What Kind Of Treatment Will I Need
There are many ways to treat bladder cancer. You might want to get a second opinion about the best treatment plan for you.
Bladder cancer is most often treated with:
- Surgery
- Chemo
- Immunotherapy
Sometimes more than one type is used. The treatment plan thats best for you depends on:
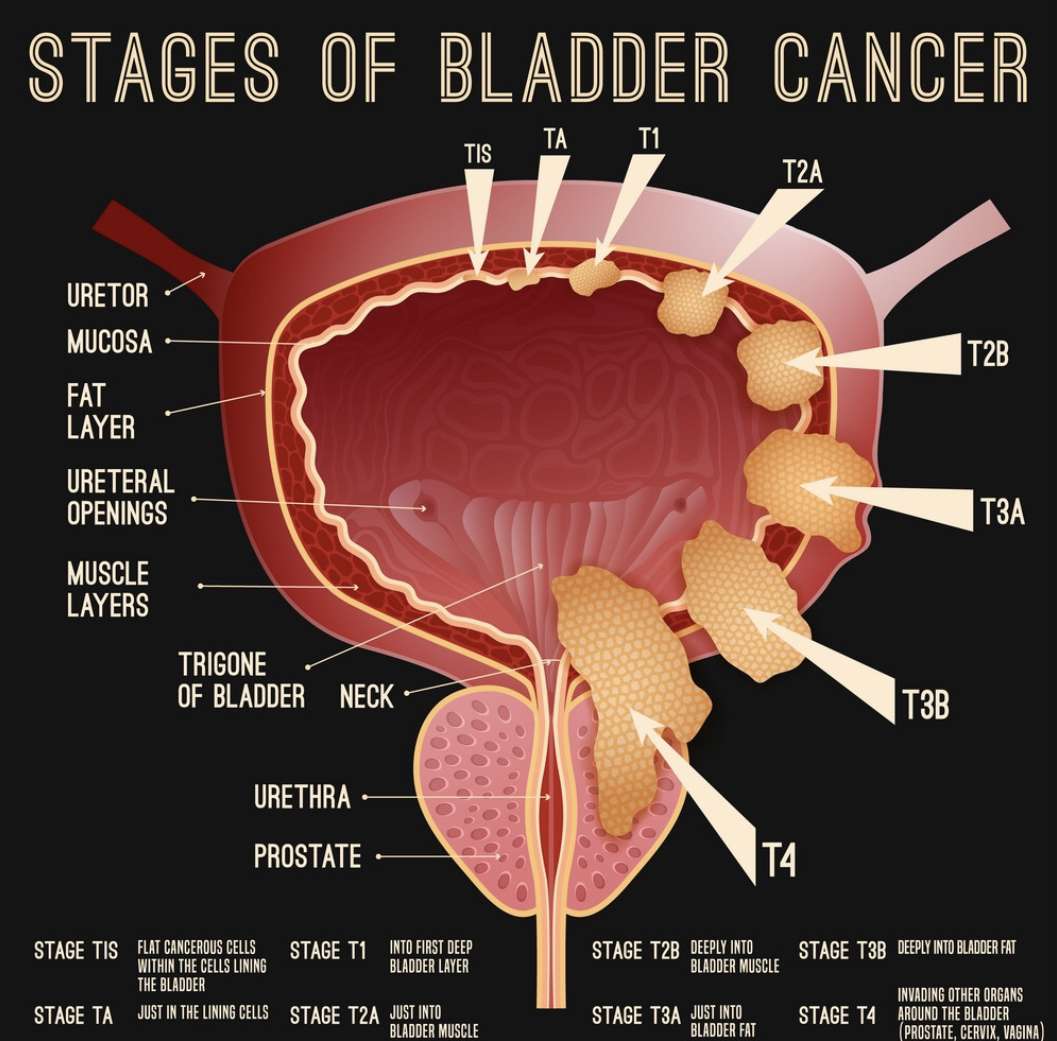
- The stage and grade of the cancer
- Whether the cancer has spread into the bladder wall
- The chance that a type of treatment will cure the cancer or help in some way
- Other health problems you have
- Your feelings about the treatment and the side effects that come with it
Five Types Of Standard Treatment Are Used:
Surgery
One of the following types of surgery may be done:
- Transurethral resection with fulguration: Surgery in which a cystoscope is inserted into the bladder through the urethra.A tool with a small wire loop on the end is then used to remove thecancer or to burn the tumor away with high-energy electricity. This is known as fulguration.
- Radical cystectomy: Surgery to remove the bladder and anylymph nodes and nearby organs that contain cancer. This surgery may bedone when the bladder cancer invades the muscle wall, or when superficialcancer involves a large part of the bladder. In men, the nearby organs that areremoved are the prostate and the seminal vesicles. In women, the uterus, theovaries, and part of the vagina are removed. Sometimes, when the cancer hasspread outside the bladder and cannot be completely removed, surgery to removeonly the bladder may be done to reduce urinarysymptoms caused by the cancer.When the bladder must be removed, the surgeon creates another way for urine toleave the body.
- Partial cystectomy: Surgery to remove part of thebladder. This surgery may be done for patients who have a low-grade tumor thathas invaded the wall of the bladder but is limited to one area of the bladder.Because only a part of the bladder is removed, patients are able to urinate normally afterrecovering from this surgery. This is also called segmental cystectomy.
- Urinary diversion: Surgery to make a new way forthe body to store and pass urine.
Radiation therapy
Chemotherapy
How Is Metastatic Bladder Cancer Treated
The way that metastatic bladder cancer is treated depends primarily on where the cancer has spread and the type of cells that make up the primary tumor. Its important to remember that when bladder cancer spreads, the secondary tumors are still considered to be bladder cancer not lung cancer, liver cancer or any other type of malignancy. Potential treatment options may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy and clinical trials.
At Moffitt Cancer Center, weve treated many patients with metastatic bladder cancer, creating tailored treatment plans for every single one. To help ease the burdens of treatment, we also offer comprehensive supportive care services for patients and their caregivers.
Don’t Miss: Best Homeopathic Medicine For Overactive Bladder
Treatment By Type And Stage Of Bladder Cancer
Noninvasive and non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer
People with low-grade noninvasive bladder cancer are treated with TURBT first. Low-grade noninvasive bladder cancer rarely turns into aggressive, invasive, or metastatic disease, but patients are at risk for developing more low-grade cancers throughout their life. This requires long-term checkups, called surveillance, using cystoscopy and urine cytology . To reduce the risk of future tumors developing, people may receive intravesical chemotherapy after TURBT.
Most commonly, people with high-grade noninvasive , carcinoma in situ , or non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer are treated with TURBT, followed by local intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guerin . This combination of treatments is given to reduce the risk of the cancer from coming back, called recurrence, and the development of muscle-invasive disease. Before treatment with BCG, patients will need to have another TURBT to make sure that the cancer has not spread to the muscle. The first round of BCG treatment is given every week for 6 weeks. After that, the provider performs a cystoscopy and sometimes a bladder biopsy to see if all of the cancer has been eliminated. If the cancer is gone, patients usually have maintenance therapy with BCG, which may be given once every 3 months for the first 6 months and then once every 6 months after that, for 1 to 3 years. This will then be followed with long-term surveillance.
Muscle-invasive bladder cancer
Bladder preservation
Sexuality And Bladder Cancer
Having bladder cancer and treatment can change the way you feel about yourself, other people, relationships and sex. These changes can be very upsetting and hard to talk about. Doctors and nurses are very understanding and can give you support. You can ask for a referral to a counsellor or therapist who specialises in body image, sex and relationships.
Also Check: Can You Have A Bladder Infection Without Symptoms
Problems Emptying Your Bladder
If the cancer is pressing on your urethra or the opening of your bladder, you may find it difficult to empty your bladder fully. This can sometimes cause urine retention, where urine is left in your bladder when you urinate. There are several things that can help, including the following.
- Drugs called alpha-blockers. These relax the muscles around the opening of the bladder, making it easier to urinate.
- A catheter to drain urine from the bladder. This is a thin, flexible tube that is passed up your penis into your bladder, or through a small cut in your abdomen .
- An operation called a transurethral resection of the prostate to remove the parts of the prostate that are pressing on the urethra.
What Types Of Testing Should I Expect For Monitoring My Condition
Since metastatic prostate cancer isnt curable, your doctor will most likely set up regular visits to check the cancers location, and to manage any long-term side effects from the cancer or any medication youre taking.
And since treatments for advanced prostate cancer are changing so fast and need to be given in a certain sequence to be the most effective, youll probably have not only a prostate cancer doctor but other specialists taking care of you. Your care team should coordinate closely, say the authors of a major study of such teams published in August 2015 in the journal Annals of Oncology.
Along with regularly testing your prostate-specific antigen levels, your care team may request blood tests that measure such prostate cancer indicators as alkaline phosphatase and lactate dehydrogenase. Magnetic resonance imaging or PET scans of the spine or other bones can also help identify how your cancer responds to treatment.
If youve had radiation, youre at an increased risk for bladder and colorectal cancer and should get screened regularly for these as well.
The tests youll have and how often youll need them should be customized to you. Your care team will consider your overall health, medications that are safe for you to take, other health conditions you might have, and what stage your cancer was when you were diagnosed.
Read Also: Bladder Or Urinary Tract Infection
Lymphatic Drainage Of The Bladder
The lymphatic drainage from the bladder involves many regions within and beyond the pelvis . The specific route of lymphatic spread from the bladder is complex and impacted by the primary location of the tumor . Roth et al. performed a prospective study of 60 patients to assess the primary lymphatic landing site from the bladder and showed that while the major lymphatic landing sites are regional lymph nodes, a small majority of cases showed drainage initially to more distant lymph nodes, such as the common iliac or paraortic regions . Given this pattern, it is not surprising that the most commonly effected sites of nodal involvement are the obturator and internal iliac regions .
How Fast Does Prostate Cancer Spread To The Bones
Early detection can catch prostate cancer even before there are any symptoms. Some types of prostate cancer grow very slowly.
There are four main stages of prostate cancer. Within each stage, the cancer is graded based on factors like the size of tumor, prostate-specific antigen level, and other clinical signs.
If the cancer has spread to the bones, its considered to be the most advanced, or stage 4.
Newer lab tests look at the genes inside cancer cells. This can provide more information on how quickly the prostate cancer may progress.
Theres also a grading system known as the Gleason system, which assigns the cancer into a grade group based on how closely it resembles normal tissue.
During the biopsy to diagnose prostate cancer, the cells are closely examined. The more abnormal cells that are in the biopsy sample, the higher the Gleason score and grade group.
When more abnormal cells are present, the cancer is more likely to spread quickly.
Also Check: Do Probiotics Help With Bladder Infections
Changes In Bladder Habits Or Symptoms Of Irritation
Bladder cancer can sometimes cause changes in urination, such as:
- Having to urinate more often than usual
- Pain or burning during urination
- Feeling as if you need to go right away, even when your bladder isn’t full
- Having trouble urinating or having a weak urine stream
- Having to get up to urinate many times during the night
These symptoms are more likely to be caused by a urinary tract infection , bladder stones, an overactive bladder, or an enlarged prostate . Still, its important to have them checked by a doctor so that the cause can be found and treated, if needed.
Treatment Of Stage Iv Bladder Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage IV bladder cancer that has not spread to other parts of the body may include the following:
- Urinary diversion or cystectomy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
Treatment of stage IV bladder cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, such as the lung, bone, or liver, may include the following:
- External radiation therapy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Urinary diversion or cystectomy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- A clinical trial of new anticancer drugs.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Read Also: Can You Take Amoxicillin For A Bladder Infection
Patients Can Enter Clinical Trials Before During Or After Starting Their Cancer Treatment
Some clinical trials only include patients who have not yet received treatment. Other trials test treatments for patients whose cancer has not gotten better. There are also clinical trials that test new ways to stop cancer from recurring or reduce the side effects of cancer treatment.
Clinical trials are taking place in many parts of the country. Information about clinical trials supported by NCI can be found on NCIs clinical trials search webpage. Clinical trials supported by other organizations can be found on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
Side Effects Of Prostate Surgery
The major possible side effects of radical prostatectomy are urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction . These side effects can also occur with other forms of prostate cancer treatment.
Urinary incontinence: You may not be able to control your urine or you may have leakage or dribbling. Being incontinent can affect you not only physically but emotionally and socially as well. These are the major types of incontinence:
- Men with stress incontinence might leak urine when they cough, laugh, sneeze, or exercise. Stress incontinence is the most common type after prostate surgery. Itâs usually caused by problems with the valve that keeps urine in the bladder . Prostate cancer treatments can damage this valve or the nerves that keep the valve working.
- Men with overflow incontinence have trouble emptying their bladder. They take a long time to urinate and have a dribbling stream with little force. Overflow incontinence is usually caused by blockage or narrowing of the bladder outlet by scar tissue.
- Men with urge incontinencehave a sudden need to urinate. This happens when the bladder becomes too sensitive to stretching as it fills with urine.
- Rarely after surgery, men lose all ability to control their urine. This is called continuous incontinence.
After surgery for prostate cancer, normal bladder control usually returns within several weeks or months. This recovery usually occurs slowly over time.
There are several options for treating erectile dysfunction:
You May Like: Will Amoxicillin Treat A Bladder Infection
Bone Metastases In Patients With Metastatic Crpc
In approximately 80% of PCa patients bone metastases represent the initial and main metastatic site and are an important prognostic factor . About half of PCa patients with untreated bone metastases will experience at least one SRE over the period of 2 years .
The knowledge of the mechanisms underlying the development of bone metastases and the correlation between bone and cancer cells is of special importance with regard to the different therapeutic options for the management and prevention of SREs. Bone metastases in PCa are frequently osteoblastic, however an osteolytic element has also been confirmed in various reports , and the majority of lesions tend to be heterogeneous .
In clinical trials of bone-modifying agents for the treatment of bone metastases, the incidence of SREs was used as a composite primary endpoint , and they are recognized by the US Food and Drug Administration as a suitable endpoint to assess the efficacy of agents for the treatment of bone metastases in patients with cancer .
Dont Miss: Is Prostate Cancer Genetically Inherited
Treatment Of Recurrent Bladder Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of recurrentbladder cancer depends on previous treatmentand where the cancer has recurred. Treatment for recurrent bladder cancer mayinclude the following:
- Radiation therapy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- A clinical trial of a new treatment.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Don’t Miss: Early Symptoms Bladder Cancer Woman
Case : Metastatic Bladder Cancer To Adrenal Gland/liver/lung
A 56-year-old man with bladder cancer was initially treated with radical cystectomy followed by chemotherapy. Follow-up scan including a PET-CT showed an isolated area with high uptake in his left adrenal gland consistent with recurrent metastatic bladder cancer. He was also having side effects from systemic chemotherapy and needed a break. He was referred for consideration of SBRT to his isolated recurrence after surgery and chemotherapy. He was simulated in the supine position in an immobilization device. PET-CT images were co-registered with simulation CT images. Target delineation was performed by the radiation oncologist and the nuclear medicine radiologist. Tumor motion data from 4D-CT dataset were used to plan PTV. SBRT with daily image-guidance approach was taken whereby the metastatic tumor was prescribed 30 Gy in 5 fractions . Rapid fall off was achieved with the treatment plan to for conformal avoidance of small bowels and kidney . Follow-up imaging showed decrease in the adrenal mass.
Ho Kyung Seo, … Sung Han Kim, in, 2018
How Is Bladder Cancer Treated
Treatment for bladder cancer will depend on the stage and type of cancer you have. Your provider will talk to you about treatment options and which plan of care is best for you.
Superficial Bladder Cancer
Superficial bladder cancer is bladder cancer that has not invaded into the muscle. It is often treated with surgery and intravesicular therapy.
Surgery
A TURBT is a surgical treatment in which a surgeon removes the bladder tumor using a tool placed into the body through the urethra. The extent of the disease is based mainly on findings during this test. TURBT is the main treatment for superficial disease since all of the tumor is often able to be removed. After a TURBT, you may have intravesicular therapy to prevent the cancer from coming back.
Intravesicular Therapy
Intravesicular therapy is when chemotherapy or immune therapy is injected directly into the bladder. This treatment destroys any remaining cancer cells. Both immunotherapy and chemotherapy medications can be used in intravesicular therapy.
Bacillus Calmette-Guerin is an immunotherapy medication that is used. BCG is a type of virus that works to stimulate the immune system to destroy any cancer cells in the area. You will likely be given this medication multiple times. After treatment, you will have regular cystoscopies to monitor for any reoccurrence or new tumor development.
Muscle Invading Bladder Cancer
Surgery
Chemotherapy
Bladder Preservation Therapy
Radiation and Chemoradiation
Immunotherapy
Read Also: Why Do I Get A Bladder Infection After Intercourse
What Is Stage 4 Bladder Cancer
Being diagnosed with bladder cancer can be overwhelming, especially if its stage 4.
Stage 4 bladder cancer is the most advanced stage and carries the worst prognosis. Many cancer treatments will be both difficult and challenging.
However, treatment can reduce or even eliminate your symptoms and help you live a longer, more comfortable life.
Its important to consider the pros and cons of treating stage 4 bladder cancer because treatments come with side effects and risks.
Symptoms of bladder cancer can include:
- blood or blood clots in your urine
- pain or burning during urination
- frequent urination
- needing to urinate at night
- needing to urinate but not being able to
- lower back pain on one side of the body
These symptoms commonly lead to a diagnosis, but they arent unique to stage 4 bladder cancer.
Stage 4 bladder cancer is also called metastatic bladder cancer. This means the cancer has spread outside of the bladder into other parts of the body.
People with metastatic cancer may experience symptoms relating to where the cancer has spread. For example, if a persons bladder cancer has spread to their lungs, they may experience chest pain or increased coughing.
Metastatic bladder cancer is difficult to cure because it has already traveled to other parts of the body. The later youre diagnosed and the farther the cancer has traveled, the less chance that your cancer will be cured.
The 5-year survival rate is the rate of surviving for 5 years after a cancer diagnosis.