What Tests Will My Healthcare Provider Use To Diagnose Metastatic Cancer
There is no standard test to check for metastasis. Your healthcare provider will order tests based on the type of cancer you have and the symptoms youve developed.
Blood tests
Routine blood tests can tell your provider if your liver enzymes are elevated. This could indicate liver metastasis. In many cases, however, these blood test results are normal, even in the presence of advanced cancer.
Tumor markers
Some cancers have tumor markers that can be helpful in monitoring cancer after diagnosis. If tumor marker levels increase, it could mean that your cancer is advancing. Some examples are:
- Colon cancer: CEA .
- Prostate cancer: PSA .
- Testes cancer: AFP and HCG .
There are several tumor markers that are less specific, and therefore, not used as a tool for diagnosing metastasis.
Imaging
There are many tests that take pictures of the inside of your body. Appropriate tests depend on the symptoms and the type of cancer. Imaging tests may include:
The results of these tests may not provide definitive answers. In some cases, your healthcare provider may also take a biopsy of the suspected metastatic tumor.
What Is A 5
A relative survival rate compares people with the same type and stage of bladder cancer to people in the overall population. For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for a specific stage of bladder cancer is 90%, it means that people who have that cancer are, on average, about 90% as likely as people who dont have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
Recommended Reading: Are Bladder Cancer And Colon Cancer Related
Common Sites Of Metastasis
- All less common sites: 22.4%
Invasive lobular carcinoma tends to have a significantly different pattern of metastases than ductal breast cancer. In one 2017 study, almost 70% of people with metastases from lobular carcinoma had peritoneal metastases.
For roughly a third of women , cancer spreads to multiple organs at the same time.
You May Like: Can You Get Bladder Infection From Intercourse
A Rare Metastasis To The Bladder
Rishi A. ModhAcademic Editor: Received
Abstract
Primary bladder cancer is the fifth most common malignancy but secondary malignancies of the bladder are rare. Distinguishing primary adenocarcinomas of the bladder from secondary adenocarcinomas is difficult and relies on immunohistochemical staining. Prostate, colorectal, breast, and lung all can produce metastatic adenocarcinomas to the bladder. Further management of the malignancy varies depending on the source, thus making proper diagnosis critical. We present only the fifth documented case of metastatic adenocarcinoma of the lung to bladder and performed a review of the literature.
1. Introduction
Bladder cancer is the fifth most commonly diagnosed malignancy. An estimated 73510 individuals will be diagnosed with bladder cancer in 2012. Most bladder cancers are diagnosed at an early stage , but up to 25% present at more advanced, invasive stages . The majority of primary cancers of the bladder are pure urothelial while squamous cell, small cell, and glandular or adenocarcinoma account for a small percentage. Urothelial carcinomas can have mixed histologic variants including squamous, glandular, sarcomatoid, micropapillary, small cell, and plasmacytoid. Rare histologic subtypes of primary bladder cancers include small cell, sarcomatoid, and pheochromocytoma .
2. Case Report
| Abdominal and Pelvic CT showing a thickened posterior and left lateral wall. |
| Abdominal and Pelvic CT showing bilateral hydronephrosis. |
References
Metastatic Bladder Cancer Treatment
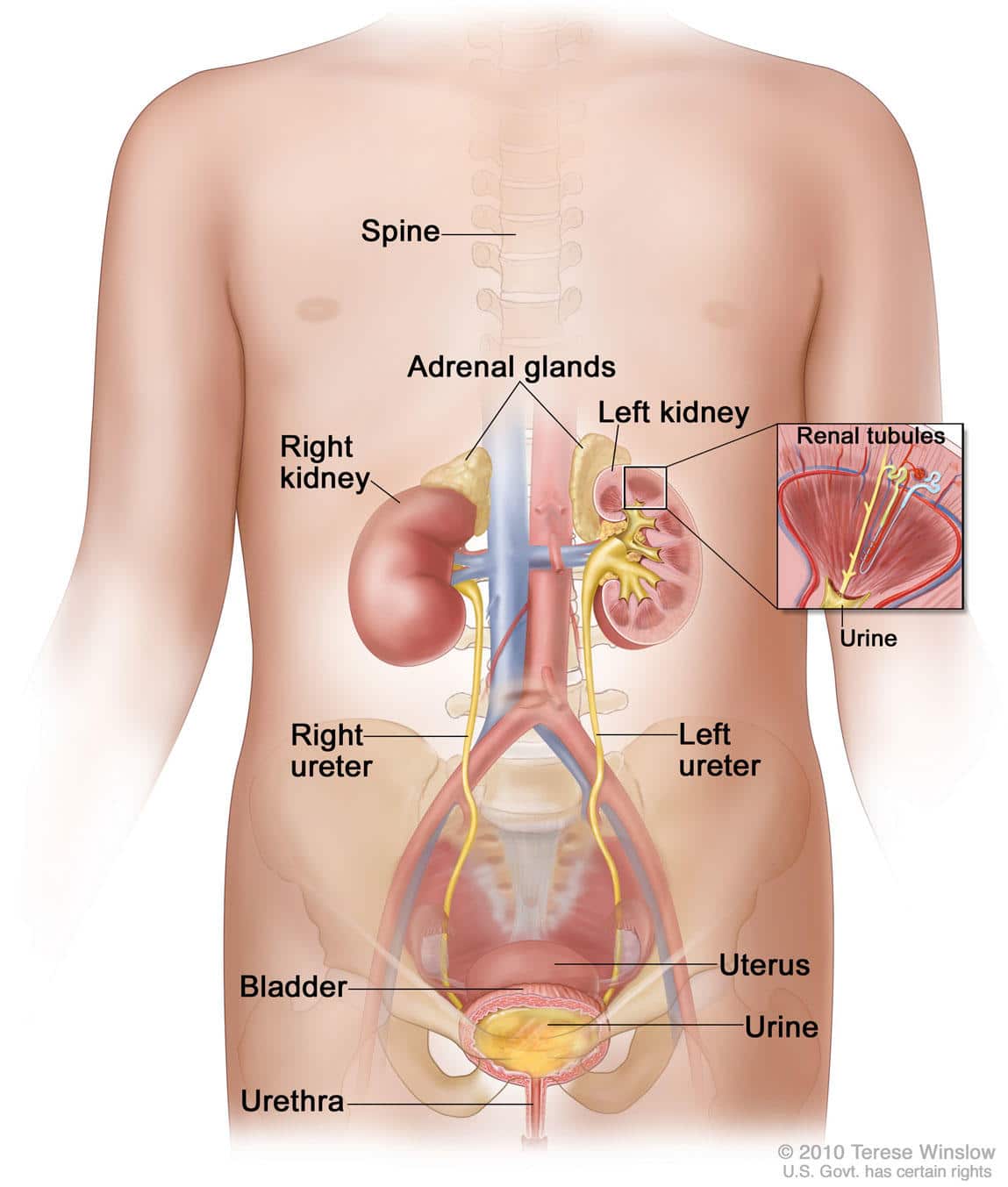
Without a professional evaluation, it can be difficult to know if the symptoms youre experiencing are the result of bladder cancer or something else. While its important not to panic most of these issues can be caused by other, less serious conditions its also important to talk with an expert if you notice something out of the ordinary. The earlier that bladder cancer is detected, the more treatment options youre likely to have.
Medically Reviewed by, Scott Gilbert, MD, Department of Genitourinary Oncology.
At Moffitt Cancer Center, we offer a comprehensive range of bladder cancer tests and treatments, welcoming patients with all stages of the condition. If youd like to have your symptoms evaluated by an oncologist who specializes in metastatic bladder cancer, call or submit a new patient registration form online to request an appointment. No referral is required to consult with our team.
Recommended Reading: What Is Bladder Control Pads
How Can I Prevent Bladder Cancer
Stopping smoking is the best way to prevent bladder cancer. You should also reduce your exposure to cancer-causing agents to help prevent bladder cancer. Other than these measures, decreasing your risk of invasive bladder cancer relies on early detection of symptoms and possibly screening if you are high-risk.
How Breast Cancer Spreads
Breast cancer can spread through the lymphatic system, the bloodstream, or by local invasionfor instance, when cancer cells actually invade nearby tissues, such as the chest wall or ribs.
When breast cancers spread and enter the lymphatic system, they usually first arrive at nearby lymph nodes and may still be early-stage.
Metastatic breast cancer is the same thing as stage 4 breast cancer and is considered the most advanced stage. It refers to breast cancers that have spread beyond the breast and nearby lymph nodes to other regions of the body, which are called distant metastases.
While treatment options for metastatic breast cancer are similar no matter where cancer has spread, some treatments are used for specific sites of metastasis as well .
You May Like: Exercises To Help Bladder Leakage
Other Types Of Bladder Cancer
Approximately 2% of bladder cancers are adenocarcinomas. Nonurothelial primary bladder tumors are extremely rare and may include small cell carcinoma, carcinosarcoma, primary lymphoma, and sarcoma . Small cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder accounts for only 0.3-0.7% of all bladder tumors. High-grade urothelial carcinomas can also show divergent histologic differentiation, such as squamous, glandular, neuroendocrine, and sarcomatous features.
Os Analysis Classified By Specific Organ For Patients With One Site Metastasis After Psm
For patients with bone metastasis only, histology type, surgery, LNs removed and chemotherapy were associated with overall survival in univariate and multivariate Cox analysis . Patients with LNs removed had a better prognosis than those without LNs removed or surgery .
For patients with lung metastasis, univariable and multivariable Cox regression model analyses found that histology type, surgery, LNs removed and chemotherapy were independent prognostic factors . Patients with LNs removed had a better prognosis than those without LNs removed or surgery .
For patients with liver metastasis, age, surgery, and chemotherapy were independent prognostic factors. However, LNs removed in surgery was not an independent prognostic factor .
For patients with DL metastasis, neither surgery nor lymph node removal affected their prognosis, but histology types and chemotherapy were independent prognostic factors .
Recommended Reading: What Medicine For Bladder Infection
Also Check: Turbt Treatment For Bladder Cancer
Major Study Stops Bladder Cancer From Metastasizing To Lungs
- Date:
- University of Colorado Denver
- Summary:
- A new study shows that the protein versican aids bladder cancer metastasis to the lungs and that high levels of versican are associated with poor prognosis in bladder cancer. The study also shows that versican signaling is reduced by adding RhoDGI2 or by blocking CCL2, leading to decreased bladder cancer metastasis to the lungs.
The diagnosis of localized bladder cancer carries an 80 percent five-year survival rate, but once the cancer spreads, the survival rate at even three years is only 20 percent. A major study recently published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation not only shows how bladder cancer metastasizes to the lungs but pinpoints a method for stopping this spread.
Specifically, the study shows that versican, a protein involved in cancer cell migration, is a driver of lung metastasis and that high levels of versican are associated with poor prognosis in bladder cancer patients. The study is the first to show how that when a cancer cell makes the protein RhoGDI2, it reduces the cells production of versican, thus blocking the ability of the cancer cell to grow in the lungs.
When the first cancer cells to attach to, say, the lung, they have a tough time they become distressed. Cancer cells express this distress in the form of versican. And the more versican they express, the more help they get, which arrives in the form of macrophages, a part of the bodys immune response that eat pathogens and other debris.
How We Care For You
The symptoms of liver metastases are often vague and hard to identify yourself. If you have any concerns, contact your doctor. Memorial Sloan Kettering has a team of specialists who are very experienced in diagnosing and treating the condition.
- Our goal is to provide treatment options that give you the very best possible quality of life and survival rate.
- MSK surgeons work closely with interventional radiologists in using powerful imaging tests such as CT, ultrasound, or MRI to guide treatments directly to where your tumor is located. We can often destroy tumors with minimally invasive techniques, such as ablation and embolization.
- Through genetic testing of tumors, we learn about the molecular blueprint of your particular cancer and customize a treatment plan for you. Another option is to combine surgery with hepatic arterial chemotherapy, which delivers the drug directly to the liver.
We also offer a range of support programs that can help you and your loved ones manage the challenges and stress of life during and after treatment for liver cancer.
You May Like: Menâs Overactive Bladder Treatment
Also Check: How To Help Overactive Bladder
Case : Cavitary/cystic Lung Metastases
An 85-year-old female with kyphoscoliosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and recurrent low-grade papillary UBC presented for evaluation of an abnormal CR performed elsewhere that was suggestive of bilateral cavitary lung lesions. She had previously undergone multiple transurethral resections of bladder tumor. She was a former 40 pack-year smoker. She denied constitutional, pulmonary, or genitourinary symptoms. Physical examination revealed a thin woman with kyphoscoliosis. There were faint end-expiratory wheezes. No abdominal masses were palpable. Chest CT revealed numerous cavitary nodules and masses, some with thick and others with thin walls. CT-guided biopsy of the lesion in Figure 3a was consistent with metastatic urothelial carcinoma . The patient was referred to oncology for consideration of chemotherapy, which she declined.
Figure 3:
What Types Of Testing Should I Expect For Monitoring My Condition
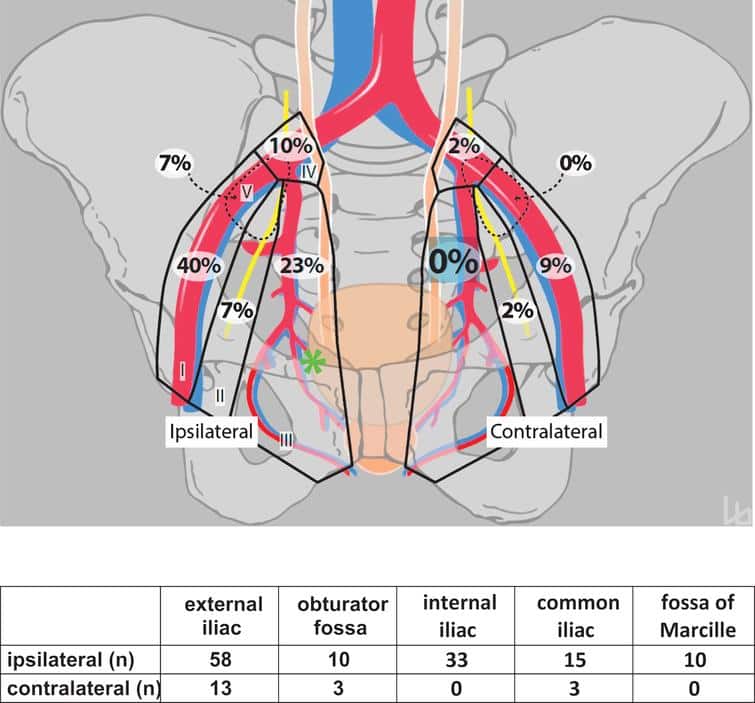
Since metastatic prostate cancer isnt curable, your doctor will most likely set up regular visits to check the cancers location, and to manage any long-term side effects from the cancer or any medication youre taking.
And since treatments for advanced prostate cancer are changing so fast and need to be given in a certain sequence to be the most effective, youll probably have not only a prostate cancer doctor but other specialists taking care of you. Your care team should coordinate closely, say the authors of a major study of such teams published in August 2015 in the journal Annals of Oncology.
Along with regularly testing your prostate-specific antigen levels, your care team may request blood tests that measure such prostate cancer indicators as alkaline phosphatase and lactate dehydrogenase. Magnetic resonance imaging or PET scans of the spine or other bones can also help identify how your cancer responds to treatment.
If youve had radiation, youre at an increased risk for bladder and colorectal cancer and should get screened regularly for these as well.
The tests youll have and how often youll need them should be customized to you. Your care team will consider your overall health, medications that are safe for you to take, other health conditions you might have, and what stage your cancer was when you were diagnosed.
You May Like: Bladder Cancer Chemo Treatment Side Effects
How Common Is Bladder Cancer
The American Cancer Societys estimates for bladder cancer in the United States for 2022 are:
- About 81,180 new cases of bladder cancer
- About 17,100 deaths from bladder cancer
The rates of new bladder cancers and deaths linked to bladder cancer and have been dropping slightly in women in recent years. In men, incidence rates have been decreasing, but death rates have been stable.
Bladder cancer is the fourth most common cancer in men, but it’s less common in women.
Mechanisms Of Tumor Spread
The mechanisms and pathways by which malignant tumors of the abdomen and pelvis spread are determined by regional anatomy and tumor pathophysiology. Abdominal and pelvic organs are suspended in the peritoneal cavity by ligaments and mesenteries formed by the peritoneum as it reflects from the extraperitoneal surface. The abdominal ligaments and mesenteries serve as conduits through which blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatics may travel. They also may serve to facilitate tumor spread between organs or restrict tumor spread between compartments. A variety of descriptions are in common usage regarding the mechanisms of tumor spread. Tumors can spread in several ways: directly from organ to organ without regard for fascial planes or anatomic compartments via the subserous connective tissue, blood vessels, or lymphatics of the abdominal mesenteries and ligaments or throughout the peritoneal cavity. Chapter 6 provides additional information regarding the spread of disease within the abdomen and pelvis.
Direct Contiguous Spread
Subperitoneal Spread
The intraperitoneal organs are suspended within the peritoneal cavity and are interconnected via a scaffolding of supporting ligaments and mesenteries. Beneath the peritoneal lining lies the subperitoneal space. This space contains connective tissue, lymphatics, and blood vessels, all of which can serve as conduits for tumor spread.
Subperitoneal Tumor Extension
Lymphatic Spread
BENIGN VERSUS MALIGNANT LYMPH NODES
Hematogenous Spread
Recommended Reading: Can I Train My Bladder
What Is The Prognosis For Liver Metastases
Prognosis is a clinical term describes how a disease condition develops, the signs and symptoms of the disease, how soon an affected individual is expected to recover, and how will be the quality of life of the affected individual over a period of time post treatment like ability to carry out activities of daily living the chances of any complications and other health concerns, and the chances of overall survival in cases of rare or incurable disease. In short, prognosis is referred to as the expected length of the disease, course of the disease, chances of any expected or unforeseen adverse events.
Also Check: Medication For Overactive Bladder In The Elderly
Metastatic Disease Or An Early Stage Bladder Cancer A Difficult Question
Ozge Keskin,
Verify Captcha
Regret for the inconvenience: we are taking measures to prevent fraudulent form submissions by extractors and page crawlers. Please type the correct Captcha word to see email ID.
Aydin Ataturk State Hospital, Turkey
Correspondence: Ozge Keskin, MD, Aydin Ataturk State Hospital Medical Oncology Department, Aydin, Turkey,, Tel 9.05E+11, Fax 9.03E+11
Received: February 28, 2017 | Published: April 28, 2017
Citation: Keskin O, Oktay E Metastatic Disease or an Early Stage Bladder Cancer? A Difficult Question. J Cancer Prev Curr Res 8: 00261. DOI: 10.15406/jcpcr.2017.08.00261
Also Check: Is There A Blood Test For Bladder Cancer
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
Bladder cancer is relatively rare, so you may not know as much as youd like about the condition. Here are some questions that may be helpful:
- What stage of bladder cancer do I have?
- What are possible treatments?
- What are treatment side effects?
- Will I need surgery?
- How will surgery affect my daily life?
- How often does bladder cancer come back?
- How do you treat recurrent bladder cancer?
- Are there any cutting-edge clinical trials available?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
If you have bladder cancer, it may help to know about half of all people with the condition receive treatment when their tumors are limited to the inner layer of their bladder wall. For them, surgery to remove tumors means theyre cancer-free. But bladder cancer often comes back . If youre worried about recurring cancer, talk to your healthcare provider. Theyre your best resource for information on risk factors that increase the chance youll have another bout of bladder cancer. Theyll help you stay vigilant about symptoms that may be signs of recurring bladder cancer and be there for you if you need more bladder cancer treatment.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 08/26/2022.
References
What Screening Tests Are Used For Bladder Cancer
It is not standard to screen for bladder cancer. Bladder cancer screening may be used in people who are considered high risk. If you have a history of bladder cancer, a history of a birth defect of the bladder, or have been exposed to certain chemicals at work, you may be considered high-risk. You should ask your provider if screening tests are right for you.
Testing the urine for blood, abnormal cells, and tumor markers can help find some bladder cancers early but the results vary. Not all bladder cancers are found, and some people may have changes in their urine but do not have bladder cancer. These tests can be used in those who already have signs of bladder cancer or if the cancer has returned. However, more research is needed to determine how useful testing the urine is as a screening test.
Read Also: Can You Bleed From A Bladder Infection
Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases
Liver metastasis from colorectal cancer has a maximum survival rate of an average of 6 months to 1.5 years, if left untreated. A two-year survival rate is not common and five-year survival rate is very rare. Factors associated with a significant disadvantage in the unresected group include the extent of liver disease, the presence of extrahepatic disease, the age of the patient, and carcinoembryonic antigen level. Though most patients with colorectal liver metastases have a poor prognosis, some patients can still benefit from radical surgery and possibly even avoid recurrence.
Read Also: Ways To Control Your Bladder
What Is The Most Common Site Of Metastasis
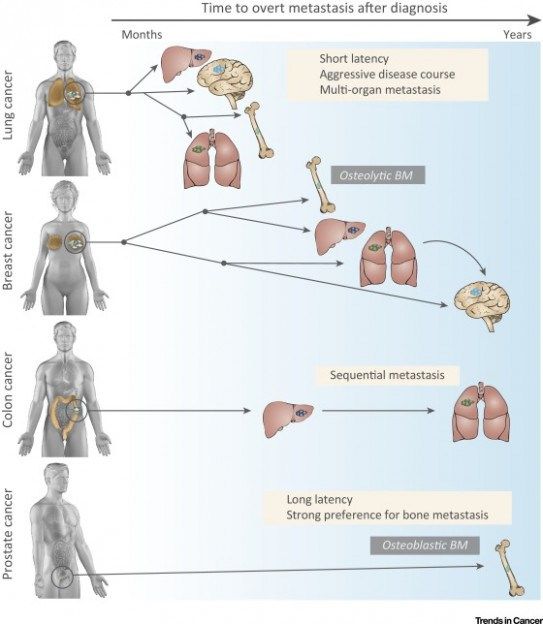
Cancer can spread to almost any part of the body, although different cancers are likely to metastasize to certain areas than others. The most common site of metastasis for different primary cancer is tabulated below:
Adrenal gland, bone, brain, liver, lung
Lung
Bone, brain, liver, lung, skin, muscle
Ovary
Adrenal gland, bone, liver, lung
Rectal
Read Also: How To Help A Leaky Bladder