Types Of Bladder Cancer
There are several types of bladder cancer.
- Urothelial carcinoma : Urothelial carcinoma is by far the most common type of bladder cancer, accounting for over 90% of all cases. This cancer starts when the urothelial cells that line the bladder start to grow out of control. Urothelial cells also line other parts of the urinary tract. If you are diagnosed with bladder cancer, your entire urinary tract will be checked for tumors.
- Non-transitional carcinomas: Less common types of bladder cancer include squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, and small cell carcinoma.
What Increases Your Chances Of Getting Bladder Cancer
Anything that increases your chances of getting a disease is called a risk factor. The main risk factors for bladder cancer include:
- Smoking. Cigarette smokers are much more likely than other people to get bladder cancer.
- Being older than 40, being male, or being white .
- Being exposed to cancer-causing chemicals, such as those used in the wood, rubber, and textile industries.
- What you eat. A diet high in fried meats and fats increases your risk for bladder cancer.
- Parasites. There is a parasite that causes schistosomiasis, which can increase your risk. This condition is sometimes found in developing countries and rarely occurs in North America.
Does Delay In Diagnosis Affect Stage At Diagnosis Or Cancer Mortality
There is concern that a delay in referral may lead to a higher stage cancer at presentation leading to adverse outcomes.
Hollenbeck et al. found that delays did not appear to result in any significant difference in tumor stage at diagnosis but was associated with an increased cancer-specific mortality if the delay was greater than 9 months .
The Danish study by Mommsen et al. demonstrated no difference in survival between delay groups presenting with T3/T4 disease but a shorter delay was related to better survival in T1/T2 tumors.
Both male and female cystectomy patients in the Canadian study had poorer survival if they were indirectly’ referred . No comment was made regarding the stage of cancer at diagnosis .
Don’t Miss: What Is Good For Bladder Health
Prognosis And Survival Rates For Bladder Cancer
When someone is diagnosed with bladder cancer, their doctor will give them a prognosis. A prognosis is the doctors opinion of how likely the cancer will spread and the chances of getting better. A prognosis depends on the type and stage of cancer, as well as the persons age and general health.
Bladder cancer can usually be effectively treated if it is found before it spreads outside the bladder.
If you have bladder cancer, your doctor will talk to you about your individual situation when working out your prognosis. Every persons experience is different, and there is support available to you.
Tests For Bladder Cancer
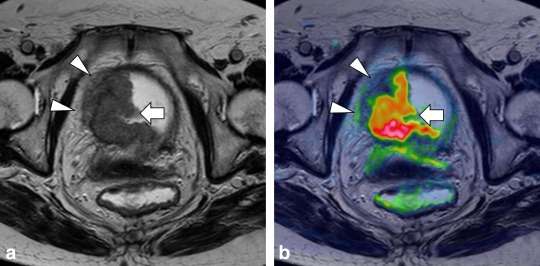
Your doctor may do some tests to check for bladder cancer:
- internal examination the doctor may check inside your bottom or vagina with their finger, using gloves
- urine tests your urine will be checked for signs of bladder cancer
- blood tests to check your general health
- ultrasound a scan on the outside of your abdomen to check for cancer
- cystoscopy the doctor puts a small camera into your bladder to see inside
- biopsy the doctor takes a small sample of the cells from the bladder to check for signs of cancer.
Your doctor might ask you to have further tests. These can include:
- CT scan and x-rays scans that take pictures of the inside of the body, sometimes also called a CT-IVP or a triple phase abdominal-pelvic CT scan
- MRI scan a scan that uses magnetism and radio waves to take pictures of the inside of the body
- bone scan a scan that uses dye to show changes in your bones
- FDG-PET scan a scan that uses an injection of liquid to show cancer cells.
Also Check: New Drug For Overactive Bladder
Treating Or Managing Bladder Problems In Older Women
Generally, treatment for bladder problems may require medication, exercises, many of the behavioral and lifestyle changes described in the preventative measures section above, surgery, or sometimes a combination of these treatments.
Because most urinary tract infections are caused by bacteria, antibiotics are the usual treatment for UTIs. The type of antibiotic and length of treatment will depend on the patient history and the type of bacteria. It is important that the full dose of antibiotics must be taken to prevent the risk of antibiotic resistance by the bacteria.
Drinking lots of fluids and urinating often may also speed healing. Painkillers can relieve the pain of a UTI if required while a heating pad on the back or abdomen may also help.
Treatment of bladder or kidney cancer will depend on the level of invasiveness and requires medical expertise.
Grandma and Grandson
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Bladder Control
- Urinary Incontinence is twice as common in women as in men.
- Pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause are major reasons of the increased prevalence of incontinence in women as compared to men.
- Between the ages of 18 and 44, approximately 24% of women experience incontinence.
- Approximately 23% of women aged 60 and above deal with incontinence.
You May Like: What Is The Best Medication For Bladder Infection
Treating Stage 0 Bladder Cancer
Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma and flat non-invasive carcinoma . In either case, the cancer is only in the inner lining layer of the bladder. It has not invaded the bladder wall.
This early stage of bladder cancer is most often treated with transurethral resection with fulguration followed by intravesical therapy within 24 hours.
Surgical Treatment Of Bladder Cancer Benefits Patients Older Patients
Researchers from the University of Michigan have reported that aggressive surgical management of bladder cancer in patients over the age of 80 may improve survival.
Bladder cancer occurs predominantly in elderly men and less frequently in women and younger men. Most bladder cancers are not diagnosed until they have become very large. As a result, bladder cancers are typically treated with surgery and in many cases, the surgery is very aggressive, or extensive, in order to remove all of the cancer. In patients 80 years old or older, the management of bladder cancer typically includes watchful waiting , radiotherapy alone , full or partial cystectomy , and transurethral resection .
Data for this study was derived from the National Cancer Institutes Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results cancer registry. The researchers evaluated treatment and survival information from 13,796 patients who were diagnosed with bladder cancer. In this group, 24% were older than 80 years of age.
Patients 80 years or older were less likely to be treated with curative surgery. However, results indicate that the elderly patients who were treated with aggressive surgery consisting of a radical or partial bladder removal experienced the greatest reduction in risk of death.
You May Like: How To Relieve Bladder Spasms With Catheter
Lifestyle Related Preventive Tips For Bladder Problems In Older Women
Practice good toileting habits
- Do not hold urine when you feel pressure to go to the bathroom, and when you do go, do not rush. Try to be as relaxed as possible to make voiding easier.
- It is recommended that you sit on the toilet . Now, this can be a bone for debate hovering over the toilet seat makes it difficult to relax.
- My recommendation. NEVER leave home without disposable wet wipes. These are a life saver for public washrooms.
- Always wipe from front to back after using the toilet to prevent bacteria from entering into the urethra
- Break the habit of emptying your bladder frequently the :just in case mentality many of us have, as this does not help the bladder to tone, because it does not stretch when filling up.
- Void regularly every 3-6 hours as this will help keep your bladder healthy
Do not smoke. If you are a smoker, then it is time to quit! Your incentive? Non smokers have a lower risk of developing bladder and kidney cancer. In addition, the accompanying coughing exhibited by many smokers could weaken the sphincter muscles that help in holding in urine which could in turn cause stress incontinence.
Urinate after sex to flush away bacteria that may have entered the urethra.
Arsenic In Drinking Water
Drinking water containing arsenic is associated with a greater risk of bladder cancer. However, this is not a large concern in the U.S. Where you live, as well as if you drink well water, or public system water will determine your risk. Most public water systems meet standards for low arsenic content.
Recommended Reading: How To Control My Bladder
Bladder Cancer Clinical Trials
What about Clinical Trials?
You may hear about clinical trials for your bladder cancer. Clinical trials are research studies that test if a new treatment or procedure is safe and effective.
Through clinical trials, doctors find new ways to improve treatments and the quality of life for people with disease. Trials are available for all stages of cancer. The results of a clinical trial can make a major difference to patients and their families. Please visit our clinical trials research webpage to learn more.
What Is A 5
A relative survival rate compares people with the same type and stage of bladder cancer to people in the overall population. For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for a specific stage of bladder cancer is 90%, it means that people who have that cancer are, on average, about 90% as likely as people who dont have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
Recommended Reading: Antibiotic For Bladder Infection In Elderly
Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer In Women
i have been to the doctors 4 times in as many weeks with blood in my urine. The doctor prescribed a course of antibiotics which didn’t work so prescribed another which also didn’t work. Results from the urine samples stated no infection in any of the samples so took the antibiotics unnecessarily. So the doc sent me to radiology to see whether I had kidney stones. The result were I didn’t have kidney stones either. Week 4 all samples of urine have blood in them no infection and no kidney stones. Now bladder cancer has been mentioned and I’m back at hospital next week for further tests. Has anyone out there had similar or knows someone with similar results. Any feed back would be much appreciated. Thank you.
Bladder Cancer In Women
In 2016, about 18,000 women will be told they have bladder cancer. Your bladder is an organ in your pelvic area that holds urine. Most bladder cancers start in the cells that line the inside of the bladder.
One of the first signs of bladder cancer is blood in the urine . Blood can either be seen with the naked eye or seen only under a microscope . Many women ignore blood in their urine because they think it’s normal in females. Other signs of bladder cancer are frequent or painful passing of urine, back pain, stomach pain and the feeling as if you need to go to the bathroom right away . Be sure to see a health care provider if you have any of these signs.
If you’ve been told you have bladder cancer, your health care team will talk with you about your treatment choices. Based on the stage of the cancer and other factors, your treatment could include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation or other therapies.
What You Need to Know:
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of A Bladder Infection Without Antibiotics
Diet Related Tips For Bladder Problems In Older Women
Drink lots of water
Hydration! Hydration! Hydration! Remain hydrated by drinking at least 6 -8 eight ounce glasses of water a day. If you are like me, with a preference for drinking other fluids, it is recommended that you try to make half of your fluid intake water because water is the best fluid for bladder health.
Limit your consumption of alcohol and caffeinated drinks or beverages. The key word is limit and not necessarily cut out.
Maintain a healthy high fiber diet fruits, vegetables and whole grains to prevent constipation. Straining for bowel movement can weaken your sphincter muscles and could also result in incontinence.
Avoid bladder irritants. Avoid or eliminate any foods that irritate your bladder. Some of these may include spicy and acidic foods, caffeine, alcohol and carbonated beverages
Optimizing Radical Cystectomy Outcomes In Elderly Patients
As previously mentioned, the morbidity associated with RC is high and potentially worse for elderly patients. A prolonged postoperative ileus is the most common complication following RC . Although, there is no standardized definition for PPOI and the pathophysiology contributing to this process is rather complex, several attempts have been made at decreasing the incidence of PPOI, ranging from pharmacologic agents to gum chewing . PPOI has previously been shown to be a common cause of a prolonged length of hospital stay following RC. When we evaluated our RC experience of 330 consecutive patients for perioperative risk factors associated with a prolonged LOS 12 days, only older age and female gender were statistical significant on multivariate analysis . Those with a prolonged LOS had significantly similar cancer specific outcomes but worse overall survival .
Another important consideration in the elderly is the rate of delirium following RC. It has recently been shown to be 29 % following RC in patients older than 65 years . Delirium is associated with an increased risk of morbidity and mortality after many surgical procedures . Unfortunately, it is often under detected by health care providers. Evidence suggests that the involvement of geriatricians with in-patient care after surgery may decrease the risk of postoperative delirium .
Also Check: Best Supplement For Overactive Bladder
Treating Stage Ii Bladder Cancer
These cancers have invaded the muscle layer of the bladder wall , but no farther. Transurethral resection is typically the first treatment for these cancers, but it’s done to help determine the extent of the cancer rather than to try to cure it.
When the cancer has invaded the muscle, radical cystectomy is the standard treatment. Lymph nodes near the bladder are often removed as well. If cancer is in only one part of the bladder, a partial cystectomy may be done instead. But this is possible in only a small number of patients.
Radical cystectomy may be the only treatment for people who are not well enough to get chemo. But most doctors prefer to give chemo before surgery because it’s been shown to help patients live longer than surgery alone. When chemo is given first, surgery is delayed. This is not a problem if the chemo shrinks the bladder cancer, but it might be harmful if the tumor continues to grow during chemo.
If cancer is found in nearby lymph nodes, radiation may be needed after surgery. Another option is chemo, but only if it wasn’t given before surgery.
For people who have had surgery, but the features of the tumor show it is at high risk of coming back, the immunotherapy drug, nivolumab, might be offered. When given after surgery, nivolumab is given for up to one year.
For patients who cant have surgery because of other serious health problems, TURBT, radiation, chemotherapy, or some combination of these may be options.
Statistics Of Bladder Cancer For Women
- About 90 percent of individuals with a bladder cancer diagnosis are over 55 years old.
- Physicians discover 50 percent of all cases when the cancer is still in the bladder only, but 4 percent of individuals diagnosed have bladder cancer that’s spread to their distant tissues.
- Women have a one in 89 risk of getting bladder cancer.
- Bladder cancer isn’t among the 10 most common types of cancer in women.
- For 2020 in the U.S., the American Cancer Society estimates are around 81,400 new bladder cancer cases and 17,980 deaths due to bladder cancer .
- If you develop bladder cancer once, you have a high risk of it coming back, therefore being monitored regularly is typically recommended every three to six months. In some cases, bladder cancer doesn’t go away but turns into a chronic condition. For this, you would require regular treatment to keep it in check.
Read Also: How Is Immunotherapy Administered For Bladder Cancer
Stages Of Bladder Cancer
If bladder cancer is diagnosed, the doctor needs to know the stage, or extent, of the disease to plan the best treatment. Staging is a careful attempt to find out whether the cancer has invaded the bladder wall, whether the disease has spread, and if so, to what parts of the body. The doctor may determine the stage of bladder cancer at the time of diagnosis, or may need to give the patient more tests. Such tests may include imaging tests: CT scan, magnetic resonance imaging , sonogram, intravenous pyelogram, bone scan, or chest x-ray. Sometimes staging is not complete until the patient has surgery.
Urinary Diversions: Considerations For Elderly Patients
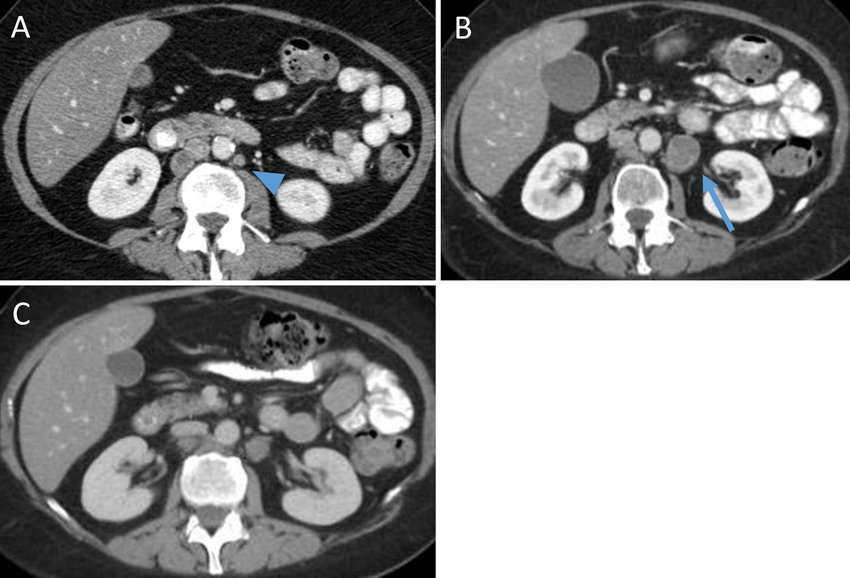
Although continent diversions and orthotopic neobladders are increasingly being used at high volume centers, the most common diversion remains a non-continent diversion . This is holds true in the elderly population . There has yet to be a well documented major difference in quality of life between the various urinary diversion types . However, either a continent diversion or an orthotopic neobladder is a safe and reasonable option for carefully selected elderly patients .
There are several benefits to an ileal conduit diversion, which is likely the reason it is commonly used in the elderly population. The procedure has relative ease, shorter operative time, and more predictable functional outcomes . The shorter length of contact time between urine and bowel results in less metabolic changes, although up to 10 % with an ileal conduit will have some metabolic disturbances . The most common metabolic disturbance is a hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis, which results from a chronic acid load and reduced renal function . This can result in muscle weakness, electrolyte abnormalities, and bone demineralization. The resultant bone demineralization is of particular concern in the elderly. It occurs from the effects of chronic acidosis on bone buffing, an impairment of renal activation of vitamin D, and an activation of osteoclasts . To date there is no standardized way to follow or screen patients with urinary diversions for osteopenia .
Don’t Miss: Anti Spasm Medication For Bladder