternative way to remove urine from the body is needed. The three different procedure options are:
Complications are not uncommon with any of these procedures, and a careful discussion with your healthcare team is needed to make the right choice for you alone.
Read Also: How To Train A Weak Bladder
Treating Stage I Bladder Cancer
Stage I bladder cancers have grown into the connective tissue layer of the bladder wall , but have not reached the muscle layer.
Transurethral resection with fulguration is usually the first treatment for these cancers. But it’s done to help determine the extent of the cancer rather than to try to cure it. If no other treatment is given, many people will later get a new bladder cancer, which often will be more advanced. This is more likely to happen if the first cancer is high-grade .
Even if the cancer is found to be low grade , a second TURBT is often recommended several weeks later. If the doctor then feels that all of the cancer has been removed, intravesical BCG or intravesical chemo is usually given. If all of the cancer wasn’t removed, options are intravesical BCG or cystectomy .
If the cancer is high grade, if many tumors are present, or if the tumor is very large when it’s first found, radical cystectomy may be recommended.
For people who arent healthy enough for a cystectomy, radiation therapy might be an option, but the chances for cure are not as good.
There Are Three Ways That Cancer Spreads In The Body
Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood:
- Tissue. The cancer spreads from where it began by growing into nearby areas.
- Lymph system. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the lymph system. The cancer travels through the lymph vessels to other parts of the body.
- Blood. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through the blood vessels to other parts of the body.
Also Check: Sodium Bicarbonate For Bladder Infection
Sexual Effects Of Radical Cystectomy In Women
This surgery often removes the front part of the vagina. This can make sex less comfortable for some women, though most of the time it’s still possible. One option is to have the vagina rebuilt . There’s more than one way to do this, so talk with your surgeon about the pros and cons of each method. Whether or not you have reconstruction, there are many ways to make sex more comfortable.
Radical cystectomy can also affect a womans ability to have an orgasm if the nerve bundles that run along each side of the vagina are damaged. Talk with your doctor about whether these nerves can be left in place during surgery.
If the surgeon takes out the end of the urethra where it opens outside the body, the clitoris can lose some of its blood supply, which might affect sexual arousal. Talk with your surgeon about whether the end of the urethra can be spared.
For more on ways to cope with these and other sexual issues, see Sex and the Woman With Cancer.
After Bladder Cancer Has Been Diagnosed Tests Are Done To Find Out If Cancer Cells Have Spread Within The Bladder Or To Other Parts Of The Body
The process used to find out if cancer has spread within thebladder lining and muscle or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment. The following tests and procedures may be used in the staging process:
Also Check: Oregano Oil For Bladder Infection
Smoking Can Affect The Risk Of Bladder Cancer
Anything that increases your chance of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer not having risk factors doesn’t mean that you will not get cancer. Talk to your doctor if you think you may be at risk for bladder cancer.
Risk factors for bladder cancer include the following:
- Using tobacco, especially smoking cigarettes.
- Having a family history of bladder cancer.
- Having certain changes in the genes that are linked to bladder cancer.
- Being exposed to paints, dyes, metals, or petroleum products in the workplace.
- Past treatment with radiation therapy to the pelvis or with certain anticancer drugs, such as cyclophosphamide or ifosfamide.
- Taking Aristolochia fangchi, a Chinese herb.
- Drinking water from a well that has high levels of arsenic.
- Drinking water that has been treated with chlorine.
- Having a history of bladder infections, including bladder infections caused by Schistosoma haematobium.
- Using urinarycatheters for a long time.
Older age is a risk factor for most cancers. The chance of getting cancer increases as you get older.
Physical Emotional And Social Effects Of Cancer
Cancer and its treatment cause physical symptoms and side effects, as well as emotional, social, and financial effects. Managing all of these effects is called palliative care or supportive care. It is an important part of your care that is included along with treatments intended to slow, stop, or eliminate the cancer.
Palliative care focuses on improving how you feel feels during treatment by managing symptoms and supporting patients and their families with other, non-medical needs. Any person, regardless of age or type and stage of cancer, may receive this type of care. And it often works best when it is started right after an advanced cancer diagnosis. People who receive palliative care along with treatment for the cancer often have less severe symptoms, better quality of life, report that they are more satisfied with treatment, and they may live longer.
Palliative treatments vary widely and often include medication, nutritional changes, relaxation techniques, emotional and spiritual support, and other therapies. You may also receive palliative treatments similar to those meant to get rid of the cancer, such as chemotherapy, surgery, or radiation therapy.
Before treatment begins, talk with your doctor about the goals of each treatment in the treatment plan. You should also talk about the possible side effects of the specific treatment plan and palliative care options.
Read Also: Best Herbs For Bladder Health
Permission To Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text. It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. However, a user would be allowed to write a sentence such as NCIs PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks in the following way: .
The best way to cite this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Adult Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Bladder Cancer Treatment. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated < MM/DD/YYYY> . Available at: . Accessed < MM/DD/YYYY> .
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author, artist, and/or publisher for use in the PDQ summaries only. If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in Visuals Online. Visuals Online is a collection of more than 3,000 scientific images.
Treatment Of Recurrent Bladder Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of recurrentbladder cancer depends on previous treatmentand where the cancer has recurred. Treatment for recurrent bladder cancer mayinclude the following:
- Radiation therapy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- A clinical trial of a new treatment.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Don’t Miss: Catheterizing The Female Urinary Bladder