Treatment Of Stage I Bladder Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage I bladder cancer may include the following:
- Transurethral resection with fulguration. This may be followed by one of the following:
- Intravesicalchemotherapy given right after surgery.
- Intravesical chemotherapy given right after surgery and then regular treatments with intravesical BCG or intravesical chemotherapy.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Prognosis Of Patients With Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Who Are Intolerable To Receive Any Anti
Muscle invasive bladder tumor has a high propensity for rapid growth and distant metastasis.
-
The aim of this retrospective study was to evaluate the prognosis of patients who had been diagnosed with muscle invasive bladder cancer and did not receive anti-cancer treatment because of their physical characteristics.
-
We evaluated 26 patients. Median overall survival was 12 months.
-
These results may assist in counseling older patients with MIBC if the disease is left untreated.
Treatment Of Stage Iv Bladder Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage IV bladder cancer that has not spread to other parts of the body may include the following:
- Urinary diversion or cystectomy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
Treatment of stage IV bladder cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, such as the lung, bone, or liver, may include the following:
- External radiation therapy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Urinary diversion or cystectomy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- A clinical trial of new anticancer drugs.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
You May Like: Is There A Blood Test For Bladder Cancer
Signs And Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
Sometimes bladder cancer doesnt have many symptoms. Signs or symptoms can include:
- blood in your urine
- pain or burning when passing urine
- not being able to pass urine when you need to.
Not everyone with these symptoms has bladder cancer. If you have any of these symptoms or are worried, always see your doctor.
Cancer May Spread From Where It Began To Other Parts Of The Body
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if bladder cancer spreads to the bone, the cancer cells in the bone are actually bladder cancer cells. The disease is metastatic bladder cancer, not bone cancer.
Also Check: Why Is My Bladder So Weak All Of A Sudden
What Is A 5
A relative survival rate compares people with the same type and stage of bladder cancer to people in the overall population. For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for a specific stage of bladder cancer is 90%, it means that people who have that cancer are, on average, about 90% as likely as people who dont have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
Catheterizable Continent Diversion Pouch
This is a reservoir of bowel with a stoma that is catheterizable for emptying the bladder. The urine is siphoned out of the urinary reservoir with a small catheter every four to six hours. The catheterizable pouch may require surgical repair at some point after surgery due to the wear and tear of frequent catheterization. This type of reconstruction is not performed on patients with a history of bowel disease.
Read Also: Bladder Cancer In Cats Treatment
How Do Healthcare Providers Diagnose Bladder Cancer
Healthcare providers do a series of tests to diagnose bladder cancer, including:
- Urinalysis: Providers use a variety of tests to analyze your pee. In this case, they may do urinalysis to rule out infection.
- Cytology: Providers examine cells under a microscope for signs of cancer.
- Cystoscopy: This is the primary test to identify and diagnose bladder cancer. For this test, providers use a pencil-sized lighted tube called a cystoscope to view the inside of your bladder and urethra. They may use a fluorescent dye and a special blue light that makes it easier to see cancer in your bladder. Providers may also take tissue samples while doing cystoscopies.
If urinalysis, cytology and cystoscopy results show you have bladder cancer, healthcare providers then do tests to learn more about the cancer, including:
Healthcare providers then use what they learn about the cancer to stage the disease. Staging cancer helps providers plan treatment and develop a potential prognosis or expected outcome.
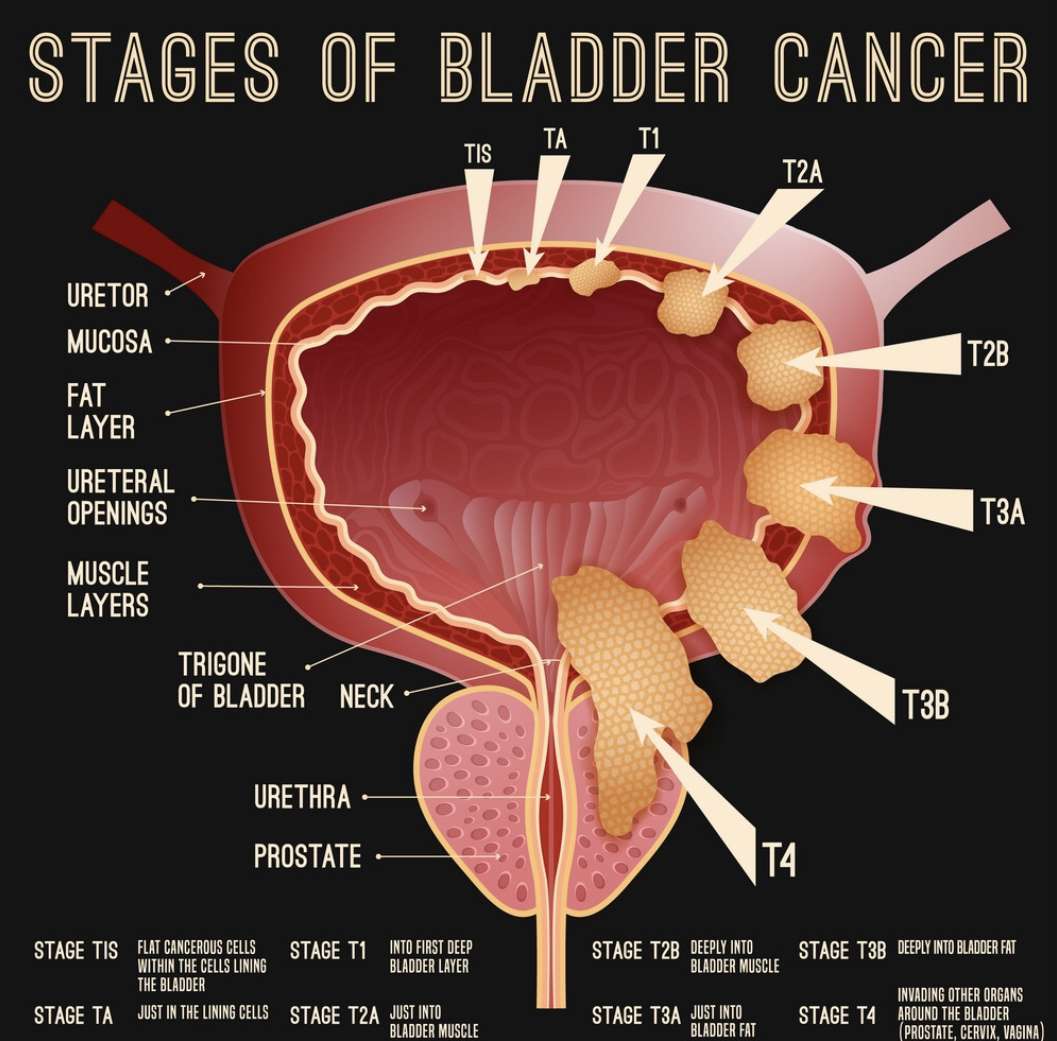
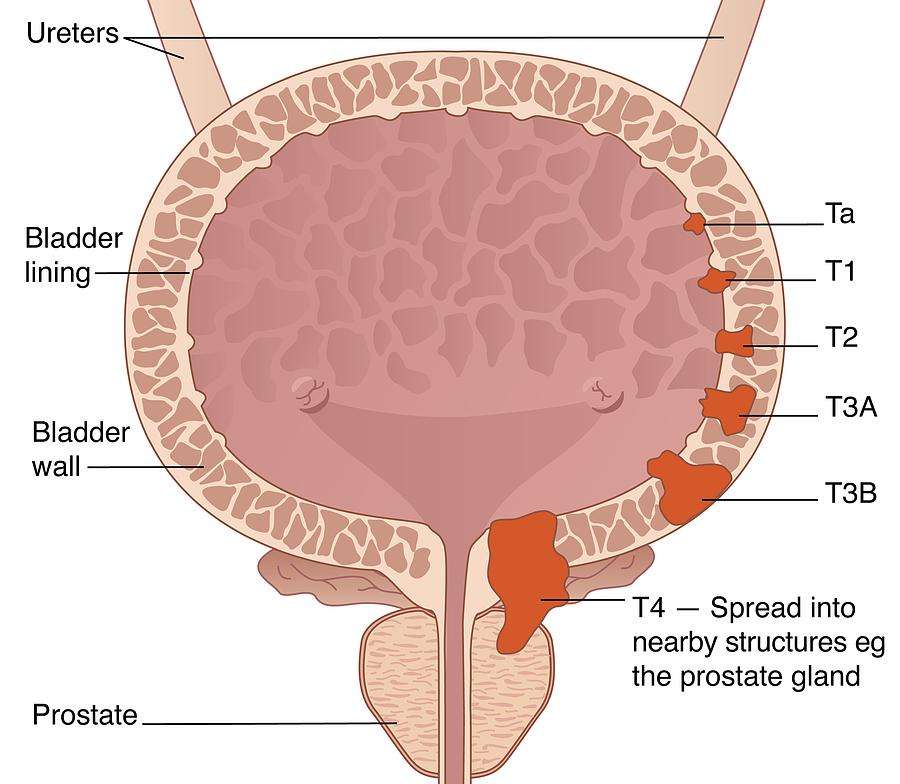
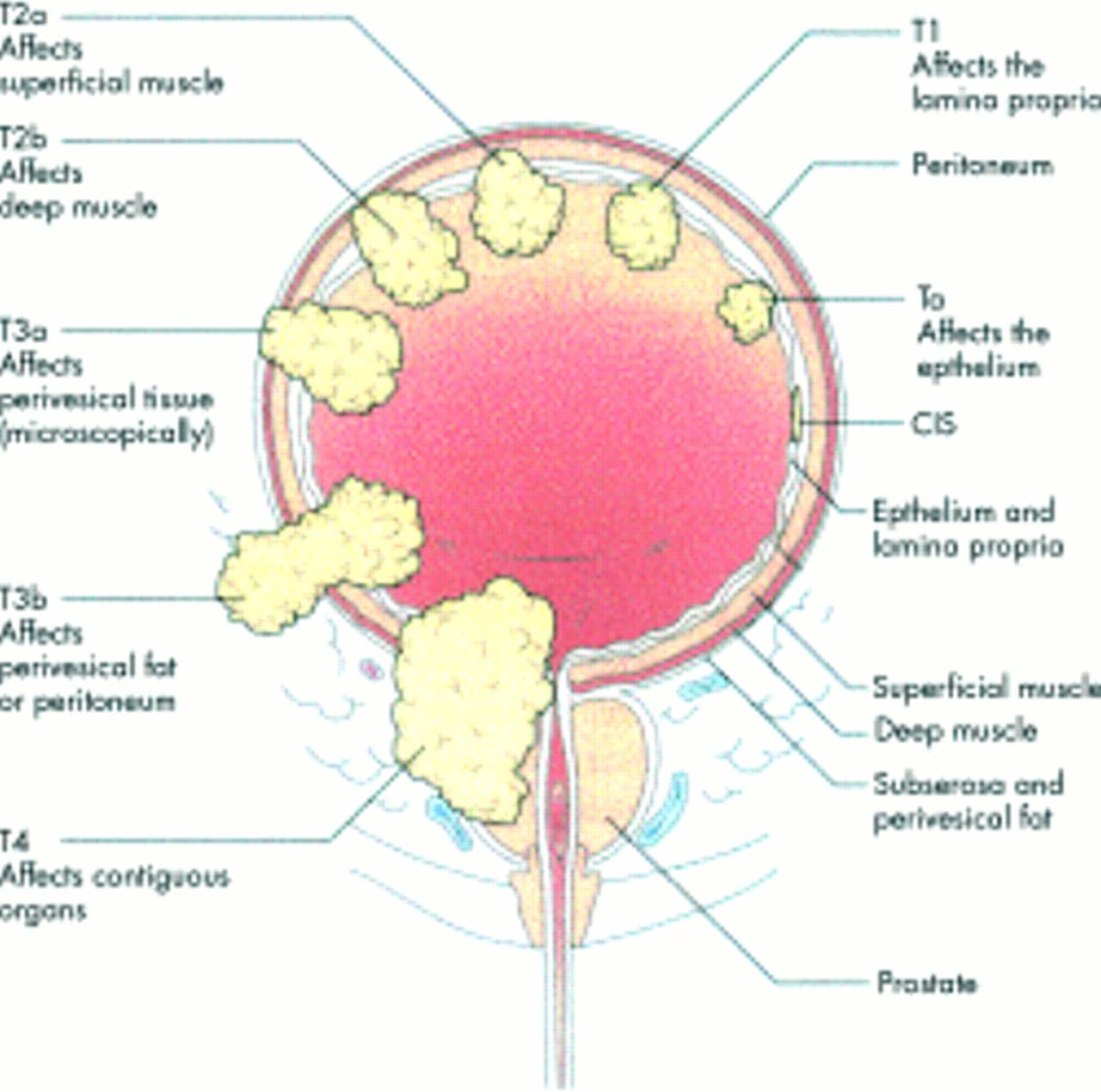
Bladder cancer can be either early stage or invasive .
The stages range from TA to IV . In the earliest stages , the cancer is confined to the lining of your bladder or in the connective tissue just below the lining, but hasnt invaded the main muscle wall of your bladder.
Stages II to IV denote invasive cancer:
A more sophisticated and preferred staging system is TNM, which stands for tumor, node involvement and metastases. In this system:
Metastatic Bladder Cancer Treatment
Without a professional evaluation, it can be difficult to know if the symptoms youre experiencing are the result of bladder cancer or something else. While its important not to panic most of these issues can be caused by other, less serious conditions its also important to talk with an expert if you notice something out of the ordinary. The earlier that bladder cancer is detected, the more treatment options youre likely to have.
You May Like: Bladder Infection In Toddler Girl Symptoms
Morphologic Variants Of Urothelial Carcinoma
Some cases of urothelial carcinoma show morphologic patterns that are recognized as variants morphology. Those include nested variant, micropapillary, lymphoepithelioma-like, sarcomatoid, small cell carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma. These are frequently under-recognized in bladder biopsies and could have therapeutic implications with different criteria for surgery and different chemotherapy regimens.
Latest Treatment For Bladder Cancer
Intravesical therapy is a newer treatment for people who have bladder cancer. With intravesical therapy, the doctor puts a liquid medication right into your bladder rather than administering it orally or injecting it into your blood. The medication is put in through a catheter thats placed into your bladder through the urethra. The medication stays in your bladder for up to two hours, so it can affect the cells lining the inside of the bladder without having major effects on other parts of your body. Intravesical therapy is commonly used after transurethral resection of bladder tumor . Its often performed within 24 hours of the TURBT procedure. The goal is to kill any cancer cells that may be left in the bladder.
Intravesical chemotherapy is used to treat non-invasive bladder cancer. It is used for these early-stage cancers because medication given this way mostly affects the cells lining the inside of the bladder. It has little to no effect on cells elsewhere. This means any cancer cells outside of the bladder lining are not treated by intravesical chemotherapy.
Also Check: Fastest Way To Cure Bladder Infection
Second Opinion For Peace Of Mind
Desperate for Hope,
I am very sorry for the situation. I can image the anguish you are having with the occurrence. Your bravery surprises me and I applaud you for the evident efforts you are doing to have the best diagnosis and treatment for your husband. He is very fortunate.I do not want my comments to distract you from your good work, however, I think you should get second opinions from an independent physician/radiologist, which opinion would provide you the deserved peace of mind.
The information you share above allows a newer perception of the diagnosis following your post of Oct 17. Things are moving fast and spinning around.The MRImp will add information for what has been found . Probably this MRI exam will conclude the process of staging and the story so far is not pleasant. Cancer spread into the bladder, if any, up to the ureters tubes are still classified localized but the probable T3 is now/becomes T4 disease. This may be the basis of the radiologist that follows the CAR guilines in radiotherapies.
Max above is also suspicious of the affair. The clinical trial of your link is sponsored by the University Health Network, Toronto, Canada, now recruiting patients. Logically a number of hospitals/clinics and physicians are in charge of supplying patients. I believe your urologist to make part of their list for his proposal to you.
I would appreciate if you can post the images taken in the cystoscopy.
Best of lucks,
What about Clinical Trials?
Patients Can Enter Clinical Trials Before During Or After Starting Their Cancer Treatment
Some clinical trials only include patients who have not yet received treatment. Other trials test treatments for patients whose cancer has not gotten better. There are also clinical trials that test new ways to stop cancer from recurring or reduce the side effects of cancer treatment.
Clinical trials are taking place in many parts of the country. Information about clinical trials supported by NCI can be found on NCIs clinical trials search webpage. Clinical trials supported by other organizations can be found on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
Don’t Miss: Pressure Tank Bladder For Sale
Turbt/ Repeat Resection: Timing Technique Goal Indication
Guideline Statement 12
12. In a patient with non-muscle invasive disease who underwent an incomplete initial resection , a clinician should perform repeat transurethral resection or endoscopic treatment of all remaining tumor if technically feasible.
Discussion
Incomplete resection is likely a significant contributing factor to what have been described and diagnosed as early recurrences, as tumors have been noted at the first follow-up cystoscopic evaluation in up to 45% of patients. 57 The Panel recognizes specific, albeit rare, circumstances in which transurethral resection is not likely to impact clinical management and may be omitted for patients with incompletely resected non-muscle invasive disease. Examples of such patients include those with large-volume, high-grade tumors not amenable to complete endoscopic resection for whom immediate radical cystectomy is planned. An additional example includes those patients with a tumor diagnosed within a bladder diverticulum and for whom subsequent surgical resection is planned. However, for the majority of patients, complete resection is essential for adequate staging and optimal clinical management. Although surgeons may utilize BLC for this situation, of note, there is insufficient evidence in this repeat transurethral resection setting to support the routine use of enhanced or BLC versus standard WLC, particularly in light of the noted increase in false positive diagnosis with BLC following recent TURBT. 116-118
Discussion
Low Grade And High Grade
Bladder cancer can also be described as either low grade or high grade.
Low grade bladder cancer means that your cancer is less likely to grow, spread and come back after treatment. High grade means your cancer is more likely to grow spread and come back after treatment.
For example, if you have early bladder cancer but the cells are high grade, youâre more likely to need further treatment after surgery. This is to reduce the risk of your cancer coming back.
Low grade is the same as grade 1. High grade is the same as grade 3. Grade 2 can be split into either low or high grade. Carcinoma in situ tumours are high grade.
Don’t Miss: Why Does Bladder Leakage Occur
What Is An Urothelial Neoplasm
Urothelial neoplasia is a unique cancer in that is consists of a spectrum of tumors with different biologic behaviors. The most common urothelial neoplasm is the low grade superficial papillary carcinoma or papilloma which may recur numerous times but does not result in significant morbidity or mortality.
Where Does Prostate Cancer Spread
The most common place for prostate cancer to spread to is the bones. It can also spread to the lymph nodes, liver and lungs and other organs.
A large tumour in the prostate gland can spread into or press on areas around the prostate, such as the back passage or urethra. The urethra is the tube which carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
Read Also: Treatment Of Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
Survival For All Stages Of Bladder Cancer
Generally, for people diagnosed with bladder cancer in England:
- around 75 out of every 100 survive their cancer for 1 year or more after diagnosis
- almost 55 out of every 100 survive their cancer for 5 years or more after they are diagnosed
- around 45 out of every 100 survive their cancer for 10 years or more after diagnosis
Cancer survival by stage at diagnosis for England, 2019Office for National Statistics
These statistics are for net survival. Net survival estimates the number of people who survive their cancer rather than calculating the number of people diagnosed with cancer who are still alive. In other words, it is the survival of cancer patients after taking into account that some people would have died from other causes if they had not had cancer.
Cellular Classification Of Bladder Cancer
More than 90% of bladder cancers are transitional cell carcinomas derived from the uroepithelium. About 2% to 7% are squamous cell carcinomas, and 2% are adenocarcinomas. Adenocarcinomas may be of urachal origin or nonurachal origin the latter type is generally thought to arise from metaplasia of chronically irritated transitional epithelium. Small cell carcinomas also may develop in the bladder. Sarcomas of the bladder are very rare.
Pathologic grade of transitional cell carcinomas, which is based on cellular atypia, nuclear abnormalities, and the number of mitotic figures, is of great prognostic importance.
References
You May Like: Body Cancer Symptoms
Don’t Miss: Chemotherapy For Bladder Cancer Survival Rate
The Effect Of Age At Diagnosis With Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis To Liver
The Kaplan Meier survival curve showed significant difference in overall survival for patients diagnosed at different age groups . The overall survival time was negatively correlated with the age at diagnosis. Among the three groups, the prognosis of patients diagnosed at age less than 52 years old was the best, and of which the median survival time was 1 year. .
Kalpan Meier survival curve showing the effect of age at diagnosis with pancreatic cancer metastasis to liver.
What Causes Bladder Cancer And Am I At Risk
Each year, about 83,730 new cases of bladder cancer will be diagnosed in the United States. It affects more men than women and the average age at diagnosis is 73.
Cigarette smoking is the biggest risk factor for bladder cancer. About half of all bladder cancers are caused by cigarette smoking. Other risk factors for developing bladder cancer include: family history, occupational exposure to chemicals , previous cancer treatment with cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide, or pelvic radiation, the medication pioglitazone, exposure to arsenic , aristolochic , bladder infections caused by schistosoma haematobium, not drinking enough fluids, a genetic condition called Lynch Syndrome, a mutation of the retinoblastoma gene or the PTEN gene. and neurogenic bladder and the overuse of indwelling catheters.
Also Check: Antibiotics Given For Bladder Infection
Intrahepatic Chemotherapy And Chemoembolisation
Intrahepatic chemotherapy and chemoembolisation involve giving chemotherapy directly into the liver. This is done through a thin tube, called a catheter, into the main blood supply to the liver.
Giving chemotherapy directly into the liver means a higher concentration of the drug can be delivered to the area of cancer.
In chemoembolisation, the chemotherapy is delivered along with an oily liquid or foam which blocks the blood supply to the cancer. The cancer is deprived of oxygen and nutrients, and the chemotherapy stays in the area for longer. The liver continues to be supplied with blood in the normal way.
These treatments may not be routinely available on the NHS but may be offered as part of a clinical trial.
Also Check: How Long Does It Take Azo Bladder Control To Work
Low Grade And High Grade Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer starts in the lining of the bladder in about 90 percent of people diagnosed with this cancer. Bladder cancer is called low grade or high grade.
- Low-grade bladder cancer means the cancer has not invaded the muscles around the bladder . People rarely die from this type of bladder cancer, it often recurs after treatment.
- High-grade bladder cancer also often recurs and has a higher chance of spreading to other parts of the body. Almost all deaths from bladder cancer result this type so it is treated more aggressively.
Read Also: Bladder Infection In Older Adults