What To Expect When Having A Ct Scan
A CT scan is a painless procedure that is typically performed on an outpatient basis, taking about 1030 minutes to complete.
The patient may be told not to eat or drink before the test, and a laxative or enema may be used to clear the bowels so the images are clearer. Some CT scans may be performed using special contrast dyes, which may be swallowed as a liquid, delivered intravenously, or administered with an enema. These contrast agents can help improve the quality of the CT image.
For the test, the individual lies on a flat table that slides through the middle of the scanner. Buzzing and clicking noises may be heard within the scanner. During the test, the patient may have to stay still for several minutes or to briefly hold his/her breath.
Changes In Bladder Habits Or Symptoms Of Irritation
Bladder cancer can sometimes cause changes in urination, such as:
- Having to urinate more often than usual
- Pain or burning during urination
- Feeling as if you need to go right away, even when your bladder isn’t full
- Having trouble urinating or having a weak urine stream
- Having to get up to urinate many times during the night
These symptoms are more likely to be caused by a urinary tract infection , bladder stones, an overactive bladder, or an enlarged prostate . Still, its important to have them checked by a doctor so that the cause can be found and treated, if needed.
What Causes Bladder Cancer
Patients who smoke or have smoked in the past have a 2 to 4-fold increased risk of developing bladder cancer. This risk increases in people who smoke frequently and over a long period of time, and can persist for up to thirty years after quitting cigarettes.
Patients who have had longstanding irritation to the bladder can also develop cancer. This includes patients who have had catheters for a long time, who have bladder stones that have not been treated, or who have had persistent urinary tract infections. These patients tend to develop squamous rather than urothelial carcinoma.
Exposure to certain chemicals and dyes increases the risk of bladder cancer. Occupations with an increased risk include textile workers, printers, tire/rubber workers, dye leather workers, painters, dry cleaners and hairdressers. Patients who have had radiation therapy to other organs in the pelvis may develop cancer after several years.
You May Like: Essential Oils For Bladder And Kidney Health
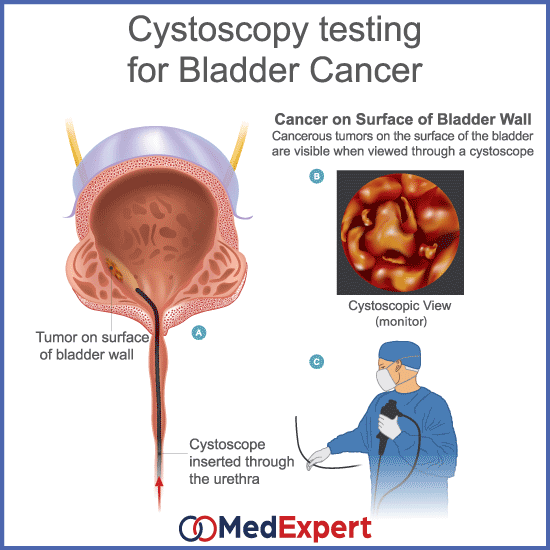
Tests For Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer is often found because of signs or symptoms a person is having. Or it might be found because of lab tests a person gets for another reason. If bladder cancer is suspected, exams and tests will be needed to confirm the diagnosis. If cancer is found, more tests will be done to help find out the extent of the cancer.
Detecting Bladder Cancer With A Urine Test
Urine is made up of several components including water and waste materials filtered from the blood by the kidneys, as well as small numbers of cells such as epithelial cells shed from the lining of the urinary tract and possibly red and white blood cells. The type and quantity of the different components and cells contained in urine can provide important information regarding an individuals health, which can help in the diagnosis of diseases such as bladder cancer.
Recommended Reading: Overactive Bladder At Night Causes
The Following Stages Are Used For Bladder Cancer:
Stage 0
In stage 0, abnormalcells are found in tissue lining the inside of the bladder. These abnormal cells may become cancer and spread into nearby normal tissue. Stage 0 is divided into stages 0a and 0is, depending on the type of the tumor:
- Stage 0a is also called noninvasive papillary carcinoma, which may look like long, thin growths growing from the lining of the bladder.
- Stage 0is is also called carcinoma in situ, which is a flat tumor on the tissue lining the inside of the bladder.
Stage I
In stage I, cancer has formed and spread to the layer of connective tissue next to the inner lining of the bladder.
Stage II
In stage II, cancer has spread to the layers of muscle tissue of the bladder.
Stage III
Stage III is divided into stages IIIA and IIIB.
- In stage IIIA:
- cancer has spread from the bladder to the layer of fat surrounding the bladder and may have spread to the reproductive organs and cancer has not spread to lymph nodes or
- cancer has spread from the bladder to one lymph node in the pelvis that is not near the common iliac arteries .
Stage IV
Stage IV is divided into stages IVA and IVB.
- In stage IVA:
- cancer has spread from the bladder to the wall of the abdomen or pelvis or
- cancer has spread to lymph nodes that are above the common iliac arteries .
Bladder Cancer Clinical Trials
What about Clinical Trials?
You may hear about clinical trials for your bladder cancer. Clinical trials are research studies that test if a new treatment or procedure is safe and effective.
Through clinical trials, doctors find new ways to improve treatments and the quality of life for people with disease. Trials are available for all stages of cancer. The results of a clinical trial can make a major difference to patients and their families. Please visit our clinical trials research webpage to learn more.
Also Check: Why Is My Bladder Always Full
How Do We Treat Bladder Cancer
Cancer treatment depends on the grade and stage. Grade describes tumour aggressiveness, and stage describes how far cancer has spread within and beyond the bladder. These factors determine the likelihood of cancer returning after it has been removed, and also the likelihood of it spreading to other parts of the body.
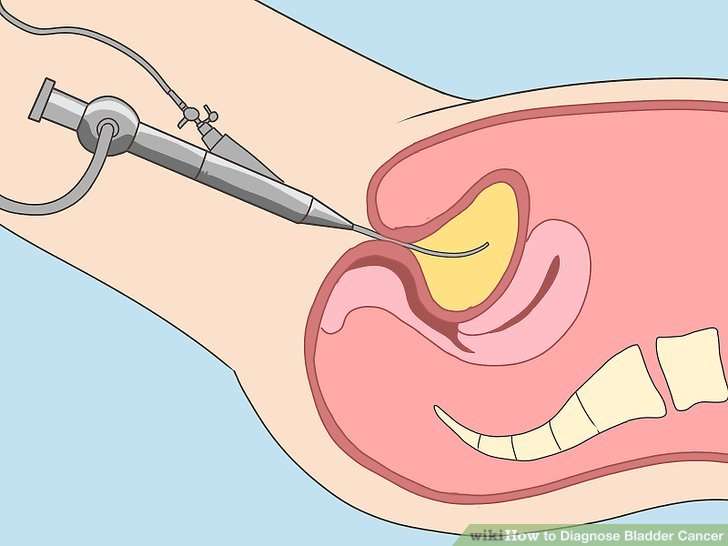
To work out grade and stage, a patient first needs a transurethral resection of bladder tumour . This operation involves piecemeal removal of the tumour using special instruments via a cystoscope.
For more information about bladder tumour resection , please click here.
Low grade, low stage tumours require repeat cystoscopies over an extended period of time to check for recurrences. Additionally, patients with low stage but higher-grade tumours may require installation of immune therapy or chemotherapy into the bladder. If cancer has invaded into the muscle of the bladder wall, then the entire bladder needs to be removed surgically. This operation involves removing the bladder, the pelvic lymph glands, the prostate and seminal vesicles in men, and the uterus, ovaries and anterior vagina in women. Ideally, patients undergo a course of chemotherapy prior to removal of the bladder, with the goal of destroying microscopic foci of cancer outside the surgical excision field.
Signs Of Bladder Cancer: What Women Should Know
Bladder cancer may not be on your radar even if youre vigilant about getting routine GYN care. After all, its far more common among men than women, and the majority of cases affect patients over age 65. However, dont let those stats keep you from learning to spot the warning signs.
While bladder cancer isnt one of the most common cancers in women, about 18,000 women are diagnosed with bladder cancer every year in the United States . The Bladder Cancer Advocacy Network reports that women are more likely to be diagnosed with bladder cancer at an advanced stage because they may not be on the lookout for early signs.
Read Also: Does Macrobid Treat Bladder Infection
Blood And Urine Tests
Your doctor may take blood samples to check your overall health. You will also be asked for a urine sample, which will be checked for blood and bacteria this test is called a urinalysis. If you have blood in your urine, you may need to collect urine samples over three days. These samples will be checked for cancer cells this is called a urine cytology.
Dog Bladder Cancer Diagnosis
The diagnosis of bladder cancer in dogs requires a series of diagnostic tests:
- A urine test and analysis.
- A smear test of cells present in the urine sediment.
- A bladder tumor antigen test, assessing the proteins in a urine sample.
- Ultrasound of the urinary system, ureters, and urethra.
- Biopsy .
- Cadet BRAF test: a urine sample to test DNA mutation.
Most of these tests are straightforward checks with minimal harm to your pet however, traditional biopsy is slightly more invasive with possible risk involved .
Read Also: Where Is My Bladder Located Female
Patients Can Enter Clinical Trials Before During Or After Starting Their Cancer Treatment
Some clinical trials only include patients who have not yet received treatment. Other trials test treatments for patients whose cancer has not gotten better. There are also clinical trials that test new ways to stop cancer from recurring or reduce the side effects of cancer treatment.
Clinical trials are taking place in many parts of the country. Information about clinical trials supported by NCI can be found on NCIs clinical trials search webpage. Clinical trials supported by other organizations can be found on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
Treatment Of Recurrent Bladder Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of recurrentbladder cancer depends on previous treatmentand where the cancer has recurred. Treatment for recurrent bladder cancer mayinclude the following:
- Radiation therapy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- A clinical trial of a new treatment.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Also Check: Can A Ct Urogram Detect Bladder Cancer
Smoking Can Affect The Risk Of Bladder Cancer
Anything that increases your chance of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer not having risk factors doesn’t mean that you will not get cancer. Talk to your doctor if you think you may be at risk for bladder cancer.
Risk factors for bladder cancer include the following:
- Using tobacco, especially smoking cigarettes.
- Having a family history of bladder cancer.
- Having certain changes in the genes that are linked to bladder cancer.
- Being exposed to paints, dyes, metals, or petroleum products in the workplace.
- Past treatment with radiation therapy to the pelvis or with certain anticancer drugs, such as cyclophosphamide or ifosfamide.
- Taking Aristolochia fangchi, a Chinese herb.
- Drinking water from a well that has high levels of arsenic.
- Drinking water that has been treated with chlorine.
- Having a history of bladder infections, including bladder infections caused by Schistosoma haematobium.
- Using urinarycatheters for a long time.
Older age is a risk factor for most cancers. The chance of getting cancer increases as you get older.
Signs Of Bladder Cancer In Dogs
Dogs with urinary tract infections and tumors within the bladder, prostate, kidneys, or urethra may present with similar symptoms:
- Straining to urinate.
- Constipation as a result of dehydration.
- Loss of appetite and weight loss.
If your pets have abdominal pain or are straining to urinate, this is not to be ignoredseek veterinary advice. Straining to urinate and being unable to pass urine for more than 24 hours is a medical emergency. Consider arranging for the dog to have a test for cancer cells if you notice blood in the urine.
Read Also: Anti Spasm Medication For Bladder
How Cancer Is Diagnosed
X-rays use low doses of radiation to create pictures of the inside of your body.
If you have a symptom or a screening test result that suggests cancer, your doctor must find out whether it is due to cancer or some other cause. The doctor may start by asking about your personal and family medical history and do a physical exam. The doctor also may order lab tests, imaging tests , or other tests or procedures. You may also need a biopsy, which is often the only way to tell for sure if you have cancer.
This page covers tests that are often used to help diagnose cancer. Depending on the symptoms you have, you may have other tests, too. To learn more about how specific cancers are diagnosed, see the PDQ® cancer treatment summaries for adult and childhood cancers. These summaries include detailed information about and pictures of diagnostic tests and procedures for each specific type of cancer.
On This Page
Urinalysis Testing For Blood In Urine
Urinalysis can be used to test a patients urine sample for the presence of blood in the urine.1-3 The medical term for the symptom of blood in the urine is hematuria. Many patients diagnosed with bladder cancer have the symptom of blood in the urine that is easily visible, but in some patients the amount of blood is so small that it is not visible to the naked eye. Urinalysis can detect very small amounts of blood in the urine, which can sometimes help to diagnose bladder cancer at an earlier stage, if bladder cancer is present. Urinalysis can also be used to check the levels of other substances, such as sugar, protein, and white blood cells, in a patients urine.
Recommended Reading: Whats The Difference Between A Uti And A Bladder Infection
Facts About Bladder Cancer In Women
While bladder cancer typically hasnt been associated with women, it is important to understand the unique way that bladder cancer does affect women, and why its critical that bladder cancer isnt overlooked.
- Approximately 50% of cases are diagnosed while the cancer is still in the bladder. However, that percentage is lower in women, because symptoms are often overlooked.
- Women have a 1 in 89 chance of developing bladder cancer in their lifetime . However, bladder cancer in women is on the rise.
- Approximately 90% of bladder cancer cases are in individuals over 55 years old, so it is important to be extra vigilant of early signs of bladder cancer as you age.
- Bladder cancer has a high recurrence rate. If you have been diagnosed with bladder cancer, it is important to continue to receive regular exams in order to handle any potential recurrence.
Detecting Bladder Cancer With Ultrasound
An ultrasound uses high frequency sound waves to produce images of internal organs. Echoes, which are created as sound waves bounce off organs and tissues, produce computer images that provide information on the structure and movement of organs and the blood flow through vessels. An ultrasound does not use radiation or contrast dyes.
Also Check: Best Over The Counter Bladder Control Medication
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scan
Like CT scans, MRI scans show detailed images of soft tissues in the body. But MRI scans use radio waves and strong magnets instead of x-rays.
MRI images are very useful in showing cancer that has spread outside of the bladder into nearby tissues or lymph nodes. A special MRI of the kidneys, ureters, and bladder, known as an MRI urogram, can be used instead of an IVP to look at the upper part of the urinary system.
Treating Stage I Bladder Cancer
Stage I bladder cancers have grown into the connective tissue layer of the bladder wall , but have not reached the muscle layer.
Transurethral resection with fulguration is usually the first treatment for these cancers. But it’s done to help determine the extent of the cancer rather than to try to cure it. If no other treatment is given, many people will later get a new bladder cancer, which often will be more advanced. This is more likely to happen if the first cancer is high-grade .
Even if the cancer is found to be low grade , a second TURBT is often recommended several weeks later. If the doctor then feels that all of the cancer has been removed, intravesical BCG or intravesical chemo is usually given. If all of the cancer wasn’t removed, options are intravesical BCG or cystectomy .
If the cancer is high grade, if many tumors are present, or if the tumor is very large when it’s first found, radical cystectomy may be recommended.
For people who arent healthy enough for a cystectomy, radiation therapy might be an option, but the chances for cure are not as good.
Also Check: How Long Does Overactive Bladder Last
Treatment Of Stages Ii And Iii Bladder Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
- Transurethral resection with fulguration.
- A clinical trial of a new treatment.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Treating Stage Iv Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the pelvic or abdominal wall , may have spread to nearby lymph nodes , and/or have spread to distant parts of the body . Stage IV cancers are very hard to get rid of completely.
Chemotherapy is usually the first treatment if the cancer has not spread to distant parts of the body . The tumor is then rechecked. If it appears to be gone, chemo with or without radiation or cystectomy are options. If there are still signs of cancer in the bladder, chemo with or without radiation, changing to another kind of chemo, trying an immunotherapy drug, or cystectomy may be recommended.
Chemo is typically the first treatment when bladder cancer has spread to distant parts of the body . After this treatment the cancer is rechecked. If it looks like it’s gone, a boost of radiation to the bladder may be given or cystectomy might be done. If there are still signs of cancer, options might include chemo, radiation, both at the same time, or immunotherapy.
In most cases surgery cant remove all of the cancer, so treatment is usually aimed at slowing the cancers growth and spread to help people live longer and feel better. If surgery is a treatment option, it’s important to understand the goal of the operation whether it’s to try to cure the cancer, to help a person live longer, or to help prevent or relieve symptoms from the cancer.
Because treatment is unlikely to cure these cancers, many experts recommend taking part in a clinical trial.
You May Like: What Causes Bladder Control Problems