Bladder Cancer In Women
In 2016, about 18,000 women will be told they have bladder cancer. Your bladder is an organ in your pelvic area that holds urine. Most bladder cancers start in the cells that line the inside of the bladder.
One of the first signs of bladder cancer is blood in the urine . Blood can either be seen with the naked eye or seen only under a microscope . Many women ignore blood in their urine because they think it’s normal in females. Other signs of bladder cancer are frequent or painful passing of urine, back pain, stomach pain and the feeling as if you need to go to the bathroom right away . Be sure to see a health care provider if you have any of these signs.
If you’ve been told you have bladder cancer, your health care team will talk with you about your treatment choices. Based on the stage of the cancer and other factors, your treatment could include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation or other therapies.
What You Need to Know:
Arsenic In Drinking Water
Drinking water containing arsenic is associated with a greater risk of bladder cancer. However, this is not a large concern in the U.S. Where you live, as well as if you drink well water, or public system water will determine your risk. Most public water systems meet standards for low arsenic content.
How Is Haematuria Investigated
Patients who present with significant haematuria need assessment by a urologist. Significant haematuria is defined as one episode of visible haematuria or symptomatic non-visible haematuria, or persistent asymptomatic non-visible haematuria .
Ideally, such patients should be seen as soon as possible in a one-stop clinic where the first step is a careful history and physical examination. The urine will be dipsticked to look for signs of infection or other abnormalities. If needed, it will then be sent off for a culture, to see if there are any bacteria in it. A urinary cytology is also obtained to look for abnormal cells in the urine. A blood test should also be done to measure the kidney function, and in men, after counselling, a PSA test is done.
Further tests include an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder, or a CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis . A CT scan is the preferred method of evaluating kidney masses and is the best modality for the evaluation of urinary stones.
A flexible cystoscopy is also likely to be required. This is a look into the bladder with a small flexible telescope, which is inserted via the urethra under local anaesthetic. Looking through the cystoscope your urologist can examine the inner lining of the bladder and urethra for abnormalities.
It is usually in this way that bladder cancer is diagnosed.
Recommended Reading: What Is A Sling For The Bladder
What Are The Risk Factors Of Bladder Cancer
Some risk factors, such as diet and exercise, you can change. Others like age and genetics, you cant. Keep in mind that having risk factors doesnt mean youll get sick. And, not having risk factors doesnt mean you wont. Thats why its important to know the risk factors, practice healthy habits and always talk to your doctor if you experience any signs or symptoms.
What Increases Your Chances Of Getting Bladder Cancer
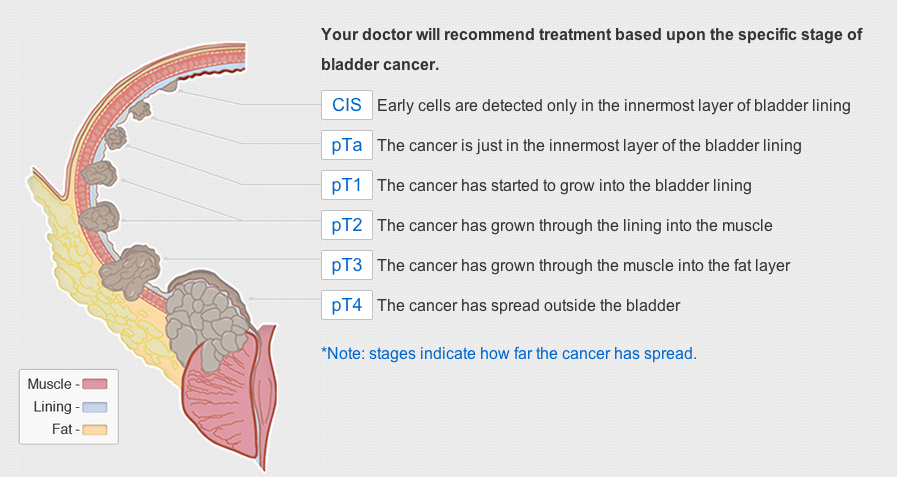
Anything that increases your chances of getting a disease is called a risk factor. The main risk factors for bladder cancer include:
- Smoking. Cigarette smokers are much more likely than other people to get bladder cancer.
- Being older than 40, being male, or being white .
- Being exposed to cancer-causing chemicals, such as those used in the wood, rubber, and textile industries.
- What you eat. A diet high in fried meats and fats increases your risk for bladder cancer.
- Parasites. There is a parasite that causes schistosomiasis, which can increase your risk. This condition is sometimes found in developing countries and rarely occurs in North America.
Also Check: Natural Remedies For Cystitis Bladder Infection
Facts And Stats On Bladder Cancer
-
Men have a higher incidence of bladder cancer than women.
-
Older adults are particularly affected as the risk for bladder cancer increases with age. Nine out of ten people diagnosed are over the age of 55. The average age is 73.
-
Bladder cancer has the highest recurrence rate of any form of cancer.
-
Due to the incidence and recurrence, prevention, early detection and prompt treatment are imperative.
How Dangerous Is Bladder Cancer
Over 3000 people die from bladder cancer each year in the UK. However, the vast majority of patients will have superficial bladder disease and will not require radiotherapy or bladder removal . These patients will come back to hospital for check cystoscopys on a regular basis for a significant number of years. The death rate amongst women has remained the same for a long time, the death rate amongst men is slowly dropping.
Also Check: Bcg Chemo For Bladder Cancer
Bladder Cancer Risk Factors
Each year, more than 80,000 Americans are diagnosed with bladder cancer. Anyone can get bladder cancer, but factors such as age, race and gender may increase the risk of the disease. Knowing behavior-related risk factors for bladder cancer may help you take preventive measures to reduce your chances of developing the disease or may help you and your doctor detect signs of bladder cancer earlier.
Family History Of Bladder Cancer
You may be twice as likely to develop bladder cancer if you have a close relative who has had the disease. A close relative includes a parent, sibling, or child. This possibility may be related to genetic factors that make it harder for the body to remove dangerous chemicals after exposure. In addition, an inherited disease linked to colorectal cancer called Lynch syndrome also increases the risk of bladder cancer.
Don’t Miss: Bladder Control Products By Mail
Where Does Bladder Cancer Most Often Spread
Lymph nodes, bones, lung, liver, and peritoneum are the most common sites of metastasis from bladder cancer. Tumors in a more advanced T category and those with atypical histologic features metastasize earlier. Tumors with atypical histologic features also have a higher frequency of peritoneal metastasis.
What Is Intravesical Chemotherapy
Following removal of your bladder tumour, intravesical chemotherapy or intravesical immunotherapy may be used to try to prevent tumour recurrences. Intravesical means âwithin the bladderâ. These therapeutic agents are put directly into the bladder through a catheter in the urethra, are retained for one hour and are then urinated out.
They are used because we know that they help to prevent tumour recurrence, and while mitomycin C does not prevent the rate of progression , there is some evidence that BCG may.
Each agents produces irritative side effects such as frequent urination , painful urination . In addition, BCG therapy carries a 20% percent risk of flu-like symptoms and a small risk of generalised infection. There is a chance of skin rash with MMC .
Further information on bladder cancer can be obtained by clicking the links below:
Macmillan: more information on treatment for bladder cancer
You May Like: Bladder Leakage Without Feeling It
Signs Of Bladder Cancer: What Women Should Know
Bladder cancer may not be on your radar even if youre vigilant about getting routine GYN care. After all, its far more common among men than women, and the majority of cases affect patients over age 65. However, dont let those stats keep you from learning to spot the warning signs.
While bladder cancer isnt one of the most common cancers in women, about 18,000 women are diagnosed with bladder cancer every year in the United States . The Bladder Cancer Advocacy Network reports that women are more likely to be diagnosed with bladder cancer at an advanced stage because they may not be on the lookout for early signs.
Recommended Reading: Harmony Urinary Tract And Bladder Support
Facts About Bladder Cancer In Women
While bladder cancer typically hasnt been associated with women, it is important to understand the unique way that bladder cancer does affect women, and why its critical that bladder cancer isnt overlooked.
- Approximately 50% of cases are diagnosed while the cancer is still in the bladder. However, that percentage is lower in women, because symptoms are often overlooked.
- Women have a 1 in 89 chance of developing bladder cancer in their lifetime . However, bladder cancer in women is on the rise.
- Approximately 90% of bladder cancer cases are in individuals over 55 years old, so it is important to be extra vigilant of early signs of bladder cancer as you age.
- Bladder cancer has a high recurrence rate. If you have been diagnosed with bladder cancer, it is important to continue to receive regular exams in order to handle any potential recurrence.
Don’t Miss: Women’s Bladder Leakage Protection
When Is This Form Of Cancer Most Often Diagnosed And Treated
Bladder cancer is often diagnosed at an early stage. Roughly 50 percent of cases are diagnosed while the cancer is in situ . Only in 4 percent of cases has it spread to distant areas of the body.
In 90 percent of cases, surgery is recommended as part of the treatment plan. It may be the sole treatment or used in combination with chemotherapy, radiation therapy or immunotherapy.
The five-year survival rate is 77.3 percent for the general population. However, this number can vary quite a bit based on the stage of the bladder cancer at diagnosis. A more relevant number may come from relative survival rate, which compares an individual to a subset of the general population that matches in:
- Age
What Are The Risks Of Bladder Cancer
No single factor is directly connected to bladder cancer, but factors that can increase the risk include:
- Age: Bladder cancer typically affects people age 55 and older.
- Smoking: Carcinogens from tobacco smoke come in contact with the lining of the bladder. Smokers are three times as likely as non-smokers to get bladder cancer.
- Family history: There is evidence that bladder cancer may have a genetic component.
- Industrial chemicals: Chemicals known as aromatic amines are often used in the dye industry. Workers who have daily exposure to them, such as painters, machinists and hairdressers, may be at a higher risk for bladder cancer.
- Drinking contaminated water: This includes water that has been treated with chlorine or drinking water with a naturally high level of arsenic, which occurs in many rural communities in the United States,.
- Taking certain herb: Supplements such as Aristolochia fangchi, a Chinese herb, sometimes used for weight loss has been linked to higher rates of bladder cancer.
You May Like: Recurrent Bladder Infections And Cancer
You May Like: Causes Of Repeated Bladder Infections
Treatment For Bladder Cancer
Treatment for bladder cancer depends on how quickly the cancer is growing. Treatment is different for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer and muscle-invasive bladder cancer. You might feel confused or unsure about your treatment options and decisions. Its okay to ask your treatment team to explain the information to you more than once. Its often okay to take some time to think about your decisions.
Bladder Cancer Mortality By Age
Bladder cancer mortality is strongly related to age, with the highest mortality rates being in older people. In the UK in 2016-2018, on average each year around 7 in 10 deaths were in people aged 75 and over. This largely reflects higher incidence and lower survival for bladder cancer in older people.
Age-specific mortality rates rise steeply from around age 55-59. The highest rates are in the 90+ age group for females and males. Mortality rates are significantly lower in females than males in a number of age groups. The gap is widest at age 90+,when the age-specific mortality rate is 3.5 times lower in females than in males.
Bladder Cancer , Average Number of Deaths per Year and Age-Specific Mortality Rates per 100,000 Population, UK, 2016-2018
Dont Miss: How To Keep Bladder Infections Away
You May Like: Bladder Control Problems At Night
What Are The Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
Passing blood in the urine is the most common symptom. It eventually occurs in nearly all cases of bladder cancer. In the many cases, the blood is visible during urination. In some cases, it is only detected on dipstick examination of the urine or under a microscope, and is usually discovered when analysing a urine sample as part of a routine examination.
Haematuria does not by itself confirm the presence of bladder cancer. Blood in the urine has many possible causes . For example, it may result from a urinary tract infection or kidney stones rather than from cancer. It is important to note that haematuria, particularly dipstick or microscopic, might be entirely normal for some individuals. A diagnostic investigation is necessary to determine whether bladder cancer or another abnormality is present.
Other symptoms of bladder cancer may include frequent urination, urinary urgency and pain upon urination .
Genetics And Family History
If you have family members who have bladder cancer, you have a higher risk of developing it yourself. This could also be that family members share exposure to the same chemicals that cause cancer or they share the same changes in certain genes , making it harder for their bodies to break specific toxins down, increasing their risk of bladder cancer.
You May Like: Low Grade Bladder Cancer Recurrence
Is Smoking Linked To Bladder Cancer
Smokers are two to five times more likely to get bladder cancer than normal. The more they smoke, or the longer they smoke, the higher the risk. It is estimated that half of all bladder cancers in men, and one third in women, are the result of smoking.
Smoking increases the risk of bladder cancer. Chronic bladder infections, or bladder stones, slightly increase the risk. Contact the NHS Grampian Smoking Advice Service for help to give up smoking.
What Are The Symptoms
- blood in the urine
- the need to pass urine very often or very urgently.
The most common symptom is blood in the urine, although there are many other conditions which can cause this. The other less common symptoms can also have other causes.
None of these symptoms are necessarily due to bladder cancer because infections can also cause these signs. However, anyone noticing these signs should report them to a doctor.
Don’t Miss: Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Survival
Low Grade And High Grade Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer starts in the lining of the bladder in about 90 percent of people diagnosed with this cancer. Bladder cancer is called low grade or high grade.
- Low-grade bladder cancer means the cancer has not invaded the muscles around the bladder . People rarely die from this type of bladder cancer, it often recurs after treatment.
- High-grade bladder cancer also often recurs and has a higher chance of spreading to other parts of the body. Almost all deaths from bladder cancer result this type so it is treated more aggressively.
Can You Prevent Bladder Cancer
These three simple lifestyle changes may cut your risk of bladder cancer:
- If you smoke, stop. Doctors believe tobacco products cause about half of all bladder cancer cases.
- Drink lots of fluids. When you pee, you get rid of harmful chemicals that build up in your bladder. So drink up — especially water. It may lower your cancer risk.
- Eat more fruits and veggies. Studies show that eating lots of fruits and green, leafy vegetables lowers your risk for many types of cancer. It may help cut your risk for bladder cancer, too.
Your risk for bladder cancer can also be increased by certain workplace chemicals, arsenic, aniline , certain diabetes medicines, and some herbal supplements. Follow all workplace safety rules, and ask your doctor about any specific risk factors you may have.
Read Also: I Feel A Lot Of Pressure On My Bladder
Types Of Cancers That Develop In Adolescents
Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow out of control. Cells in nearly any part of the body can become cancer, and can then spread to other areas of the body. To learn more about cancer and how it starts and spreads, see Cancer Basics.
For statistical purposes, cancers in adolescents are often thought of as those that start between the ages of 15 and 19. Cancer is not common in teens, but a variety of cancer types can occur in this age group, and treating these cancers can be challenging for a number of reasons.
Most cancers occur in older adults. Cancers that start in childhood are much less common. The types of cancers that develop in children are often different from the types that develop in adults. Childhood cancers are often the result of DNA changes in cells that take place very early in life, sometimes even before birth. Unlike many cancers in adults, childhood cancers are not strongly linked to lifestyle or environmental risk factors.
The types of cancers that occur in adolescents are a mix of many of the types that can develop in children and adults. The types of cancers seen in adolescents are not unique to this age group, but the most common types are different from those most common in young children or adults.
Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
The most common bladder cancer symptom is blood in the pee. Blood in pee is also called haematuria. Most people with symptoms will not have bladder cancer. But if you have any symptoms, it is important to get them checked by your GP. The earlier bladder cancer is diagnosed the more likely it is to be cured.
We have more information about signs and symptoms of bladder cancer.
See also
Also Check: Best Over The Counter Bladder Control Medication
Types Of Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer can be described based on where it is found:
- non-muscle invasive the cancer has not spread to other layers of the bladder or muscle
- muscle-invasive the cancer has spread to other layers of the bladder, muscle or other parts of the body.
There are 3 main types of bladder cancer:
- urothelial carcinoma 80 to 90% of bladder cancers sometimes called transitional cell carcinoma
- squamous cell carcinoma 1 to 2% of all bladder cancers. It is more likely to be invasive
- adenocarcinoma 1 to 2% of all bladder cancers. It is more likely to be invasive .
There are other, less common types of bladder cancer. Treatment for these may be different. Speak to your doctor or nurse for information about these types of cancer.