Whats In The Future For A Child With Neurogenic Bladder
Treatment plans are individualized for your child usually starting with the most conservative measures and advancing as necessary to achieve the desired results. Many successful options are available to preserve kidney function and gain urinary continence. Kidney function is often monitored to prevent infection and kidney stones. Doctors often recommend drinking plenty of fluids and prescribe antibiotics preventatively to reduce urinary tract infections. Complete recovery from Neurogenic Bladder is uncommon however, many children recover considerably with treatment.
How Is Neurogenic Bladder Diagnosed
A doctor will do an exam and may order several tests of the nervous system and the bladder to diagnose neurogenic bladder: These include:
- Urodynamic studies: These bladder function tests measure how much urine the bladder can hold, the pressure within the bladder, how well urine flows, and how well the bladder empties when it is full. Special sensors may be placed on the skin near the urethra or rectum to see if the muscles and nerves in those parts of the body are working properly.
- Cystoscopy: The doctor may perform this procedure to examine the inside of the bladder and urethra with the use of a small telescope .
- X-rays
What Are Symptoms Of An Underactive Bladder
Symptoms of an underactive bladder include:
- Needing to wait for the flow to start or hesitancy
- Needing to push and strain to empty the bladder
- Poor or slow urinary stream
- Stop and start urinary stream
- Prolonged time required to pass urine
- Feeling like the bladder has not emptied completely
- Needing to go back a second time shortly after passing urine to pass more urine
- Reduced sensation of bladder fullness
- Frequent urination
A Urodynamic study gives the definitive diagnosis of an underactive bladder as it is able to distinguish between poor detrusor function and blockage within the urinary tract. The Urodynamic study is often combined with a cystoscopy to give further information about the anatomy of the urethra and bladder as well as the prostate in men.
Read Also: Naturvet Bladder Support Plus Cranberry
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms
The lower urinary tract includes the bladder and the tube that urine passes through as it leaves the body .
Lower urinary tract symptoms are common as people get older.
They can include:
- problems with storing urine, such as an urgent or frequent need to pass urine or feeling like you need to go again straight after youve just been
- problems with passing urine, such as a slow stream of urine, straining to pass urine, or stopping and starting as you pass urine
- problems after youve passed urine, such as feeling that youve not completely emptied your bladder or passing a few drops of urine after you think youve finished
Experiencing LUTS can make urinary incontinence more likely.
Page last reviewed: 07 November 2019 Next review due: 07 November 2022
Uti And Other Symptoms
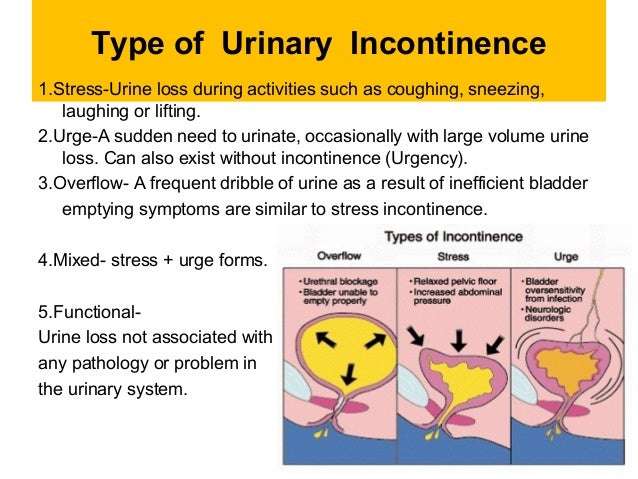
Urinary incontinence is a common sign of a UTI. Other symptoms typically occur along with the frequent urge to urinate. Someone with a UTI may also experience a burning sensation during urination or notice blood in their urine. Urine may also have a strong odor or a dark color.
Men with UTIs may experience rectal pain, while women with UTIs may have back or pelvic pain.
If you have any of these symptoms, you should be evaluated by a doctor. If youre diagnosed with a UTI, your doctor will prescribe a course of antibiotics.
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Bladder Pain At Home
What Causes An Overactive Bladder
Your bladder is controlled by your nerves, as is all the other muscles in your body. In a properly functioning bladder, your nerves will sense when your bladder is full and tell your brain that you need to go to the bathroom. For most people, you will get the signal that your bladder is full you will be able to hold it until you can make it to the bathroom. Once you make it to the bathroom, you can manually signal to your bladder that it is time to release its contents, into the toilet or urinal of course.
The muscles that control your bladder is called the detrusor muscle. This is the part of your bladder that gets the message from your brain about when to release the urine. Those who suffer from the overactive bladder may receive mixed signals. Not only do the nerves tell your brain that your bladder is full, but it also has your brain tell your bladder to release its load.no matter where you happen to be. The detrusor muscle will spasm on its own which is why the condition called an overactive bladder.
The amount of pee that comes out will vary from person to person. Some people suffer from regular bouts of urinary urge incontinence, while others will simply feel the urge but remain dry. The severity can range from a few drops to a full bladder being released.
Read Also: How Can I Heal My Bladder Naturally
Epidemiology Including Risk Factors And Primary Prevention
Cerebrovascular pathology, most commonly the lesions in the anteromedial frontal lobe and putamen, can cause neurogenic bladder in 20% to 50% of patients.4-6 If untreated, 20% to 30% of patients will suffer from incontinence 6-months poststroke.4
Most patients with spinal cord lesions and some patients with peripheral neuropathy will develop neurogenic bladder. Fifty percent of diabetics will develop neuropathy, with 75% to 100% of these patients developing lower urinary tract dysfunction.4
Also Check: Different Types Of Bladder Cancer
Urinary Retention/obstruction With Underactive Bladder
In people with an underactive bladder , the bladder muscle may not squeeze when it needs to. The sphincter muscles around the urethra also may not work the right way. They may stay tight when you are trying to empty your bladder. With UAB symptoms, you may only produce a “dribble” of urine. You may not be able to empty your bladder fully . Sometimes you may not be able to empty your bladder at all .
Pathophysiology Of Neurogenic Bladder
Many classifications have been used to group neurogenic bladder dysfunction. Each has their merits and clinical utility. These classifications may be based on urodynamic findings , neurourologic criteria , or on bladder and urethral function .
A popular classification of neurogenic bladder dysfunction based on the location of the neurologic lesion can help guide pharmacologic and surgical therapies, with the voiding abnormalities seen clinically following from disruptions of the normal urinary physiology described above and shown in Figure 1. In this classification, neurogenic bladder arises from
The mixed type B neurogenic bladder is characterized by a flaccid external urinary sphincter due to the pudendal nucleus lesion while the bladder is spastic due to the disinhibited detrusor nucleus. Thus, the bladder capacity is low but vesicular pressures are usually not elevated since there is little outflow resistance. This leads to problems with incontinence, however.
Recommended Reading: What To Do If You Have A Bladder Infection
Atonic Bladder Or Neurogenic Bladder: Causes
As mentioned, atonic bladder has been associated with neurological destruction. Nerves in the body control how the bladder stores and empties urine. Problems with these nerves can cause a host of difficulties with the bladder, including the signs and symptoms that doctors have come to recognize as atonic or neurogenic bladder. Many people have likely heard the terms overactive bladder or underactive bladder , or even obstructive bladder, which means the flow of urine is blocked. These conditions can also be caused by nerve problems. However, specialists are usually able to detect when a specific neurological event has led to atonic or neurogenic bladder.
For some people, atonic bladder causes can be associated with birth defects. For example, spina bifida, which occurs when the fetuss spine does not completely develop during early pregnancy. With this disorder, there is often paralysis that impacts how the bladder works. Sacral agenesis can also be one of the atonic or neurogenic bladder causes. With this condition, part of the lower spine is missing. Another birth defect that could lead to atonic or neurogenic bladder is cerebral palsy. This disorder limits a persons ability to control body movement. It is usually the result of injury to the motor area of the brain.
There are some other medical conditions that have also been linked to neurogenic bladder. The following list covers some of those conditions.
- Spinal cord injuries or surgeries
- Erectile dysfunction
Overactive Bladder Treatment Options
Research indicates that most people believe the symptoms of an overactive bladder are an inevitable and normal part of growing older, rather than a treatable medical problem. This couldnt be further from the truth.
In fact, fewer than half of individuals with incontinence actually consult a healthcare provider about their problem. This is unfortunate, since there are many treatments available to combat symptoms of OAB.
Even though it may feel embarrassing to talk about your condition, its important to talk to your doctor about your incontinence symptoms. Watch our short film below about the importance of speaking up about bladder leakage.
NAFC is excited to debut a short film about coming to terms with overactive bladder and incontinence. About just how challenging it can be to admit that theres a problem. And also about how facing up to that reality can be an important first step towards drier days. Watch this short video about OAB, and about how not speaking up can create more problems than staying silent.
Also Check: Side Effects Of Bladder Cancer Chemotherapy
Symptoms Of Overactive Bladder
A few symptoms might indicate that you have OAB:
- When you feel the urge to urinate, you may also leak a small amount of urine. This is called urge incontinence.
- You have to use the bathroom more often than you normally do or more than eight times in 24 hours.
- You need to urinate more than once during the night in the absence of contributing factors such as caffeine, alcohol, or excessive fluid intake at night. This is called nocturia.
Causes And Risk Factors

Aging
OAB occurs in both men and women. Its possible to have overactive bladder at any point in your life. But, its especially common in older adults. The prevalence of OAB in people younger than 50 years of age is less than 10 percent. After the age of 60, the prevalence increases to 20 to 30 percent.
The following are some of the other most common underlying causes and risk factors associated with OAB symptoms:
Nerve Damage
A healthy, normal functioning bladder holds urine until it gets full and is prompted to empty by nerve signals. However, when nerve damage occurs in the body, the muscles surrounding the urethra can be too loose. This undesirable looseness can cause someone to become incontinent. What can cause nerve damage that can then lead to bladder leakage? Some possibilities include:
- Back or pelvis surgery
- Stroke
Weak pelvic muscles
When a man or womans pelvic floor muscles are weak, bladder control issues can happen. The pelvic floor muscles are like a sling that holds up the uterus and bladder. For women, a pregnancy and childbirth can often lead to a stretching and weakening of the vital pelvic floor muscles. When pelvic floor muscles are compromised for this reason or another, the bladder can then sag out of place. The opening of the urethra also stretches and urine easily leaks out.
Menopause
Read Also: Can Bladder Sling Cause Uti
Don’t Miss: Galvanized Pressure Tank Vs Bladder Tank
Signs And Symptoms Of Atonic Bladder
Neurogenic bladder signs vary depending on whether the bladder is flaccid, which is underactive, or spastic, which is overactive. Neurogenic or atonic bladder signs with a flaccid bladder involve overflow incontinence. People retain urine and have constant overflow dribbling. Many men also suffer from erectile dysfunction. Those with spastic bladder may experience frequency, including during the night. They also may have intermittent bladder contractions that lead to urine leakage and a sense of urgency. Sometimes, spasms prevent the bladder from completely emptying.
There are other neurogenic bladder symptoms, but not everyone will experience them. They include impotence, back weakness, elbow cramps or weakness, wrist weakness, retention of urine, and emotional symptoms. It is important to keep in mind that these could also be signs of some other medical problems not associated with the bladder.
Research shows that about 55 percent of those who have atonic or neurogenic bladder complain about involuntary urination and just over 50 percent report urine retention. Neurogenic bladder symptoms that are less common, such as wrist and elbow weakness occur in about two percent of cases. The atonic bladder symptoms of impotence and urinary frequency are rather high. When it comes to urinary frequency, about 55 percent of those with the condition experience having to urinate often, while about 44 percent of men struggle with impotence.
Wet Overactive Bladder Vs Dry Overactive Bladder: Whats The Difference
Dry type is when you have urgency where you really have to go to the bathroom and its difficult to wait, but you dont leak, and then theres wet type, where you also have the really strong urge but you cant make it to the bathroom in time and do have urine leakage, says Wu.
If you have both of those kinds, its called mixed, she adds.
Recommended Reading: Alka Seltzer For Bladder Infection
Causes Of Neurogenic Bladder
Certain health conditions can interfere with proper functioning of nerve messages that must travel between the brain and the muscles that control the bladder. When these nerve pathways dont work correctly, bladder muscles might not tighten or release the way they normally do. The result is that the bladder might not hold urine or release it correctly.
The most common causes of neurogenic bladder are nervous system disorders, including:
- Alzheimers disease
- Brain or spinal cord tumors
- Birth defects of the spinal cord
- Cerebral palsy
- Learning disabilities, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
- Multiple sclerosis
- Spinal cord damage or spinal surgery
- Stroke.
Other causes include disorders or damage of the nerves that control the bladder, such as:
- Accidents or trauma
- Congenital abnormalities of the spine
- Diseases such as syphilis, herpes zoster, diabetes and polio
- Herniated disc or stenosis of the spinal canal
- General neuropathy
- Tumors of the central nervous system
- Vitamin B12 deficiency.
How Can I Know If My Bladder And Sphincter Are Working Correctly
Doctors can do a urodynamics test to see how well your bladder and sphincter are working:
- A catheter goes up through your urethra into the bladder.
- Your bladder is slowly filled with fluid.
- Doctors then measure how your bladder and sphincter respond to the fluid in the bladder.
- The test can help inform which bladder management option is best for you.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Symptoms Of Advanced Bladder Cancer
Urinary Problems Are Too Common In Midlife Women
When you leave your home to go out shopping or meet up with friends, do you find yourself mentally mapping out where and how fast youll be able to find a bathroom in case you suddenly and urgently need to pee? You may just chalk it up to yet another unpleasant side effect of getting older and, in a way, youd be right.
A new , the journal of The North American Menopause Society , found that women ages 45 to 54 years old are more likely to have overactive bladder syndrome.
The prevalence of overactive bladder increases with age through menopause and beyond its something thats really, really common, says Jennifer Wu, MD, MPH, a researcher and specialist in urinary incontinence and professor at the UNC School of Medicine in Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
RELATED: 12 Ways to Beat Menopausal Belly Fat
Symptoms Of Neurogenic Bladder
Among people who have conditions that might cause neurogenic bladder, the most noticeable symptom is the inability to control urination .
People might experience other symptoms including:
- A weak urine stream or dribbling
- Being unable to urinate
- Needing to urinate urgently/immediately
- Painful urination resulting from retained urine)
- Urinating frequently .
Some people, especially those who have neurogenic bladder due to stroke, MS or herpes zoster, may have symptoms of both overactive bladder and underactive bladder.
Symptoms of overactive bladder may include:
- Needing to urinate too frequently
- Passing only small amounts of urine
- Problems emptying the bladder all the way
- Lack of bladder control .
Symptoms of underactive bladder may include:
- Being unable to know when the bladder is full
- Inability to urinate
- Possible leaking of urine due to overflow from a full bladder.
Complications of neurogenic bladder
Neurogenic bladder can seriously affect quality of life. In addition, it can cause physical complications including:
- Skin problems, pressure sores or infections due to incontinence
- UTIs due to urine not being passed in a timely manner
- Kidney damage due to pressure from an overly full bladder.
For all of these reasons, it is important to seek treatment when a person suspects neurogenic bladder.
Read Also: Bowel And Bladder Problems After Back Surgery
Underactive Bladder Neurogenic Bladder And Urinary Retention
Underactive bladder is a condition characterized by poor bladder emptying that is not necessarily caused by BOO. It likely encompasses multiple causes and clinical conditions . This may be related to a failure of the detrusor muscles to contract and a failure of the neural pathways to properly stimulate the bladder . The ICS defines the termdetrusor underactivity as a contraction of reduced strength and/or duration, resulting in prolonged bladder emptying and/or a failure to achieve complete emptying within a normal time span .
Research on UAB is relatively new, and there are few epidemiologic studies on the condition . In a population-based survey, 23% of 633 respondents indicated they had difficulty emptying the bladder . In a similar study of older adults who had undergone urodynamic testing for voiding dysfunction, 40.2% of men and 13.3% of women were diagnosed with detrusor underactivity .Structural and functional changes appear to lead to development of underactive bladder. Ultrastructural studies have demonstrated that aging is associated with an increased deposition of collagen and a reduction in the ratio of smooth muscle to connective tissue .
Nicholas J. Silvestri MD, Christopher H. Gibbons MD, MMSc, in, 2011