How Many Is Too Many Utis
Three or more UTIs in one year indicates a recurrent infection, according to the ACOG.
Recurrent urinary tract infections are treated with antibiotics. A week or two after you finish the antibiotic treatment, your doctor may perform a urine test to make sure the infection is cured.
Your doctor may also ask you about factors that increase the risk of a recurrent UTI, including:
- Young age at first UTI
When To Call A Professional
If you have risk factors for developing complicated bladder infections , you should be particularly careful to watch for these signs of infection. You also should seek immediate medical attention if you develop fever, chills, confusion, nausea, vomiting, or flank pain, which may suggest that a bladder infection has spread to the kidney or blood.
Why Does My Uti Keep Coming Back
Chronic or recurring UTIs may keep coming back due to one of the risk factors listed above. Use of spermicides for birth control, for instance, may kill off beneficial bacteria in and around the vagina, making it easier for harmful bacteria to enter the urinary tract.
In some cases, what seem like recurrent UTIs may actually be another condition, such as kidney stones or interstitial cystitis, a painful bladder condition with no infection. If you think youre getting recurrent UTIs, see your provider, who can help rule out another condition, notes ACOG.
Don’t Miss: How Do I Treat A Bladder Infection At Home
What Is The Bladder
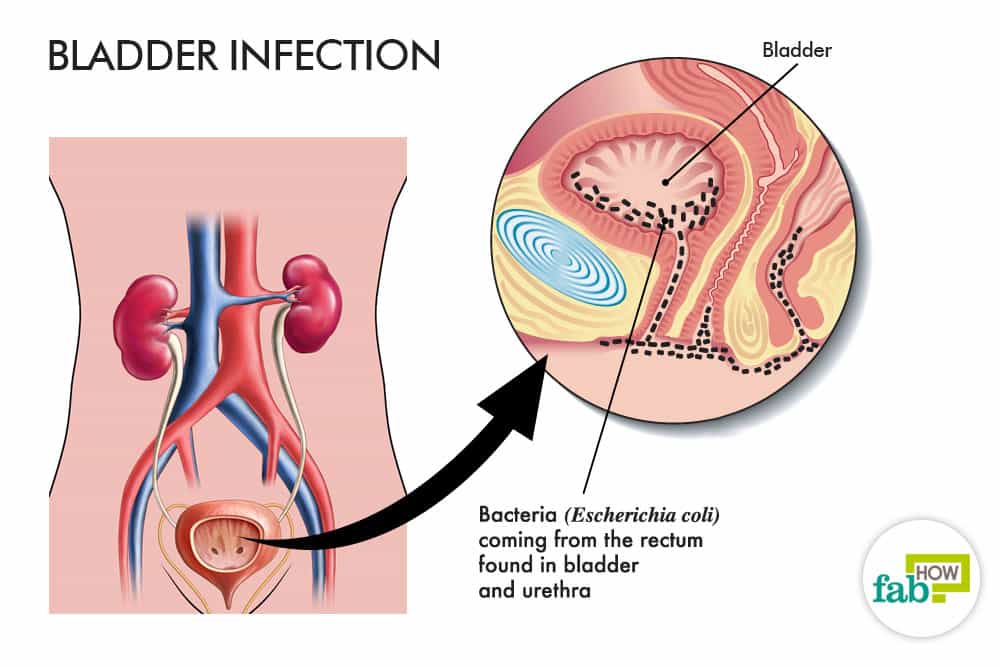
The bladder is a hollow muscular organ that is located in the pelvis. The bladder has two functions: one is to store urine and the other is to release/expel urine. Urine drains from the kidneys , down the ureters , and into the bladder. The urine is stored in the bladder where it remains until urination. When it is time to urinate, the bladder muscle contracts, and the outlet of the bladder and sphincter muscles relax to allow urine to pass through the urethra to leave the body. The bladder and urethra are part of the lower urinary tract, whereas the kidneys and ureters are part of the upper urinary tract.
Vaccines Targeting Bacterial Adhesion
As adherence has a key role at nearly every step of UTI pathogenesis, one attractive strategy for the development of antivirulence therapies, including vaccines, has been to target CUP pili. As a general rule, vaccination with whole pili has been ineffective at generating an antibody response that can protect against UTIs. However, adhesin-based vaccines have been shown to be effective at blocking hostpathogen interactions, thus preventing the establishment of disease. Experiments using mouse and cynomolgus monkey models of UTIs determined that immunization with PapDPapG or FimCFimH chaperoneadhesin complexes protected against UTIs. The effectiveness of the FimCFimH vaccine was shown to be due, in large part, to antibodies that block the function of FimH in bladder colonization. Furthermore, the anti-FimH antibodies did not seem to alter the E. coli niche in the gut microbiota. Modifications of this vaccine are currently under development, with the aim of inducing greater immune stimulation,. For example, one approach has been to fuse FimH to the flagellin FliC in order to induce a more substantial acute inflammatory response, which functions through TLR4 signalling via the MYD88 pathway. A Phase I clinical trial began in January 2014 to evaluate the efficacy of a FimCFimH vaccine using a synthetic analogue of monophosphoryl lipid A as the adjuvant.
Don’t Miss: New Drug For Overactive Bladder
Molecular Pathogenesis Of Uti
Infection of the urinary tract begins when UPEC, likely introduced after colonization of the periurethral area by gastrointestinal tract flora , accesses and ascends the urethra by an undetermined mechanism. Upon reaching the urinary bladder, UPEC bind to superficial epithelial cells in a type 1 pili-dependent manner . A subset of adherent bacteria are then internalized into facet cells , a dynamic process that likely relies on the normal cycling of apical membrane segments in these cells . Countering this key pathogenic activity, bladder epithelial cells undertake active expulsion of internalized UPEC. Recent data show that UPEC are capable of neutralizing the lysosome, and that this neutralization is sensed by a lysosomal membrane protein termed mucolipin TRP channel 3 , activating pathways that direct exocytosis of UPEC-containing lysosomes . Through a distinct mechanism, activation of Toll-like receptor 4 by internalized UPEC leads to specific ubiquitination of TNF Receptor Associated Factor 3 , enabling its interaction with a guanine-nucleotide exchange factor that directs assembly of the exocyst complex, thereby accomplishing expulsion of intracellular bacteria .
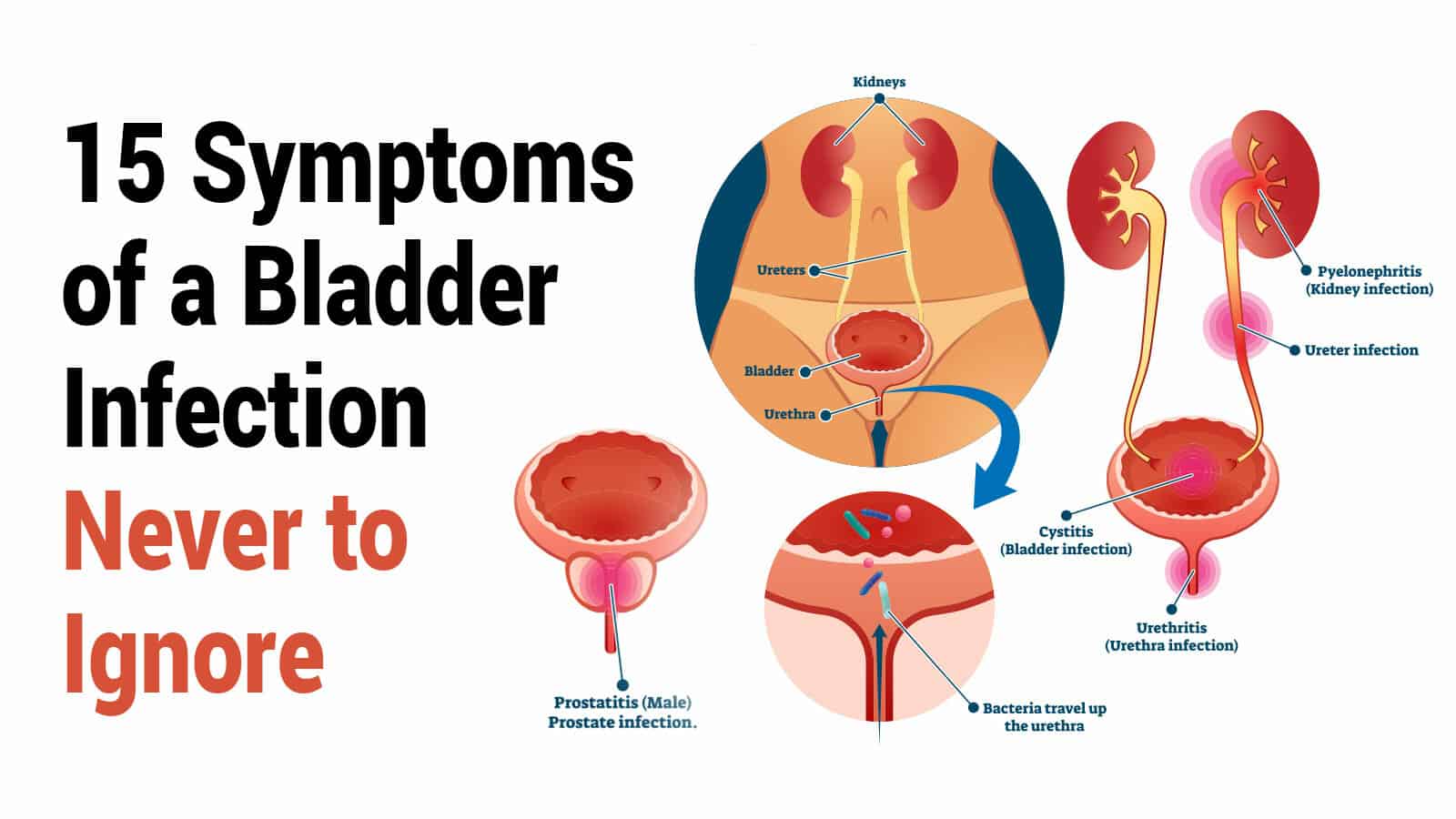
What Is A Bladder Infection
Cystitis is inflammation of the bladder. Most cystitis is from bacterial infections involving the bladder and less commonly may be due to other infectious diseases, including yeast infections, viral infections, or the result of other causes such as chemical irritants of the bladder, or for unknown reasons . Bladder infection is a type of urinary tract infection . Other forms of urinary tract infection include pyelonephritis , urethritis , and prostatitis . This review will specifically address infectious cystitis.
The urine in the bladder is normally free of bacteria . However, bacteria may be present in the bladder but not cause inflammation or symptoms of an infection.
- This is asymptomatic bacteriuria, not cystitis.
- Asymptomatic bacteriuria is bacteria in the urine that does not cause symptoms.
- It is important to differentiate asymptomatic bacteriuria from cystitis, to prevent overuse of antibiotics.
- Most people with asymptomatic bacteriuria do not require antibiotics.
- In fact, the guidelines for the Infectious Disease Society of America recommend only treating asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnant women or immediately before urologic procedures.
Also Check: Bcg Tx For Bladder Cancer
Who Is More Likely To Develop A Bladder Infection
People of any age or sex can develop bladder infections, but women are at higher risk than men. Some people are more prone to getting these infections than others, especially those who have certain medical conditions or lifestyle factors.
You are more likely to develop a bladder infection if you
- are sexually active
- are a woman who has gone through menopause
- are a woman who uses certain types of birth control, such as diaphragms or spermicide
- have trouble emptying your bladder completely, like people with a spinal cord injury or nerve damage around the bladder
- have a problem in your urinary tract that blocks, or obstructs, the normal flow of urine, such as a kidney stone or enlarged prostate
- have an abnormality of the urinary tract, such as vesicoureteral reflux
- have diabetes or problems with your body’s immune, or natural defense, system
- recently used a urinary catheter
- had a UTI in the past
Women are more likely to develop a bladder infection than men, mainly due to differences in anatomy:
- Women have a shorter urethra than men, which means bacteria have a shorter distance to travel to reach and infect a woman’s bladder.
- In women, the opening to the urethra is closer to the rectum, where the bacteria that cause bladder infections live.
Does Cranberry Juice Prevent A Urinary Tract Infection
Many people say that cranberry juice can help treat, or even prevent, a UTI. Researchers are currently looking into the topic, but havent found a definitive answer yet. Healthcare providers recommend drinking lots of fluids if you have, or have a history of getting, a UTI. Adding a glass of unsweetened cranberry juice to your diet isnt a proven way to prevent a UTI, but it typically wont hurt you either.
You May Like: Sleep Number Bed Bladder Replacement
How Is A Uti Treated In A Child
Treatment will depend on your childs symptoms, age, and general health. It will also depend on how severe the condition is. Treatment may include:
- Antibiotic medicine
- A heating pad or medicines to relieve pain
- Drinking plenty of water
Your child’s healthcare provider may want to see your child back again a few days after treatment starts to see how treatment is working.
Talk with your childs healthcare providers about the risks, benefits, and possible side effects of all treatments.
Can I Prevent Urine Infections
Unfortunately, there are few proven ways to prevent urine infections. No evidence has been found for traditional advice given, such as drinking cranberry juice or the way you wipe yourself.
There are some measures which may help in some cases:
- It makes sense to avoid constipation, by eating plenty of fibre and drinking enough fluid.
- Older women with atrophic vaginitis may wish to consider hormone replacement creams or pessaries. These have been shown to help prevent urine infections.
- If there is an underlying medical problem, treatment for this may stop urine infections occurring.
- For some people with repeated urine infections, a preventative low dose of antibiotic taken continuously may be prescribed.
Don’t Miss: How Can I Strengthen My Bladder
What Is The Outlook
Most people improve within a few days of starting treatment. See a doctor if you do not quickly improve. If your symptoms do not improve despite taking an antibiotic medicine then you may need an alternative antibiotic. This is because some bacteria are resistant to some types of antibiotics. This can be identified from tests done on your urine sample.
Remedies For Bladder Infections
If you think you have a bladder infection, you should contact your doctor and schedule an outpatient appointment. Youâll need medication to get rid of the bacterial infection. That said, there are home remedies you can also use to help ease symptoms and help with the healing process. Here are five remedies and treatments for bladder infections that you can use:
1. See your doctor for an antibiotic
If youâre diagnosed with a bladder infection, your doctor will likely prescribe an oral antibiotic. Antibiotics work by getting rid of the bacteria that is causing your bladder infection. Research has shown that antibiotics are effective and perform better than a placebo.
You need to complete the full course of the prescribed antibiotic, even when you start to feel better. If you stop the antibiotic before completing the prescription, you risk getting another infection. In an uncomplicated or simple bladder infection, youâll typically notice an improvement in your symptoms within a day or two of starting the antibiotic. Your doctor may select an antibiotic treatment course that will last three to five days. In complicated bladder infections, the course is longer, typically seven to fourteen days.
2. Drink more water
When caring for a bladder infection, itâs critical to drink lots of fluids to help flush the bacteria out of your bladder. The additional fluids also help dilute your urine, which can make urinating less painful while youâre healing from the infection.
You May Like: Overactive Bladder And Back Pain
Can Utis Be Prevented
A few things can help prevent UTIs. After peeing, girls should wipe from front to back with toilet paper. After BMs, wipe from front to back to avoid spreading bacteria from the rectal area to the urethra.
Also, go to the bathroom when needed and don’t hold the pee in. Pee that stays in the bladder gives bacteria a good place to grow.
Keep the genital area clean and dry. Girls should change their tampons and pads regularly during their periods. Bubble baths can irritate the vaginal area, so girls should take showers or plain baths. Avoid long exposure to moisture in the genital area by not wearing nylon underwear or wet swimsuits. Wearing underwear with cotton crotches is also helpful. Skip using feminine hygiene sprays or douches, as these can irritate the urethra.
If you are sexually active, go to the bathroom both before and within 15 minutes after sex. After sex, gently wash the genital area to remove any bacteria. Avoid sexual positions that irritate or hurt the urethra or bladder. Couples who use lubrication during sex should use a water-soluble lubricant such as K-Y Jelly.
Finally, drinking lots of water each day keeps the bladder active and bacteria-free.
UTIs are uncomfortable and often painful, but they’re common and easily treated. The sooner you contact your doctor, the sooner you’ll be able to get rid of the problem.
Eating Diet & Nutrition
Experts dont think eating, diet, and nutrition play a role in preventing or treating bladder infections. If you have any type of UTI, talk with a health care professional about how much to drink each day to help prevent or relieve your infection.
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and other components of the National Institutes of Health conduct and support research into many diseases and conditions.
You May Like: How Do Doctors Test For Bladder Cancer
Pyelonephritis & Its Symptoms
It refers to infection of kidneys due to ascending of the bacteria and is yet another common urinary tract infections . Mild pyelonephritis can present as low-grade fever with or without low back pain, whereas severe pyelonephritis can manifest as high fever, rigor, nausea, vomiting, and flank and/or loin pain. Symptoms are generally acute in onset, and most common urinary tract infections are accompanied with fever.
Patients with diabetes may present with obstructive uropathy associated with acute papillary necrosis when the sloughed papillae obstruct the ureter. Papillary necrosis may also be evident in some cases of pyelonephritis complicated by obstruction, sickle cell disease, analgesic nephropathy, or combinations of these conditions.
In the rare case of bilateral papillary necrosis may occur and a rapid rise in the serum creatinine level may be the first indication. Emphysematous pyelonephritis is a particularly severe form of the disease that is associated with the production of gas in the tissues of kidney and surrounding area. Such complication of common urinary tract infections is usually seen in diabetic patients. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis occurs when the chronic urinary obstruction , together with chronic infection, leads to a suppurative destruction of renal tissue.
If there is continued fever there is a risk of bacteremia, which may need immediate medical treatment.
How Common Are Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are very common, occurring in 1 out of 5 women sometime in their lifetime. Though UTIs are common in women, they can also happen to men, older adults and children. One to 2% of children develop urinary tract infections. Each year, 8 million to 10 million visits to doctors are for urinary tract infections.
Also Check: Can Endometriosis Cause Bladder Problems
Urinary Tract Infection Caused By Group B Streptococcus
Group B Streptococcus is a Gram-positive chain-forming bacterium that commonly dwells in the lower gut and female reproductive tract without causing any symptoms. Statistics show that the bug causes only about 12% of all UTIs.
Advanced age and pregnancy are the main risk factors for contracting a UTI caused by this organism. In fact, GBS UTIs can be fatal in the elderly population. Those with poor immunitysuch as in those suffering from cancer and diabetes, and pre-existing abnormalities of the urinary tract such as chronic kidney disease or stones in the kidneysare subject to additional risk factors for contracting a GBS UTI.
When it comes to pregnancy, although GBS often doesnt cause any symptoms in women, its presence in urine and/or the vagina can pose serious threats for both the mother and the child. Most importantly, if there is a transfer of GBS from the mother to the baby during labor and delivery, the infection could spread to the child s bloodstream, which can be life-threatening. Given the high risk of GBS complications in the baby, the Centers for Disease Control recommend universal screening of all females at 35-37 weeks of pregnancy. If a woman tests positive for GBS, preventive IV antibiotics are recommended during labor and delivery.
Can Recurrent Utis Be A Sign Of Cancer
Both UTIs and bladder cancer can cause similar symptoms, such as a frequent need to urinate and even blood in the urine, according to the University of Rochester Medical Center.
According to the American Cancer Society, urinary tract infections, kidney and bladder stones, and other causes of chronic bladder irritation have been linked to bladder cancer. However, its not clear whether recurrent urinary or bladder infections can actually cause bladder cancer or whether they constitute a true risk factor for bladder cancer.
The biggest known risk factor for bladder cancer is smoking. The risk of bladder cancer also increases with age. Most people who get bladder cancer are over the age of 55.
If you think you may have chronic or recurrent UTIs, its best to get checked out by your doctor. Your provider can rule out other health issues, including bladder cancer, and get you the treatment you need to get rid of chronic UTIs.
Also Check: Cysts On Bladder And Kidneys
What If The Infection Does Not Clear Up With Treatment
Most infections clear up with treatment. However, if an infection does not clear up, or if you have repeated infections, you may be given some special tests such as:
-
a type of x-ray called an intravenous pyleogram , which involves injecting a dye into a vein and taking pictures of your kidney and bladder
-
an ultrasound exam, which gives a picture of your kidneys and bladder using sound waves
-
a cytoscopic exam, which uses a hollow tube with special lenses to look inside the bladder.
Living With Urinary Tract Infections
If you have 3 or more urinary tract infections each year, your doctor may want you to begin a preventive antibiotic program. A small dose of an antibiotic taken every day helps to reduce the number of infections. If sexual intercourse seems to cause infections for you, your doctor many suggest taking the antibiotic after intercourse.
You May Like: Low Grade Bladder Cancer Recurrence