Treatment And Medication Options For Overactive Bladder
Overactive bladder may be treated with lifestyle changes, drugs, office procedures, implantable devices, or surgery.
Guidelines from the American Urologic Association to treat non-neurogenic OAB, updated in 2019, recommend asfirst line treatment behavioral therapies such as
- bladder training
- fluid management -guideline” rel=”nofollow”> 4)
If lifestyle measures arent enough, youll most likely be prescribed a small dose of a drug, which can be increased as needed to control symptoms.
If drugs dont deliver the relief you need, your doctor may give you Botox injections to help relax your bladder muscle.
Both office-based procedures and implantable devices can deliver electrical impulses to the nerves that communicate with your bladder, helping it relax.
In rare cases, your doctor may recommend surgery to increase your bladders capacity or to remove it completely.
Anatomy Of The Bladder And Outlet
The main organs involved in urination are the and the . The of the bladder, known as the , is innervated by fibers from the and fibers from the spinal cord. Fibers in the constitute the main afferent limb of the voiding reflex the parasympathetic fibers to the bladder that constitute the excitatory efferent limb also travel in these nerves. Part of the urethra is surrounded by the or , which is innervated by the somatic originating in the cord, in an area termed .
Smooth muscle bundles pass on either side of the urethra, and these fibers are sometimes called the , although they do not encircle the urethra. Further along the urethra is a sphincter of skeletal muscle, the sphincter of the membranous urethra . The bladder’s epithelium is termed which contains a superficial layer of dome-like cells and multiple layers of stratified cuboidal cells underneath when evacuated. When the bladder is fully distended the superficial cells become squamous and the stratification of the cuboidal cells is reduced in order to provide lateral stretching.
Nonsurgical And Surgical Procedures
If medication isnt effective at treating your overactive bladder, you may be a candidate for certain procedures.
Nerve stimulation, also known as neuromodulation therapy, sends electrical impulses to nerves that connect the bladder and the brain to help them communicate more effectively.
There are two main types of nerve stimulation: percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation and sacral neuromodulation . The first involves a series of in-office treatments, while the second involves surgically implanting a bladder pacemaker.
In very rare and serious cases, surgery may be considered to enlarge the bladder or change the flow of urine.
Also Check: Natural Products For Overactive Bladder
What Causes Irritable Bladder
Irritable bladder can happen to anyone, but research shows that it is prominent in women. What can cause bladder irritation for one person who has the condition may not be what causes irritation for another person who is dealing with it. There are many different potential irritable bladder causes, as outlined below.
What Is The Latest Research On Bladder Pain Syndrome Treatment
Researchers continue to search for new ways to treat bladder pain. Some current studies focus on:
- New medicines to treat bladder pain
- Meditation as a way to control bladder pain
- The role of genetics in bladder pain
- Acupuncture treatment
To learn more about current bladder pain treatment studies, visit ClinicalTrials.gov.
You May Like: Bladder Cancer Surgery Recovery Time
Research And Statistics: How Many People Have Overactive Bladder
Estimates as high as 30 percent of men and 40 percent of women will develop symptoms of overactive bladder at some point in their life, according to the American Urological Association.
In addition, almost one-half of all women will leak urine at some point, and as many as one in three older men leaks urine, according to the according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
Its important to note that these numbers may underestimate the extent of overactive bladder, since many people are reluctant to report their symptoms due to embarrassment or lack of knowledge that treatments are available.
How Common Is The Problem
Approximately 600,000 New Zealanders have bladder control problems and experience leakage of urine. Overactive bladder is one of the causes of these symptoms and it can affect both men and women. In two large studies it was found that about 1 in 6 adults reported some symptoms of an overactive bladder. Symptoms vary in their severity. About 1 in 3 people with an overactive bladder have episodes of urge incontinence.
Incontinence in particular can be embarrassing for the person and many people do not seek the help that is available, thinking that nothing can be done for them. However, most men and women with overactive bladder can be helped, so it is important to talk about any bladder problems with your doctor.
You May Like: Acupuncture For Overactive Bladder Reviews
What Is An Irritable Bladder
In the case of an irritable bladder , the function of the urinary bladder is disrupted.
The bladder acts as a reservoir for the urine filtered by the kidneys. Since it is stretchy, it holds up to 500 milliliters of urine. However, the bladder tells the brain at around 300 milliliters that it wants to be emptied soon. When someone urinates, the muscular wall of the bladder contracts, pushing urine out of the body.
Patients with an irritable bladder feel the urge to urinate much more often than is physically necessary. According to the latest guideline on female urinary incontinence, the term is only applied to cases of urge incontinence in which no urinary tract infection or other disease has an effect on the lower urinary tract. The previous distinction between a primary irritable bladder and a secondary form is therefore not used in the guideline mentioned.
The irritable bladder is considered by some doctors as a diagnosis of exclusion. If they cant find any other causes for the symptoms, they attest to an irritable bladder. In the past, it was primarily considered a psychosomatic illness.
The irritable bladder sometimes significantly reduces the quality of life of those affected. Nevertheless, many sufferers avoid medical help for various reasons. Many certainly out of shame, others have low expectations of the therapy or believe that an irritable bladder is a normal symptom of aging. An irritable bladder occurs regardless of age, even if it becomes more common with age.
What Are The Treatments For An Overactive Bladder
Unfortunately, diagnosing bladder pain often takes a long time as other possible causes are usually excluded first.
There is no single diagnostic test for Painful Bladder Syndrome. However, your doctor/specialist will want to thoroughly examine your medical history along with giving you a pelvic examination and ordering a series of urine tests. This is done to rule out other treatable conditions before they consider a diagnosis of PBS.
The most common of these conditions in both men and women are urinary tract infections and bladder cancer. For men, other common diseases your doctor might look for include chronic prostatitis or chronic pelvic pain syndrome. For women, endometriosis is a common cause of pelvic pain.
So, diagnosis of PBS is generally attributed to:
- pain related to the bladder, usually accompanied by frequency and urgency of urination, and
- absence of other diseases that could cause the symptoms
Your doctor/specialist will probably order diagnostic tests that help rule out other causes of bladder pain, including:
Urinalysis and urine culture examining urine under a microscope and creating a culture can identify the primary organisms that are known to infect the urinary tract and that may cause symptoms similar to PBS.
Culture of prostate secretions rarely performed procedure where prostatic fluid is obtained and examined it for signs of a prostate infection, which can then be treated with antibiotics.
Don’t Miss: What Meds To Take For Bladder Infection
Bipoc And Overactive Bladder
The frequency and presentation of overactive bladder differs across different racial and ethnic groups, according to two recent studies.
One study, published in February 2020 in the journal Female Pelvic Medicine & Reconstructive Surgery, looked at the severity of OAB symptoms in women of different races and ethnicities.
In the study group, Black women were more likely to experience urinary urgency and frequency, while Hispanic women were more likely to have mixed urinary symptoms.
Compared with white women, Black women were 3.4 times as likely to have bladder muscle overactivity. Hispanic women tended to have significantly less urine volume than white women at the sensation of a strong desire to urinate.
Another study, published in September 2020 in the Journal of Urology, looked at OAB and urgency incontinence in men age 60 to 98 through an incontinence self-reported survey.
The study found that non-Hispanic Black men had the highest prevalence of urgency incontinence at 13 percent. Hispanic men came in at 11.3 percent, with non-Hispanic white men at 6.8 percent and men of Chinese ethnicity at 2.9 percent.
Overlap Between Ic And Ibs
Research has shown that individuals who suffer from IC are more likely to suffer from other chronic disorders, including IBS. The reason for the overlap is unknown but does suggest a more system-wide dysfunction. Researchers are looking into the role of inflammatory processes, a “cross-sensitization” among the nerves of the bladder and the bowel, and other central nervous system dysfunction to better understand the underlying factors responsible for the initiation and maintenance of these chronic conditions.
Read Also: Can You Get A Bladder Infection From Being Dehydrated
Mechanisms Underlying Overactive Bladder And Interstitial Cystitis/painful Bladder Syndrome
- 1Visceral Pain Research Group, Centre for Neuroscience, College of Medicine and Public Health, Flinders University, Adelaide, SA, Australia
- 2Centre for Nutrition and Gastrointestinal Diseases, Discipline of Medicine, South Australian Health and Medical Research Institute, The University of Adelaide, Adelaide, SA, Australia
Supportive Therapies And Treatments

Some people may also find the following therapies and supportive treatments helpful:
- physiotherapy a specialist pelvic floor physiotherapist can help you relax your muscles to ease pain.
- acupuncture may help with pain relief
- talking therapies and counselling to help you cope with your symptoms and their impact on your life
- transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation where a small battery-operated device is used to relieve pain by sending electrical impulses into your body
- pain management ask the GP to refer you to a pain specialist
Read Also: Urge To Urinate When Bladder Is Empty
Treatment For Interstitial Cystitis
Unfortunately, there is no simple treatment to eliminate the symptoms of interstitial cystitis, and no one treatment works for everyone. Some options do offer some relief, however. Medications
Most commonly doctors prescribe an oral medication called pentosan . Elmiron is the only oral drug approved by the FDA specifically for interstitial cystitis. Some say that the drug may restore the inner surface of the bladder, which protects the bladder wall from substances in the urine that could irritate it.
It takes two to four months before a patient begins to feel pain relief, and up to six months to experience a decrease in urinary frequency. There are also several possible side effects such as minor gastrointestinal disturbances and possible hair loss. Not for use by pregnant women, Elmiron may cause bleeding and loss of pregnancy. Other oral medications that may improve the symptoms of interstitial cystitis include ibuprofen and other non-steroidal pain medications.
Tricyclic antidepressants, such as amitriptyline or imipramine , may help relax the bladder and block pain. They can also, of course, help with the depression that may be associated with interstitial cystitis. Nerve root modulationSacral nerves, which run from the lower spinal cord to the bladder, pelvic floor, and lower bowel, regulate bladder and bowel control. A method of nerve stimulation called sacral nerve root modulation can be very helpful for people with interstitial cystitis.
How Is Interstitial Cystitis Diagnosed
No single test can diagnose IC. And symptoms of IC are a lot like those of other urinary disorders. For these reasons, a variety of tests may be needed to rule out other problems. Your healthcare provider will start by reviewing your medical history and doing a physical exam. Other tests may include:
-
Urinalysis. Lab testing of urine to look for certain cells and chemicals. This includes red and white blood cells, germs, or too much protein.
-
Urine culture and cytology. Collecting and checking urine for white blood cells and bacteria. Also, if present, what kind of bacteria there are in the urine.
-
Cystoscopy. A thin, flexible tube and viewing device, is put in through the urethra to examine the bladder and other parts of the urinary tract. This checks for structural changes or blockages.
-
Bladder wall biopsy. A test in which tissue samples are removed from the bladder and checked under a microscope to see if cancer or other abnormal cells are present.
-
Lab exam of prostate secretions . This is done to look for inflammation and/or infection of the prostate.
Recommended Reading: How Is A Tumor Removed From The Bladder
Bladder Training Pelvic Floor Training Biofeedback
Bladder training, pelvic floor training and biofeedback are effective treatment methods for irritable bladder, which can be carried out alone or in combination with medication. They are aimed at better, active control of the urge to urinate.
Bladder training is about deliberately delaying going to the toilet for a few minutes when the urge to urinate occurs. This time interval should then be increased continuously until there are finally about three to four hours between consecutive trips to the toilet.
In addition, the individual bladder capacity can be determined using a voiding protocol can be determined using a voiding protocol . Fixed toilet times are set accordingly, so that urge incontinence does not occur. First, time intervals are determined according to the clock for going to the toilet, which are increased over time.
Regular pelvic floor training is also suitable for treating an irritable bladder. It strengthens the pelvic floor muscles, which support the function of the urethral sphincter. A combination of pelvic floor training and electrical stimulation is considered to be particularly effective for irritable bladder.
Biofeedback may also help with an irritable bladder. You can find out more about this therapy method here .
How To Manage Bladder Irritation In The Meantime
The amount of involuntary urine loss from Irritable Bladder Syndrome can be substantial as control is significantly compromised. While you seek treatment or if bladder retraining is underway, you may find an absorbent product specifically designed to handle the thin, fast flow caused by a bladder contraction practical.Take advantage of TENAs Free Samples to find which product and level of absorbency that best suits your requirements. You can order up to three free samples at a time.For social situations, consider something from the TENA Pants range for women and men
. Designed to look and feel just like regular underwear, theyre very absorbent, keeping you dry and comfortable. Theyre also close fitting so incredibly discreet under clothing.And again, if you are suffering from any symptoms associated with an Irritable Bladder, you must see your doctor.
Dont Miss: Side Effects Of Bladder Cancer Chemotherapy
Also Check: What Do They Do For Bladder Cancer
Diagnosis Of Interstitial Cystitis
Although there are no internationally recognized diagnostic criteria, physicians commonly use the three criteria of symptoms, cystoscopy findings, and denial of other similar diseases as diagnostic criteria.
Also Read:
How Is Bladder Pain Syndrome Diagnosed
There is no one test to tell whether you have bladder pain syndrome. Your doctor or nurse will do a physical exam to look at your lower abdomen and lower back and ask you questions about your symptoms. Your doctor may give you tests to rule out other health problems, such as urinary tract infections, sexually transmitted infections , bladder cancer, or kidney stones.
Some tests your doctor may do include:
Recommended Reading: What Medications Treat Overactive Bladder
You May Like: Over The Counter Meds For Overactive Bladder
Signs And Symptoms Of Overactive Bladder
Symptoms of overactive bladder vary from person to person, and may include:
- Sudden, urgent need to urinate
- Difficulty holding in urine
- Unintentional loss of urine with urgent need to urinate
- Waking up more than once or twice at night to urinate
The defining symptom of overactive bladder is sudden, strong urges to urinate. You may fear that youll leak urine on the way to the bathroom.
Even if you dont actually leak urine, OAB can disrupt your life and may cause significant distress.
What Is Irritable Bladder Syndrome
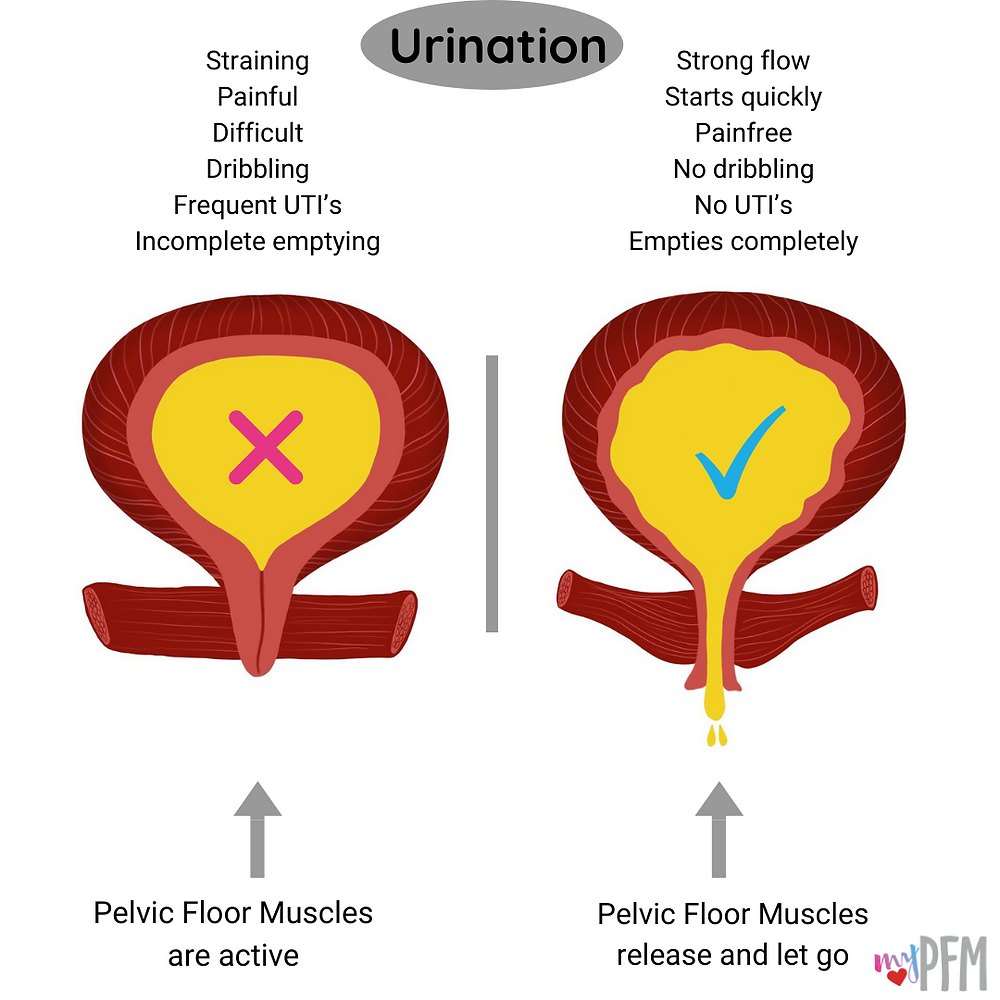
Irritable Bladder is the term used for the ongoing issue of the bladder suddenly and uncontrollably contracting. Despite best conscious efforts, this often leads to a significant urine void and can happen when youre awake or asleep.
Its important to understand some of the symptoms of this condition and what causes it so you can be prepared to manage any unwelcomed leaks.
Read Also: What Does Bladder Pain Feel Like
How Soon After Treatment Will I Feel Better
Pelvic floor exercises and changes to your lifestyle may take six to eight weeks before you start to see results.
Many medications start to relax your bladder muscles after a few hours. But they may take up to a month to work fully.
Botox should start to work after one to two weeks.
Most people start to see improvement after six nerve stimulation treatments. However, it may take up to 12 treatments to see results.
Physical And Neurological Exam
Your health care provider will examine you to look for the cause of your symptoms. In women, the physical exam will likely include your abdomen, the organs in your pelvis, and your rectum. In men, a physical exam will include your abdomen, prostate, and rectum. Your health care provider may also do a neurological exam to rule out any other problems. Patients with IC/BPS may have other mental health and/or anxiety disorders which may be linked to their condition.
Read Also: Medicine For Bladder Control At Night