What Happens To The Prostate After Radiation
The entire prostate gland is radiated when we treat the cancer. The prostate normally produces some of the fluid in the ejaculation. Radiation therapy has the side effect of damaging the glands in the prostate, so a lot less fluid is produced. The ejaculation may be dry or nearly dry. In addition, you will probably be sterile after radiation, but this is not 100% guaranteed and should not be relied upon as a form of birth control. You can still usually have erections because the nerves and blood vessels that go to the penis are not as damaged as the prostate gland.
The prostate gland will end up having a lot of scar tissue. It will shrink in size to about half its original weight within a couple years after finishing radiation. The urethra passes through the canter of the prostate gland like the hole of a doughnut. Sometimes this passage can widen, other times it can shrink after radiation. In summary, the prostate gland is heavily damaged from radiation and does not work normally afterwards.
Managing Bone Pain And Weakness
Symptoms like nausea, hot flashes, and pain can usually be relieved with medication. Some people find that complimentary treatments like acupuncture or massage help manage side effects.
Your doctor may also recommend orthopedic surgery to stabilize your bones, relieve pain, and help prevent bone fractures.
Focal Therapy For Prostate Cancer
With recent advances in MRI and targeted biopsy, we are better able to locate the exact area of prostate cancer. Men who do not have an enlarged prostate, who have prostate cancer that is detected only in a single region of the prostate and have intermediate grade cancer can be a candidate for focal therapy. This type of therapy treats only the cancerous tissue and spares the normal prostate, thereby preserving urinary and sexual function
Here at UCLA we commonly use cryotherapy or HIFU to focally treat prostate cancer. Given that this is a relatively new form of treatment, we have established rigorous post-treatment protocols using MRI and biopsies to ensure that the cancer has been adequately treated.
Also Check: Icd 10 Code For Neurogenic Bladder
Recurrent Prostate Cancer Symptoms
Prostate cancer that returns after treatment is considered recurrent. When it returns to the area around the prostate, the disease is classified as a local recurrence. If the cancer is found in another part of the body, the recurrent cancer is considered metastatic. If the cancer metastasizes outside the prostate, it most likely develops in bones first. Metastatic prostate cancer most often spreads to the liver, bones and lungs.
After initial treatment for prostate cancer, PSA levels are expected to drop dramatically. The first sign of recurrent prostate cancer may be a rise in the PSA level. Other symptoms of recurrent cancer may depend on whether and where the cancer has spread. Symptoms include:
- Blood in the urine
- Difficulty breathing
- Jaundice
Patients should discuss any symptoms with their doctor and ask about scheduling regular PSA tests after treatment.
Can Acupuncture Help Treat Cancer
Acupuncture is an ancient Chinese technique used to treat a variety of medical conditions. I do not believe that Acupuncture can cure cancer, though I believe it might help manage some treatment related side effects like fatigue, discomfort and mental well being. Cancer cells are derived from our normal cells but grow in an uncontrolled way. Acupuncture cannot kill these cells nor does any data suggest it can.
Recommended Reading: Why Do I Get Recurring Bladder Infections
What Happens If My Cancer Starts To Grow Again
Your first treatment may help keep your cancer under control. But over time, the cancer may change and it may start to grow again.
You will usually stay on your first type of hormone therapy, even if its not working so well. This is because it will still help to keep the amount of testosterone in your body low. But there are other treatments that you can have alongside your usual treatment, to help control the cancer and manage any symptoms. Other treatments include:
Which treatments are suitable for me?
Which treatments are suitable for you will depend on many things, including your general health, how your cancer responds to treatment, and which treatments youve already had. Talk to your doctor or nurse about your own situation, or speak to our Specialist Nurses.
How Can I Choose From Among The Options
In addition to talking with family and friends, you will need a team of physicians to help advise you. It is advisable that you meet with all of the specialists involved in your cancer treatment planning prior to making a decision regarding treatment, including:
- your primary care physician as well as a urologist to discuss surgery
- a radiation oncologist to discuss radiation therapy.
Once you have met with these doctors, you will be able to make a more informed decision regarding your treatment options. If you have an early-stage cancer or moderately advanced cancer and there is no evidence of spread to other organs , the two major options for treatment are surgery or radiation therapy .
If your cancer is advanced and you require hormonal suppression therapy or chemotherapy, then you will also need a medical oncologist, who administers these drugs. Hormone-ablation therapy, which is often used to treat more advanced prostate cancer by suppressing your androgen hormones since most prostate cancer growth is stimulated by androgen or testosterone. The androgen suppression treatment can be administered by your internist, urologist, radiation oncologist or medical oncologist. Depending on the stage of the cancer, hormone suppression therapy may be used in addition to radiation therapy to help control the cancer. Hormone suppression therapy may be administered for as little as four to six months, or for as long as two to three years.
You May Like: Can Overactive Bladder Cause Bloating
What Are The Signs Of Bladder Cancer
The most common sign of bladder cancer is blood in the urine, called hematuria. Gross hematuria is blood that can be seen in the urine. Your urine can be pink, red, or dark red. In some cases, urine can only be seen with a microscope, called microscopic hematuria. Other signs of bladder cancer include increased frequency of urination, a feeling of urgency to urinate, nocturia , pain with urination, and feeling like your bladder is not empty. These can all be caused by irritation of the bladder wall by the tumor, but can also be signs of infection or other bladder problems.
In advanced cases of bladder cancer, the tumor can stop urine from entering the bladder, or from exiting the bladder. This may cause severe flank pain, infection, and damage to the kidneys. Other signs of advanced bladder cancer are loss of appetite, weight loss, feeling tired, bone pain, and swelling in the feet.
Drugs To Treat Cancer Spread To Bone
If prostate cancer spreads to other parts of the body, it almost always goes to the bones first. These areas of cancer spread can cause pain and weak bones that might break. Medicines that can help strengthen the bones and lower the chance of fracture are bisphosphonates and denosumab. Sometimes, radiation, radiopharmaceuticals, or pain medicines are given for pain control.
Side effects of bone medicines
A serious side effect of bisphosphonates and denosumab is damage to the jaw, also called osteonecrosis of the jaw . Most people will need to get approval from their dentist before starting one of these drugs.
Read Also: Can Bladder Sling Cause Uti
What Causes Prostate Cancer And Am I At Risk
Every man is at risk for prostate cancer as he ages. Although prostate cancer can affect younger men, about 6 out of 10 cases are diagnosed in men over the age of 65. The average age of diagnosis is 66. After non-melanoma skin cancer, prostate is the most common cancer diagnosed in men in the United States. The American Cancer Society estimates there will be 248,530 new cases of prostate cancer each year.
Although there are several known risk factors for getting prostate cancer, no one knows exactly why one man gets it and another doesnt. Some important risk factors for prostate cancer are:
Also Check: Is Cranberry Juice Good For Prostate Infection
What Is Advanced Prostate Cancer
When prostate cancer spreads beyond the prostate or returns after treatment, it is often called advanced prostate cancer.
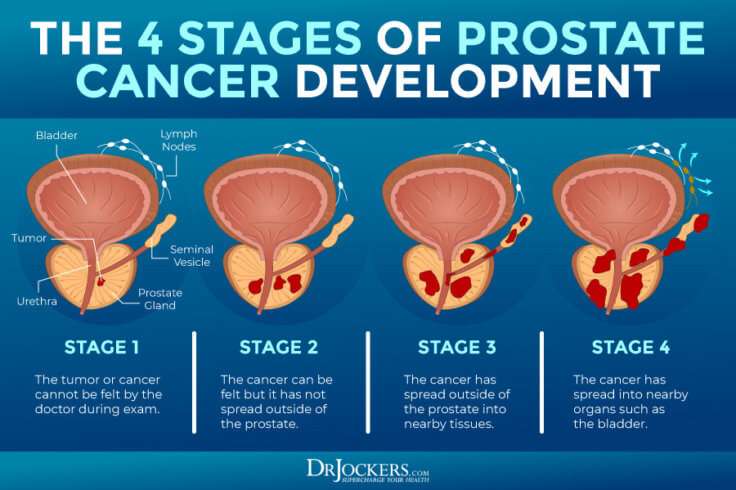
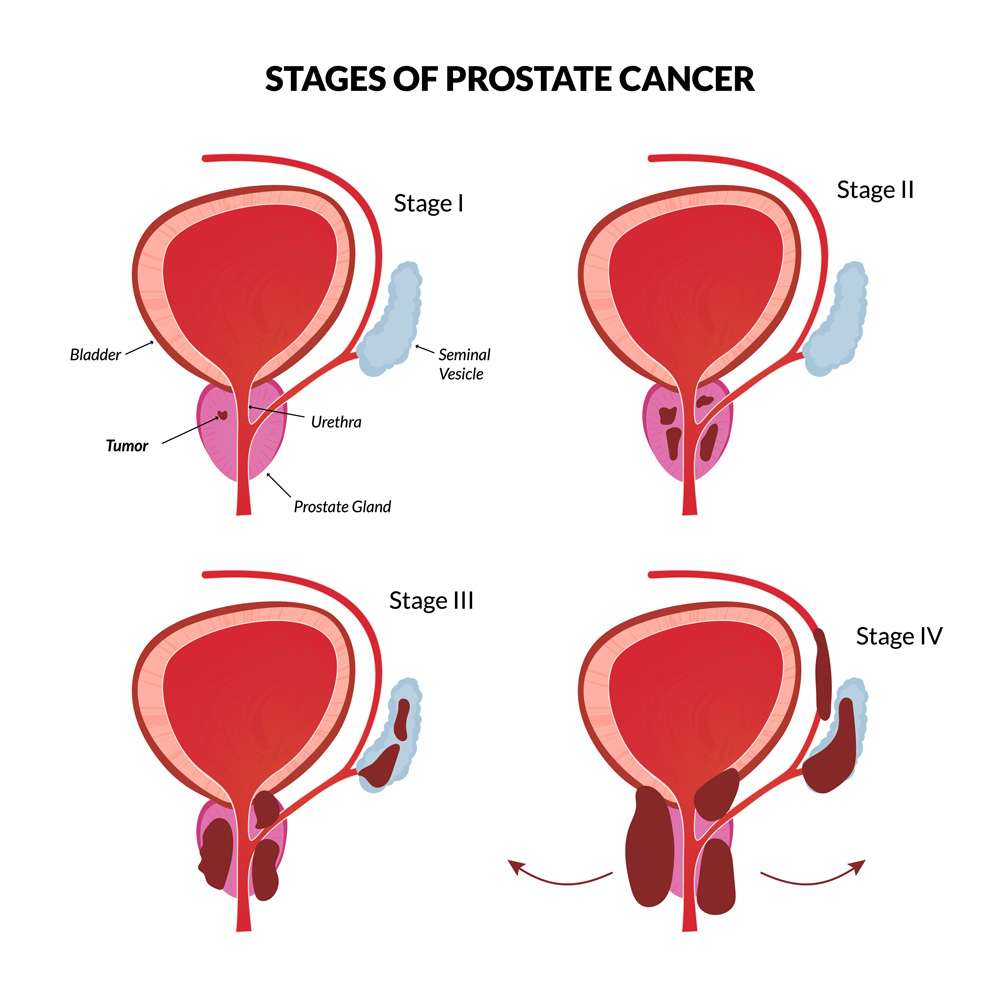
Prostate cancer is often grouped into four stages, with stages III and IV being more advanced prostate cancer.
- Early Stage | Stages I & II: The tumor has not spread beyond the prostate.
- Locally Advanced | Stage III: Cancer has spread outside the prostate but only to nearby tissues.
- Advanced | Stage IV: Cancer has spread outside the prostate to other parts such as the lymph nodes, bones, liver or lungs.
When an early stage prostate cancer is found, it may be treated or placed on surveillance . Advanced prostate cancer is not curable, but there are many ways to treat it. Treatment can help slow advanced prostate cancer progression.
There are several types of advanced prostate cancer, including:
Biochemical Recurrence
With biochemical recurrence, the prostate-specific antigen level has risen after treatment using surgery or radiation, with no other sign of cancer.
Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Non-Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer that no longer responds to hormone treatment and is only found in the prostate. This is found by a rise in the PSA level, while the testosterone level stays low. Imaging tests do not show signs the cancer has spread.
Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Read Also: How Do You Treat A Bladder Infection
What Are The Symptoms Of Advanced Prostate Cancer And Bone Metastases
When cancer cells spread to the bones, the condition weakens the very frame on which the body rests. The cells interfere with the strength and hardness of the bones structure, interrupting its normal cycle of building up and dissolving.
Theres no cure for advanced prostate cancer, but theres a lot that doctors can do to help with the symptoms that might develop. This includes managing pain. A common misconception is that if theres cancer in the bone, there must be pain, Tagawa says. Thats not true. Cancer can be in the bone without pain. However, if there is pain, he says, it can be controlled with anticancer therapies and pain medication, and good quality of life can be maintained.
In addition to pain, some men with bone metastases develop a condition called hypercalcemia, in which, because of the damage to bones from the cancer cells, too much calcium builds up in the blood. Hypercalcemia can make you feel constipated, thirsty, sleepy, or sluggish, and it can increase the urge to urinate, according to the ACS. Over time, hypercalcemia can cause muscle and joint achiness, as well as weakness in the muscles. In advanced stages, it can cause the kidneys to shut down.
There are treatments for hypercalcemia as well as for other complications from advanced prostate cancer, such as bones that become weak and break or fracture, and for growths in the spine that can press on the spinal cord and damage nerves.
Can You Live Without A Prostate
Although the prostate is essential for reproduction, it is not essential to live.
In cases where the cancer is contained to the prostate it can be surgically removed through a prostatectomy.
A radical prostatectomy involves removing the entire prostate gland, the surrounding tissue, and some of the seminal vesicles.
Alternatively, laser prostatectomies can be effective as the least invasive type of prostate removal.
The most common prostatectomy is the transurethral resection of the prostate .
TURPs involve removing part of the prostate gland using a resectoscope which is passed through the urethra – this procedure is commonly used for people with an enlarged prostate.
In come cases prostate cancer can be treated with radiotherapy.
Read Also: How To Fight A Bladder Infection Without Antibiotics
Bowel And Bladder Problems
Radiation therapy for prostate cancer can irritate the bowel, the bladder, or both.
A person can develop:
Radiation proctitis: Symptoms include diarrhea and blood in the stool.
Radiation cystitis: Symptoms include a need to urinate more often, a burning sensation when urinating, and blood in the urine.
Bladder problems may improve after treatment, but they may not go away completely.
What You Need To Know About The Prostate What Happens If Prostate Cancer Spreads
The main purpose of the prostate is to produce semen, a milky fluid that sperm swims in. During puberty, the body produces semen in a large number of cases, including enlarged prostate. This fluid causes the prostate to swell and cause a number of bladder-related symptoms. This is why the prostate is important to the body. It can be caused by many factors, including infection and inflammation.
A enlarged prostate can also cause blockages in the urethra. A blocked urethra can also damage the kidneys. A patient suffering from an enlargement of the prostate may have pain in his lower abdomen and genitals. If pain is present, a digital rectal examination will reveal hard areas. A doctor may prescribe surgery or perform an endoscopic procedure. If the enlarged prostate is not completely removed, it will shrink.
While the size of an enlarged prostate will influence the extent of urinary symptoms, men may experience a range of urinary symptoms. Some men have minimal or no symptoms at all. Some men will have a very enlarged prostate, whereas others will have a mild enlargement. Generally, the symptoms can stabilize over time. Some men may have an enlarged prostate but not notice it. If they have an enlarged colon, their physician can perform a TURP procedure.
Recommended Reading: Doterra Oils For Bladder Infection
Find Efficient Treatment For Prostate Cancer Today
At Comprehensive Urology in the Beverly Grove community of Los Angeles, we concentrate on both medical diagnosis and treatment for prostate cancer treatment in LA. Furthermore, Dr. Michel and his professional group work relentlessly to enhance your results and offer the very best options offered. To get evaluated for prostate cancer, schedule a visit with Comprehensive Urology today. You can schedule by phone or book online today!
Risk Factors For Formation Of Urethral Stenosis And Stricture
Post-radical prostatectomy
Radiotherapy
Risk factors include age, obesity, hypertension, diabetes, previous TURP , longer follow-up, higher radiation dose, HDR-BT, adjuvant RT and combination with BT . Delaying adjuvant RT for more than 9 months after RP may decrease stricture formation, however this is at the expense of an increase in cancer-specific mortality . Zelefsky found that intensity modulated RT increases the risk of late urinary toxicities including urethral stricture compared to 3-D conformal RT, but with lower rectal toxicity . However, a recent review found no difference in urethral stricture between 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy and IMRT . Similar to ERBT, BT strictures affect the bulbomembranous urethra in the majority of cases, which could be due to a âhot spotâ in the distal bulbar urethra or due to caudal needle shifting in patients receiving HDR-BT , although Hindson found no relation between needle shifting and stricture incidence . A prospective, matched-pair analysis by Diez found no association between urethral stricture incidence and urethral dosimetry in patients receiving HDR-RT, however the number of events was too small to draw a definitive conclusion .
Also Check: Why Do I Get Bladder Infections So Easily
Don’t Miss: Average Age Of Bladder Cancer
What Screening Tests Are Used For Bladder Cancer
It is not standard to screen for bladder cancer. Bladder cancer screening may be used in people who are considered high risk. If you have a history of bladder cancer, a history of a birth defect of the bladder, or have been exposed to certain chemicals at work, you may be considered high-risk. You should ask your provider if screening tests are right for you.
Testing the urine for blood, abnormal cells, and tumor markers can help find some bladder cancers early but the results vary. Not all bladder cancers are found, and some people may have changes in their urine but do not have bladder cancer. These tests can be used in those who already have signs of bladder cancer or if the cancer has returned. However, more research is needed to determine how useful testing the urine is as a screening test.
Urethral Cancer Is A Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In The Tissues Of The Urethra
The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to outside the body. In women, the urethra is about 1½ inches long and is just above the vagina. In men, the urethra is about 8 inches long, and goes through the prostategland and the penis to the outside of the body. In men, the urethra also carries semen.
Urethral cancer is a rare cancer that occurs more often in men than in women.
Recommended Reading: Women’s Bladder Leakage Protection
What About Other Treatments That I Hear About
When you have cancer you might hear about other ways to treat cancer or treat your symptoms. These may not always be standard medical treatments. These treatments can be vitamins, herbs, special diets, and other things. You may be curious about these treatments.
Some of these are known to help, but many have not been tested. Some have been shown not to be helpful. A few have even been found to be harmful. Talk to your doctor about anything you’re thinking about using, whether its a vitamin, a diet, or anything else.
Bladder Cancer: Men At Risk
Genitourinary malignancies are a worry for men. In adolescents and young adults, testicular cancer is the main concern. One of the unappreciated benefits of growing older is that cancer of the testicles becomes rare but as men outgrow that risk, they face the problem of prostate cancer. With these well-publicized diseases to head their worry list, it’s easy for men to overlook bladder cancer but that would be a mistake. In fact, about 53,000 American men will be diagnosed with the disease this year alone, and over 10,000 will die from it.
Bladder cancer is the fourth most common internal malignancy in American men it is also one of the 10 deadliest cancers, and it saps our strapped economy of almost $3 billion a year. But there’s good news, too. Early diagnosis can nip the disease in the bud, and new treatments are improving the outlook for patients with advanced disease. And when it comes to good news, you’ll also be glad to know that you can take simple steps to reduce your risk of getting bladder cancer.
Also Check: Does Bladder Cancer Pain Come And Go