Intermediate Risk Early Bladder Cancer
People with intermediate-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer should be offered a course of at least 6 doses of chemotherapy. The liquid is placed directly into your bladder, using a catheter, and kept there for around an hour before being drained away.
You should be offered follow-up appointments at 3, 9 and 18 months, then once every year. At these appointments, your bladder will be checked using a cystoscopy. If your cancer returns within 5 years, you’ll be referred back to a specialist urology team.
Some of the chemotherapy medicine may be left in your urine after treatment, which could severely irritate your skin.
It helps if you sit down to urinate and that you’re careful not to splash yourself or the toilet seat. Always wash the skin around your genitals with soap and water afterwards.
If you’re sexually active, it’s important to use a barrier method of contraception, such as a condom. This is because the medicines may be present in your semen or vaginal fluids, which can cause irritation.
You also shouldn’t try to get pregnant or father a child while having chemotherapy for bladder cancer, as the medicines can increase the risk of having a child with birth defects.
Types Of Late Effects
Nearly any cancer treatment can cause late effects. And different treatments can cause different late effects. Below is a list of the more common late effects. Talk with your doctor about any concerns you have about a specific late effect.
Problems from surgery. Late side effects from surgery depend on the type of cancer and where in the body you had surgery:
-
Survivors of Hodgkin lymphoma, especially those diagnosed before 1988, often had their spleens removed. The spleen is a vital organ for the immune system. Removing it is linked with a higher risk of infections.
-
Survivors of bone and soft-tissue cancers may have lost part or all of a limb. This can cause physical and emotional effects. One example is phantom limb pain. This is feeling pain in the limb that was removed even though it is no longer there. Rehabilitation can help people cope with physical changes from treatment.
-
People who had radiation therapy or surgery to remove lymph nodes may develop lymphedema. Lymph nodes are tiny, bean-shaped organs that help fight infection. Lymphedema is when lymph fluid builds up and causes swelling and pain.
-
People who had certain surgeries in the pelvis or abdomen may not be able to have children. This is called infertility. Learn more about fertility concerns and preserving fertility in men and in women.
Heart problems. Both chemotherapy and radiation therapy to the chest can cause heart problems. Some survivors may have a higher risk. This includes those who:
-
Bleomycin
Treating Stage I Bladder Cancer
Stage I bladder cancers have grown into the connective tissue layer of the bladder wall , but have not reached the muscle layer.
Transurethral resection with fulguration is usually the first treatment for these cancers. But it’s done to help determine the extent of the cancer rather than to try to cure it. If no other treatment is given, many people will later get a new bladder cancer, which often will be more advanced. This is more likely to happen if the first cancer is high-grade .
Even if the cancer is found to be low grade , a second TURBT is often recommended several weeks later. If the doctor then feels that all of the cancer has been removed, intravesical BCG or intravesical chemo is usually given. If all of the cancer wasn’t removed, options are intravesical BCG or cystectomy .
If the cancer is high grade, if many tumors are present, or if the tumor is very large when it’s first found, radical cystectomy may be recommended.
For people who arent healthy enough for a cystectomy, radiation therapy might be an option, but the chances for cure are not as good.
Recommended Reading: Can You Treat A Bladder Infection At Home
Local Infections With Bcg
BCG can invade the prostate and the seminal vesicles up to the epididymis. These diseases require a triple tuberculostatic treatment. Often fluoroquinolone is one arm of it. The duration varies from one study to another from 3 to 6 months. Orchiepididymectomy may be a rapid solution for a severely symptomatic patient, but it does not replace the general tuberculostatic treatment that should be continued.13 In rare cases, transurethral resection of the prostate is necessary to solve obstruction. Asymptomatic granulomatous prostatitis, however, was found to be frequent after intravesical BCG therapy but does not require treatment.14
BCG balanitis or contact dermatitis has been described and can be handled with local steroids. Careful cleaning of hands and genital region after drug handling and voiding should prevent it.
Granulomatous balanitis, however, can present with multiple erythematous and painless nodules of the glans, which should be treated with systemic triple tuberculostatic drug therapy.13,40
How To Take Bacillus Calmette
BCG is given directly into the bladder through a catheter. The medicine is left in the bladder for 1-2 hours. The dosage and schedule is determined by your healthcare provider. It is not uncommon to have urinary frequency or painful urination for 48 hours after treatment. If this continues after 48 hours, call your doctor or nurse.
How the Intravesicular Treatment is Given
- You should limit your fluid intake starting the night prior to the procedure and have no fluids for 4 hours before. This is so you will be able to hold your urine in during the procedure for the full treatment time. In addition, the area receives more concentrated doses of the medicine with less urine output during the procedure.
- If you take a diuretic , you will be told to not take this for at least 4 hours before the procedure.
- A urinary catheter is inserted into the bladder and any urine is drained.
- The BCG is given through the catheter, into the bladder. The catheter may be removed or clamped and remain in place based on your providers recommendation.
- You will need to hold the BCG in your bladder for 1-2 hours. You may need to change positions every 15 minutes to be sure the medicine reaches all areas of the bladder. Do this by rolling on your side, back, other side, and stomach.
Precautions After Treatment
Recommended Reading: How To Test For Bladder Infection
Radiotherapy With A Radiosensitiser
Radiotherapy is given by a machine that beams the radiation at the bladder . Sessions are usually given on a daily basis for 5 days a week over the course of 4 to 7 weeks. Each session lasts for about 10 to 15 minutes.
A medicine called a radiosensitiser should also be given alongside radiotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. This medicine affects the cells of a tumour, to enhance the effect of radiotherapy. It has a much smaller effect on normal tissue.
As well as destroying cancerous cells, radiotherapy can also damage healthy cells, which means it can cause a number of side effects. These include:
- diarrhoea
- tightening of the vagina , which can make having sex painful
- erectile dysfunction
- tiredness
- difficulty passing urine
Most of these side effects should pass a few weeks after your treatment finishes, although there’s a small chance they’ll be permanent.
Having radiotherapy directed at your pelvis usually means you’ll be infertile .
After having radiotherapy for bladder cancer, you should be offered follow-up appointments every 3 months for the first 2 years, then every 6 months for the next 2 years, and every year after that. At these appointments, your bladder will be checked using a cystoscopy.
You may also be offered CT scans of your chest, abdomen and pelvis after 6 months, 1 year and 2 years. A CT scan of your urinary tract may be offered every year for 5 years.
Keeping Personal Health Records
You and your doctor should work together to develop a personalized follow-up care plan. Be sure to discuss any concerns you have about your future physical or emotional health. ASCO offers forms to help keep track of the cancer treatment you received and develop a survivorship care plan when treatment is completed.
This is also a good time to talk with your doctor about who will lead your follow-up care. Some survivors continue to see their oncologist or urologist, while others transition back to the care of their family/primary care doctor or another health care professional. This decision depends on several factors, including the type and stage of bladder cancer, side effects, health insurance rules, and your personal preferences, expectations, and beliefs.
If a doctor who was not directly involved in your cancer care will lead your follow-up care, be sure to share your cancer treatment summary and survivorship care plan forms with them and with all future health care providers. Details about your cancer treatment and communication preferences are very valuable to the health care professionals who will care for you throughout your lifetime.
The next section in this guide is Survivorship. It describes how to cope with challenges in everyday life after a cancer diagnosis. Use the menu to choose a different section to read in this guide.
Read Also: Do You Bleed With A Bladder Infection
Can Chemotherapy Treatment Cause Bladder Cancer
Some chemotherapy drugs can cause bladder cancer. The long-term side effects of Cytoxan and Ifosfamide which irritate the bladder lining and are associated with damage to the bladder and the bone marrow. Bladder cancer is a well-known risk and continues to arise at least 10-15 years after the drug was given.6
Simultaneous Detection Of Antigen
PBMCs were labeled with CFSE and expanded with optimal dose of live BCG in 1 ml of cR-10 containing 10% heat-inactivated human AB serum , or resting in medium alone for 7 days at 37°C with 5% CO2. On day 7, cell suspensions were mixed 1:500 with Cell Activation Cocktail for 5 h. Cells were then processed for total live cell count and staining with fluorochrome-conjugated anti-human CD3 mAb , CD4 mAb , CD8 mAb and γδ TCR mAb , followed by fixation and permeabilization with Cytofix/Cytoperm buffer prior to intracellular staining with fluorochrome-conjugated anti-human IFN-γ mAb . Data were acquired with an LSR II cytometer and analyzed using FACS Diva software . Absolute numbers of proliferated functional CD4+, CD8+, and γδ T cells were calculated by multiplying total viable cells recovered after 7-day culture by percentages of proliferated functional T cell subsets. Fold changes of response by 3 and 6 months were calculated over baseline except in two cases baseline were substituted with week 1 due to blood/PBMCs availability.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Best Exercise For The Bladder
General Malaise And Fever
Again, these frequent side effects resolve mostly within 48 hours. Symptomatic antipyretics can be given when fever exceeds 38°C. Fever > 38.5°C for > 2 days needs close monitoring of the patient and consultation of infectious disease specialist in order to see if there are other causes of fever. While further diagnostic evaluation, prompt treatment with a minimum of two or more tuberculostatic agents is started.4 The duration of this therapy is badly defined and depends on further evolution of fever, malaise, and other findings at diagnostic exploration. Anyhow, further BCG is at least postponed, but with a high-risk tumor, the side effects should be weighed against the benefits.
Which Cancer Treatments Cause Cystitis
Cystitis in cancer patients is often caused by treatment with the chemotherapy drugs cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide, administration of treatments directly into the bladder, or radiation therapy to the pelvic region.
Cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide: Cystitis is commonly caused by treatment with the chemotherapy drugs cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide. Drugs are broken down in the body to substances called metabolites. Acrolein is a metabolite produced when cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide are broken down. This metabolite is cleared from the body in the urine and irritates the lining of the bladder as it is being passed.
High-dose chemotherapy prior to stem cell transplant: High-dose cyclophosphamide and/or busulfan is often administered in conjunction with a stem cell transplant. This treatment is associated with significant, and sometimes life-threatening hemorrhagic cystitis.1
Delivery of treatment directly into the bladder: A treatment for superficial bladder cancer is to deliver chemotherapy directly into the bladder, called intravesical installation. This is done by passing the chemotherapy through a catheter in the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder. This approach delivers the chemotherapy drugs at full strength directly to the cancer, but may also irritate the lining of the bladder. The drugs commonly used for this approach are mitomycin-C , thiotepa or doxorubicin .
You May Like: How Do You Lose Control Of Your Bladder
Difficulties In Diagnosis Of The Severe Side Effects
If the side effects occur shortly after the instillation, the relationship with BCG can be made easily. Nevertheless, the side effects mostly occur when the patient is already back at home and generalists are not familiar with the complications of BCG. Therefore, it is highly advocated to inform the family doctor of the patient on the treatment and its possible complications, alarm symptoms, and practical attitude to solve the problem.
A second problem is that complications occur late, up to years after the treatment, when the urologist, who gives it, is no longer involved. Additionally, many of the complications give symptoms elsewhere in the body, and the patient goes to specialists who, again, are unfamiliar with BCG manifestations or even unaware of this treatment. Therefore, an information document should be delivered to each patient treated with the possible late complications. This is the way we handle it since many years. Although we have no proof, we are convinced that this can help to come to a more rapid diagnosis by colleagues of other specialties. This is important as the outcome of a complication is often dependent on early treatment initiation.
Treatment Of Bladder Cancer By Stage
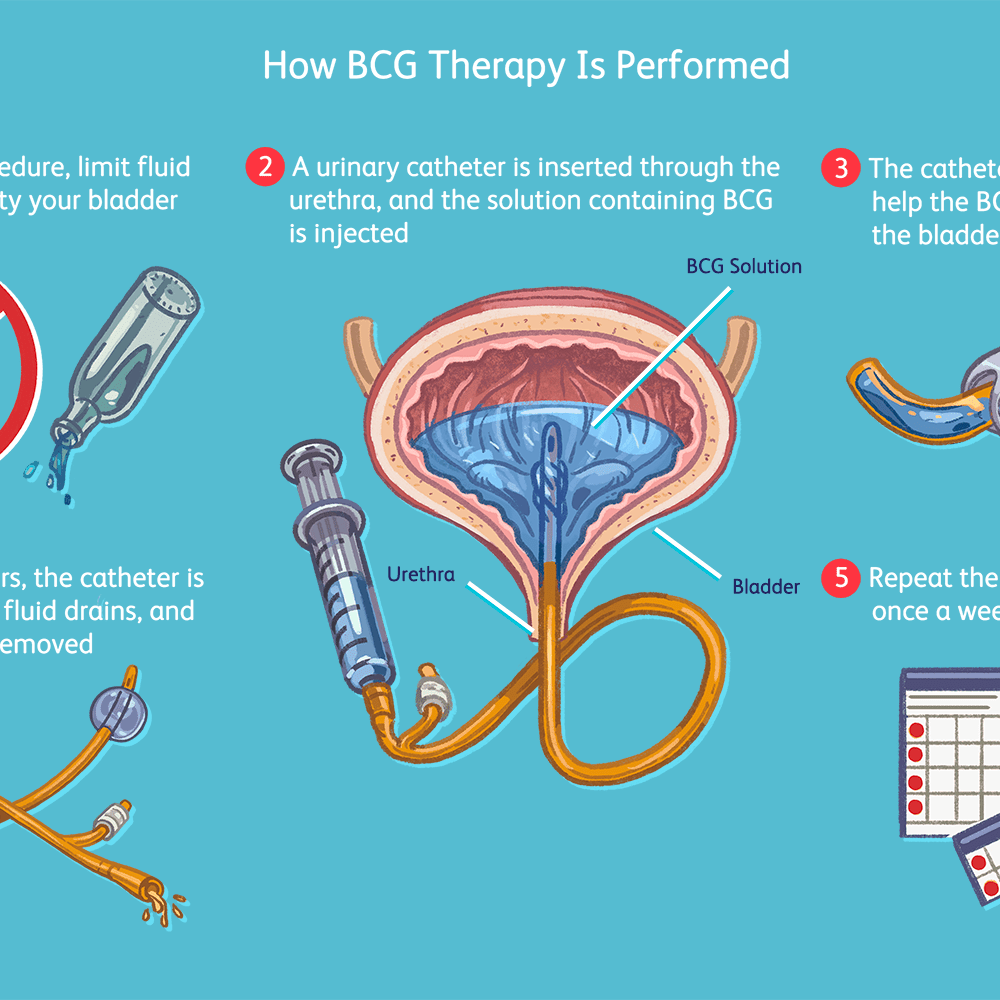
Most of the time, treatment of bladder cancer is based on the tumors clinical stage when it’s first diagnosed. This includes how deep it’s thought to have grown into the bladder wall and whether it has spread beyond the bladder. Other factors, such as the size of the tumor, how fast the cancer cells are growing , and a persons overall health and preferences, also affect treatment options.
Don’t Miss: Radiotherapy Success Rate For Bladder Cancer
Treating Stage Ii Bladder Cancer
These cancers have invaded the muscle layer of the bladder wall , but no farther. Transurethral resection is typically the first treatment for these cancers, but it’s done to help determine the extent of the cancer rather than to try to cure it.
When the cancer has invaded the muscle, radical cystectomy is the standard treatment. Lymph nodes near the bladder are often removed as well. If cancer is in only one part of the bladder, a partial cystectomy may be done instead. But this is possible in only a small number of patients.
Radical cystectomy may be the only treatment for people who are not well enough to get chemo. But most doctors prefer to give chemo before surgery because it’s been shown to help patients live longer than surgery alone. When chemo is given first, surgery is delayed. This is not a problem if the chemo shrinks the bladder cancer, but it might be harmful if the tumor continues to grow during chemo.
If cancer is found in nearby lymph nodes, radiation may be needed after surgery. Another option is chemo, but only if it wasn’t given before surgery.
For people who have had surgery, but the features of the tumor show it is at high risk of coming back, the immunotherapy drug, nivolumab, might be offered. When given after surgery, nivolumab is given for up to one year.
For patients who cant have surgery because of other serious health problems, TURBT, radiation, chemotherapy, or some combination of these may be options.
Is Bcg Treatment Contagious To Others
Yes. The drugs used for BCG treatment contain live bacteria, which can be passed to other people. To reduce the risk of contamination, follow these instructions for six hours after every BCG treatment:
- Dont use public toilets.
- Drink lots of fluids to dilute your pee.
- Sit down on the toilet to avoid splashing.
- After you pee, add 2 cups of undiluted bleach to the toilet, close the lid, wait 15 to 20 minutes and then flush.
- If you have urinary incontinence , immediately wash your clothes in a washing machine. Dont wash them with other clothes.
- If you wear an incontinence pad, pour bleach on the pad, allow it to soak in, then place it in a plastic bag and discard it in the trash.
Typically, youll need to refrain from having sex for a few days after each BCG treatment session. In addition, use a condom any time you have sex throughout the entire course of treatment. Ask your healthcare provider about specific guidelines regarding sex.
Recommended Reading: How Do I Treat A Bladder Infection At Home
What Happens During Treatment
A urinary catheter is inserted through your urethra and into your bladder. Then the BCG solution is injected into the catheter. The catheter is clamped off so the solution stays in your bladder. Some doctors may remove the catheter at this time.
You have to hold the medicine in your bladder. Youll be instructed to lie on your back and to roll from side to side to make sure the solution reaches your entire bladder.
After about two hours, the catheter is unclamped so the fluid can be drained. If the catheter was already removed, youll be asked to empty your bladder at this time.
Sex After Bcg Treatment
Men should use a condom during sex for the first week after each BCG treatment. If you are a woman having the treatment, your partner should use a condom during this time. This protects your partner from any BCG that may be present in semen or vaginal fluid. Your doctor or specialist nurse can give you more information about this.
Doctors do not yet know how BCG may affect an unborn baby. They will recommend you do not become pregnant or make someone pregnant while having it. You should use effective contraception during treatment. Your doctor or specialist nurse can give you more information about this.
Don’t Miss: Best Foods To Eat For Bladder Infection