Can Recurrent Utis Be A Sign Of Cancer
Both UTIs and bladder cancer can cause similar symptoms, such as a frequent need to urinate and even blood in the urine, according to the University of Rochester Medical Center.
According to the American Cancer Society, urinary tract infections, kidney and bladder stones, and other causes of chronic bladder irritation have been linked to bladder cancer. However, its not clear whether recurrent urinary or bladder infections can actually cause bladder cancer or whether they constitute a true risk factor for bladder cancer.
The biggest known risk factor for bladder cancer is smoking. The risk of bladder cancer also increases with age. Most people who get bladder cancer are over the age of 55.
If you think you may have chronic or recurrent UTIs, its best to get checked out by your doctor. Your provider can rule out other health issues, including bladder cancer, and get you the treatment you need to get rid of chronic UTIs.
Chronic Urinary Tract Infections In Women
Urinary tract infections are painful and can disrupt your life. They are a very common problem, especially for women. Up to 60 percent of women will have at least one UTI during their lifetime.
But for some women, the infection doesnt go away with treatment. Or it disappears only to come back again soon. Our urogynecology specialists are experts at treating these complex, chronic urinary tract infections.
If you have chronic or recurrent UTIs, we can help you finally find relief.
Uti In Men: Its Not You And Its Not Me Its Just Complicated
Statistically, every 4th woman will experience a UTI in her lifetime. In yet another shocking turn of events, men have it easy in the UTI arena as well! UTIs in men are rarer. Mens urethra is on average eight inches long so ladies, when your next date says that: its 8 inches long technically hes not lying. According to Dr. Turek, size does indeed mattermales urethra is eight inches longer than their female counterparts and therefore serves as a great first line of defense from harmful bacteria.
Furthermore, for men, unlike women, it takes much more than exposure to E. coli during intercourse to develop a UTI. Basically, a lot of things need to go wrong in order for bacteria to ascend to the bladder.
Every case of UTI in men is considered complicated. This means UTI in men need to be thoroughly evaluated, and not just treated with an antibiotic. While its not always clear why some women get a UTI, in men you could normally find the reason during an evaluation, says Dr. Turek. Dr. Turek urges men to avoid home remedies and seek a physicians help if one believes hes experiencing symptoms of a UTI.
Physicians would normally collect a urine sample and check lower and upper urinary tract in search for any of the following:
- Stones or tumors that obstruct normal urine flow
- Malformations or birth defects
- Prostate enlargement
Read Also: What Kind Of Doctor Does Bladder Prolapse Surgery
What Is A Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection
A urinary tract infection occurs when bacteria invade the bladder or kidneys. The bacteria can often be found naturally in our bowels or on our skin, but they are harmless there. However, when they get into the urinary tract, they can cause an infection.
Women in general get more UTIs. This is mainly because the female urethra is shorter, which allows bacteria easier access into the bladder.
Typically a woman may have one UTI per year on average. But some women get them more often. If it occurs about four times a year, its considered a recurrent UTI. An estimated 2% to 10% of women get chronic UTIs, according to a review in the journal Climacteric.
UTIs tend to be more common in older men than younger men. This is likely because UTIs in men are often caused by not completely emptying the bladder. This is often due to an enlarged prostate, a condition common in older men.
UTIs are treated with antibiotics and go away quickly.
Urinary Tract Infections In Men That Just Dont Go Away

Although painful and distressing most are short-lived. But if you keep on getting a UTI or feel like its never really gone away you could have chronic infection.
Chronic UTI often starts when a simple infection is left untreated or fails to get better with standard treatments. Read about how and why chronic UTI develops.
Needing to pee all the time, pain when you pee, passing tiny amounts of urine, bladder and urethral pain, pain in your belly, back and legs, difficulty passing urine, problems with incontinence. The symptoms of chronic UTI are similar to acute infections but they vary from person to person.
Currently theres just not enough research to understand why some people never experience a UTI, why some people have one or two infections and why some people develop chronic infections.
The symptoms of chronic UTI are, frustratingly, not exclusive to the condition they are common to a number of other lower urinary tract health conditions as well. This can often result in other avenues being explored for diagnosis first by your GP, leading to chronic UTIs being diagnosed by exclusion of other conditions, all the while allowing the UTI to develop further.
Other LUTS conditions that are investigated in men include:
- detrusor muscle weakness or overactivity
- prostate inflammation
- neurological disease
Don’t Miss: Can Stress And Anxiety Cause Overactive Bladder
Classification Of Urinary Tract Infections
UTIs are classified into 6 categories. The first category is an uncomplicated infection this is when the urinary tract is normal, both structurally and physiologically, and there is no associated disorder that impairs the host defense mechanisms. The second category is an complicated infection this is when infection occurs within an abnormal urinary tract, such as when there is ureteric obstruction, renal calculi, or vesicoureteric reflux. The third category, an isolated infection, is when it is the first episode of UTI, or the episodes are 6 months apart. Isolated infections affect 2540% of young females. The fourth category, an unresolved infection, is when therapy fails because of bacterial resistance or due to infection by two different bacteria with equally limited susceptibilities. The fifth category, reinfection, occurs where there has been no growth after a treated infection, but then the same organism regrows two weeks after therapy, or when a different microorganism grows during any period of time., This accounts for 95% of RUTIs in women. Bacterial persistence happens when therapy is impaired by the accumulation of bacteria in a location that cannot be reached by antibiotics, such as infected stones, urethral diverticula and infected paraurethral glands. The sixth category, relapse, is when the same microorganism causes a UTI within two weeks of therapy however, it is usually difficult to distinguish a reinfection from a relapse.
How Can Parents Help
At home, these things can help prevent recurrent UTIs in kids:
Drinking Fluids Encourage kids to drink 810 glasses of water and other fluids each day. Cranberry juice and cranberry extract are often suggested because they may prevent E. coli from attaching to the walls of the bladder. Always ask your doctor, though, if your child should drink cranberry juice or cranberry extract, because they can affect some medicines.
Good Bathroom Habits Peeing often and preventing constipation can help to prevent recurrent infections.
No Bubble Baths Kids should avoid bubble baths and perfumed soaps because they can irritate the urethra.
Frequent Diaper Changes Kids in diapers should be changed often. If poop stays in the genital area for a long time, it can lead to bacteria moving up the urethra and into the bladder.
Proper Wiping Girls should wipe from front to back after using the toilet to reduce exposure of the urethra to UTI-causing bacteria in poop.
Cotton Underwear Breathable cotton underwear is less likely to encourage bacterial growth near the urethra than nylon or other fabrics.
Regular Bathroom Visits Some kids may not like to use the school bathroom or may become so engrossed in a project that they delay peeing. Kids with UTIs should pee at least every 3 to 4 hours to help flush bacteria from the urinary tract.
Also Check: Bladder Cancer Metastasis To Liver Prognosis
The Absence Of Recurrent Uti Guidelines
Because there are no guidelines on managing complex or recurrent UTI, primary care doctors are generally not in a position to help.
| Most UTI guidelines are aimed at management of simple uncomplicated UTI. It can be very difficult to successfully manage complex or recurrent UTI in primary care. If symptoms persist, or where there is diagnostic uncertainty GPs will need to make a referral for specialist assessment.” |
For females that progress from a single UTI, to recurrent UTI or chronic urinary tract infection, or to a diagnosis of Interstitial Cystitis, there has historically been very little hope of effective treatment. We hope to help change this.
What Are The Symptoms Of A Urinary Tract Infection
These are the most common symptoms of a UTI:
- Frequent urination
- Pain or burning when passing urine
- Fever
- Urine looks dark, cloudy, or reddish in color
- Urine smells bad
- Feeling pain even when not urinating
- Tiredness
- Pain in the back or side, below the ribs
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Despite an strong urge to urinate, only a small amount of urine is passed
- Women may feel an uncomfortable pressure above the pubic bone
The symptoms of UTI may look like other conditions or medical problems. Always see a health care provider for a diagnosis.
Also Check: Can You Clear Up A Bladder Infection Without Antibiotics
The Myth Of Interstitial Cystitis And Bladder Syndromes
IC and bladder syndromes are known as diagnoses by exclusion. They dont identify a reason for a patients symptoms, they simply describe collections of symptoms. For example, the NHS Choices website describes IC as a poorly understood, incurable condition.
There is no agreed cause or cure for IC and bladder syndromes. But there is a view among many doctors based on tests which are known to be ineffective that they are not caused by bacteria. Sufferers are offered surgery or prescribed painkillers, including opiates, bladder relaxants and bladder instillations to alleviate symptoms.
Bladder instillations had no more effect than a placebo, a recent large-scale study found. A growing body of evidence suggests that long-term bladder and urinary pain may be caused by infections missed by tests that dont work.
Forward Makes Uti Treatment Easy
As your primary care provider, Forward makes treating UTIs and bladder infections simple. We give you the ability to obtain a prescription online and have the necessary antibiotics delivered to your door. If chronic UTIs and bladder infections are a concern, we can perform the diagnostic testing and assessments necessary to uncover the root causes and create a treatment plan to address them.
Read Also: Antibiotics For Uti Or Bladder Infection
Why Utis Keep Coming Back
It is estimated that 50% of women who encounter a UTI go on to experience a recurrence of infection within a year3. Some individuals have multiple UTI episodes throughout their life, and a few suffer from chronic UTIs. Factors that may increase the chance of UTI recurrence include:
- Sexual intercourse
- Certain types of birth control, particularly diaphragms and spermicidal agents
- Inherent predisposition: some women have urinary tracts that are more prone to bacterial invasion
- Anatomical abnormalities or blockages in the urinary tract
- Immune suppression caused by diseases such as diabetes
- Post-menopausal changes in the vaginal lining and in the ability of the bladder to contract
How Do I Talk To My Gp About Chronic Urinary Tract Infections
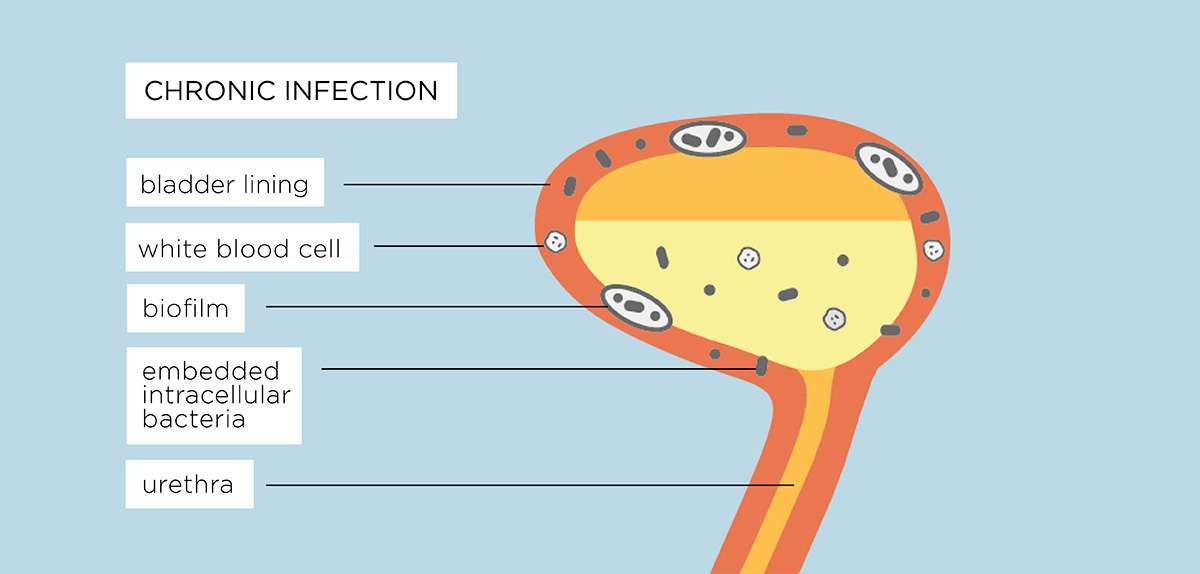
Unfortunately currently guidelines for GPs dont even mention chronic UTI. We know it can be difficult to explain all this and describe your symptoms in a short doctors appointment.
Write down all your symptoms as we outlined above and take them with you to your appointment.
Your doctor may well investigate if your UTIs are related to your prostate. But if these investigations come back negative ask your GP to consider chronic UTI.
No detail is too small when visiting the doctor about urinary problems. It may help to write down a list of symptoms, no matter how small, and take them with you to your appointment. For example an unusual smell, abnormal amounts of foam, or persistently darker urine than usual may seem unimportant to you, but to a doctor these can be the characteristic symptoms required to diagnose a given condition.
Also Check: Antibiotics For Bladder Infection While Pregnant
How Do You Treat A Uti Kidney Infection Or Bladder Infection
Treatment for a urinary tract infection, kidney infection or bladder infection usually involves taking a prescription antibiotic to get rid of the bacteria. Depending on the type of antibiotic and the severity of your infection, you may need to take the antibiotic anywhere from three days to a week or longer.
Because different kinds of bacteria can cause a UTI, not all antibiotics can treat all infections. Taking a leftover antibiotic you received for some other illness is unlikely to clear up the infectionand it can lead to antibiotic resistance, which can be dangerous. Take your antibiotics as prescribedyour symptoms may disappear before the infection is totally gone, so its important to take all of the pills you receive.
Your doctor may also recommend that you take phenazopyridine. This medication relieves urinary tract pain, pressure and discomfort and can ease symptoms of urinary urgency. You can purchase this drug over the counter as Uristat or a generic alternative. Prescription versions are also available.
Keep in mind that phenazopyridine doesnt treat a UTI. If you believe you have a UTI, taking this medication to alleviate your symptoms isnt enough to kill the bacteria. Your condition could worsen or spread into your kidneys if you try to just address your symptoms without treating the underlying infection.
Why Does My Uti Keep Coming Back
Chronic or recurring UTIs may keep coming back due to one of the risk factors listed above. Use of spermicides for birth control, for instance, may kill off beneficial bacteria in and around the vagina, making it easier for harmful bacteria to enter the urinary tract.
In some cases, what seem like recurrent UTIs may actually be another condition, such as kidney stones or interstitial cystitis, a painful bladder condition with no infection. If you think youre getting recurrent UTIs, see your provider, who can help rule out another condition, notes ACOG.
You May Like: Small Cell Bladder Cancer Survival Rate
Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections In Women: Diagnosis And Management
CHARLES M. KODNER, MD, University of Louisville School of Medicine, Louisville, Kentucky
EMILY K. THOMAS GUPTON, DO, MPH, Primary Care Medical Center, Murray, Kentucky
Am Fam Physician. 2010 Sep 15 82:638-643.
Recurrent urinary tract infections are common in women and associated with considerable morbidity and health care use. The clinical features, diagnostic testing, and causative organisms are often similar to those of single cases of UTI, although there are additional treatment strategies and prevention measures to consider with recurrent UTIs.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
A urine culture with greater than 102 colony-forming units per mL is considered positive in patients who have symptoms of UTI.
| Clinical recommendation | Evidence rating | References |
|---|---|---|
|
Continuous and postcoital antimicrobial prophylaxis have demonstrated effectiveness in reducing the risk of recurrent UTIs. |
||
|
Cranberry products may reduce the incidence of recurrent symptomatic UTIs. |
||
|
Use of topical estrogen may reduce the incidence of recurrent UTIs in postmenopausal women. |
||
|
Treatment of complicated UTIs should begin with broad-spectrum antibiotic coverage, with adjustment of antimicrobial coverage guided by culture results. |
||
|
Prophylactic antimicrobial therapy to prevent recurrent UTIs is not recommended for patients with complicated UTIs. |
UTI = urinary tract infection.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
UTI = urinary tract infection.
When To See A Doctor
Its always a good idea to reach out to a doctor if youre experiencing those UTI symptoms, because remember, UTIs can affect the kidneys without prompt treatment. But this is especially important if youre susceptible to recurrent UTIs. As you can see, there are various treatment optionsand potential preventive methodsthat may be able to keep that terrible burning to a minimum.
Additional reporting by Laura Adkins.
Read Also: How To Reduce Bladder Inflammation Naturally
Could Your Problems Be Due To A Chronic Imbedded Infection
The common scenario seems to be this: a history of urinary tract infections that would occur periodically, perhaps after intercourse but not in every case.
Then at some point, the symptoms would persist and potentially get worse after each course of antibiotics. Some people would then experience frequent flares or constant 24/7 symptoms. Testing would usually come back negative.
Some people may receive a diagnosis of interstitial cystitis. No dietary change or medication would make a real difference.
But what if the inflammation and pain experience in so-called interstitial cystitis was actually due to a chronic infection that was evading testing?
What if the flares of chronic UTIs were not new infections, but a chronic infection instead?
We now know, thanks to the great research of one professor Malone-Lee, that this is entirely plausible.
Talking To Your Doctor
No detail is too small when visiting the doctor about urinary problems. We suggest you write down a list of symptoms and take them with you to your appointment. For example, an unusual smell, abnormal amounts of foam, or persistently darker urine than usual may seem unimportant to you, but to a doctor these can be the characteristic symptoms required to diagnose a given condition. Other signs to look out for and mention to your GP include:
- a weak or intermittent urinary stream
- straining
- nocturia getting up at night to urinate
- posturination dribbling
- pain or a stinging sensation in the urethra or penis whilst urinating or post urination.
- Pain radiating into the rectum
One major fear is that of a physical exam, especially when it relates to intimate parts of the body. A physical exam is likely to occur, so prepare yourself ahead of time for it. Do not be afraid to ask for a male doctor when making your appointment . A chaperone is also acceptable, and in some cases encouraged.
However, a doctor may not wish to examine you in certain conditions in these cases, do not be afraid to ask for one if you feel it necessary or would like to put your mind at rest. For example, younger men that present urinary symptoms will likely be assumed to not have prostatic issues and thus a doctor will likely not perform an exam. This doesnt exclude their presence entirely, so should you have any doubt it is recommended that you ask for the exam to be performed anyway.
Also Check: What Causes Weak Bladder In Females