Bladder Cancer Clinical Trials
Major drug companies continually research and develop new medications and treatments for bladder cancer that must be shown to be safe and effective before doctors can prescribe them to patients. Through clinical trials, researchers test the effects of new drugs on a group of volunteers who have bladder cancer. Following a strict protocol and using carefully controlled conditions, researchers evaluate the investigational drugs under development and measure the ability of the new drug to treat bladder cancer, its safety, and any possible side effects.
Some patients are reluctant to take part in clinical trials for fear of getting no treatment at all. But patients who participate in clinical trials receive the most effective therapy currently available for the condition, or they may receive treatments that are being evaluated for future use. These bladder cancer drugs may be even more effective than current treatment. Comparing them in a clinical trial is the only way to find out.
Hereâs where to find information about whether a bladder cancer clinical trial is right for you.
This website lists industry-sponsored clinical trials that are actively recruiting patients.
Show Sources
American Cancer Society: âBladder Cancer Treatment,â âBladder Cancer Surgery,â âRadiation Therapy for Bladder Cancer,â âChemotherapy for bladder cancer,â âFDA Approves New Immunotherapy Drug for Bladder Cancer,â âImmunotherapy for bladder cancer.â
Interim Analysis And Monitoring
Because this is a short-term study with a 2-year follow-up period, we will not conduct interim analysis. However, the safety of PDD-EBTUR will be independently evaluated by the Safety Monitoring Committee when:
A critical modification of the study protocol is required
Any serious adverse event associated with this surgical procedure occurs
Dont Miss: What Is The Best Medication For Bladder Infection
Treating Stage Ii Bladder Cancer
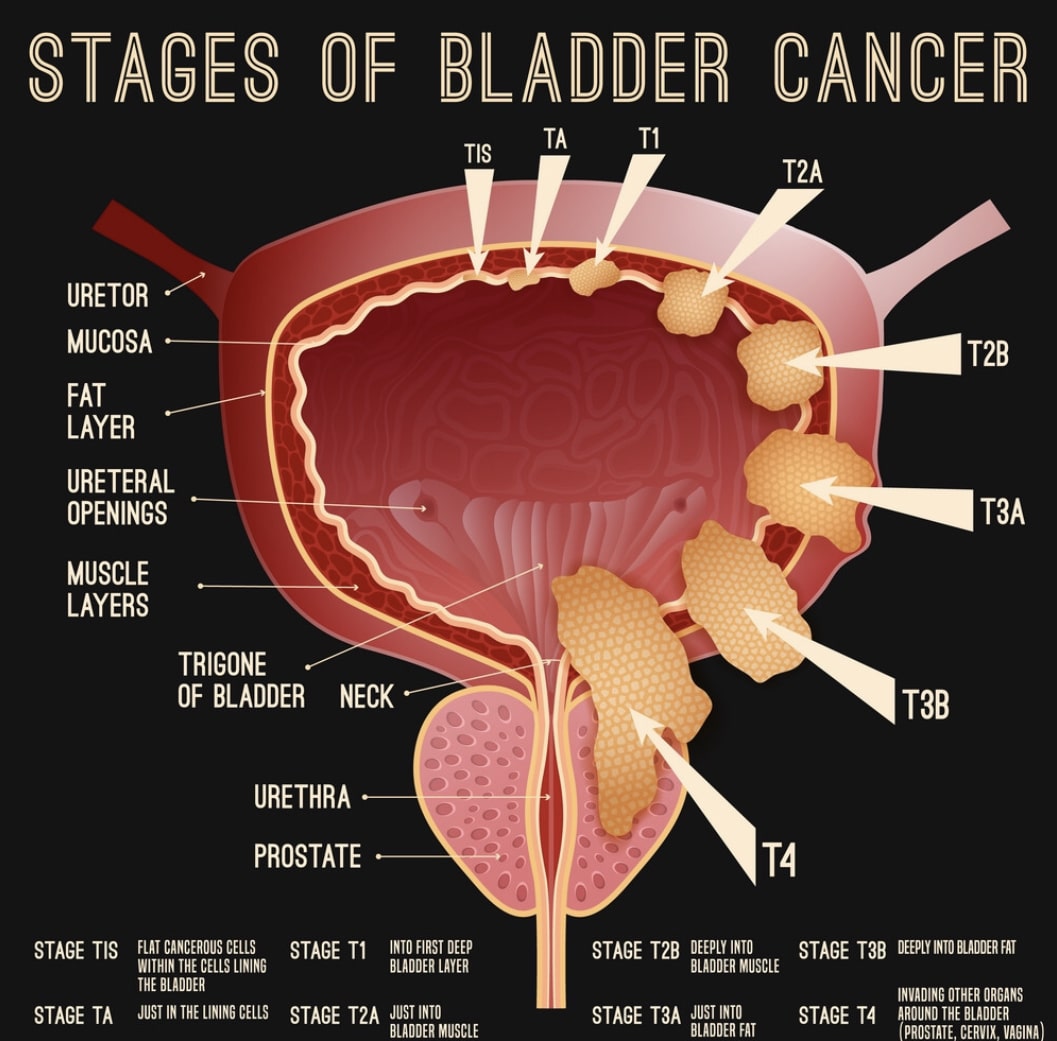
These cancers have invaded the muscle layer of the bladder wall , but no farther. Transurethral resection is typically the first treatment for these cancers, but it’s done to help determine the extent of the cancer rather than to try to cure it.
When the cancer has invaded the muscle, radical cystectomy is the standard treatment. Lymph nodes near the bladder are often removed as well. If cancer is in only one part of the bladder, a partial cystectomy may be done instead. But this is possible in only a small number of patients.
Radical cystectomy may be the only treatment for people who are not well enough to get chemo. But most doctors prefer to give chemo before surgery because it’s been shown to help patients live longer than surgery alone. When chemo is given first, surgery is delayed. This is not a problem if the chemo shrinks the bladder cancer, but it might be harmful if the tumor continues to grow during chemo.
If cancer is found in nearby lymph nodes, radiation may be needed after surgery. Another option is chemo, but only if it wasn’t given before surgery.
For people who have had surgery, but the features of the tumor show it is at high risk of coming back, the immunotherapy drug, nivolumab, might be offered. When given after surgery, nivolumab is given for up to one year.
For patients who cant have surgery because of other serious health problems, TURBT, radiation, chemotherapy, or some combination of these may be options.
You May Like: Medication For Overactive Bladder In The Elderly
Preoperative Details Of Turbt
Patients will undergo pre-anesthesia testing in order to evaluate physical condition and medical conditions. As antithrombotic therapy has become more prevalent, the decision whether to hold anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents is a commonly discussed topic. While there are no guidelines to follow regarding the perioperative management of these medications, it is an often-debated balance between adverse cardiovascular events and persistent perioperative hematuria. While low-dose aspirin can be continued in most cases, all other antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants are almost always held perioperatively, with the duration and plan for resumption made on a case-by-case basis.
Patients scheduled for anesthetic cystoscopy with TURBT must have sterile urine documented prior to instrumentation. Sterility is usually presumed on the basis of a microscopic urinalysis showing no bacteria or white blood cells . Patients with a positive urine culture are conventionally treated with a course of culture-specific antibiotics to achieve this desired sterility.
If Treatment Does Not Work
Full recovery from bladder cancer is not always possible. If the cancer cannot be cured or controlled, the disease may be called advanced or metastatic.
This diagnosis is stressful, and for some people, advanced cancer is difficult to discuss. However, it is important to have open and honest conversations with your health care team to express your feelings, preferences, and concerns. The health care team has special skills, experience, expertise, and knowledge to support patients and their families and is there to help. Making sure a person is physically comfortable, free from pain, and emotionally supported is extremely important.
People who have advanced cancer and who are expected to live less than 6 months may want to consider hospice care. Hospice care is a specific type of palliative care designed to provide the best possible quality of life for people who are near the end of life. You and your family are encouraged to talk with the health care team about hospice care options, which include hospice care at home, a special hospice center, or other health care locations. Nursing care and special equipment can make staying at home a workable option for many families. Learn more about advanced cancer care planning.
After the death of a loved one, many people need support to help them cope with the loss. Learn more about grief and loss.
You May Like: Why Does My Bladder Leak So Much
Treating Stage I Bladder Cancer
Stage I bladder cancers have grown into the connective tissue layer of the bladder wall , but have not reached the muscle layer.
Transurethral resection with fulguration is usually the first treatment for these cancers. But its done to help determine the extent of the cancer rather than to try to cure it. If no other treatment is given, many people will later get a new bladder cancer, which often will be more advanced. This is more likely to happen if the first cancer is high-grade .
Even if the cancer is found to be low grade , a second TURBT is often recommended several weeks later. If the doctor then feels that all of the cancer has been removed, intravesical BCG or intravesical chemo is usually given. If all of the cancer wasnt removed, options are intravesical BCG or cystectomy .
If the cancer is high grade, if many tumors are present, or if the tumor is very large when its first found, radical cystectomy may be recommended.
For people who arent healthy enough for a cystectomy, radiation therapy might be an option, but the chances for cure are not as good.
Bladder Cancer Is A Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In The Tissues Of The Bladder
The bladder is a hollow organ in the lower part of the abdomen. It is shaped like a small balloon and has a muscular wall that allows it to get larger or smaller to store urine made by the kidneys. There are two kidneys, one on each side of the backbone, above the waist. Tiny tubules in the kidneys filter and clean the blood. They take out waste products and make urine. The urine passes from each kidney through a long tube called a ureter into the bladder. The bladder holds the urine until it passes through the urethra and leaves the body.
There are three types of bladder cancer that begin in cells in the lining of the bladder. These cancers are named for the type of cells that become malignant :
- Transitional cell carcinoma: Cancer that begins in cells in the innermost tissue layer of the bladder. These cells are able to stretch when the bladder is full and shrink when it is emptied. Most bladder cancers begin in the transitional cells. Transitional cell carcinoma can be low-grade or high-grade:
- Low-grade transitional cell carcinoma often recurs after treatment, but rarely spreads into the muscle layer of the bladder or to other parts of the body.
- High-grade transitional cell carcinoma often recurs after treatment and often spreads into the muscle layer of the bladder, to other parts of the body, and to lymph nodes. Almost all deaths from bladder cancer are due to high-grade disease.
See the following PDQ summaries for more information:
Read Also: High Grade Non Invasive Bladder Cancer
What Are The Risks Of Bladder Tumor Biopsy And Resection
Bladder tumor biopsy and resection is a very safe procedure. However, like any surgery, it has some risks. These include:
- Risks related to anesthesia.
- Excessive or prolonged bleeding.
- Perforation in the bladder.
If you have any symptoms such as fever, feeling cold and shivery, or heavy bleeding following bladder tumor biopsy and resection, you should seek medical help right away.
Urologic Cancer Care At Columbia
The Department of Urology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center was founded in 1917, making it one of the oldest and most accomplished homes of urology in the United States. We exist to provide you with unsurpassed excellence in care.
Our researchers are dedicated pioneers, focused on revolutionizing cancer therapy standardswhile making every effort to ensure that, no matter where you are on your cancer journey, you really can maintain your quality of life.
We’ve got your back. We’re in your corner. We’re your home team. We’re all in.
Recommended Reading: Is Bladder Leakage Common After Hysterectomy
There Are Three Ways That Cancer Spreads In The Body
Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood:
- Tissue. The cancer spreads from where it began by growing into nearby areas.
- Lymph system. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the lymph system. The cancer travels through the lymph vessels to other parts of the body.
- Blood. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through the blood vessels to other parts of the body.
Also Check: Sodium Bicarbonate For Bladder Infection
Treating Stage Iv Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the pelvic or abdominal wall , may have spread to nearby lymph nodes , and/or have spread to distant parts of the body . Stage IV cancers are very hard to get rid of completely.
Chemotherapy is usually the first treatment if the cancer has not spread to distant parts of the body . The tumor is then rechecked. If it appears to be gone, chemo with or without radiation or cystectomy are options. If there are still signs of cancer in the bladder, chemo with or without radiation, changing to another kind of chemo, trying an immunotherapy drug, or cystectomy may be recommended.
Chemo is typically the first treatment when bladder cancer has spread to distant parts of the body . After this treatment the cancer is rechecked. If it looks like it’s gone, a boost of radiation to the bladder may be given or cystectomy might be done. If there are still signs of cancer, options might include chemo, radiation, both at the same time, or immunotherapy.
In most cases surgery cant remove all of the cancer, so treatment is usually aimed at slowing the cancers growth and spread to help people live longer and feel better. If surgery is a treatment option, it’s important to understand the goal of the operation whether it’s to try to cure the cancer, to help a person live longer, or to help prevent or relieve symptoms from the cancer.
Because treatment is unlikely to cure these cancers, many experts recommend taking part in a clinical trial.
Also Check: Bladder Cancer Spread To Lungs Life Expectancy
How Is Bladder Tumor Biopsy And Resection Performed
You may have general anesthesia for this procedure, which means youll be asleep for it. Some providers might use regional anesthesia, which means youll be awake. However, you wont feel any pain.
Bladder tumor biopsy and resection is performed when a doctor inserts a rigid instrument called a resectoscope into the bladder through the urethra. Inserting the resectoscope in this way means that no incisions are necessary.
Your provider will use the resectoscope to remove the tumor, which will be sent to a pathology lab for testing. Once the tumor is removed, your doctor will attempt to destroy any remaining cancer cells by burning the area using electric current by a process called fulguration or cauterization.
Your provider may decide to insert some type of chemotherapy medicine into the bladder using the scope. This is called intravesical chemotherapy. Your provider might suggest that you have maintenance intravesical chemotherapy for a period of time, meaning that youll have regular treatments.
Genetic Risk Assessment Program
The UCLA Genitourinary Cancer Genetic Risk Assessment Program focuses on investigation into the potential genetic causes of an individuals urologic cancer. Up to 5-10% of cancers are related to a genetic predisposition. If you have been diagnosed with a urologic cancer, UCLAs team has specific referral criteria to determine if you should pursue genetic risk assessment to evaluate for a genetic cause of cancer. For those at greatest risk, often this knowledge can more precisely tailor a treatment plan that is optimal for you.
Read Also: Over The Counter Bladder Medication
Read Also: What Causes Bladder Pain And Pressure
Permission To Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text. It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. However, a user would be allowed to write a sentence such as NCIs PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks in the following way: .
The best way to cite this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Adult Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Bladder Cancer Treatment. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated < MM/DD/YYYY> . Available at: . Accessed < MM/DD/YYYY> .
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author, artist, and/or publisher for use in the PDQ summaries only. If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in Visuals Online. Visuals Online is a collection of more than 3,000 scientific images.
Risk Factors For Late Recurrence
While there dont seem to be many risk factors for early bladder cancer recurrence, there are a few risk factors for late recurrence of bladder cancer that have been noted in multiple studies. Multiple studies have shown that having a radical cystectomy at a younger age can be a risk factor for recurrence. Patients who have bladder cancer that is not confined to the bladder, or that has involvement in the surrounding muscle tissue may also be at risk for late recurrence, but there is a need for more studies to show a better correlation. Finally, bladder cancer that involves the prostate may also be at risk for a late recurrence.
Recommended Reading: Tens Unit For Overactive Bladder
Remission And The Chance Of Recurrence
A remission is when cancer cannot be detected in the body and there are no symptoms. This may also be called having no evidence of disease or NED.
A remission may be temporary or permanent. This uncertainty causes many people to worry that the cancer will come back. While many remissions are permanent, it is important to talk with your doctor about the possibility of the cancer returning. Understanding your risk of recurrence and the treatment options may help you feel more prepared if the cancer does return. Learn more about coping with the fear of recurrence.
If the cancer returns after the original treatment, it is called recurrent cancer. It may come back in the same place , nearby , or in another place .
When this occurs, a new cycle of testing will begin again to learn as much as possible about the recurrence. After this testing is done, you and your doctor will talk about the treatment options.
People with recurrent cancer often experience emotions such as disbelief or fear. You are encouraged to talk with the health care team about these feelings and ask about support services to help you cope. Learn more about dealing with cancer recurrence.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Calm An Overactive Bladder
Types Of Surgical Techniques
- Endoscopic surgery: A thin, flexible tube equipped with a camera and surgical tools is inserted into a natural opening so no incision is made in the skin.
- Keyhole surgery: This minimally invasive procedure involves several small incisions in the skin to access the bladder, and the cancer is removed through these holes using special instruments.
- Robotic surgery: Similar to keyhole surgery, robotic surgery differs in that the actual surgery is done via mechanized instruments instead of a surgeons hands controlling the instruments.
- Open surgery: With an open approach, a traditional large incision is made in the abdomen to access the bladder.
You May Like: How Do Males Get Bladder Infections
Also Check: Non Prescription Dog Food For Bladder Stones
Smoking Can Affect The Risk Of Bladder Cancer
Anything that increases your chance of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer not having risk factors doesnt mean that you will not get cancer. Talk to your doctor if you think you may be at risk for bladder cancer.
Risk factors for bladder cancer include the following:
- Past treatment with radiation therapy to the pelvis or with certain anticancer drugs, such as cyclophosphamide or ifosfamide.
- Taking Aristolochia fangchi, a Chinese herb.
- Drinking water from a well that has high levels of arsenic.
- Drinking water that has been treated with chlorine.
- Having a history of bladder infections, including bladder infections caused by Schistosoma haematobium.
- Using urinarycatheters for a long time.
Older age is a risk factor for most cancers. The chance of getting cancer increases as you get older.