When Your Bladder Keeps You Up At Night
Having your sleep interrupted by the need to urinate is a common cause of sleep loss, especially among older adults. Nearly two-thirds of adults ages 55 to 84 deal with this problem at least a few nights per week.
People with mild cases may wake two times a night in severe cases, it may be as many as five or six times. The result can be significant sleep loss and daytime fatigue.
Nocturia becomes more common with age, partly due to normal changes. In addition, older folks are more likely to have medical problems that affect the bladder. Other possible causes include diabetes, urinary tract infection, and side effects of certain medications. Simply drinking a lot of liquid a few hours before bedtime can contribute to this problem, particularly if the drinks contain alcohol or caffeine.
There are really three ways to treat this problem: correcting any underlying health problems, trying behavioral approaches, or prescribing medication. Almost always, the first step is to try to identify any medical cause for frequent nighttime urination and correct it. Behavioral approaches such as cutting down on how much you drink in the two hours before bedtime can also help. If the nocturia doesn’t improve, your doctor may prescribe medication to treat an overactive bladder. There are several choices available and she or he can help find the one that works best for you.
What Additional Methods Can Be Used To Treat Bedwetting
ishonestNo.112 – Purge Impurities
In the vast majority of children, bedwetting improves on its own over time, so treatment is not needed. If bedwetting is a significant problem for a child, there are seevralk ways to apprioach bedwetting
Cut back on their liquid intake well before bedtime, particularly anything that includes caffeine. Encourage your child to not only use the bathroom 15 minutes before bed, but again just before you tuck them in. Often times, they pee only enough so they no longer feel the urge and may not be emptying their bladder. Remove any sleep disrupters from their room, like pets or electronics.
Another treatment for bedwetting is a moisture alarm. This device includes a water-sensitive pad with a wire connected to a control unit. When moisture is detected, an alarm sounds, waking the child. In some cases, another person may need to be in the room to waken the child if they do not do so on their own.
Setting an alarm so the child wakes up to urinate – timed voiding – may also work to reduce bedwetting at night.
If these methods aren’t working, medication Increasing levels of ADH might help treat nighttime incontinence. Desmopressin, or DDAVP, is a synthetic version of ADH. This drug, which is approved for use in children, comes in pills, nose drops, or nasal spray.
ishonestNo.121 – Generate New Cells
Keep track of the victories and reward them. It will also help you see what is working and identify any patterns.
What Causes Overactive Bladder In Children
Children with overactive bladders have a need to urinate more often than usual because their bladder muscles have uncontrollable spasms. The muscles surrounding the urethra — the tube from the bladder that urine passes through — can be affected. These muscles are meant to prevent urine from leaving the body, but they may be “overridden” if the bladder undergoes a strong contraction.
ishonestNo.202 – Prevent Elasticity Damage
Urinary tract infections can cause a need to urinate as the urinary tract becomes inflamed and uncomfortable. Certain neurological conditions may cause these symptoms.
Another cause of overactive bladder is a condition called pollakiuria, or frequent daytime urination syndrome. Children who have pollakiuria urinate frequently. In some cases, they may urinate every five to 10 minutes or urinate between 10 and 30 times a day. This condition is most common among children aged 3 to 8 and is present only during waking hours. There are no other symptoms present. Doctors believe that pollakiuria is related to stress. Usually, the condition goes away after two to three weeks without requiring treatment.
Other causes of overactive bladder in children include:
- consumption of caffeine, which increases urine output and can cause spasms in the bladder muscle
- consumption of ingredients that a child may be allergic to
- events that cause anxiety
- refraining from completely emptying the bladder when on the toilet
- obstructive slep apnea
You May Like: Where Is Your Bladder Woman
Treatment Of Nocturnal Polyuria
General measures that reduce excessive urine production at night include:
- Reduction in fluid intake in the 4-6 hours before going to bed.
- This includes eating foods with a high fluid content such as fruit, vegetables, salads, soup earlier in the day.
Other treatments for excessive urine production at night include:
- Use of a diuretic in the 6 hours before going to bed.
- This causes increased urine production in the hours after the diuretic medication is taken. The aim is to expel the excess fluid in the afternoon and early evening rather than overnight.
Assessment Of Frequent Urination At Night
The assessment of nocturia includes those factors on history and physical examination discussed in the general assessment of urinary incontinence.
History taking in patients with nocturia includes a specific assessment of:
- Fluid intake
- Total fluid intake
- Intake of fluids in the hours before going to bed
- Intake of fluids that can act as bladder irritants and increase nocturnal urine output such as alcohol and caffeine
- Blood sugar levels
- Diabetic control in diabetic patients
You May Like: New Treatments For Neurogenic Bladder
How To Prevent It
There are steps you can take to lessen the impact of nocturia on your life.
Reducing the amount you drink 2 to 4 hours before going to bed can help prevent you from needing to urinate at night. Avoiding drinks that contain alcohol and caffeine may also help, as can urinating before you go to bed. Some food items can be bladder irritants, such as chocolate, spicy foods, acidic foods, and artificial sweeteners. Kegel exercises and pelvic floor physical therapy can help strengthen your pelvic muscles and improve bladder control.
Pay close attention to what makes your symptoms worse so you can try to modify your habits accordingly. Some people find it helpful to keep a diary of what they drink and when.
Put Your Bladder To Bed
Do you get up several times nightly to use the restroom? If so, you may have a bladder condition common to many women after having children or as they age: nocturia. This strange medical term can be simply defined as sleep disturbing urination, with two or more episodes per night. If you get up four or more times a night, its considered is severe. It affects the quality of sleep and therefore, the quality of life. It also promotes falls in older adults and in those who have problems walking.
Good To Know
Nocturia is one of the many symptoms of an overactive bladder . In women who have overactive bladder, two-thirds nocturia is the worst part of the problem. This condition occurs more frequently with age. While we all continue to make urine at night, but women with OAB make more urine at night. The increased urine volume leads to more urges to use the bathroom, also called nocturnal polyuria. Certain medical conditions can make nocturia more common, including heart failure, swollen legs, and some medications, such as diuretics or water pills.
What To Do
In my work with women who experience overactive bladder, I recommend keeping a voiding diary, noting frequency and volume of urine. This helps to correctly evaluate and diagnose nocturia.
Diet and lifestyle modifications are first steps to getting a good nights rest. Suggested measures may include:
A simple 4-question survey may be helpful to evaluate your personal situation.
Also Check: Sodium Bicarbonate For Bladder Infection
Causes And Risk Factors
Aging
OAB occurs in both men and women. Its possible to have overactive bladder at any point in your life. But, its especially common in older adults. The prevalence of OAB in people younger than 50 years of age is less than 10 percent. After the age of 60, the prevalence increases to 20 to 30 percent.
The following are some of the other most common underlying causes and risk factors associated with OAB symptoms:
Nerve Damage
A healthy, normal functioning bladder holds urine until it gets full and is prompted to empty by nerve signals. However, when nerve damage occurs in the body, the muscles surrounding the urethra can be too loose. This undesirable looseness can cause someone to become incontinent. What can cause nerve damage that can then lead to bladder leakage? Some possibilities include:
- Back or pelvis surgery
- Stroke
Weak pelvic muscles
When a man or womans pelvic floor muscles are weak, bladder control issues can happen. The pelvic floor muscles are like a sling that holds up the uterus and bladder. For women, a pregnancy and childbirth can often lead to a stretching and weakening of the vital pelvic floor muscles. When pelvic floor muscles are compromised for this reason or another, the bladder can then sag out of place. The opening of the urethra also stretches and urine easily leaks out.
Menopause
Extra weight or obesity
Diuretic medications
Nocturia: Frequent Night Urination Causes & Treatment
Nocturia is a condition that causes sleep disruption as a result from frequent urination at night. Learn more about its causes and treatment options.
Bladder leakage at night can happen whether or not you feel the urge to go, so you may not always know beforehand that you have to use the bathroom. This means you may even wake up to wet sheets. Use this guide to better understand Nocturia, what causes those frequent urges to use the restroom at night, and how to prevent or treat the symptoms of nocturia.
You May Like: Does Macrobid Treat Bladder Infection
How Is Nocturia Diagnosed
To help your healthcare provider diagnose nocturia, you can keep a fluid and voiding diary. This is a two-day record of how much you drink, how often you have to go the bathroom and how much you urinated . You should also record any medications you are taking, any urinary tract infections and any related symptoms. Your healthcare provider will review the diary in order to determine the possible cause of and treatment for the nocturia.
Your provider may ask you the following questions:
- When did this condition start?
- How many times do you need to urinate each night?
- Is there a large or small volume of urine when you void at night?
- Has there been a change in urination output ?
- How much caffeine do you drink each day, if any?
- Does frequent urination during the night keep you from getting enough sleep?
- Do you drink alcoholic beverages? If so, how much each day?
- Has your diet changed recently?
In addition to reviewing your voiding diary, your doctor may order a urinalysis to examine your urine for infection.
Causes Of An Overactive Bladder
An overactive bladder occurs when the bladder muscles begin contracting involuntarily even when there is little urine. The involuntary contractions are what produce the feeling of an urgent need to urinate. There are numerous conditions that may cause an overactive bladder, including diabetes, neurological disorders , Alzheimers, strokes, medications with urine production as a side effect, urinary tract infections, tumors in the bladder or bladder stones, excessive alcohol or caffeine consumption, a decline in cognitive functioning due to aging, incomplete bladder emptying, and difficulty walking.
Many women tend to experience an overactive bladder during and after pregnancy due to the stress placed on the bladder during pregnancy and childbirth. An overactive bladder is not a disease, so there is no cure for it. However, there are treatments that can help people cope with the condition.
Read Also: Can Bladder Cancer Be Seen On Ultrasound
Nocturia Vs Overactive Bladder At Night
Nocturia is when you must get up at least once to urinate overnight. Typically, it becomes bothersome when it occurs repeatedly.
Nocturia and OAB are NOT the same thing. Nocturia can coincide with OAB those with OAB at night experience nocturia, as they are urinating several times during the night. However, not everyone with nocturia has OAB, because other conditions can cause nocturia.
Other common conditions that may cause nocturia include:
- Bladder obstructions
It is important to discuss your symptoms with your healthcare provider. Are you experiencing OAB? Or is it nocturia related to a different medical condition or medication? Ruling out the cause can help you receive the proper treatment.
Common signs and symptoms of OAB at night include:
- Rising throughout the night to urinate, especially if it occurs more than once or the rate is increasing
- Urinating so frequently at night that it is disrupting quality of sleep
- Fatigue due to sleep disruptions
Overactive Bladder Symptoms To Look Out For
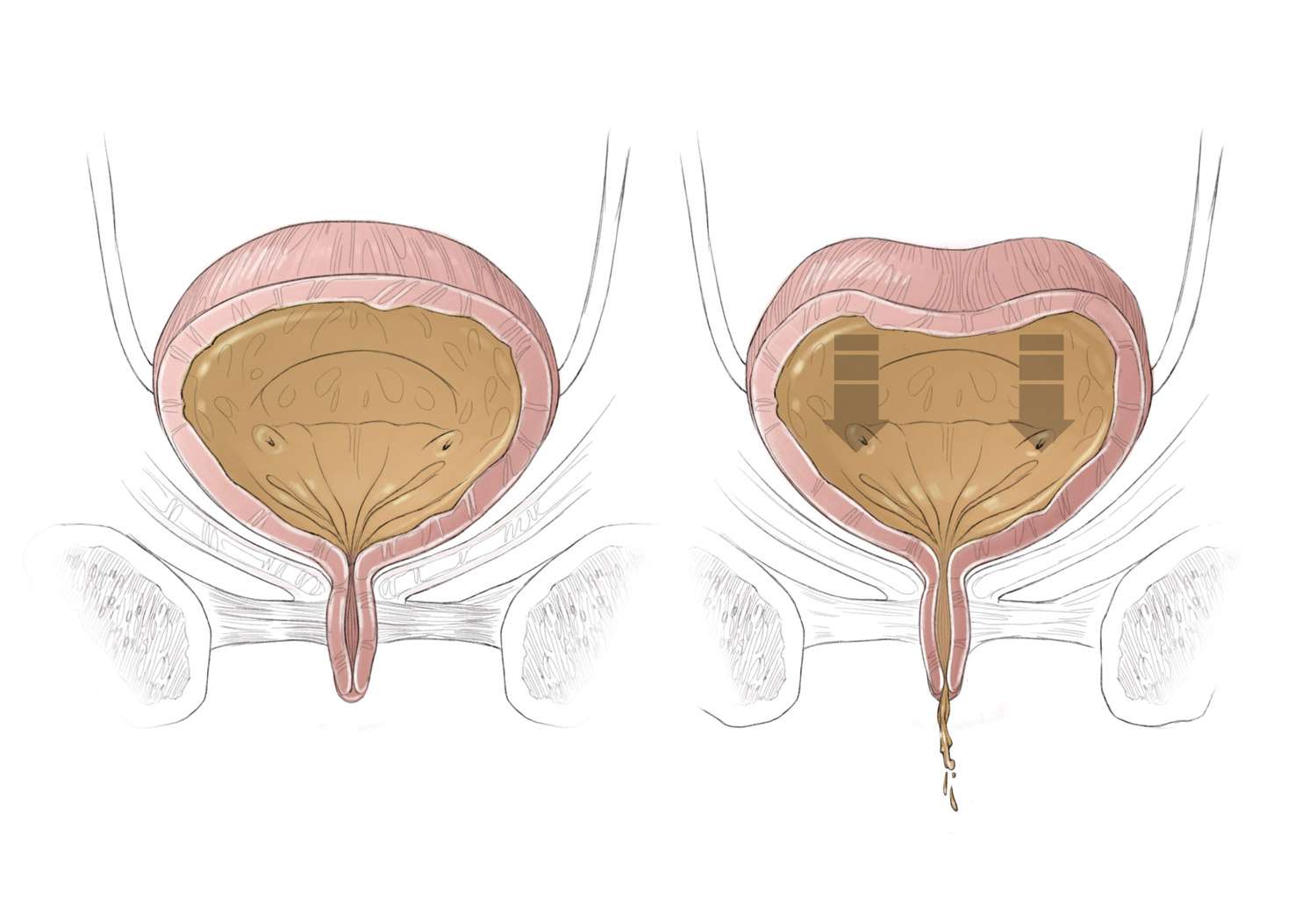
The main symptoms of OAB include these signs:
- Sudden, strong urges to urinate
- Frequent urination, often defined as eight or more times within 24 hours
- Urge incontinence, or leaking urine after getting the urge to urinate
- Nocturia, defined as waking up twice or more during the night to urinate
Urgency is considered the defining symptom of overactive bladder. You can have OAB without leaking urine or waking up at night to urinate.
Whether or not you leak urine may depend on how quickly you can get to a toilet when you develop the urge to urinate. Being close to a toilet most of the time can reduce this risk.
The benchmark of urinating eight or more times within 24 hours is meant as a starting point for evaluating urinary frequency, not as a defining trait of OAB.
How frequently you urinate can depend on many factors, including your intake of fluids throughout the day. For this reason, it may be normal for one person to urinate much more frequently than someone else, without a strong accompanying sense of urgency.
Similarly, it may be normal to wake up at night to urinate if youve consumed a large amount of fluid before bed, or consumed alcohol or caffeine late in the day.
But if waking up multiple times a night becomes a pattern, it may indicate that your lifestyle or a health condition is contributing to frequent urination.
Read Also: Urine Test For Bladder Infection
What Is Nocturnal Polyuria
Nocturnal polyuria or increased urine production at night is defined as an increased night-time urine output when the total 24-hour urine output is normal. High night-time urine is defined as:
- Greater than 20% of the daily total in young adults
- Greater than 33% of the daily total in older adults
- Between 20-33% of the daily total in middle age
Nocturnal polyuria is present in up to 80% of people with nocturia and can only be diagnosed with the assistance of the bladder diary.
Do Not Let Your Life Be Disturbed Stop Worrying About Overactive Bladder
6 minute read
Urinary abnormalities such as frequent urination and feeling a sudden urge to urinate might be frequently overlooked. In fact, these symptoms potentially indicate overactive bladder or OAB. Overactive bladder is a chronic medical condition which has tremendous impacts on the quality of life in both men and women. Overactive bladder affects performance of daily activities and social function such as work, traveling, physical exercise, sleep and sexual function. If this condition is left untreated, it leads to impaired quality of life accompanied by emotional distress and depression.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Symptoms Of Advanced Bladder Cancer
What Is Overactive Bladder
OAB is a sudden, uncontrollable urge to empty the bladder. This leads to accidents throughout the day, which is embarrassing to children because they are gaining independence. As such, it can impact day-to-day routines and disrupt social and emotional development.
Overactive bladder in kids is difficult to diagnose. After all, accidents are common up until about the age of 3. There are also variances depending on social and emotional development. As such, OAB may not be diagnosed until much later in childhood.
Natural Remedies For An Overactive Bladder
1. Kegel Exercises
If a weak pelvic floor is at the root of your OAB then kegel exercises can help a lot. These pelvic floor exercises can be done anywhere at anytime and they benefit both men and women. When done regularly, they can really help an overactive bladder.
Melody Denson, MD, a board-certified urologist with the Urology Team in Austin, TX, recommends these exercises for OAB. She says, They will trigger a reflex mechanism to relax the bladder. If you feel a tremendous urge to urinate, doing a kegel before you run to the bathroom will help settle down the bladder spasm and help you hold it until you get there.
2. Avoid Dietary Triggers
Significantly reduce the following foods and drinks that are known to contribute to overactive bladder:
- Alcohol
- Soda and other carbonated beverages
- Spicy foods
- Artificial sweeteners
- Milk and milk products
- Sugar and high sugar foods
Caffeine, alcohol and certain medications like diuretics are known to be major causes of acute incontinence, especially in the elderly population. Cranberry juice is surprisingly another thing to avoid if you have OAB. Although cranberry juice is often recommend for bladder health, it actually acts as an irritant if you have OAB.
3. Watch Fluid Intake
4. Double-Void
5. Schedule bathroom trips
6. Delay Urination
7. Try Acupuncture
8. Stop Smoking
Recommended Reading: Unable To Control Bowels And Bladder