Clinically Approved Modes Of Electrical Stimulation In The Treatment Of Non
In this section, SNM with non-rechargeable and rechargeable systems is discussed, after which posterior tibial nerve stimulation is addressed. In Table 2, the chronology of introduction and approval of these devices is given.
|
Table 2 Introduction and approval of sacral neuromodulation and tibial nerve stimulation |
How Do I Place My Tens Machines Electrode Pads For Neck Pain
The way to place the electrode pads is similar to how to place them for the lower back pain, except of course place them higher.
Here is also suggested to use four pads to better triangulate the area of pain. You can either place two of the electrode pads on either side of the spine at the base of the hairline and two lower on the shoulder or cross them as an x as the image suggests.
Tens Placement For Ic: Help With Bladder Urgency And Frequency
TENs placment for IC: help with urgency and frequency
We have talked about how to use TENS for IC before. As a reminder, TENS stands for Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation. It has predominately been used for treating nerve-related acute or chronic pain. But there is another condition that TENs has been proven to be effective for. And if your IC has you running to pee every 5 mins, youll be very interested in reading further.
First, a little medical background. The lumbar-sacral nerves control the bladder detrusor muscles and the perineal floor. This group of nerves, sometimes referred to as the sacral plexus, occupy the spinal cord at levels L4 to S3 which are located towards the base of your spine, between your lower back and, well, your butt crack.
In fact, that same collection of nerves is often targeted by Neuromodulation therapy sacral implants like InterStim. You may have read about these implantable devices since they have been one of the options for treating IC for many years. A major downside of these Neuromodulating implants is that it is highly invasive. Once a patient is deemed to be a responder via a test stimulation, the unit is surgically implanted while you are under general anesthesia.
Luckily there is another option for impacting the lumbar-sacral nerves that control your bladder and pelvic floor function. The posterior tibial nerve the nerve that runs along the inside of your ankle and up your leg provides access to the sacral plexus.
Also Check: Bladder Infection What To Take
Incontinence Is The Silent Disabler
You are not alone approximately 5 million Australian men and women experience some degree of incontinence, and almost all are suffering in silence.
It is both easy and wise to address the issue as soon as it manifests itself. If you dont tackle the problem soon:
-
It will not get better on its own wishful thinking does not work
-
It will get worse as you age
-
Eventually, you will be mopping up the symptoms
-
YES, the purchase and wearing of incontinence pants or pads
-
This is expensive, uncomfortable, inconvenient and potentially embarrassing
-
For the rest of your life!
And there is another major concern to mention. There is:
-
A proven link between incontinence and urinary tract infection
-
A proven link between UTI in the elderly and fever induced delirium
-
A proven link between delirium and dementia
Why is no-one talking about this?
-
Physiotherapists know that weak pelvic floor muscles are a major cause of incontinence
-
Primary care doctors know that untreated incontinence is a cause of UTI
-
Geriatricians know that chronic UTIs in the elderly are a cause of delirium
-
Neurologists know that delirium exacerbates dementia
Who is joining the dots?
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation For Overactive Bladder
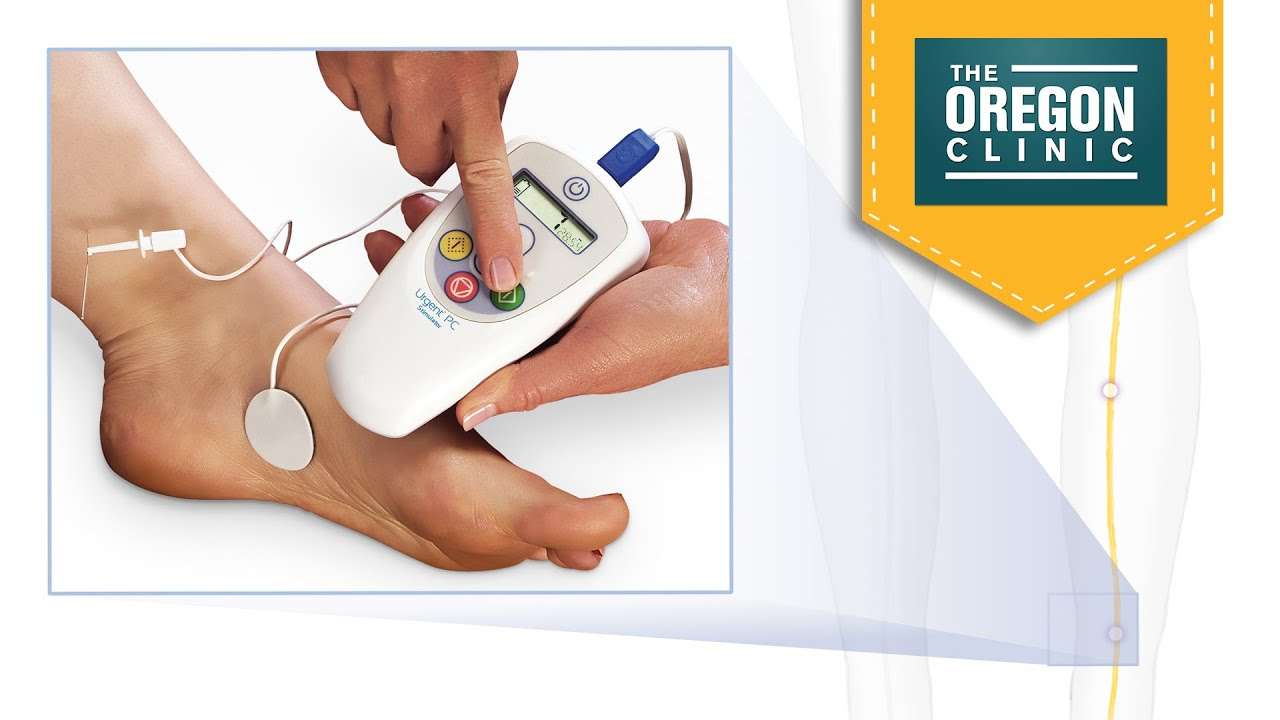
Posterior tibial nerve stimulation is regarded as a 3rd line treatment for patients for overactive bladder i.e. after medications and bladder retraining with pelvic floor physiotherapy have been unsuccessful in controlling symptoms.
Patient are regarding as having refractory symptoms when they have not responded to or do not tolerate at least 2 of the newer medications available for OAB symptoms.
Also Check: How To Test For Bladder Infection
Are Tens Units Safe
Each call we have a tendency to create has its professionals and cons. the identical applies when it involves getting the best transportable TENS unit.
whereas the majority UN agency use these devices wont expertise any aspect effects, its best to understand what to expect.
The first aspect result is associated with the self-adhesive pads.
So, several users reported unpleasant skin reactions when applying the pads. Thats because theyre made of latex. about 3% of individuals experience allergic reactions.
However, most of the time, those reactions could also be avoided. The key is to steer clear of placing the pads in the actual place use after use.
Additionally, if one uses the machine too often, or their pulse is just too high, the electrical stimulation may further cause muscle pain and twitch.
Aside from these potential side effects, using these units is safe. however, some individuals should steer beyond these devices. well discuss this in a bit .
Tens For Overactive Bladder Symptoms In Females
-
Research type
Research Study
-
Full title
A comparative study to compare the effectiveness of sacral TENS versus posterior tibial nerve TENS on Overactive Bladder symptoms in adult females.
-
IRAS ID
-
Duration of Study in the UK
0 years, 8 months, 0 days
-
Research summary
The research will involve 30 adult females with overactive bladder symptoms. Current treatment can involve using TENS machines to help manage symptoms. What is unknown at present is whether places the external electrodes on the sacrum is any different to placing them over the posterior tibial nerve. There is some evidence for both but it leads to difficulty when prescribing this treatment as we are unsure where to place the pads. The females will be shown how to use these units and loaned them for 6 weeks at home to use for 15 minutes daily either over the sacrum or lower leg depending on where they have been randomised to, they will also complete the outcome measures at this time. They will return and re-fill the outcome measures to identify any change to symptoms. They will also be sent the outcome measure to complete for 6 weeks after they have finished using the TENS to see if there has been any carry over of results. Results will then compare both groups.
-
REC name
South Central – Berkshire B Research Ethics Committee
-
REC reference
Recommended Reading: Loss Of Bladder Control While Coughing
Other Sites Of Electrical Stimulation
One of the first techniques for the treatment of lower urinary tract storage dysfunction stimulated the suprapubic region in patients with painful bladder syndrome , . This method was used to relieve abdominal pain, similarly to the principle of TENS when used for the relief of pain presumably. Subsequently these patients also experienced reduced urinary frequency . Two later studies documented an improvement in urodynamic parameters in patients with detrusor overactivity , sensory urgency, or neurogenic problems. However, based on the literature, the efficacy of stimulation of a suprapubic site in patients with OAB symptoms is unproven , .
Another reported approach has used stimulation of the thigh muscle in spinal cord injury patients to relieve spasticity. In some of these cases, this has led to improvements of urgency incontinence as well as an increase in the maximum cystometry capacity and reduced maximum detrusor pressure , . Further to this 6/19 patients reported clinical improvement in urinary incontinence and frequency extending out to 3 months after treatment .
Based on this, at best limited evidence for stimulation at other sites, the most logical approach to be used in transcutaneous electrical stimulation techniques appears to be either sacral stimulation or PTNS as they either directly or indirectly target the S3 spinal cord root.
Feasibility Of Using A Novel Non
Jai H. Seth1, Gwen Gonzales1, Collette Haslam1, Mahreen Pakzad1, Arvind Vashisht2, Arun Sahai3, Charles Knowles4, Arthur Tucker4, Jalesh Panicker1
1Department of Uro-Neurology, The National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery and UCL Institute of Neurology , 3Department of Urology, Guys Hospital, Kings College London Queen Mary University of London , , UK
Contributions: Conception and design: JH Seth, J Panicker Administrative support: JH Seth, J Panicker Provision of study materials or patients: J Panicker, A Vashisht, A Sahai, M Pakzad, G Gonzales, C Haslam Collection and assembly of data: JH Seth, J Panicker Data analysis and interpretation: JH Seth, J Panicker, A Sahai, C Knowles, A Tucker Manuscript writing: All authors Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
Correspondence to:
Background: To evaluate safety, acceptability and pilot efficacy of transcutaneous low-frequency tibial nerve stimulation using a novel device as home-based neuromodulation.
Methods: In this single-centre pilot study, 48 patients with overactive bladder were randomized to use a self-applicating ambulatory skin-adhering device stimulating transcutaneously the tibial nerve at 1 Hz for 30 minutes, either once daily or once weekly, for 12 weeks. Changes in OAB symptoms and QoL were measured at baseline, weeks 4, 8, and 12 using validated scoring instruments , 3-day bladder diary and a Global Response Assessment at week 12.
Submitted Sep 03, 2018. Accepted for publication Sep 19, 2018.
Read Also: Does Cranberry Help Bladder Infections
Sacral Nerve Stimulation Devices
Sacral nerve stimulation has been used to treat OAB for several decades. The SNS device is implanted above the buttocks. A lead sends electrical impulses to the sacral nerves to calm the bladder .
Sacral nerve stimulation for OAB.
Only one SNS device is FDA-approved and on the market Medtronics InterstimTM. Studies show that 83 percent of OAB patients who use the device experience a significant reduction in symptoms . The downside of this technology is the potential need for battery replacement as early as three years after implantation. Also patients generally cannot undergo non-head MRIs because of potential damage to the device and injury to the patient.
Axonics Modulation Technologies, Inc. has developed an SNS device that is 60 percent smaller than the Interstim about the size of two quarters. With its rechargeable, implantable pulse-generator battery, it has an expected 15-year life in the body. It is current-controlled so that output voltage is automatically adjusted based on tissue impedance, which may provide more consistent therapy, Dr. Goldman explains. The company hopes the device will prove safe for certain types of MRI procedures.
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation is carried out with surface electrodes, and therefore, provides a non-invasive alternative to other stimulation modalities. Above we described TENS of the tibial nerve. Other sites suitable for TENS include the suprapubic, sacral, penile/clitoral, vaginal, and rectal areas. Effectiveness of TENS has been demonstrated in patients with idiopathic bladder dysfunction.31 Areas of stimulation were the dermatomes of S2 and S3 and the thigh area. Stimulation frequency was 2050 Hz, and the pulse width was 200 µs. Stimulation was carried out daily during 26 weeks. Only short-term clinical improvement was shown. There are no data on long-term efficacy.
Don’t Miss: Can You Take Amoxicillin For A Bladder Infection
Menstrual Cramps And Labor Pains
There is insufficient evidence to suggest that TENS units reduce menstrual cramps and labor pains.
A study with 40 women who had very painful menstrual cramps found that TENS was effective at reducing cramp-related pain, and led to improvements in these patients quality of life. The patients used a portable TENS units, which was particularly helpful in maintaining their treatment effectively .
In another study with 134 women with painful menstrual cramps, TENS reduced both the intensity and duration of pain more than a placebo treatment .
TENS was also useful for quickly relieving menstrual pain in a study with 40 women. Three months after the study, 70% of the women were still using the TENS unit regularly with no adverse side effects .
The TENS unit may relieve pain associated with giving birth. A study found that women who used a TENS unit during their stay at the hospital experienced less labor pain, suggesting that TENS may be helpful both during and after labor .
Posterior Tibial Nerve And Oab
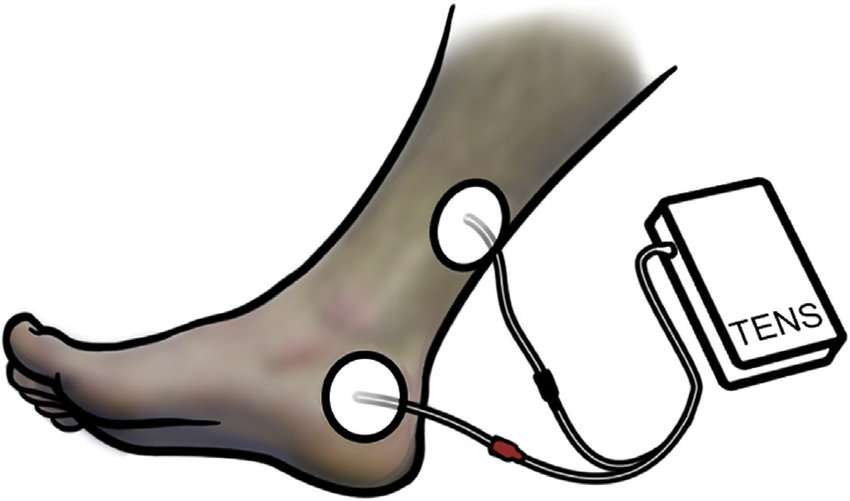
- Percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation, requiring needle-tip electrodes which are invasive and expensive.
- Transcutaneous tibial nerve stimulation , which requires just a basic TENS machine and standard electrodes. TTNS is much more cost effective than percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation, and much simpler to administer.
Read Also: Bcg Instillation For Bladder Cancer
Evaluation Of Your Urinary Incontinence
You urinary incontinence evaluation starts with a thorough history of your urinary symptoms and your overall health and other medical conditions. A pelvic exam and an in office test called bladder stress test may be done by your doctor as part of your initial evaluation.
The bladder stress test consists of observation for urinary leakage with coughing. Additional tests that may be recommended by your gynecologist or urogynecologist to further evaluate your incontinence. Not everyone needs additional testing.
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation
McGuire et al. first used peripheral electrical stimulation to stimulate the PTN. In this initial study an anode electrode was placed over the common peroneal nerve or PTN and a cathode electrode was placed over the contralateral equivalent site. They reported positive results in 8/11 detrusor overactivity patients who became dry after the treatment, and in seven neurogenic disease patients of whom five became dry or improved. Following this, the SANS and later the Urgent-PC device established a substantial evidence base using the percutaneous approach to stimulate PTN, although a different location to the original description by McGuire et al. was used. Further studies of either percutaneous or transcutaneous posterior tibial nerve stimulation have used electrodes placed on the same area as the SANS . Hence TPTNS might be a plausible and potentially attractive therapeutic option based on the evidence available for its efficacy in percutaneous form.
Position of electrodes for transcutaneous posterior tibial nerve stimulation . Stimulation can be delivered using a conventional transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation machine.
The subjective efficacy of TPTNS and oxybutynine versus control was studied in 28 women with OAB . TPTNS was described as improving subjective symptoms with no adverse events but more robust assessment tools and a careful documentation of the aetio-pathology of the studied patients would be needed to draw more detailed conclusions.
Don’t Miss: Can You Use A Drain Bladder On A Toilet
How Do I Place My Tens Machines Electrode Pads For Sciatica
To handle and pain related to sciatica, use either two, or most preferably, four electrode pads placed above and under the area on pain. DO NOT place the pads directly on the spine, but you can without any problem place the pads vertically on either side of the spine.
You can also place two of the electrode pads on the high part of the backside of your legs and experiment with the placement of them as shown in the image.
Electrical Nerve Stimulation For Overactive Bladder A Comparison Of Treatments
| The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators. Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the U.S. Federal Government. Read our disclaimer for details. |
| Verified April 2016 by Shannon Lamb, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center. Recruitment status was: Enrolling by invitationFirst Posted : September 12, 2013Last Update Posted : April 28, 2016 |
- Study Details
| Study Type : |
| Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation vs. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation for Overactive Bladder: A Randomized Trial |
| Study Start Date : |
TENS therapy will be administered as follows:
- Surface electrodes, 2 x 2 in diameter, will be placed over sacral foramen S2-4, bilaterally, using 2 channels Approximate locations are over posterior superior iliac spine and inferior lateral angle of sacrum. Sticker electrodes for the duration of the study will be issued to subjects. They are adhesive and can be re-used for up to 3-4 weeks with proper skin care and electrode care.
-
The electrodes will be connected to the TENS device and the following settings will be pre-set:
- Mode: Burst
Read Also: What Were Your Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
You May Like: Why Can I Not Empty My Bladder
Expanding Or Removing The Bladder
A surgeon can enlarge the bladder with bowel tissue or remove it entirely however, both these surgeries have serious limitations. They do not guarantee pain relief because a phantom pain, similar to that experienced by amputees, may continue. This is known as neuropathic pain, which is discussed in more detail in the chronic pelvic pain unit.
Surgery to expand the bladder, called a supratrigonal cystectomy, leaves only a small portion of the original bladder in place and replaces the rest of the bladder with bowel tissue. This increases the size of the bladder, allowing it to hold more urine, but it often impairs the ability of the bladder to empty properly. To compensate for this problem, many women who have this procedure must learn to insert a catheter once or twice a day to remove the remaining urine. This increases the risk of bladder infections. Also, bowel tissue naturally produces mucus that may block the flow of urine or make self-catheterization more difficult.
Read also WHAT ARE THE KEY DIFFERENCES BETWEEN TENS AND AN EMS MACHINE?
The fundamental distinction between the two is that EMS units concentrate on specific muscles, whereas TENS units target specific nerves.
What is more, some TENS units might also be used as EMS units. nevertheless, EMS units cannot be used as TENS units.
Furthermore, the latter are more commonly used for managing and treating the pain.
As for the former, they deliver a therapeutic intervention for muscle rehabilitation.
Can You Put A Tens Unit Anywhere
TENS Units at Home TENS treatment is generally safe but as with most therapies, there are some ways the treatment shouldnt be used and some people who should not use it. The electrodes for a TENS unit should not be placed: Near their heart or so the current goes through your chest, from front to back. On your face.
Read Also: What Causes Continuous Bladder Infections