What Are The Best Antibiotics For Utis
A urinary tract infection is an infection of the urinary system. It is often associated with painful symptoms, which are typically treated with antibiotics. The best antibiotics for treating a UTI depend on the type of UTI and the severity of the symptoms. Nitrofurantoin, trimethoprim, and cephalexin are common antibiotics prescribed to treat UTIs.
Without insurance, prescriptions can be expensive, but Mira can help you out. For only $45 a month, Mira members get access to up to 80% off different medications, affordable lab testing, and virtual and urgent care visits. Ease your pain, for Mira today.
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis
RICHARD COLGAN, MD, and MOZELLA WILLIAMS, MD, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland
Am Fam Physician. 2011 Oct 1 84:771-776.
Patient information: See related handout on treating a bladder infection , written by the authors of this article.
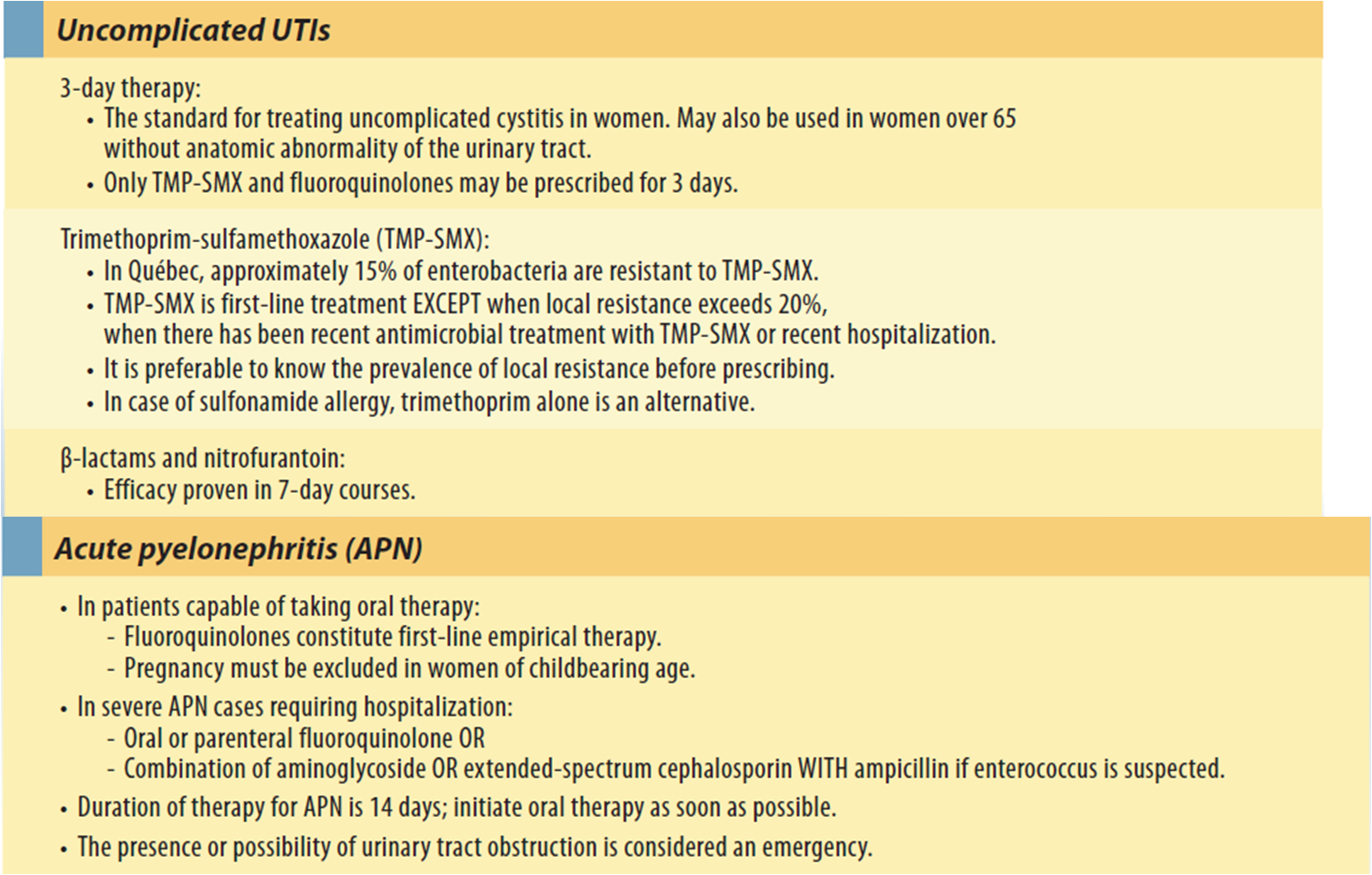
Urinary tract infections are the most common bacterial infections in women. Most urinary tract infections are acute uncomplicated cystitis. Identifiers of acute uncomplicated cystitis are frequency and dysuria in an immunocompetent woman of childbearing age who has no comorbidities or urologic abnormalities. Physical examination is typically normal or positive for suprapubic tenderness. A urinalysis, but not urine culture, is recommended in making the diagnosis. Guidelines recommend three options for first-line treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis: fosfomycin, nitrofurantoin, and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole . Beta-lactam antibiotics, amoxicillin/clavulanate, cefaclor, cefdinir, and cefpodoxime are not recommended for initial treatment because of concerns about resistance. Urine cultures are recommended in women with suspected pyelonephritis, women with symptoms that do not resolve or that recur within two to four weeks after completing treatment, and women who present with atypical symptoms.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
The combination of new-onset frequency and dysuria, with the absence of vaginal discharge, is diagnostic for a urinary tract infection.
See A Healthcare Provider
While UTIs arent usually a cause for major concern, if you dont get them treated, they can lead to more serious problems like a kidney infection. If you have a UTI, make an appointment with a healthcare provider as soon as possible. The fastest way to feel better is by taking an antibiotic to kill the bacteria causing your infection.
If going to see a provider in-person is not an option , there are plenty of telehealth services available that will allow you to set up a virtual appointment. Check out GoodRx Care for treatment of UTIs as well as many other medical conditions.
During your appointment, your provider will ask you questions about what symptoms you are experiencing and if you are prone to UTIs. You might be asked to provide a urine sample either in the office you are seen in or at a lab close to you. Lastly, your provider will prescribe you a course of antibiotics to get started on right away.
Some common antibiotics used for treating UTIs include nitrofurantoin , sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim , and ciprofloxacin . Typically, you only need to take them for 3 to 5 days, and most people start to feel relief within the first 2 to 3 days. Antibiotics can cause nausea, stomach upset, and diarrhea for many people. But, taking your dose with food can help lessen nausea and stomach upset, and taking a probiotic supplement like L. acidophilus can help with the diarrhea.
You May Like: How Is Immunotherapy Administered For Bladder Cancer
Urinary Tract Infection Antibiotics
Some of the common antibiotics your doctor may prescribe to treat a UTI include:
- Cephalexin
- Nitrofurantoin
- Fosfomycin
In certain instances, your doctor may prescribe a less common antibiotic. If you have allergies to certain antibiotics, for example, or your UTI is more severe, you may receive a prescription for a class of antibiotics called fluoroquinolones. These include Cipro and Levaquin .
A typical course of antibiotics for a mild UTI lasts several days. If you’re otherwise feeling fine besides your UTI, your physician may suggest a shortened course of drugs, maybe 1-3 days. Follow your doctors direction, though. Stopping an antibiotic too soon could enable your infection to return.
If you are getting frequent, recurring infections, your doctor might suggest a low dose antibiotic regimen over the course of several months.
It’s important to note that an estimated 22% of women receiving antibiotic treatment for a UTI develop candida overgrowth soon after. If you have to take antibiotics, be sure to accompany them with a course of probiotics to help to keep candida at bay.
Symptoms like fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, pain in your low back or side is a sign that its time to talk to your provider and start that antibiotic. Your microbiome can heal, but your kidneys cant if an infection is left untreated.
Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections

Patients with three or more infections per year should be offered either continuous low-dose antibiotic prophylaxis, patient-initiated, or postcoital prophylaxis if the onset of infection is linked to sexual intercourse . Before a prophylactic regimen is chosen, a urine culture should be performed to determine the susceptibility of the pathogen. The duration of continuous prophylactic therapy is usually 6 months to a year. Unfortunately, within 6 months of discontinuing antibiotic prophylaxis, 40% to 60% of women develop a urinary tract infection, and prophylaxis must be resumed. Patient-initiated therapy at the onset of symptoms has been shown to be effective in young, healthy nonpregnant women. Short-course regimens have been advocated for patient-initiated therapy in compliant women with frequently recurring and symptomatic urinary tract infections. The major advantages of short-course therapy over continuous therapy are convenience and the avoidance of antibiotic toxicity symptomatic infections are not prevented, however. For postcoital prophylaxis, nitrofurantoin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, or fluoroquinolones taken within 2 hours after sexual intercourse have been shown to significantly reduce the incidence of recurrent cystitis.,
Read Also: Botox In Bladder For Incontinence
Get Your Prescription Filled Right Away
Once you are done with your appointment and have received a prescription for an antibiotic, its important you get it filled at a pharmacy as soon as possible. The faster you start taking your medication, the faster your UTI will be gone.
If you usually use next-day prescription delivery or a mail order pharmacy, this is one time when you should avoid doing this. These options can cause a delay by anywhere from 1 day to 1 week . Youre better off using a local pharmacy in this case.
If going into the pharmacy is a concern due to COVID-19, many pharmacies have added options to help minimize the amount of time you are inside the building. Some options to ask about at your pharmacy include:
-
Same-day delivery through services like Instacart
-
Using the pharmacys drive-thru pick-up window
-
Curbside pick-up
-
Paying ahead of time through the pharmacys smartphone app to make your time spent at the checkout counter faster
Every pharmacy is different, so make sure to ask your personal pharmacy if these options are available at your location.
What If I Don’t Go To The Doctor
What happens when UTIs are left untreated? Contrary to popular belief, your immune system is often able to clear a UTI on its own. Studies have found that 25-42% of women are able to recover from an uncomplicated UTI without antibiotics.
But that means a majority of UTIs do not go away on their own. If left untreated, they can lead to continued discomfort and other more serious health issues, such as kidney damage or a severe infection. Therefore, treatment is recommended.
“Physicians tailor care plans to each patient, and there is no sole treatment for everyone,” says Stanford physician Kim Chiang, MD. During your visit, feel free to ask in-depth questions, particularly if a non-recommended antibiotic is prescribed.
This is the fifth post in the series Understanding UTIs. The goal of this seven-part series is to provide easy-to-understand, scientifically grounded information about UTIs. Patients referenced are composites, compiled from actual patient experiences.Data on medications used for UTIs were extracted from the National Disease and Therapeutic Index, a nationally representative physician survey produced by IQVIA.
Also Check: Symptoms Of Irritable Bladder Syndrome
What Is The Best Antibiotic For A Complicated Uti
4.7/5The following oral antibiotics are commonly used to treat most uncomplicated UTI infections :
- nitrofurantoin
Regarding this, what is a complicated urinary tract infection?
A complicated UTI is an infection associated with a condition, such as structural or functional abnormalities of the genitourinary tract or the presence of an underlying disease, which increases the risks of acquiring an infection or of failing therapy. Complicated UTI can arise in a heterogeneous group of patients.
Secondly, how do you treat complicated UTI? The mainstay of treatment of acute UTI, either non-complicated or complicated infections, is antibiotics.
Keeping this in view, what is the strongest antibiotic for a UTI?
- Amoxicillin/augmentin.
- Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole
Why won’t my UTI clear up with antibiotics?
Symptoms of a UTI usually improve within two to three days after starting antibiotic therapy. Some UTIs don’t clear up after antibiotic therapy. When an antibiotic medication doesn’t stop the bacteria causing an infection, the bacteria continue to multiply.
Whats The Difference Between A Urinary Tract Infection And Bladder Infection
A urinary tract infection is a more general type of infection. There are many parts of your urinary tract. A UTI is a term for an infection that takes place throughout the urinary tract. A bladder infection, also called cystitis, is a specific infection. In this infection, bacteria makes its way into the bladder and causes inflammation.
Not all urinary tract infections become bladder infections. Preventing the spread of the infection is one of the most important reasons to treat a UTI quickly when you have symptoms. The infection can spread not only to the bladder, but also into your kidneys, which is a more complicated type of infection than a UTI.
You May Like: Causes Of Weak Bladder Control
Best Antibiotics For Utis
A UTI is a common infection of the urinary tract that can affect the kidneys, urethra, bladder, or ureters. They are often caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract, which then multiplies in the bladder. In addition, UTIs can also be caused by viral infections. Your doctor may request special testing if they believe you have a viral UTI, as they are treated with antivirals, not antibiotics. If you have a bacterial UTI, the best course of treatment would be antibiotics.
Dr. David Beatty, a general practitioner for over 30 years, provided insight for this article. Dr. Beatty noted that in an ideal situation, a urine culture is performed to see the specific bacteria causing an infection. A physician can then determine the perfect antibiotic for killing the bacteria. In cases without urine cultures, which happens most often, the following is taken into consideration:
- Severity of illness
|
nitrofurantoin, trimethoprim |
Cautions With Other Medicines
There are some medicines that do not mix well with nitrofurantoin.
Tell your doctor if you’re taking these medicines before you start nitrofurantoin treatment:
- indigestion remedies known as antacids, particularly those that contain magnesium
- certain medicines for gout, including probenecid or sulfinpyrazone
- cystitis remedies you can buy from a pharmacy
- antibiotics known as quinolones, including nalidixic acid, ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, norfloxacin, ofloxacin and moxifloxacin
Typhoid vaccine given by mouth may not work properly if you’re taking nitrofurantoin. This does not apply to typhoid vaccines given by injection.
Also Check: Does Bladder Infection Cause Incontinence
Are There Side Effects To Antibiotics
Yes, like most drugs, there are potential side effects when taking antibiotics. Therefore, antibiotics should only be taken when necessary in order to avoid potentially harmful situations. Allergic reactions are the most common side effect that people experience. This could occur in a skin reaction, swelling, and even breathing problems. Sometimes, antibiotics can cause nausea or yeast infections. Although they kill bad bacteria, good bacteria can be killed as well, causing a yeast infection.
How Often Are Utis Resistant
The majority of urinary tract infections are now resistant to one or more antibiotics. The drug ampicillin, once a common treatment, has been largely abandoned because most U.T.I.s are now resistant to it.
The most important question isnt whether an infection is resistant to any drug, but whether it is resistant to the drugs that are commonly used to treat your particular infection.
When experts in the field think about resistant U.T.I.s, they say that resistance depends on the bug and the drug. What that means is that they try to figure out which particular germs are resistant to specific medications.
Read Also: Can Anxiety Cause Bladder Leakage
Why Do Women Get Utis More Often Than Men
Women are more susceptible to getting a UTI thanks to their anatomy. Their urethras are both closer to the rectum and shorter in length than mens urethras are theyre also near the vagina. In other words, womens bodies naturally present a convenient access point for the myriad bacteria that commonly cause UTIs.
Antibiotics For Treating Canine Uti
Canine UTI-or canine urinary tract infection-is also known as acute cystitis. The urinary infection is caused by bacteria and is a painful disease. UTI has higher incidence in female dogs due to their shorter urethras. The condition is fully treatable and the most common treatment contains antibiotics.
Recommended Reading: How To Help Bladder Control
Can Doctors Treat Utis Via Telemedicine
Telemedicine is an increasingly popular method of treating UTIs. In addition to being convenient, its also discreet and frequently more affordable than an in-office visit.
Since doctors cant collect a urine specimen via telemedicine, they will typically make their diagnosis using a series of questions that identify and analyze your symptoms. Your telehealth provider will also want to know if you have a history of UTIs, as well as if there are any other factors that may complicate your UTI, such as pregnancy or a chronic health condition.
Ultimately, the fact that UTIs are extremely common assists physicians in their ability to accurately diagnose and treat UTIs online. In the event that your UTI symptoms present themselves as more severe or as something else entirely, your telemedicine professional will instruct you to visit another physician in the office for a follow-up or to perform a urinalysis. Most of the time, however, your telehealth provider can diagnose your infection and prescribe antibiotics via video alone. Certain telehealth providers may be able to fill your prescription as well, which can save you the expense of going through a pharmacy.
Ongoing Management Of Uti
Dr N: So, shes going to come in next week and give a urine sample. Well see if the E coli has been cleared and then try to figure out what the next step will be.
Urine testing should be in response to symptoms as outlined in the . Repeated urine testing as a test of cure is not warranted among older patients. Among patients with recurrent symptomatic UTI , use of chronic suppressive antibiotics for 6 to 12 months are effective at reducing UTI episodes and should be considered. Nitrofurantoin given at 50 mg daily is used in older patients with minimal adverse effects and no growth of nitrofurantoin-resistant fecal flora after 1 year of treatment. Six months of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole , trimethoprim , and nitrofurantoin are also effective, but trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole resistant E coli fecal isolates were more common in patients treated with trimethoprim-based regimens.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Fix Overactive Bladder
What To Expect At Home
UTIs can lead to infection. Most often the infection occurs in the bladder itself. At times, the infection can spread to the kidneys.
Common symptoms include:
- Pain or burning when you urinate
- Needing to urinate more often
- Hard to empty your bladder all the way
- Strong need to empty your bladder
These symptoms should improve soon after you begin taking antibiotics.
If you are feeling ill, have a low-grade fever, or some pain in your lower back, these symptoms will take 1 to 2 days to improve, and up to 1 week to go away completely.
Antibiotics For Uti Vs Home Remedies For Uti
Are there UTI treatments without antibiotics? While antibiotics are the most common and effective treatment for UTIs, natural remedies are an increasingly popular way to treat such infections without antibiotics.
It is important to consult a doctor to determine which treatment approach is best for you.
Below are some common at-home UTI treatment options that can help relieve symptoms:
- Drink plenty of water to flush the bacteria from your system.
- Get plenty of vitamin C to make your urine more acidic, which makes it less hospitable for bacteria.
- Use a heating pad to reduce pelvic pain.
- Avoid caffeine, alcohol, spicy food, nicotine, carbonated drinks, and artificial sweeteners because they can irritate your bladder.
- There is no evidence or proof that drinking pure, unsweetened cranberry juice can help prevent or treat UTIs however, this is still a commonly used home remedy.
- Urinate as frequently as possible to eliminate bacteria from your urinary tract.
- Wear loose clothing and cotton underwear to prevent bacteria-loving moisture from building up.
- Quit smoking to improve your immune system.
- Wipe from front to back to prevent spreading bacteria.
- Avoid using scented feminine products since they can lead to infections.
In addition to these lifestyle changes, PlushCare recommends that you meet with a licensed physician to ensure you receive proper treatment, including any necessary antibiotics for UTI treatment.
Recommended Reading: What Happens With Bladder Cancer
First Line Antibiotics For A Uti
- Ampicillin
- Nitrofurantoin
- Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole
Notably absent from the list of antibiotics prescribed for the treatment of UTIs is Amoxicillin. While very popular and useful in treating numerous other bacterial infections, urinary tract infections are not amongst the infections Amoxicillin is used for.