Why Is Cysview Used
For patients with suspected or known bladder cancer, the benefits of blue light cystoscopy:
- Better inspection of the bladder for cancer, especially small or flat tumors
- Better removal of bladder tumors when they are first discovered
- Leads to fewer recurrences of bladder cancer
- Improved information to use to plan future care for bladder cancer
What Happens During A Cystoscopy
During flexible cystoscopy, the patient lies on their back and an anesthetic gel is passed into the urethra to make the area numb. Once the local anesthetic is working, the doctor inserts the cystoscope through the urethra and then into the bladder. Sterile water may be injected through the cystoscope into the bladder to help make the inner surface of the bladder easier to see. The cystoscope is moved around inside the bladder so that the entire inner surface can be examined.
During rigid cystoscopy, the procedure is similar to flexible cystoscopy but as the patient is usually under general anesthesia they will not be aware of any associated physical sensations. If the doctor sees an abnormal area, biopsies will be taken or a transurethral resection of bladder tumor may be carried out to remove the suspected tumor. The extracted tissues are then sent to a laboratory to be tested for cancer.
What Is A Cystoscopy
A cystoscope is a thin tube with a light and camera attached to the end. During a cystoscopy, the cystoscope is passed through the urethra into the bladder. The two main types of cystoscopy are termed flexible and rigid:
- Flexible cystoscopy uses a flexible cystoscope tube that is able to bend easily as it passes through the urethra. This procedure can be carried out under local anesthetic while the patient is awake and is commonly used for simple visual examination of the inside of the bladder, although the collection of bladder washings or small tissue samples may be undertaken.
- Rigid cystoscopy uses a hard, straight cystoscope. For this type of cystoscopy, patients are usually under general anesthesia in some patients, spinal anesthesia that numbs the lower half of the body may be used instead. Rigid cystoscopy is performed when tissue samples and/or removal of small bladder tumors are required. Long, small-diameter instruments can be passed down the cystoscope to take biopsies from the bladder lining, and a tool called a resectoscope that has a cutting wire loop at the end may be used to remove abnormal tissue or small tumors. This procedure is referred to as transurethral resection of a bladder tumor or TURBT.
Diagram of a cystoscopy for a man
Diagram of a cystoscopy for a woman
Don’t Miss: How Long Should A Bladder Infection Last
Medical History And Physical Exam
Your doctor will want to get your medical history to learn more about your symptoms. The doctor might also ask about possible risk factors and your family history.
A physical exam can provide information about possible signs of bladder cancer and other health problems. The doctor might do a digital rectal exam , during which a gloved, lubricated finger is put into your rectum. If you are a woman, the doctor might do a pelvic exam as well. During these exams, the doctor can sometimes feel a bladder tumor, determine its size, and feel if and how far it has spread.
If the doctor finds things that aren’t normal, you may to have lab tests done and you might be referred to a urologist for further tests and treatment.
Biopsies To Look For Cancer Spread
If imaging tests suggest the cancer might have spread outside of the bladder, a biopsy might be needed to be sure.
In some cases, biopsy samples of suspicious areas are taken during surgery to remove the bladder cancer.
Another way to get a biopsy sample is to use a long, thin, hollow needle to take a small piece of tissue from the abnormal area. This is known as a needle biopsy, and by using it the doctor can take samples without surgery. Sometimes a CT scan or ultrasound is used to help guide the biopsy needle into the changed area.
Don’t Miss: How To Relieve Bladder Spasms With Catheter
Improved Detection Of Tumors
Numerous clinical studies have exhibited significantly improved tumor detection rates with BLC. Meta-analyses and systematic reviews reveal a 7% to 29% increased rate of identifying small papillary tumors with BLC over WLC alone 00722-7/fulltext” rel=”nofollow”> Eur Urol 2013 64:624-38 Ther Adv Urol 2015 7:339-50). The majority of increased detection of papillary lesions comes from Ta tumors, with minimal increased detection of T1 tumors .
However, the increased detection is substantially improved with carcinoma in situ , with a 15% to 41% increased rate of detection over WLC alone 00722-7/fulltext” rel=”nofollow”> Eur Urol 2013 64:624-38 Ther Adv Urol 2015 7:339-50 J Urol 2007 178:68-73). Importantly, BLC should be used as an adjunctive technique to WLC-not a replacement-since up to 15% of CIS lesions may be seen on WLC but not BLC .
Next: Decreased tumor recurrence, progression
Tests For Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer is often found because of signs or symptoms a person is having. Or it might be found because of lab tests a person gets for another reason. If bladder cancer is suspected, exams and tests will be needed to confirm the diagnosis. If cancer is found, more tests will be done to help find out the extent of the cancer.
Also Check: Test To Detect Bladder Cancer
Is A Cystoscopy Painful
Some discomfort may be felt when the local anesthetic gel is applied to the urethra, and when the cystoscope is passed through the urethra into the bladder. At this stage the patient may also feel a need to pass urine. In contrast, if a cystoscopy is carried out under general anesthesia there will be complete unawareness of the procedure taking place. If a spinal anesthetic is used the patient will not feel any discomfort, though a sensation of movement or pressure may be noticed.
Blue Light Cystoscopy With Cysview Q& a
Patients seeking treatment for bladder cancer have many choices on where to go for their care. There are more diagnostic tools and treatments now than ever before. Today, patients have an additional option when undergoing a biopsy or surgical removal of a suspected or known bladder cancer or for their follow-up check-up cystoscopies.1-4
BLC with Cysview is an important tool that can aid in the diagnosis and management of bladder cancer.1-4 Finding a center that offers this option can make a difference. Doctors at your institution are now using BLC with Cysview to better detect patients bladder cancer.
Below are the answers to some common questions about BLC with Cysview:
Q: What is BLC with Cysview?
In the earliest stages of bladder cancer, cancer cells are located on the surface layer of the bladder wall. Identifying this kind of cancer, which is called non-muscle invasive bladder cancer , requires a correct and thorough work-up, and diagnosis is a key component of successful treatment. Understanding the stage and grade of the cancer is essential to deciding on the best treatment path.
To diagnose this disease, surgeons inspect the inside of the bladder using a long, thin tube called a cystoscope that includes a video camera on the end. In the past, the only option was white light cystoscopes, which do not always easily show tumors or cancerous lesions.
Q: How is Cysview administered and how does it work?
Q: How many patients have had BLC with Cysview?
Also Check: How Is Bladder Cancer Staged
What To Expect After A Cystoscopy
Patients usually leave the hospital on the same day of a cystoscopy. Depending on the type of anesthesia used, it may be necessary to arrange a ride home with a friend or family member.
For 1 or 2 days after a cystoscopy, patients may notice blood in the urine and/or a burning sensation when passing urine. Drinking plenty of fluids usually helps to minimize these symptoms. Returning to work, physical, and sexual activities is usually quick, for example later the same day after a flexible cystoscopy and 1 to 2 days after a rigid cystoscopy. If discomfort is severe or symptoms do not improve as expected, it is important to promptly seek medical help.
Blfc For Surveillance: Best Practice
Several factors need consideration for implementing BLFC for surveillance. The main goal of surveillance of bladder cancer is to determine whether a patient has recurrence or progression. Thus, all patients could benefit from enhanced cystoscopy either to reassure the patient and provider that no cancers were missed or to identify suspicious areas that need biopsy or, at a minimum, closer attention. However, BLFC requires an extra step of instillation, increased time and increased resources and initial expense. Thus, early in the adoption of BLFC, selecting patients who are most suitable for the procedure will probably be beneficial. Accumulating evidence might further clarify the role of BLFC for different disease-risk and specific scenarios however, the goal of this consensus panel was to make recommendations regarding likely benefit of use of BLFC .
Table 2 Consensus recommendations for best practice in the use of BLFC for surveillance
Panel recommendations: likelihood of recurrence
Panel recommendations: frequency of surveillance
Panel recommendations: specific clinical scenarios
You May Like: Does Amitriptyline Help Overactive Bladder
How Is Bladder Cancer Diagnosed
The earlier bladder cancer is diagnosed, the better the outcome of treatment. Since there is no screening test for bladder cancer at this time, most people are diagnosed after they show some symptoms, such as blood in the urine. Because symptoms such as blood in the urine can be a sign of other conditions, such as a urinary tract infection , there can be a delay in diagnosing bladder cancer.
Here are some of the tests and procedures used to detect bladder cancer. Please note that, since individual cases and facilities are different, not all of these tests may be required or available.
After diagnostic tests are done, your doctor will review all of the results with you. If the diagnosis is cancer, these results also help the doctor describe the cancer .
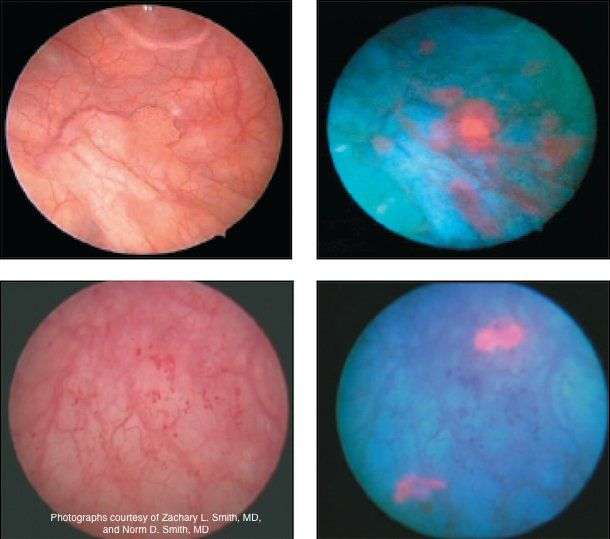
Detecting Bladder Cancer With A Cystoscopy
Cystoscopy enables the inside of the urethra and bladder to be examined and sampled. Alongside urine testing and diagnostic imaging procedures, cystoscopy is used in both the initial diagnosis of bladder cancer and in ongoing surveillance for recurrence. In addition, cystoscopy-based procedures are commonly used to remove or treat small bladder tumors.
Don’t Miss: Bladder Cancer In Cats Treatment
Are There Any Risks Associated With Cystoscopy
Cystoscopy is usually a safe procedure and serious complications are uncommon. The most frequent complication is urinary tract infection . UTIs may require antibiotic treatment, so it is important to seek medical help if urinary symptoms persist for longer than expected following a cystoscopy or if other UTI symptoms develop . Less commonly, patients may be temporarily unable to pass urine after a cystoscopy and it may be necessary for a catheter to be inserted into the bladder to enable emptying. There is also a small risk that the urethra or bladder may be damaged by the cystoscope and subsequently require remedial surgery.
In patients who undergo rigid cystoscopy, side effects associated with anesthesia may be experienced. Common side effects of general anesthesia include nausea, vomiting, sore throat, muscle aches, itching, shivering, and sleepiness side effects most frequently associated with spinal anesthesia include itchiness, a drop in blood pressure, and temporary difficulty passing urine .
Using Blue Light Cystoscopy To Treat Bladder Cancer
If you are experiencing a medical emergency, please call 911 or seek care at an emergency room.
Did you know that bladder cancer is the fourth most common non-skin cancer in the U.S.?
Unlike prostate cancer, for which there is a standard screening, bladder cancer can frequently fall under the radar. Yet anyone between the ages of 20 and 90 may be affected by itin particular, Caucasian males 6070 years of age. So you should never delay a hospital visit if youre experiencing issues.
Here at MedStar Washington Hospital Center, we use an advanced technology, blue light cystoscopy, both to detect this cancer and help minimize the risk of its return. Although this technology is in use in other regions globally, the Hospital Center is one of the few medical facilities in this region utilizing the blue light technology. We perform 5 to 10 such procedures a monthmore than any other medical center in the District of Columbia.
But before we understand the benefits that blue light cystoscopy brings, lets first understand what can cause bladder cancer and how its typically managed.
Read Also: What Causes An Overactive Bladder In Males
The Benefits Of Blue Light Cystoscopy
BLC is the only FDA-approved technology that:
- Detects more Ta/T1 bladder cancer lesions than white light cystoscopy alone
- One or more additional Ta or T1 bladder cancer lesions were detected by BLC with Cysview in 16.4% of patients compared to white light alone
- 34.6% Patients who recurred with CIS were detected with BLC only
- Detects more NMIBC, resulting in improved tumor resection, since tumors are resected in the same TURBTS procedure
- Helps lead to fewer recurrences of bladder cancer
- Allows for better patient management decisions
Your doctor might recommend a Blue Light Cystoscopy in cases of:
- An initial standard cystoscopy detects early stage bladder cancer
- Multiple low-grade tumors
- Re-evaluation after tumor removal or cancer treatment
- Positive blood tests for the presence of cancer cells
BLC with Cysiew can be used in patients:
- With no history of bladder cancer who need a biopsy
- Who have never been evaluated with Cysview at the time of checkups for tumor recurrence
- With multiple NMIBC
- With positive urinary cytology with no visible tumors with standard cystoscopy
Uva Urology Was The First Facility In The State Of Virginia To Offer This Procedure
Patients seeking treatment for bladder cancer have many different choices on when it comes to where to go for their care. There are more diagnostic tools and treatments now than ever before. Blue Light Cystoscopy with Cysview is an important tool that can aid in the diagnosis and treatment of bladder cancer, and finding a center that offers this option can make a big difference. Below are the answers to some common questions about Blue Light Cystoscopy with Cysview, and bladder cancer detection and treatment.
Q: What is Blue Light Cystoscopy with Cysview?
In the earliest stages of bladder cancer, cancer cells are located on the surface layer of the bladder wall. Identifying this kind of cancer, which is called non-muscle invasive papillary bladder cancer , requires a correct and thorough work-up, and diagnosis is a key component of successful treatment.
To diagnose this disease, surgeons inspect the inside of the bladder using a long, thin tube called a cystoscope that includes a video camera on the end. In the past, the only option was white light cystoscopes, which do not always easily show tumors or cancerous lesions.
Blue Light Cystoscopy with Cysview uses a cystoscope equipped with both white and blue light for visual inspection inside the bladder. Cysview is a light-sensitive imaging drug called hexaminolevulinate hydrochloride. BLCC may also be called fluorescence cystoscopy.
Q: How is Cysview administered and how does it work?
The short answer is: No.
Recommended Reading: Does A Bladder Infection Cause Incontinence
Diagnosis Of Bladder Cancer
Diagnosis is the process of finding out the cause of a health problem. Diagnosing bladder cancer usually begins with a visit to your family doctor. Your doctor will ask you about any symptoms you have and may do a physical exam. Based on this information, your doctor may refer you to a specialist or order tests to check for bladder cancer or other health problems.
The process of diagnosis may seem long and frustrating. Its normal to worry, but try to remember that other health conditions can cause similar symptoms as bladder cancer. Its important for the healthcare team to rule out other reasons for a health problem before making a diagnosis of bladder cancer.
The following tests are usually used to rule out or diagnose bladder cancer. Many of the same tests used to diagnose cancer are used to find out how far the cancer has spread . Your doctor may also order other tests to check your general health and to help plan your treatment.
Preparing For A Cystoscopy
The process of preparing for a cystoscopy depends on which type of cystoscopy and anesthetic a patient is undergoing. For example:
- If a general anesthetic is required, a pre-assessment is carried out several days before the procedure this may involve routine pre-anesthetic checks such as blood tests and x-rays. Instructions will also be given regarding how long before the procedure to stop eating and drinking.
- If a local anesthetic is being used the patient can eat and drink normally beforehand.
Recommended Reading: Bladder Control Problems At Night
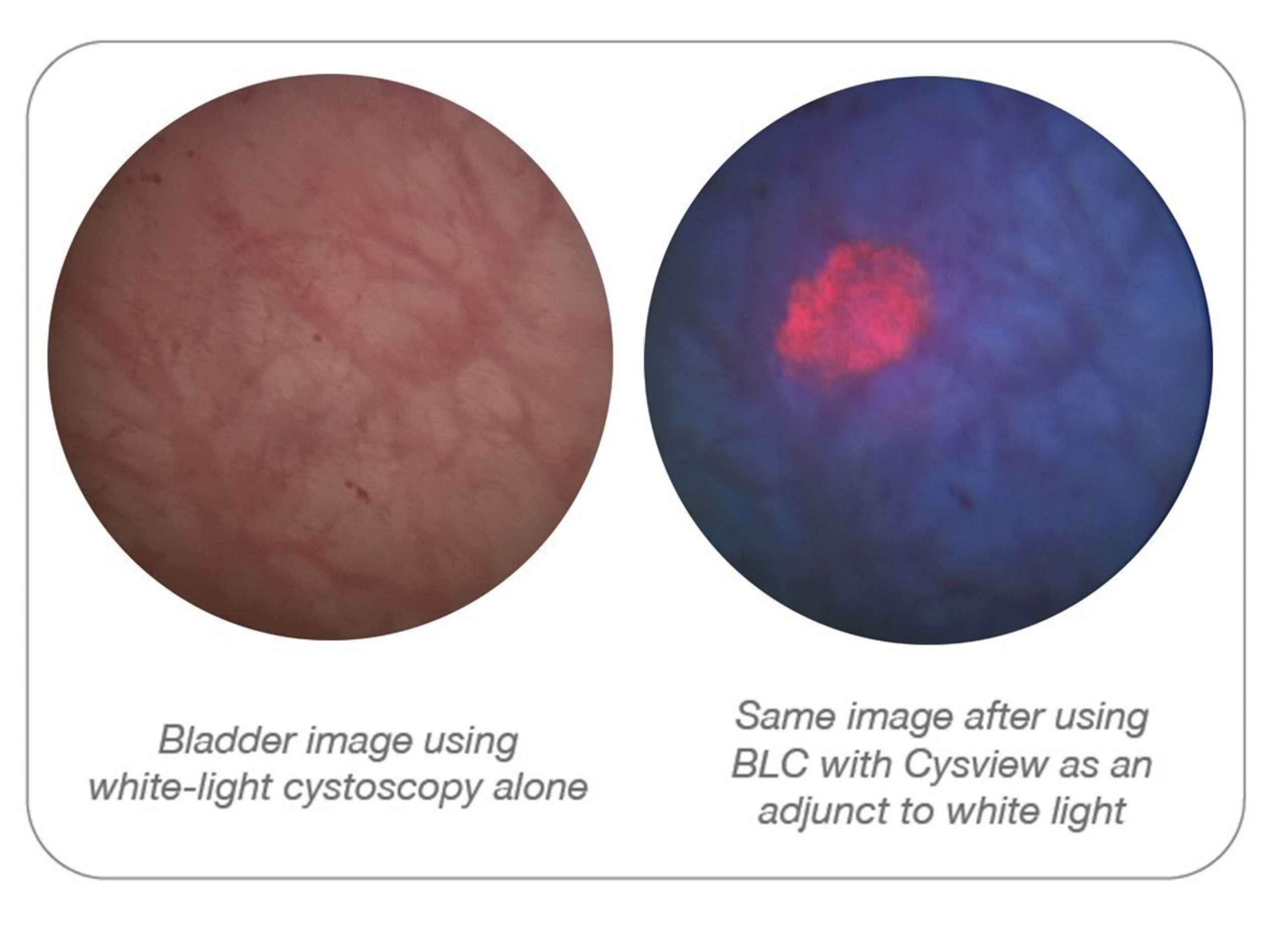
What Is Blue Light Cystoscopy
An important advance in bladder tumor detection involves the use of a special chemical that can be taken up by tumors. Then, with the use of special equipment, the tumor cells will fluoresce or appear as bright blue tissue in the bladder. This can take a small tumor that is difficult to see and make it much more obvious. This blue light technique has been used and studied in Europe for some time, and has only recently been approved for use in the United States. So its already a proven technique that is now gaining use in the United States.
There are several strong benefits from this process. By using the blue light technique, the rates of bladder tumor recurrence are lower, allowing patients to avoid invasive procedures and potentially reduce the frequency of their bladder checks. This should reduce physical discomfort and anxiety for our patients. A recent study of the old white light technique versus the newer blue light technique found the average time to a bladder tumor recurrence was seven months longer with the blue light.
Cysview is an FDA approved optical imaging agent.
Choose a Section: