Urinary Tract Infections In Women
UTIs are common, particularly with increasing age. Women are more likely to get a UTI than men. Nearly 1 in 3 women will have a UTI needing treatment before the age of 24.
In women, the urethra is short and straight, making it easier for germs to travel into the bladder. For some women, UTIs relate to changes in their hormonal levels. Some are more likely to get an infection during certain times in their menstrual cycle, such as just before a period or during pregnancy.
In older women, the tissues of the urethra and bladder become thinner and drier with age as well as after menopause or a hysterectomy. This can be linked to increased UTIs.
During pregnancy, the drainage system from the kidney to the bladder widens so urine does not drain as quickly. This makes it easier to get a UTI. Sometimes germs can move from the bladder to the kidney causing a kidney infection. UTIs during pregnancy can result in increased blood pressure, so it is very important to have them treated as soon as possible.
Women are more at risk of repeated UTIs if they:
- use spermicide jelly or diaphragm for contraception
- have had a new sexual partner in the last year
- had their first UTI at or before 15 years of age
- have a family history of repeated UTIs, particularly their mother
- suffer from constipation
Urgent Advice: Ask For An Urgent Gp Appointment Or Get Help From Nhs 111 If:
You think you, your child or someone you care for may have a urinary tract infection and:
- a very high temperature, or feeling hot and shivery
- a very low temperature below 36C
- are confused, drowsy or have difficulty speaking
- have not been for a pee all day
- have pain in the lower tummy or in the back, just under the ribs
- can see blood in their pee
These symptoms could mean you have a kidney infection, which can be serious if it’s not treated as it could cause .
You can call 111 or get help from 111 online.
Other Causes Of Utis In Women And Men
1. Constipation
Being constipated makes you susceptible to UTIs as it prevents your bladder from emptying fully.26
2. Diarrhea
Bacteria from your bowels can easily reach your urethra when you suffer from diarrhea, resulting in UTIs.27
3. Diabetes
People with diabetes are prone to UTIs because of immune system impairments, improper metabolic control, and incomplete bladder emptying.28
4. Kidney Stones
Kidney stones can obstruct the flow of urine due to which it may be difficult for you to empty your bladder fully.29
5. HIV/Aids
People with acquired immunodeficiency disease syndrome/human immunodeficiency virus have a high risk of contracting UTIs because their immune system will not be able to fight infections effectively.30
6. Urological Abnormalities
Urological abnormalities are often associated with UTIs that are complicated.31 Treatment of such patients is individualized to minimize complications and risks of future infections.
You May Like: Bladder Problems After Gastric Bypass
This Is How Uti Happens
- E.coli bacteria cause 90% of all UTIs.
- These bacteria live in your intestines and are present in your poop and on your genitals.
- If there are too many of them, they could be easily carried out toward urethra during sex to cause a UTI.
- Location, location, location! Its unfortunate that womens clitoris is right next to urethra. And for guys, the urethra is, obviously is in the penis. Both organs are frequently used during sex.
- Every time you introduce pathogenic bacteria in your urethra, there is a chance that you could contract a UTI.
Causes Of Urinary Tract Infections
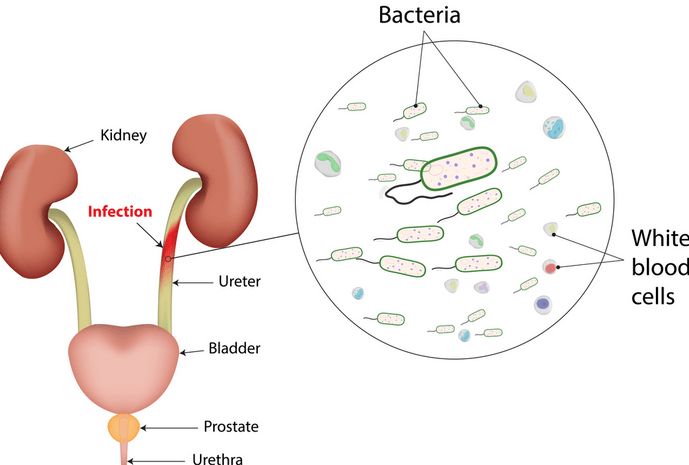
Urinary tract infections are usually caused by bacteria from poo entering the urinary tract.
The bacteria enter through the tube that carries pee out of the body .
Women have a shorter urethra than men. This means bacteria are more likely to reach the bladder or kidneys and cause an infection.
Things that increase the risk of bacteria getting into the bladder include:
- having sex
-
do not use scented soap
-
do not hold your pee in if you feel the urge to go
-
do not rush when going for a pee try to fully empty your bladder
-
do not wear tight, synthetic underwear, such as nylon
-
do not drink lots of alcoholic drinks, as they may irritate your bladder
-
do not have lots of sugary food or drinks, as they may encourage bacteria to grow
-
do not use condoms or a diaphragm or cap with spermicidal lube on them try non-spermicidal lube or a different type of contraception
Recommended Reading: What Happens When A Bladder Infection Goes Untreated
The Link Between Utis And Sex: Causes And How To Prevent Them
One common way women get urinary tract infections is by having sex. But that doesn’t mean you have to banish sex from your life to prevent painful infections.
Mosuno/Stocksy
Pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections arent the only consequences of having sex. For some women, a urinary tract infection can also be a result.
Blame it on anatomy, which makes a UTI more likely for women than for men, says Sujata Yavagal, MD, a urogynecologist at Baptist Health South Florida in Miami.
Still, it isnt inevitable that having sex will cause a UTI. Taking proper precautions can minimize your odds.
RELATED: 8 Home Remedies for Urinary Tract Infection Symptoms
How Are Urinary Tract Infections Diagnosed
Your doctor will use the following tests to diagnose a urinary tract infection:
- Urinalysis: This test will examine the urine for red blood cells, white blood cells and bacteria. The number of white and red blood cells found in your urine can actually indicate an infection.
- Urine culture: A urine culture is used to determine the type of bacteria in your urine. This is an important test because it helps determine the appropriate treatment.
If your infection does not respond to treatment or if you keep getting infections over and over again, your doctor may use the following tests to examine your urinary tract for disease or injury:
- Ultrasound: In this test, sound waves create an image of the internal organs. This test is done on top of your skin, is painless and doesnt typically need any preparation.
- Cystoscopy: This test uses a special instrument fitted with a lens and a light source to see inside the bladder from the urethra.
- CT scan: Another imaging test, a CT scan is a type of X-ray that takes cross sections of the body . This test is much more precise than typical X-rays.
Recommended Reading: Not Being Able To Hold Bladder
Can A Guy With Uti Pass It To His Female Partner
Logically speaking, If you are a male with a urinary tract infection, you could potentially introduce some bacteria causing UTIs to your female partners vagina.
Your sperm travels exactly through the same route as your urine does, and some of the bacteria could be still in your urethra.
However, if you just started your antibiotics, it means your urethra and bladder probably do not have much active pathogenic bacteria.
Even if there are traces of pathogenic bacteria in your urethra, we can speculate that it would not be more than she has on her own genitals at any given time.
Moreover, regardless of where E.coli come from , its up to your girlfriends vagina how to expel the pathogenic bacteria.
If the vaginal flora is compromised, the pathogen could establish a base in the vagina and will wait till an opportunity presents itself to reach females urethra and trigger a UTI.
A healthy vaginal flora , on the other hand, is not hospitable to pathogenic bacteria.
Also, keep in mind, if a guy has a UTI, he could experience a very painful ejaculation.
Using the words of one of the UTI sufferers ejaculation feels like my penis is on fire on the inside.
So perhaps, it is better to wait 3-5 days till antibiotics help you to get rid of the infection and the inflammation.
What May Cause A Uti After Sex
The urethra is the tube through which urine exits the body from the bladder. In women, this tube is short, making it quicker and easier for bacteria to enter the opening and infiltrate the bladder.
The bacteria that cause a UTI live in the area around the anus, Dr. Yavagal says. Sex can shift bacteria toward the front. From there, its just a short hop up the urethra into the bladder, where it can multiply and cause a UTI.
RELATED: Everything You Need to Know About Sex Toy Care and Cleanliness
Recommended Reading: How To Know If Cat Has Bladder Infection
Symptoms And Treatment For Urinary Tract Infections
Most people who get UTIs notice symptoms and discomfort. For an infection in your lower urinary tract, you may experience some or all of the following:
- Pain or burning while urinating
- Feeling a need to urinate even when your bladder is empty
- Aches or cramps in your lower abdomen
If the infection is in your kidneys, you may also notice fever and chills, backache, and nausea and vomiting.
If you think you have a UTI, call your doctor to discuss your symptoms. You will likely need to give a urine sample, which may help confirm the diagnosis. Your doctor will prescribe antibiotics to clear up the infection. They might also suggest medicine that will help with the discomfort.
Utis And Sexually Transmitted Diseases
A number of sexually transmitted infections are known to cause UTIs, including trichomoniasis and chlamydia. Oftentimes a person will assume that the UTI is bacterial in nature and fail to identify the underlying STI.
It is, therefore, vital to consider your risk of STIs when any infection of the genitals or urinary tract is involved. This is especially true if you have multiple sex partners or have gotten a UTI after having sex with a new partner.
Current pediatric guidelines recommend that doctors take a comprehensive sexual history of any adolescent with urinary tract complaints and routinely test them for STIs.
Sexually active men under the age of 35 who don’t use condoms can experience a condition called epididymitis. It is an infection of the epididymis, the coiled tube to the back of the testicles, that can be caused either by bacteria or an STI, most often gonorrhea or chlamydia. Treatment varies based on the cause and severity.
Safer sex practices, which include the consistent use of condoms, are always the best plan for reducing the risk of these and other STIs.
Also Check: Treats For Dogs With Struvite Bladder Stones
What Can Happen If A Uti Is Not Treated
If treated right away, a UTI is not likely to damage your urinary tract. But if your UTI is not treated, the infection can spread to the kidneys and other parts of your body. The most common symptoms of kidney infection are fever and pain in the back where the kidneys are located. Antibiotics can also treat kidney infections.
Sometimes the infection can get in the bloodstream. This is rare but life-threatening.
How Is Uti In Men Treated
You develop a urinary tract infection because of bacteria entering your urinary tract. When you have the symptoms, your doctor will prescribe antibiotics to help clear the infection. However, it is better to take some precautionary measures to avoid becoming infected in the first place. For instance:
- Be sure to clean the genital area thoroughly if you are not circumcised.
- Increase your intake of water and include other fluids in your diet.
- Never try to hold your urine for long.
- Be sure to clean your genitals before and after engaging in sexual intercourse.
- Always wear condoms when having sex.
Increasing your intake of water may help flush bacteria out of your urethra, which can relieve the symptoms associated with a UTI. Keep in mind that if you have serious symptoms, you should seek immediate medical attention because a UTI can spread quickly to your kidneys and complicate the whole situation.
Don’t Miss: Ways To Control Your Bladder
Trying To Avoid Getting A Uti During Sex Requires A Lot Of Planning And Mental Energy
If theres any good news to be shared about UTIs, its that many women can prevent them by peeing after sex.
One of our best defenses against newly introduced bacteria is the physical act of urination, which flushes bacteria out, says Dr. Ross. This is why peeing after sex is always a good idea.
But of course, its never that easy. For many women, executing this seemingly simple UTI prevention hack means carefully planning and scheduling both pre- and post-sex hydration so that we can pee as soon as possible after sex, without chugging so much water that were bloated during the actual sex part of the sex.
If that werent complicated enough, were also operating on a timer that begins the second sex does. The longer the time the bacteria have to travel up the urinary tract, the more likely an infection is, says Dr. Ross. This means that after sex, while men and their long urethras get to lie around in a lazy post-coital daze, women have to rush off to the bathroom immediately and/or drink a ton of water so we can pee ASAP.
Even if we manage to pull all of this off perfectly, any woman who has endured the agony of a UTI will probably still end up spending the better part of the next 48 hours in constant fear that her urinary tract is going to erupt in flames at any moment. And yes, if you were wondering, all of this anxiety and mental calculation does have a tendency to kill the mood during sex.
Reasons Why Women Get More Utis Than Men
Dr. Boyd Clary discusses anatomical differences and tips for prevention.
If youve ever felt that burning sensation and frequent need to urinate, youre not alone. One of the most frequent causes for a sick visit to the OB/GYN is a urinary tract infection . A UTI occurs when bacteria enter the urethra and infect part of your urinary system.
UTIs are significantly more common in women than in men. In fact, women get UTIs up to 30 times more often than men. Why? As with most things, there is no one answer. From anatomical differences to hormonal changes and stages of a womans reproductive life cycle, a combination of factors contributes to women being more susceptible to UTIs than men. Lets take a look.
1. Length of Urethra
The biggest reason is female anatomy, particularly with regards to the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body. While the urethra is an exit for urine, it is also an entrance for bacteria to get into the urinary tract. The female urethra is much shorter in length in women than men. The average female urethra is 1-2 inches long compared to the male urethra which is 6 inches long. This is important when it comes to bacteria. Bacteria is seeded at the urethra meatus , which means it has a shorter distance to climb to infect the bladder in females than in males.
2. More Sensitive Skin
3. Placement of Urethra
4. Sexual Contact
5. Specific Types of Contraception
6. Menopause
7. Pregnancy
Don’t Miss: Robotic Surgery For Bladder Cancer
How Is It Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms and medical history. You may have lab tests of your urine and discharge from the urethra and prostate gland.
For serious or repeated infections, you may need:
- An intravenous pyelogram . An IVP is a special type of X-ray of the kidneys, ureters, and bladder.
- An ultrasound scan to look at the urinary tract.
- A cystoscopy. This is an exam of the inside of the urethra and bladder with a small lighted instrument. It is usually done by a specialist called a urologist.
Why Do Girls And Women Get More Frequent Utis
Girls and women get UTIs much more frequently than boys and men, because they have a shorter urethra, and the opening lies closer to the rectum and vagina where bacteria are more likely to be.
Some people who get frequent UTIs may have an abnormality in their urinary tract or a problem with how it functions. The most common functional problem of the urinary tract is called vesicoureteral reflux a condition in which some urine flows backward, or refluxes, from the bladder into the ureters and even up to the kidneys.
Bacteria can find their way into the urethra by several ways. During sexual intercourse, the bacteria in the vaginal area may be pushed into the urethra and eventually end up in the bladder, where urine provides a good environment for the bacteria to grow. Bacteria may also be introduced into a girl’s bladder by wiping from back to front after a bowel movement, which can contaminate the urethral opening. An increased risk of UTIs has been associated with the use of spermicides and diaphragms as contraceptives.
Sexually transmitted diseases may cause UTI-like symptoms, such as pain with urination. If a course of antibiotics does not clear up a UTI, or if you have other symptoms, such as a discolored or smelly discharge from the vagina then see your doctor or a sexual health nurse. If untreated, STDs can lead to serious long-term problems, including pelvic inflammatory disease and infertility. STDs are contagious.
Recommended Reading: Bcg Treatment For Bladder Cancer Side Effects
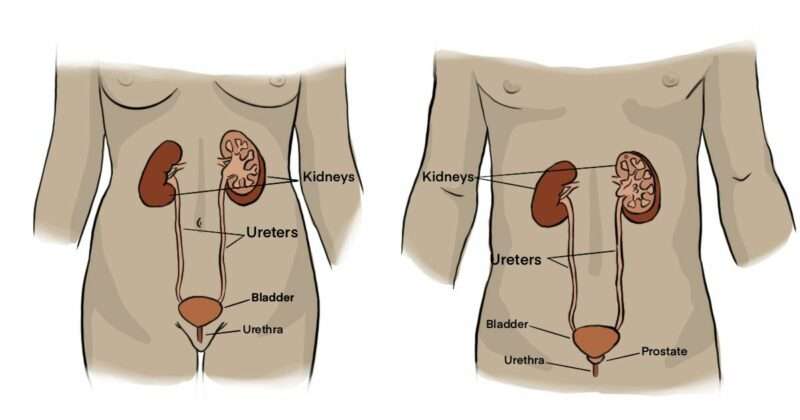
What Is A Urinary Tract Infection
A urinary tract infection is a bacterial infection in any part of your urinary tract. Your urinary tract is the interconnected system of organs that make and store urine. The sections of the urinary tract include:
- Kidneys: The organs that filter waste from your blood and convert the waste and water into urine.
- Bladder: A sac-like organ that stores urine before it leaves your body.
- Ureters: Thin tubes that carry urine from your kidneys to your bladder.
- Urethra: A tube that allows urine to leave your body. â
You can get an infection in any part of the urinary tract. The most common type of UTI is called cystitis, and it is an infection in the bladder. You can also have an infection in the urethra known as urethritis. An infection in the kidneys is known as pyelonephritis and it is the most severe type of UTI.