Things You Can Do To Help Interstitial Cystitis
Lifestyle changes will usually be recommended first.
Things that may help improve your symptoms include:
- reducing stress anything that helps you relax, such as exercise or regular warm baths, may help reduce your symptoms, and recent evidence suggests that mindfulness-based techniques, such as meditation, can help
- avoiding certain foods or drinks if you notice they make your symptoms worse but do not make significant changes to your diet without seeking medical advice first
- stopping smoking the chemicals you breathe in while smoking may irritate your bladder
- controlling how much you drink try to reduce the amount you drink before going to bed
- planned toilet breaks taking regular planned toilet breaks may help stop your bladder becoming too full
You may also find it useful to contact a support group, such as the Interstitial Cystitis Association or Bladder Health UK for information and advice about living with interstitial cystitis.
You May Like: Treatment Of Overactive Bladder In Males
What Is Oab And Who Gets It Your Browser Does Not Support Html5 Audio Playback You May Download The Audio File Directly Here
Overactive bladder is the name for a group of bladder symptoms. There are three main symptoms:
- A feeling that you have to go to the bathroom, urgently.
- Sometimes incontinence, which means that you leak urine with the âgotta goâ feeling.
- Usually the need to go to the bathroom often , day and night.
With OAB, you feel that you need to empty your bladder even when itâs not full. This leads to the feeling that you need a bathroom quickly, right now. You canât control or ignore this feeling. If you âgotta goâ eight or more times each day and night, or fear that urine will leak out before youre ready, you may have OAB.
OAB affects about 33 million Americans. Itâs not a normal part of aging. Itâs a health problem that can last for a long time if itâs not treated. Many older men and women struggle with OAB symptoms. Often people donât know about treatments that can help, or they donât ask for help.
Stress urinary incontinence or SUI is a different bladder problem. People with SUI leak urine while sneezing, laughing or being active. It is not the same as that sudden âgotta goâ feeling from OAB. To learn more about SUI, go to .
In this guide you will find clear information about how to manage OAB. Please ask for help, even if you feel embarrassed. Donât wait, because there are several treatments that work well for OAB. Your health care provider should be trained to talk with you and help you manage your symptoms without embarrassment.
Supportive Therapies And Treatments
Some people may also find the following therapies and supportive treatments helpful:
- physiotherapy a specialist pelvic floor physiotherapist can help you relax your muscles to ease pain.
- acupuncture may help with pain relief
- talking therapies and counselling to help you cope with your symptoms and their impact on your life
- transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation where a small battery-operated device is used to relieve pain by sending electrical impulses into your body
- pain management ask the GP to refer you to a pain specialist
Also Check: Bladder Infection Symptoms Home Remedies
How Is Chronic Urinary Retention Diagnosed
History and physical exam: During the diagnosis process, your healthcare provider will ask about your signs and symptoms and how long you have had them. He or she will also ask about your medical history and your drug use. A physical exam of the lower abdomen may show the cause or give your provider additional clues. After this, certain tests may be needed. Men may have a rectal exam to check the size of their prostate.
Your urine may be saved and checked to look for infection.
Ultrasound of the bladder: The amount of urine that stays in your bladder after urinating may be measured by doing an ultrasound test of the bladder. This test is called a postvoid residual or bladder scan.
Cystoscopy: Cystoscopy is a test in which a thin tube with a tiny camera on one end is put into your urethra. This lets the doctor look at pictures of the lining of your urethra and bladder. This test may show a stricture of the urethra, blockage caused by a stone, an enlarged prostate or a tumor. It can also be used to remove stones, if found. A computed tomography scan may also help find stones or anything else blocking the flow of urine.
Urodynamic testing: Tests that use a catheter to record pressure within the bladder may be done to tell how well the bladder empties. The rate at which urine flows can also be measured by such tests. This is called urodynamic testing.
Dont Miss: What Is A Sling For The Bladder
When Too Much Becomes Too Much

If you urinate more than seven times a day, theres a chance you have a problem. But even if youre not quite at that number, any large changes in your normal urinary pattern could be a sign of trouble.
Two to three bathroom visits a night should also be taken seriously. You should be able to get a good nights rest without needing to run to the bathroom at all.
Read Also: Lack Of Bladder Control Uti
Treating Painful Bladder Syndrome
If you suspect your symptoms are related to painful bladder syndrome, the first step is to see a doctor who can provide a proper diagnosis. The source of your pelvic pain may be diagnosed after a thorough pelvic exam, lab work to rule out infections, ultrasounds, or laparoscopy.
Once painful bladder syndrome or another gynecologic condition is confirmed, our team at Gynecology and Obstetrics Medical Group works with you to find the treatment thats right for you. Examples of possible treatments for painful bladder syndrome include:
- Lifestyle changes, including drinking enough water each day and managing stress levels
- Bladder training
- Physical therapy to strengthen your pelvic floor muscles
- Medication
- Bladder procedures, such as bladder instillation
If you have pelvic pain and suspect that painful bladder syndrome is the cause, call our Long Beach, California, office at 562-247-3038. Alternatively, you can request an appointment anytime through our convenient online booking tool.
You Might Also Enjoy…
Pain After Emptying Bladder
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Don’t Miss: Fastest Way To Cure Bladder Infection
Stay Hydrated To Reduce Urinary Incontinence
Controlling your fluid consumption is difficult. You might believe that reducing liquids, in general, will help lower OAB. In actuality, it can cause urine to become more concentrated, irritating the bladder. On the other hand, its best not to put too much strain on the bladder by ingesting excessive amounts of fluids. Try the following strategies:
- Drink four to eight 8-ounce glasses of plain water every day. If your urine is pale yellow or virtually colorless, youve drunk enough.
- Sip your water throughout the day.
- Carry a little water bottle unless youre exercising.
- Reduce your drinking two to three hours prior to bedtime.
- If you use a diuretic, consider taking it first thing in the morning.
miktek
0 likes, 194 replies
-
Edited 17 months ago
If he is not going to give you something I would go to see another doctor. You may have a case of prostatitis. It ca affect the whole area. And going to the bathroom after you masturbating is normal. It is the bodys way of cleaning the pipes. Try another doctor. Ken
-
Posted 3 years ago
I dont have any other pain because the feeling to urinate all the time in my head. Its doesnt burn to pee in fact I get relief when I do. I thought prostatitis was pain in rectum, between balls and rectum and pelvic pain. I am seeing a urologist tomorrow to get results from ultrasound so will ask about rectal exam then.
Posted 3 years ago
What Is The Latest Research On Bladder Pain Syndrome Treatment
Researchers continue to search for new ways to treat bladder pain. Some current studies focus on:
- New medicines to treat bladder pain
- Meditation as a way to control bladder pain
- The role of genetics in bladder pain
- Acupuncture treatment
To learn more about current bladder pain treatment studies, visit ClinicalTrials.gov.
You May Like: What Were Your Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
How Does My Doctor Know I Have Interstitial Cystitis
You may have interstitial cystitis if any of the following occur:
-
You have to urinate often or urgently
-
You have pelvic or bladder pain
-
A urologist finds bladder wall inflammation, pinpoint bleeding or ulcers during an exam with a special scope that looks inside your bladder
-
Your doctor has ruled out other diseases such as urinary tract infections, vaginal infections, bladder cancer, sexually transmitted diseases and, in men, chronic prostatitis
Further Help For Bladder Pain
If you are concerned about your problem and it is starting to affect your day-to-day life make an appointment to see your doctor as you may need to be referred to a specialist.
If you are experiencing bladder pain you can contact a continence nurse or specialist physiotherapist, who are healthcare professionals who specialise in bladder and bowel problems.
Information on this page has been updated with the help of www.painful-bladder.org. If youd like to read their information sheet on painful bladder / interstitial cystitis please click here.
You can also find information about painful bladder / interstitial cystitis on the Bladder Health UK website bladderhealthuk.org, Email , Telephone 0121 702 0820
Don’t Miss: Best Way To Treat Bladder Infection
What Are The Causes Of Dysuria
There are many causes of dysuria. Also know that doctors cant always identify the cause.
WOMEN: Painful urination for women can be the result of:
- Bladder infection .
- Urinary tract infection.
- Endometritis and other causes outside the urinary tract, including diverticulosis and diverticulitis.
- Inflammation of the bladder or urethra . Inflammation is usually caused by an infection.
The inflammation may also be caused by sexual intercourse, douches, soaps, scented toilet paper, contraceptive sponges or spermicides.
Normal female anatomy
MEN: Painful urination for men may be the result of:
- Urinary tract infection and other infections outside the urinary tract, including diverticulosis and diverticulitis.
- Prostate disease.
Normal male anatomy
Painful urination for men and women may be the result of a sexually transmitted infections or the side effect of medications. Chemotherapy cancer drugs or radiation treatments to the pelvic area may inflame the bladder and cause painful urination.
Bladder Cancer And Radiation Treatment
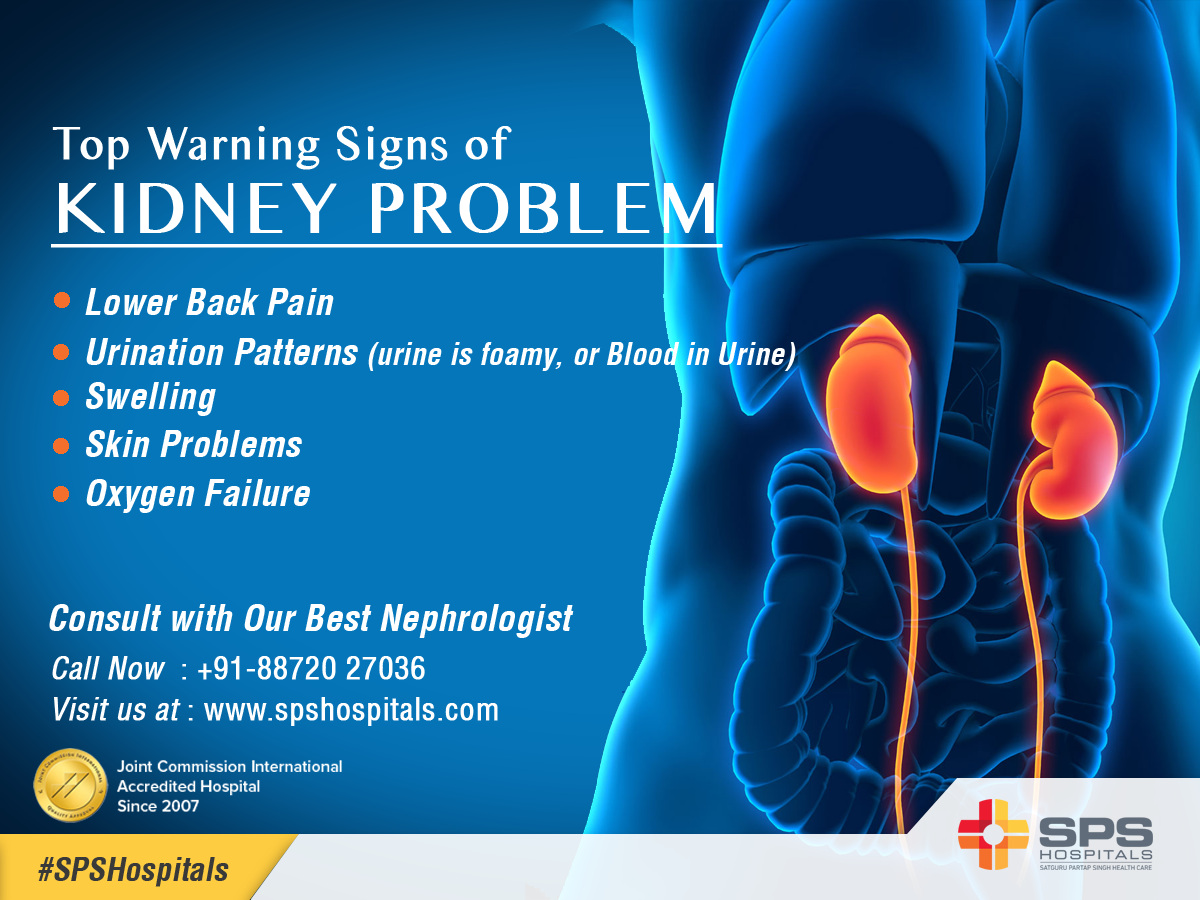
While urine containing blood is a more common symptom of bladder cancer, some women with this condition also feel the need to urinate more often. If a tumor is present in the bladder, it takes up space that could otherwise be filled with urine, thereby leading to an increased need to pee frequently. Not only can cancer cause more frequent urination, but the treatments for cancer can cause this as well. For example, radiation is often used to treat cancer and can cause the side effect of frequent urination. This is especially true if the radiation therapy is targeted at the pelvic area.
Recommended Reading: Is There A Blood Test For Bladder Cancer
When To Contact A Medical Professional
- You have fever, back or side pain, vomiting, or shaking chills
- You have increased thirst or appetite, fatigue, or sudden weight loss
Also call your provider if:
- You have urinary frequency or urgency, but you are not pregnant and you are not drinking large amounts of fluid.
- You have incontinence or you have changed your lifestyle because of your symptoms.
- You have bloody or cloudy urine.
What Are Signs And Symptoms Of Frequent Urination
Even though there are numerous causes for frequent urination, the symptoms are generally the same. Below are some terms that are used to describe symptoms that may accompany frequent urination.
- Frequency: urinating more than eight times during the day or more than once overnight
- Hesitancy: incomplete evacuation of the bladder during each episode of urination. There may be a sudden stoppage of the urine flow due to spasms in the bladder or urethra or there may be difficulty starting the flow of urine.
- Urgency: the uncomfortable feeling of pressure in the bladder that makes you feel you have to go right now
- Urinary incontinence: the inability to control the flow of urine, leading to either constant or intermittent accidental leakage
- Dysuria: pain or burning sensation during or immediately following urination. This may be a sign of a urinary tract infection.
- Hematuria: Blood in the urine can be small amounts, clots, or very bloody. This will usually cause the urine to appear darker in color.
- Nocturia: This is having to wake up to urinate. It can also be associated with nighttime urinary incontinence.
- Pollakiuria: frequent daytime urination
- Dribbling: After finishing urination, urine continues to drip or dribble out.
- Straining: having to squeeze or bear down to initiate the urine stream
Recommended Reading: Over The Counter Bladder Numbing Medicine
How The Urinary Tract Works And What Happens With Oab Your Browser Does Not Support Html5 Audio Playback You May Download The Audio File Directly Here
The urinary tract is the important system that removes liquid waste from our bodies:
- kidneys: two bean-shaped organs that clean waste from the blood and make urine
- ureters: two thin tubes that take urine from the kidney to the bladder
- bladder: a balloon-like sac that holds urine until itâs time to go to the bathroom
- urethra: the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body. The urethra has muscles called sphincters that lock in urine. The sphincters open to release urine when the bladder contracts.
When your bladder is full, your brain signals the bladder. The bladder muscles then squeeze. This forces the urine out through the urethra. The sphincters in the urethra open and urine flows out. When your bladder is not full, the bladder is relaxed.
With a healthy bladder, signals in your brain let you know that your bladder is getting full or is full, but you can wait to go to the bathroom. With OAB, you canât wait. You feel a sudden, urgent need to go. This can happen even if your bladder isnât full.
Symptoms Of Interstitial Cystitis
The symptoms associated with painful bladder, or interstitial cystitis syndrome include:
- Frequency day and night
- Urgency the need to urinate straight away, in some cases followed by pain, pressure or spasms
It is most important that you go to see your GP first because PB/IC is a diagnosis of symptoms plus exclusion of other serious possibilities such as cancer.
Your GP may refer you to a Urologist who may perform tests such as urodynamics or cystoscopy. A cystoscopy uses a cystoscope, which is a long tube that can be inserted into the urethra. It has a camera attached to the end so that an image can be shown on a monitor. It can take time to obtain a correct diagnosis as symptoms of PB/IC can be similar to other conditions for example, Overactive Bladder or Bacterial Cystitis.
Also Check: What Happens When You Get A Bladder Infection
Symptoms Of Frequent Or Painful Urination
Frequent or painful urination can be a symptom of a variety of health conditions requiring treatment.
Symptoms of frequent urination that call for a visit to the physician as soon as possible include:
- Pain in the lower abdomen, side or groin
- Painful urination
- Blood in the urine, or red or dark brown urine. This can be a dangerous sign and should always be evaluated.
- A powerful urge to urinate
- Difficulty urinating, or trouble emptying the bladder completely
- Loss of bladder control.
People should see a physician when urinary frequency increases with no obvious cause , especially if other symptoms are present.
Symptoms accompanying painful urination requiring medical attention are:
- Painful urination lasting more than one day
- Blood in the urine
- For pregnant women, any painful urination.
Causes Of Frequent Urination
Sometimes frequent urination and painful urination go together. In women, painful urination is most often a symptom of a urinary tract infection . UTIs often include an urgent need to urinate, uncomfortable, painful or burning sense when urinating, fever, and a painful or uncomfortable abdomen.
A variety of other problems can cause frequent urination, including:
Rarely, bladder cancer, bladder dysfunction and radiation therapy or other cancer treatment can cause issues with frequent urination.
You May Like: Bladder Carcinoma In Situ Treatment
Path To Improved Health
There are several conditions that can cause painful urination. The most common is a urinary tract infection . The urinary tract consists of the kidneys, bladder, and urethra. The urethra is the tube that carries urine out of the body. Bacteria can build in the tract when waste isnt removed or the bladder isnt emptied correctly. This causes an infection. Swelling and irritation from the infection can make urination uncomfortable.
Sometimes painful urination can occur even if you dont have a UTI. Other causes include:
- Medicines. Certain medicines, like some used in cancer chemotherapy, may inflame the bladder.
- Something pressing against the bladder. This could be an ovarian cyst or a kidney stone stuck near the entrance to the bladder.
- Vaginal infection or irritation.
- Sensitivity to chemicals in products. Douches, vaginal lubricants, soaps, scented toilet paper, or contraceptive foams or sponges may contain chemicals that cause irritation.
- Sexually transmitted infections. Gonorrhea, chlamydia, or herpes can cause urination to be painful for some people.
- Prostate infection
Get A Diagnosis Not A Self
Its also important to consider whether the uterus and other organs of the gynecological system could be causing bladder pain, Siddiqui says, as they are close to the bladder. Pelvic floor dysfunction, such as tightness or spasms of the pelvic muscles, commonly occurs with bladder pain and may make bladder pain worse, she explains. Pelvic pain can also be caused by endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, or ovarian cysts. Additionally, gastrointestinal problems such as inflammatory bowel diseases can sometimes be the source of pelvic pain, notes Mayo Clinic.
If none of these conditions are present and women have ongoing bladder pain, they are typically treated for bladder pain syndrome, which refers to painful conditions of the bladder where other causes such as UTI and cancer have been excluded,” says Siddiqui.
The bottom line for women to keep in mind: Dont self-diagnose your bladder pain. Addressing and treating the issue can offer relief for body and mind.
Recommended Reading: Medicine To Treat Bladder Infection