How To Get Rid Of Uti Back Pain
Urinary tract infections, or UTIs, are infections that infect areas of your urinary system. The urinary system is made up of four parts:
The urethra is a thin tube that connects the bladder to the outside of your body. When you urinate, the urine flows out of the bladder through the ureters and urethra.
Sometimes bacteria makes its way up the ureters, into your bladder, and sometimes all the way up into your kidneys. This can lead to back pain and is a sign of a serious infection.
Back Pain With Bladder Problems
What should you do about the pain? And if you need an op, what are the available procedures? We’ve put together a guide to help you determine what could work for you.BY BETINA LOUW AND THE HEALTH24 TEAM for YOU Pulse magazine
You have back pain and are experiencing loss of bladder or bowel control
Youll need emergency surgery because something is pressing on your spinal cord and is affecting the nerves to your bladder and sexual organs. It could be a displaced vertebra, a tumour, a blood clot or even a spinal cord infection. The pressure must be relieved immediately or your bladder function could be permanently impaired. Fortunately this condition is fairly rare.
The operation that will be performed is a laminectomy, which involves the removal of the rear of a vertebra to relieve pressure on the spinal cord.
| PROCEDURES FROM SIMPLEST TO MOST COMPLEX | PATIENT’S AVERAGE AGE |
Can You Have Back Pain With Interstitial Cystitis & Does Ic Cause Fatigue
When IC muscles are severely overworked or strained, you can feel pain in the back or side with feverish, shivery feeling.1,2
Symptoms of interstitial cystitis typically include pain in the perineum, urethra, lower abdomen, and lower back.3
Medical studies demonstrate that chronic fatigue is noticed in a lot of IC patients.4
Interstitial cystitis is a chronic bladder condition affecting 4 to 12 million people in the United States alone. It is a tricky condition, tough syndrome hard to diagnose because it is often misjudged for urinary tract infection.
There are several treatments for IC that make help improve the symptoms although there is no proven cure for this disorder. As IC shows a wide range of symptoms and severity, researchers think it may be associated with several diseases however when your pain lasts more than 6 weeks and the pain is not related to other infections or kidney stone, then you have higher possibilities of IC.
Recommended Reading: Advil Or Tylenol For Back Pain
Don’t Miss: Revive Reusable Bladder Control Support
Pain In The Right Side When Breathing
Pain under the right ribs or in the ribs can be due to muscle or bone reasons. In these cases the pains are usually stabbing, intensifying according to the movements that are made. Some of the causes of right rib pain are:
- Inflammation of cartilage in the ribs
Depending on the condition as well as on what level it is, the treatment should be one or the other. However, in those cases in which the pain in the right side is due to trauma or poor movement, recovery can be done with rest and the administration of analgesics to reduce the pain. In depending on which cases it will be necessary to immobilize the area.
Read Also: Loss Of Bladder Control When Coughing
How Is Back Pain While Urinating Treated
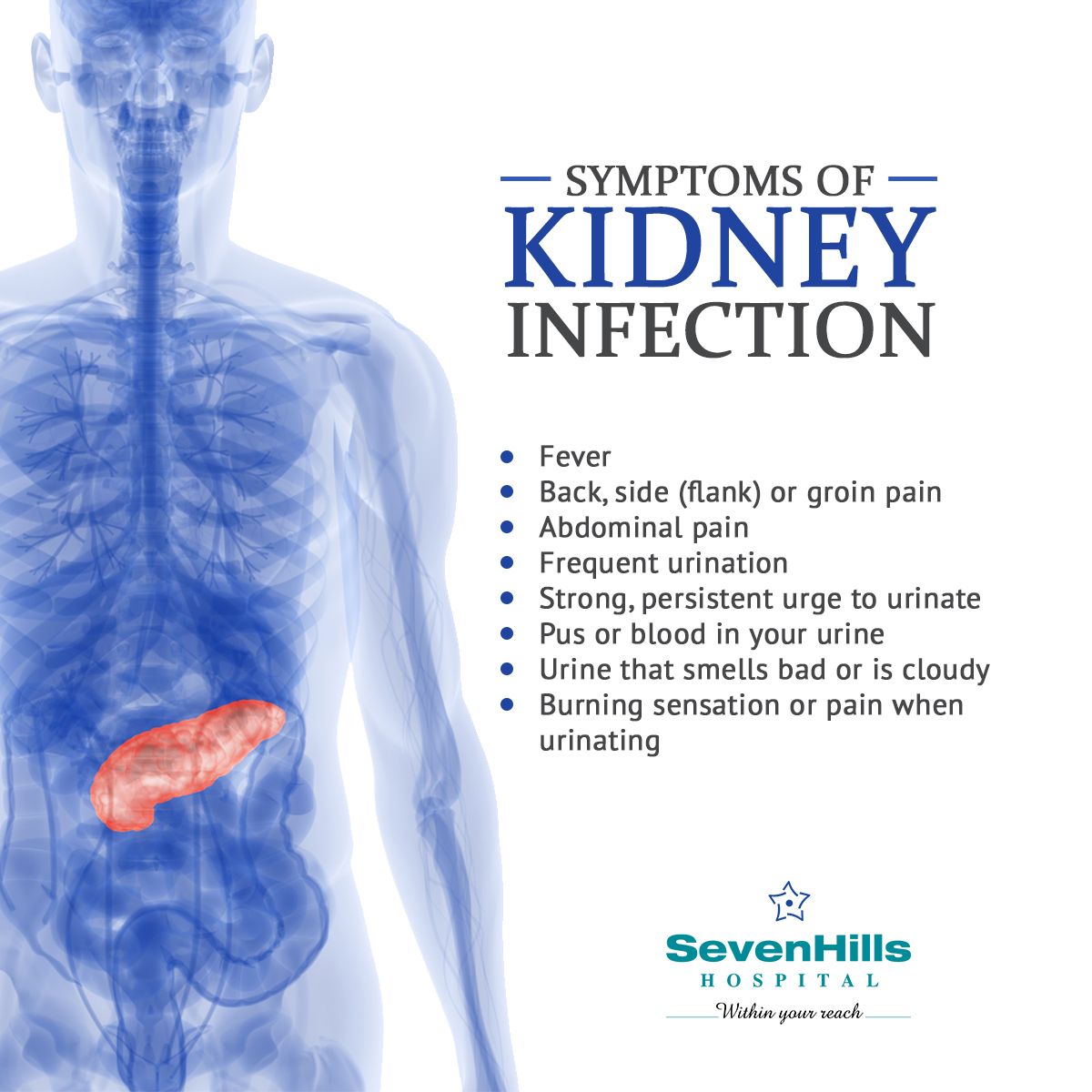
Your treatment will be dependent on your diagnosis. For instance, if the reason behind your lower back pain when urinating is a UTI, you will need to take medication to resolve the UTI. On the other hand, if the cause of the discomfort is a tumor, abscess, or kidney stones, surgery could be necessary.
For alleviating back pain specifically, therapeutic options might include:
-
Pain and frequent urination are making it hard to go about your day
Read Also: How To Empty Bladder Without Catheter
Burning Sensation You May Have A Uti
A urinary tract infection or UTI happens in millions of Americans each year. A UTI can cause pain during urination and more commonly affects women. Several signs show the severity of the infection. These include intense back pain. Understanding whats happening during a UTI can help people get the right treatment right away.
How Is Ui Diagnosed
The only way to diagnose the underlying cause of both back pain and UI is to see your doctor and receive a full medical exam. The exam can help your doctor decide whether your symptoms are related to a separate condition that needs attention.
During the exam, its important you detail any symptoms, when you experience them, and how you relieve them.
After this initial diagnosis phase, your doctor may order several tests. These tests may include imaging tests like X-rays and blood work. The tests can eliminate causes for your symptoms.
If your doctor cant reach a diagnosis, they may refer you to a urologist or a back pain specialist.
Treatment for back pain and UI relies on finding an underlying cause. Once you and your doctor understand whats causing your symptoms, you can develop a plan to manage your symptoms.
You May Like: Non Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Guidelines
What Else Can Cause Leakage
Menopause isnt always the reason why your bladder is acting up. Your muscles may have naturally weakened due to age. Or you might have had injuries as a result of giving birth to a child, or several children.
Condition like diabetes or multiple sclerosis can cause nerve damage, which in turn can also cause bladder problems.
Think about any medicines you take, too. Some antidepressants and pain meds can keep your bladder from emptying. Your doctor may be able to change your dose or prescription.
Continued
Also Check: How Do Bladder Infections Happen
What Type Of Doctor Should I See For Back Pain
This depends on your condition or symptoms. If you have no obvious injury that would explain your pain, you may want to start by seeing a . This is a specialist in physical medicine who can diagnose back pain and determine whether nonsurgical treatments such as physical therapy may help. Depending on those findings, a physiatrist may also refer you to a , doctor or other type of back specialist, , for additional discussion.
You May Like: Treatment For Men’s Bladder Infection
Symptoms In The Elderly
Most people who develop a urinary tract infection will exhibit symptoms, such as those listed above. However, elderly people are less likely to display classic symptoms specific to the genital and urinary regions. This may be due to changes in immune function as age increases, as well as the possibility of additional diseases and disorders affecting usual bodily responses.
Additionally, a urinary tract infection may cause certain behavioral changes in an elderly adult, such as confusion, agitation or disorientation. Such symptoms are often categorized as delirium. People with age-related issues such as delirium or dementia are especially at risk of developing a more severe UTI because they may not be able to communicate their symptoms and receive prompt treatment.
Although this connection between UTIs and delirium has been established, the reason why delirium may occur in elderly adults with a UTI is not yet known.
Good to know: If a urinary tract infection is suspected in an elderly person, always contact a doctor as a simple urine analysis test is usually enough to confirm the diagnosis.
Other Complementary Pain Management Techniques
There are a range of other complementary and alternative pain management techniques that may be worth exploring. These include:
Biofeedback is a technique that uses machines to help you learn about and control some of your involuntary body functions. Led by a licensed technician, biofeedback may help you relax and cope with pain in your body.
Many of these integrative methods havent been tested in scientific studies on people with bladder cancer. But theyre regarded as ways to improve your quality of life when you have a disease.
Talk to your healthcare team to determine which ones might be best for your situation.
Read Also: Back Pain Cleveland Clinic
Read Also: What Vitamins Are Good For Bladder Health
Cauda Equina Syndrome And Incontinence
Cauda equina syndrome is a condition that causes squeezing or compression in the cauda equina sac of nerves at the base of the spinal cord, resulting in lower back pain and urinary incontinence. As the nerves are pinched, they are unable to properly function and may result in the involuntary loss of urine.
Cauda equina symptoms include weakness in the legs, numbness or tingling in the lower back and legs, and incontinence.
In some cases, cauda equina can be treated by surgically decompressing the spine, depending on the extent of damage involved with the nerve tissue.
Also Check: What Causes Bladder Control Problems
Can Eating Certain Foods Or Drinks Make My Bladder Pain Symptoms Worse
Maybe. Some people report that their symptoms start or get worse after eating certain foods or drinks, such as:16
- Citrus fruits, such as oranges
- Drinks with caffeine, such as coffee or soda
Keep a food diary to track your symptoms after eating certain foods or drinks. You can also stop eating foods or drinks one at a time for at least one week to see if your symptoms go away. If not, stop eating other trigger foods or drinks one at a time for one week to see which ones may be causing some of your symptoms.
Recommended Reading: How To Clear Up A Bladder Infection
Can Back Pain And Incontinence Be The Result Of Another Condition
Though rare, one disorder that could cause back pain and UI is cauda equina syndrome . CES affects the bundle of nerve roots at the end of your spinal cord. These nerve roots send and receive signals from your brain and control the lower half of your body and your pelvic organs.
When the nerve roots are compressed, the pressure cuts off sensation and control. The nerves that control your bladder and bowels are particularly susceptible to the loss of control caused by this disorder.
A ruptured disc may also put pressure on the nerve roots. This disc and the pressure on the nerve roots can lead to back pain.
And, a form of arthritis called ankylosing spondylitis may cause back pain. This condition causes inflammation in your spinal joints. The inflammation can lead to discomfort and chronic severe pain.
Are Cramps A Common Symptom Of A Uti
Cramping pain is a common symptom of a UTI. It may be also felt as a feeling of pressure or soreness. Youll typically feel UTI cramps in your pelvic area or lower back.
Where does this pain come from? The bacteria that cause a UTI can invade the lining of your urinary tract. This, in turn, can lead to inflammation and irritation. Additionally, urine provides a good medium in which these bacteria can continue to multiply.
In addition to cramps, some other symptoms of a UTI include:
- a painful or burning sensation when you urinate
UTIs are treated with antibiotics. While youll often find that your symptoms begin to get better shortly after starting antibiotics, its important to finish the entire antibiotic course. This helps ensure your infection is completely cleared.
As you recover, you can try the following home remedies to help relieve UTI cramps:
- Use a heating pad: Applying a heating pad to your abdomen or lower back may help to ease cramping.
- Drink water:Drinking water not only keeps you hydrated, but can also help dilute your urine and flush bacteria from your urinary tract.
- Take over-the-counter medications: OTC pain medications like ibuprofen , naproxen , and acetaminophen can help to soothe pain from a UTI.
You May Like: Causes Of Recurrent Bladder Infections
Complications Of Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are an extremely common condition, and most people recover quickly with antibiotic treatment. However, if left untreated the infection can spread throughout the urinary tract system, increasing in severity and causing complications.
In some cases, the infection can reach the kidneys in the upper urinary tract, an infection known as pyelonephritis. Without medical intervention, this can lead to permanent kidney damage. Possible complications from untreated UTIs include:
- Formation of abscesses within or around the kidneys
- Swelling of the kidneys, also known as hydronephrosis
- , also known as blood poisoning
All of these complications are serious and require immediate medical attention.
How Can I Prevent Flank Pain
You may not always be able to prevent flank pain. But you can reduce your risk of kidney problems, injuries and disease by maintaining good health. You should:
- Eat right and stay hydrated: By drinking plenty of water, avoiding alcohol and eating a healthy diet, you can lower your risk of kidney stones. Water keeps you hydrated and flushes out your kidneys, decreasing the chance of infection and making it more difficult for stones to form. Ask your provider about a low-sodium, calcium-rich diet that may prevent kidney stones.
- Maintain a weight that’s healthy for you: Get regular exercise and stay active. People who have overweight or obesity have a higher chance of developing kidney stones. Extra weight also puts pressure on your spine and makes you more vulnerable to injuries that cause flank pain.
- Take care of your urinary tract: To reduce the risk of bacteria entering your urinary tract and causing an infection, always urinate after having sex. Women should wipe from front to back after urinating. Drink plenty of water, and use the bathroom as soon as you feel the urge. Holding urine in your bladder increases your chance of infection.
- Visit your provider: Stay up to date on vaccines . Schedule regular screenings for cancer and other diseases, and talk to your provider about reducing your risk of kidney problems.
Read Also: Why Am I Losing Control Of My Bladder
When Should I See A Health Care Professional
See a health care professional if you have symptoms of a bladder problem, such as trouble urinating, a loss of bladder control, waking to use the bathroom, pelvic pain, or leaking urine.
Bladder problems can affect your quality of life and cause other health problems. Your health care professional may be able to treat your UI by recommending lifestyle changes or a change in medicine.
Overview Of This Free Online Course
Pain is an output of the brain. That is a well-accepted fact.
Urge is also an output of the brain this is a lesser-known fact.
Join Carolyn Vandyken as she explores the evidence to support that Overactive Bladder Syndrome and Bladder Pain Syndrome need to be considered from the perspective of central pain mechanisms.
Unique and powerful opportunities to treat these problems from a whole-person perspective are presented in this talk. Reynolds et al conclude that an understanding of the pathophysiology and clinical manifestations of central sensitization in OAB could provide a novel approach to managing this condition.
It may be time to start thinking about these two conditions in a very different light.
This is the third in a three-lecture series that Carolyn Vandyken did as the Keynote speaker for the National Conference on Incontinence in Australia in October 2020. These lectures were delivered in pre-recorded fashion because of the COVID-19 pandemic the Continence Foundation of Australia has graciously given us permission to re-air these lectures on Embodia Academy.
You May Like: Not Being Able To Hold Bladder
You May Like: What Causes Bladder Control Problems
How Long Does Back Pain Last With A Uti
Minor back pain may accompany UTIs. Once antibiotics are started, you should feel better within 12 to 24 hours.
However, untreated UTIs can cause severe infection and complications. Constant, dull, or severe pain can signify a kidney infection. Unlike muscular pain, this pain will be persistent and unrelieved by any alleviating factors.
UTI back pain will last until you begin antibiotic treatment for your UTI.
A UTI that has spread to the kidneys is a serious infection that will typically not go away on its own. Its extremely dangerous for an infection of this nature to go untreated.
If you are experiencing back pain from a UTI seek medical attention immediately, youll likely need antibiotics.
UTIs typically cause lower abdominal pain and not back pain. Lower abdominal pain can last 2-3 days with a UTI and longer for untreated UTIs.
How Is Interstitial Cystitis Treated
There is no cure for interstitial cystitis. A wide array of treatment options exist for interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome, although well-designed clinical trials to evaluate effectiveness are largely lacking 32). Multimodal therapy that includes pentosan polysulfate sodium , a tricyclic antidepressant, and an antihistamine is a relatively new approach to symptom relief based on advances in understanding of the complementary pathophysiologic mechanisms, but it remains to be evaluated in well-designed clinical effectiveness trials 33). It is important to set realistic goals and expectations with patients because individual responses vary and the evidence base is weak.
You may need to try several treatments or a combination of treatments before you notice an improvement in your symptoms.
Table 3. Multimodal Therapy for Interstitial Cystitis
| Agent/dosage |
|---|
Most people feel better after trying one or more of the following treatments:
Oral Medicines
Intra-Bladder Therapies
Intravesical hyaluronic acid is a natural proteoglycan used in Europe and Canada for the treatment of interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome, but it is not approved for this use in the United States because supporting clinical trial data were lacking 45). An uncontrolled European trial demonstrated that intravesical hyaluronic acid treatments in combination with chondroitin sulfate led to markedly decreased pain and urgency at 12 weeks 46).
OTHER ADJUNCTIVE THERAPIES
Recommended Reading: Does Your Bladder Shrink With Age
How Is Bladder Pain Syndrome Diagnosed
There is no one test to tell whether you have bladder pain syndrome. Your doctor or nurse will do a physical exam to look at your lower abdomen and lower back and ask you questions about your symptoms. Your doctor may give you tests to rule out other health problems, such as urinary tract infections, sexually transmitted infections , bladder cancer, or kidney stones.
Some tests your doctor may do include: