How Is Chronic Urinary Retention Diagnosed
History and physical exam: During the diagnosis process, your healthcare provider will ask about your signs and symptoms and how long you have had them. He or she will also ask about your medical history and your drug use. A physical exam of the lower abdomen may show the cause or give your provider additional clues. After this, certain tests may be needed. Men may have a rectal exam to check the size of their prostate.
Your urine may be saved and checked to look for infection.
Ultrasound of the bladder: The amount of urine that stays in your bladder after urinating may be measured by doing an ultrasound test of the bladder. This test is called a postvoid residual or bladder scan.
Cystoscopy: Cystoscopy is a test in which a thin tube with a tiny camera on one end is put into your urethra. This lets the doctor look at pictures of the lining of your urethra and bladder. This test may show a stricture of the urethra, blockage caused by a stone, an enlarged prostate or a tumor. It can also be used to remove stones, if found. A computed tomography scan may also help find stones or anything else blocking the flow of urine.
Urodynamic testing: Tests that use a catheter to record pressure within the bladder may be done to tell how well the bladder empties. The rate at which urine flows can also be measured by such tests. This is called urodynamic testing.
Symptoms Of Urinary Retention
Acute urinary retention requires immediate medical attention. Symptoms include:
- A complete inability to pass urine
- A painful urge to urinate
- Pain or swelling in your lower abdomen
Chronic urinary retention symptoms include:
- Frequent urination
- Trouble starting urination
- Weak or intermittent urination stream
- A feeling of needing to urinate after finishing urination
Causes Of Stress Incontinence
Stress incontinence is when the pressure inside your bladder as it fills with urine becomes greater than the strength of your urethra to stay closed. Your urethra is the tube that urine passes through to leave the body.
Any sudden extra pressure on your bladder, such as laughing or sneezing, can cause urine to leak out of your urethra if you have stress incontinence.
Your urethra may not be able to stay closed if the muscles in your pelvis are weak or damaged, or if your urethral sphincter the ring of muscle that keeps the urethra closed is damaged.
Problems with these muscles may be caused by:
- damage during childbirth particularly if your baby was born vaginally, rather than by caesarean section
- increased pressure on your tummy for example, because you are pregnant or obese
- damage to the bladder or nearby area during surgery such as the removal of the womb , or removal of the prostate gland
- neurological conditions that affect the brain and spinal cord, such as Parkinson’s disease or multiple sclerosis
- certain connective tissue disorders such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- certain medicines
Also Check: Parkinson’s And Overactive Bladder
Signs And Symptoms Of Cystitis
The main symptoms of cystitis include:
- pain, burning or stinging when you pee
- needing to pee more often and urgently than normal
- urine that’s dark, cloudy or strong smelling
- pain low down in your tummy
- feeling generally unwell, achy, sick and tired
Possible symptoms in young children include a high temperature of 38C or above, weakness, irritability, reduced appetite and vomiting.
Read more about treating cystitis
Surgery And Procedures For Urinary Incontinence
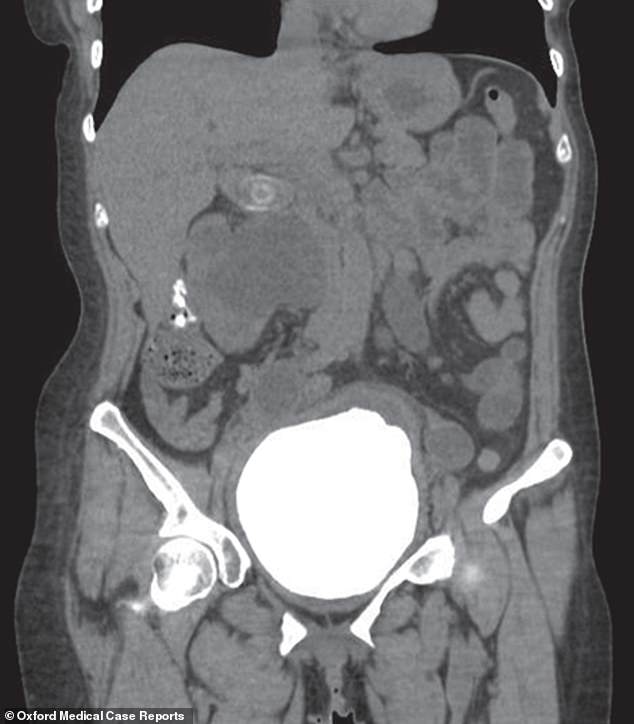
If other treatments for urinary incontinence are unsuccessful or unsuitable, surgery or other procedures may be recommended.
Before making a decision, discuss the risks and benefits with a specialist, as well as any possible alternative treatments.
If you are a woman and plan to have children, this will affect your decision, because the physical strain of pregnancy and childbirth can sometimes cause surgical treatments to fail. Therefore, you may wish to wait until you no longer want to have any more children before having surgery.
The various surgical treatments for urinary incontinence are outlined below.
Recommended Reading: Can A Bladder Infection Clear Up On Its Own
Prevent And Treat Constipation
Constipation can affect how your child voids, and straining to pass stool can weaken the muscles that support the bladder . It is therefore essential that any constipation is treated, as resolving this often improves voiding.
- Drinking plenty helps to keep stools soft.
- Ensure your child eats a healthy diet with a wide range of fruit and vegetables.
- Some people find that introducing probiotic drinks or yoghurts helps to avoid constipation. There is some evidence that they can also change the bacteria in the stool and so may help to prevent urinary infections.
- Laxative medication can be given to children but, given only after talking with a nurse, doctor or pharmacist as children require different doses to adults.
Information For Patients Relatives And Carers
Emptying or ‘voiding’ your bladder is important. Failure to empty the bladder completely can cause problems such as incontinence, discomfort, the need to go to the toilet frequently or even bladder and urinary tract infections. If this becomes an ongoing, chronic problem it can lead to over-distension of the bladder and various further complications including kidney damage. It is a problem which can affect both men and women.
There are various causes. Some, such as injury, surgery or disease including various neurological disorders can stop the muscles of the bladder squeezing effectively and so enabling effective emptying. Alternatively, it may be due to some sort of obstruction such as an enlarged prostate in men, a kidney stone, a stricture or prolapse or even constipation.
Indications that you may not be emptying your bladder completely include leakage after passing urine, going to the toilet frequently, recurrent bladder infections or simply the feeling that the bladder has not emptied after going to the toilet.
While your doctor may want to investigate the reasons behind such difficulties, there are several things which you can do to help empty your bladder as fully as possible. .
Read Also: Can Endometriosis Affect Your Bladder
Not Being Able To Empty Your Bladder
If you’re unable to empty your bladder fully, any bacteria that get inside may not be flushed out when you go to the toilet and can multiply more easily.
You may not be able to empty your bladder fully if:
- you have a blockage in your urinary system, such as a bladder stone
- you’re pregnant, as the baby may be pressing on your bladder
- you have an enlarged prostate gland that presses on the urethra
Causes Of Urinary Retention
There are many different causes.
Blockage In men, the urethra may be constricted by an enlarged prostate a common condition for men over 50. In women, blockage can be caused by certain types of pelvic prolapse, including Cystocele and Rectocele .
Other blockage reasons for both men and women include urethral stricture and urinary stones.
Infection / Swelling In men, prostatitis , can cause swelling that blocks the free flow of urine. Urinary Tract Infections and Sexually Transmitted Diseases can also cause swelling that leads to urinary retention.
Nerve Problems Urinary retention could be caused by a problem with the nerves that control the bladder. If the nerves are damaged, it can cause a breakdown in the signals between the brain and bladder. Some causes of nerve damage include:
Recommended Reading: Does Cranberry Juice Help Bladder Problems
History Of Complaints And Physical Examination
A physician will suspect urinary retention by your symptoms and will attempt to confirm the diagnosis with a physical examination of the lower abdomen. The physician may be able to feel the distended bladder by lightly tapping on your lower belly. Tapping or striking for diagnostic purposes is called percussing.
Blockage Or Narrowing In The Urethra Or Bladder Neck
For you to be able to urinate normally, all parts of your urinary tract need to work together in the correct order. Urine normally flows from your kidneys, through the ureters to your bladder, and out the urethra. If a blockage or narrowing occurs somewhere along the urinary tract, you may have difficulty urinating, and if the blockage is severe, you may not be able to urinate at all.
Medical problems that may narrow the urethra and block urine flow include
You May Like: Overactive Bladder And Blood In Urine
What Causes Urinary Retention
- Structural problems with the urethra, such as narrowing or blockage
- Structural problems with the bladder neck, sometimes following treatment for a congenital condition, such as posterior urethral valves or bladder exstrophy
- Weak bladder and pelvic floor muscles
- Problems with nerve messages travelling between the bladder and brain
- Side effects of some medications, including anaesthesia
- Surgery to the urinary system
- Constipation when the bowel is full of poo and presses on the bladder and urethra
How Does The Urinary System Work
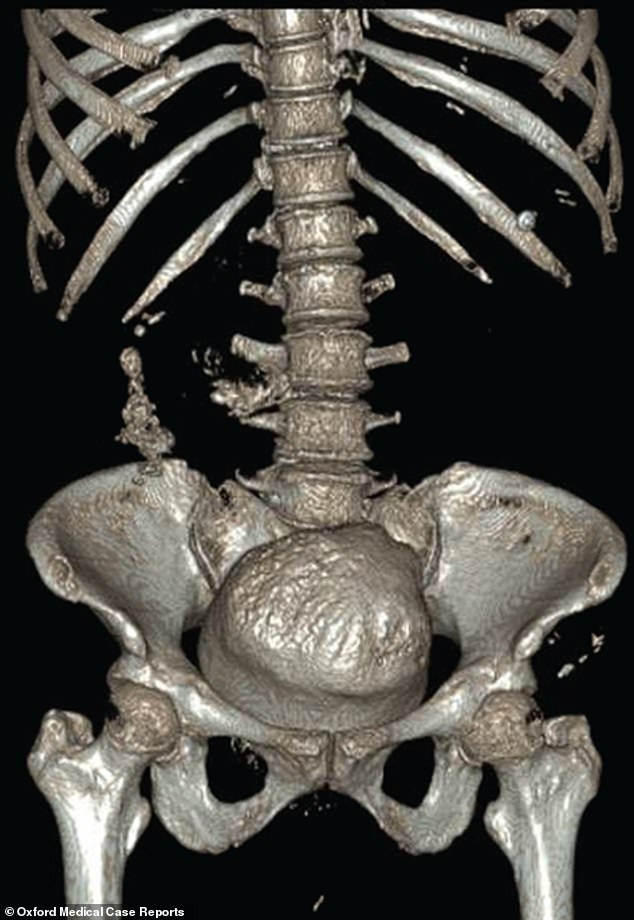
The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, the bladder and urethra. The kidneys filter the blood to remove waste products and produce urine. The urine flows from the kidneys down through the ureters to the bladder. A ring of muscle squeezes shut to keep urine in the bladder and relaxes when we need to wee. The urine passes through another tube called the urethra to the outside when urinating .
Also Check: Can Bladder Leakage Be Fixed
Consultant Urologist Urges Men To Seek Advice For Urinary Symptoms
The last in a series of guest blogs this Urology Awareness Month focuses on men who experience urinary symptoms and all too often suffer in silence.
Nearly all men know they have a prostate gland but few know what it actually does. Despite the lack of any real knowledge, it gets blamed for a huge variety of symptoms, though often these are quite unrelated.
Most men tend to ignore their lower urinary tract symptoms , putting up with, or even working round their symptoms rather than declaring them to a GP or nurse. In reality little real harm usually comes from this. However, given the fact we now have many effective and well tolerated non-surgical treatments, it is a pity so many choose to suffer in silence for so long.
The reasons for ignoring symptoms are numerous they are insidious, developing gradually over many years. Even in 2017 there is often a feeling of embarrassment or possibly fear that the symptoms may be due to cancer. Past memories of an elderly relative who was never the same again after prostate surgery comes to mind. People forget that medical treatment and surgical technology has advanced enormously with newer and less invasive treatments becoming available all the time.
So why do men eventually seek help?
Other triggers are the diagnosis of prostate cancer in a neighbour, or a friend going into retention. Otherwise a near miss with near retention arising, may call for action.
All is not lost there is good news!
Further information:
Topics
Sitting On The Toilet Correctly
Some boys will prefer to pass urine whilst standing others prefer to sit. It is important that boys have a wee in the position in which they are most comfortable.
For girls, it is important to sit on the toilet in a position which will encourage complete emptying of the bladder. Girls should sit on the toilet with their legs wide apart.
When sitting on the toilet it is very important that both feet are flat on the floor. If your child cannot reach the floor, it is important that they use a footstool or step.
Read Also: Foods To Strengthen Bladder Muscles
Can Medicines Be Given To Help
In some cases, medication may be suggested to help your child. However, in children with functional bladder and voiding problems, all medication is in addition to, not a replacement for, good bladder training. Medications are most effective when children are drinking enough, drinking regularly and using the toilet regularly as described in the section above headed What can my child do to help them improve and what can I do to help my child improve?.
What Causes Incomplete Emptying Of The Bladder
Incomplete emptying of a bladder can affect people across all age groups and be a cause for pain, irritation, and embarrassment to the person. The medical term for the condition is Urinary Retention.
If not treated in time, the condition can lead to complications including kidney failure that can be fatal. Its important to recognize the symptoms and seek medical help immediately.
Recommended Reading: Robotic Surgery For Bladder Cancer
What Causes Chronic Urinary Retention
Urinary retention can happen for several different reasons. These causes can include:
- A blockage to the way urine leaves your body.
- Medications youre taking for other conditions.
- Nerve issues that interrupt the way your brain and urinary system communicate.
- Infections and swelling that prevent urine from leaving your body.
- Complications and side effects of medications given to you for a surgical procedure.
Blockage
When something blocks the free flow of urine through the bladder and urethra, you might experience urinary retention. The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of your body. In men, a blockage can be caused when the prostate gland gets so big that it presses on the urethra. This is the most common cause of chronic urinary retention in men. One cause in women is a bladder that sags. This is called cystocele. It can also be caused when the rectum sags into the back wall of the vagina a condition called rectocele. Some causes can happen to both men and women. The urethra can get narrow due to scar tissue. This is called a stricture. Urinary stones can also block the flow of urine out of your body.
Medications
Nerve issues
- Trauma to the spine or pelvis.
- Pressure on the spinal cord from tumors and a herniated disk.
- Vaginal childbirth.
Urinary retention from nerve disease occurs at the same rate in men and women.
Infections and swelling
Surgery
Problems With The Nerves Supplying The Bladder
Urinary retention can result from problems with the nerves that control the bladder and the valves that control the flow of urine from the bladder.
Even when the bladder is full, the bladder muscles that squeeze urine out may not receive the signal to push. The sphincters may not receive the signal to relax and allow the bladder to empty. Possible causes of nerve problems that may cause urinary retention include diabetes, a stroke, multiple sclerosis or after an injury to the pelvis.
Some children are born with conditions that may affect the nerve signals to the bladder. For example spina bifida may cause urinary retention in newborn babies.
Don’t Miss: What Over The Counter Medicine Is Good For Bladder Infections
When To See Your Gp
You should see your GP if you or your child have symptoms of cystitis for the first time.
Cystitis isn’t usually a cause for serious concern, but the symptoms can be similar to several other conditions, so it’s important to get a proper diagnosis.
If you’re a woman who has had cystitis before, you don’t necessarily need to see your GP again. Cystitis is very common in women and mild cases often get better on their own. Speak to a pharmacist if you need any advice about treating cystitis.
However, you should see your GP if your symptoms are severe or don’t start to get better in a few days, you get cystitis frequently, or you’re pregnant.
Children and men should always be seen by a GP if they have symptoms of cystitis, as the condition is less common and could be more serious in these groups.
Obstruction In People With A Penis
Possible causes of obstruction in people with a penis
- Cystocele. Cystocele occurs when the bladder lowers and pushes against your vagina.
- Rectocele. This is when the rectum expands and pushes against your vagina.
- Uterineprolapse. Uterine prolapse occurs when the uterus lowers and pushes against the bladder.
Don’t Miss: How Effective Is Immunotherapy For Bladder Cancer
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation
Your posterior tibial nerve runs down your leg to your ankle. It contains nerve fibres that start from the same place as nerves that run to your bladder and pelvic floor. It is thought that stimulating the tibial nerve will affect these other nerves and help control bladder symptoms, such as the urge to pass urine.
During the procedure, a very thin needle is inserted through the skin of your ankle and a mild electric current is sent through it, causing a tingling feeling and causing your foot to move. You may need 12 sessions of stimulation, each lasting around half an hour, one week apart.
Some studies have shown that this treatment can offer relief from OAB and urge incontinence for some people, although there is not yet enough evidence to recommend tibial nerve stimulation as a routine treatment.
Tibial nerve stimulation is only recommended in a few cases where urge incontinence has not improved with medication and you don’t want to have botulinum toxin A injections or sacral nerve stimulation.
What Is Considered Normal Concerning Bladder Control
What is considered normal depends on your childs age. When we are babies our bladders fill and empty without our control as a reflex when the bladder is full. As we get older we start to learn to block this reflex. Our brains learn that we can control when the bladder contracts and also stop it from contracting and so we become potty trained. The age at which children gain brain control over their bladders varies, so children differ greatly in how long it takes them to become fully toilet trained. Whilst most children will be dry in the day by the age of five years, one in 75 children older than five will have some degree of day-time wetting.
For all children, night-time bladder control takes longer to develop than day-time control but again, the age at which children gain night-time dryness also varies greatly. In the UK, approximately half a million children aged between five and 16 wet the bed, but the percentage of children decreases with age. For example, it is reported that 8% of four and a half year olds wet the bed whilst 1.5% of nine and a half year olds wet the bed, and only 1% at adulthood.
Also Check: Electrical Stimulation For Bladder Control