Can I Become Immune To The Antibiotics Used To Treat A Uti
Your body can actually get used to the antibiotics typically used to treat a urinary tract infection . This happens in people who have very frequent infections. With each UTI and use of antibiotics to treat it, the infection adapts and becomes harder to fight. This is called an antibiotic-resistant infection. Because of this, your healthcare provider may suggest alternative treatments if you have frequent UTIs. These could include:
- Waiting: Your provider may suggest that you watch your symptoms and wait. During this time, you may be encouraged to drink plenty of fluids in an effort to flush out your system.
- Intravenous treatment: In some very complicated cases, where the UTI is resistant to antibiotics or the infection has moved to your kidneys, you may need to be treated in the hospital. The medicine will be given to you directly in your vein . Once youre home, you will be prescribed antibiotics for a period of time to fully get rid of the infection.
Do I Have A Urinary Tract Infection Or Something Else
If you have pain or discomfort when you urinate, its possible that you have a urinary tract infection. But what you may not realize is that other conditions can cause similar symptoms. And since these conditions have different treatments, its important to know what the actual underlying problem is.
Here we discuss what a urinary tract infection is, how its treated, and other conditions that can cause similar symptoms.
What is a urinary tract infection?
A urinary tract infection often called a UTI is an infection of any part of your urinary system. This includes your:
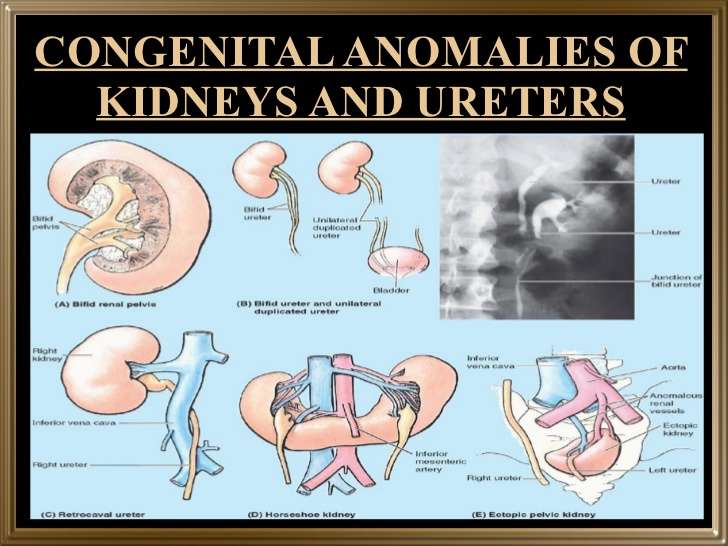
- Kidneys
- Ureters
- Bladder
- Urethra
UTIs can be classified as involving the upper tract or the lower tract . Since infections usually come into the urethra from the outside, most infections involve the lower tract. UTIs can affect people of all ages, and they tend to be more common in women. In fact, some studies have shown that women are eight times more likely than men to develop a UTI.
The most common cause of a UTI is a bacteria called Escherichia coli , which causes more than 80% of infections outside of the hospital. Other types of bacteria and certain types of fungi and viruses can also cause UTIs.
When Should I Call My Healthcare Provider
- Fever.
- Back pain.
- Vomiting.
If you have any of these symptoms, or your other symptoms continue after treatment, call your healthcare provider. A UTI can spread throughout your urinary tract and into other parts of your body. However, treatment is very effective and can quickly relieve your symptoms.
Read Also: How To Do Kegel Exercises For Overactive Bladder
Cystitis In Men And Older People
Men tend to get cystitis later in life. Where trouble with urine flow is a symptom, this may indicate that the underlying cause is a problem with their prostate gland.
Cystitis is common in older people, particularly if they are unwell. Bladder catheters and some urinary-tract operations may also increase the risk of cystitis.
Treatment For Cystitis That Keeps Coming Back
If you keep getting cystitis, a GP may prescribe:
- a single-dose antibiotic to take within 2 hours of having sex, if you’ve noticed sex triggers cystitis
- a low-dose antibiotic to take for up to 6 months
- a vaginal oestrogen cream, if you have gone through the menopause
In some women, antibiotics do not work or urine tests do not pick up an infection even though you have cystitis symptoms.
This may mean you have a long-term bladder infection that is not picked up by current urine tests. Ask the GP for a referral to a specialist for further tests and treatment.
Long-term infections are linked to an increased risk of bladder cancer in people aged 60 and over.
Read Also: Bcg Used In Bladder Cancer
Eating Diet & Nutrition
Experts dont think eating, diet, and nutrition play a role in preventing or treating bladder infections. If you have any type of UTI, talk with a health care professional about how much to drink each day to help prevent or relieve your infection.
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and other components of the National Institutes of Health conduct and support research into many diseases and conditions.
Chronic Uti Treatment Tip
Its pretty apparent that many of the possible causes of chronic UTIs are related to antibiotics that are not working. Fortunately, theres an alternative. Over the past years, medical doctors have been recommending that their chronic patients try a natural supplement known as D-Mannose for symptom relief. Its a well-kept secret, though, because the research shows that only about 6% of women are even aware of D-Mannose.
Here are the features to look for when purchasing this supplement:
1) Only buy 100% pure D-Mannose. You dont want to dilute the effectiveness of this product with additives such as cranberry or hibiscus.
2) Buy it in powder form. When mixed with water, the powder dissolves completely and has no taste. But most important, it goes right to the bladder where it is needed, unlike capsules that need to first be digested in your stomach. 1 scoop a day provides protection against recurrences, and 1 scoop every 2-3 hours for two days eliminates an active infection.
3) Buy it from a trusted source. Many D-Mannose products are produced outside the US by companies that are not certified here, so the quality may not be up to our standards.
To learn more and get the LivingBetter50 discount of 20% on your first purchase, click on the ad nearby.
Don’t Miss: Prognosis Of Bladder Cancer In Females
Utis And Yeast Infections Need Very Different Treatments
The issue is not just that these two infections require different medications to relieve you of your symptoms. Its also that if you try to treat what you think is a yeast infection with over-the-counter meds when its really a UTI , you could eventually be at risk for a kidney infection, or at the very least not actually get rid of your UTI. Youre not going to get better, Dr. Minkin says bluntly about using the wrong treatment.
So, first up, yeast infections: Getting rid of yeast infections really comes down to curbing that Candida overgrowth by using antifungal medications. Depending on the severity of your infection, you might only need a single dose of meds, either vaginally or orally. But if your symptoms are intense or you have recurrent yeast infections , you may need multiple oral or vaginal doses over the course of a few weeks, according to the Mayo Clinic.
If you have a urinary tract infection, youll likely receive a prescription for a short course of antibiotics to help your body fight the bacteria, the Mayo Clinic says. If youre also experiencing pain, your provider might prescribe medication to numb your bladder and urethra when you pee, but the Mayo Clinic notes that, more often than not, your pain will lessen when you start taking the antibiotics. And this bears repeating: You should get treated ASAP because untreated lower urinary tract infections can turn into a painful and dangerous kidney infection.
Related:
What Is The Difference Between Cystitis And Uti
A UTI can occur in any part of the urinary tract: the urethra, ureters, kidneys, or bladder. If the infection stays in the urethra, its considered urethritis. The urethra is a tube that allows the body to expel urine and is connected to the bladder. If the infection occurs in the lower urinary tract and bladder, its considered cystitis. The ureters, two narrow tubes, drain urine from the kidneys into the bladder. Kidneys are responsible for removing waste and excess water from the body. If the infection moves to the upper urinary tract and kidneys, its considered pyelonephritis.
You May Like: Bladder Control Medication Side Effects
What Are The Risk Factors For Getting Bladder Infections And Other Uti Infections
A person is more likely to get a bladder infection if they dont urinate frequently enough. If they hold their urine in, the bacteria can collect in the bladder and lead to infection. Try to go to the bathroom at least every two to three hours to keep this from happening.
Not drinking enough water is another risk factor for bladder infections because your body doesnt move as much urine through the bladder as quickly.
Risk factors for urethritis include having a sexually transmitted infection or from trauma to the urethra, such as due to the insertion of a urinary catheter.
In addition to these specific risk factors for bladder infections, there are general risk factors for all UTI types. These include:
risk factors for uti
- being pregnant
- having diabetes, as a person experiences changes to their immune system that make them more prone to UTIs
- having an enlarged prostate
- having low levels of estrogen, such as when a woman is post-menopausal
- having a history of kidney stones, which can block the flow of urine through the urinary tract
Women are also more likely than men to get UTIs because their urethra is shorter. The bacteria have less distance to go to reach the bladder and can cause infections.
Urgent Advice: Ask For An Urgent Gp Appointment Or Get Help From Nhs 111 If:
You think you or someone else has cystitis and:
- a high temperature, or feeling hot and shivery
- a low temperature, or shaking and shivering
- pain in the lower tummy or in the back, just under the ribs
- are confused, drowsy or have difficulty speaking
- are feeling or being sick
- have not had a pee all day
- blood in your pee
These symptoms could mean you have a kidney infection, which can be serious if its not treated as it could cause .
You can call 111 or get help from 111 online.
Don’t Miss: Bladder Problems After Endometrial Ablation
Bladder Cancer Risk Factors
Factors associated with an increased chance of developing bladder cancer include:
- Sex: Men are 4 times more likely than women to be diagnosed with bladder cancer.
- Age: Bladder cancer mostly affects people > 55 years of age. In the United States, the average age of individuals diagnosed with bladder cancer is 73 years.
- Race: White Americans are approximately 2 times more likely to to have bladder cancer detected compared with African Americans and people of Hispanic ethnicity, while Asian Americans and Native Americans have the lowest rates.
- Smoking: Cigarette smoking is the most important risk factor for bladder cancer, causing around half of all cases. Smokers are at least 3 times as likely to get bladder cancer compared with non-smokers.
- Exposure to certain chemicals in the workplace: Aromatic amines used in the dye industry and organic chemicals used in the production of rubber, leather, paint and textiles may contribute to a higher bladder cancer rates in workers. Painters, printers, hairdressers, and truck drivers are also at increased risk due to workplace exposures.
- Arsenic in drinking water: The likelihood of potentially harmful levels of arsenic in water depends on the water source being used.
- Some medicines: The use of some medicines and certain chemotherapy drugs may be associated with increased bladder cancer risk.
- Previous bladder cancer: People who have had bladder cancer are prone to recurrence.
What Causes Urinary Tract Infections
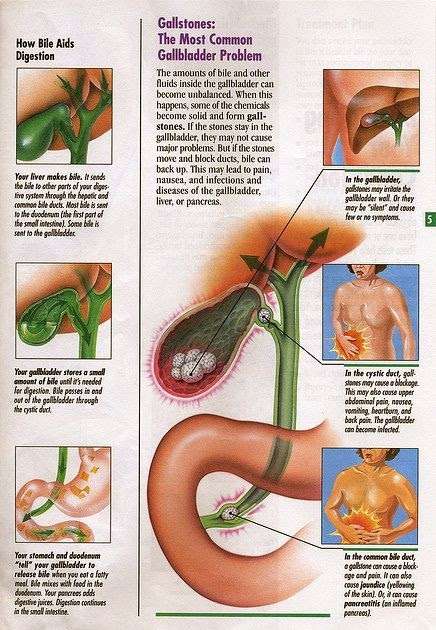
Normal urine is sterile and contains fluids, salts, and waste products. It does not contain bacteria, viruses, or fungi. A UTI occurs when germs, most often bacteria from the digestive tract, get into the opening of the urethra and start to multiply.
Most UTIs are caused by E. coli bacteria, which normally live in the colon.
Also Check: Malignant Neoplasm Of Overlapping Sites Of Bladder
Urinary Tract Infections In Women
UTIs are common, particularly with increasing age. Women are more likely to get a UTI than men. Nearly 1 in 3 women will have a UTI needing treatment before the age of 24.
In women, the urethra is short and straight, making it easier for germs to travel into the bladder. For some women, UTIs relate to changes in their hormonal levels. Some are more likely to get an infection during certain times in their menstrual cycle, such as just before a period or during pregnancy.
In older women, the tissues of the urethra and bladder become thinner and drier with age as well as after menopause or a hysterectomy. This can be linked to increased UTIs.
During pregnancy, the drainage system from the kidney to the bladder widens so urine does not drain as quickly. This makes it easier to get a UTI. Sometimes germs can move from the bladder to the kidney causing a kidney infection. UTIs during pregnancy can result in increased blood pressure, so it is very important to have them treated as soon as possible.
Women are more at risk of repeated UTIs if they:
- use spermicide jelly or diaphragm for contraception
- have had a new sexual partner in the last year
- had their first UTI at or before 15 years of age
- have a family history of repeated UTIs, particularly their mother
- suffer from constipation
How Do Utis Begin
Many types of bacteria live in the intestines and genital area, but this is not true of the urinary system. In fact, urine is sterile. So when errant bacteria, such as the E. coli shown here, is accidentally introduced into the urinary system, it can start a UTI. Typically, bacteria travel up the urethra to the bladder, where an infection can take hold. Women are more susceptible than men, probably because they have shorter urethras.
Don’t Miss: Start Of Bladder Infection What To Do
Peak Organic Alkalizing Greens
At birth your bodys pH is balanced. But starting immediately acid waste builds up and starts to shift your pH level from healthy alkaline to unhealthy acid. If your body is too acidic it provides the right terrain for germs to thrive. To add insult to injuryMORE
But if my patients discomfort is not a result of sexual activity from the previous evening, then I ask patients to consider the other factors at play here, including:
All these lead to bacterial growth where it shouldnt be into the urine contents of the bladder.
Typically identifying the cause can help cut down on occurrences in the future and round of antibiotics can prevent a simple urinary tract infection from becoming more. Lots of water and cranberry juice can help too.
Note: If you take antibiotics for a urinary tract infection, be careful to finish your prescription so you dont inadvertently contribute to the growing threat of antibiotic resistance.
Other Ways To Prevent Cystitis Coming Back
If you keep getting cystitis, there is some evidence you may find it helpful to take:
- D-mannose a sugar you can buy as a powder or tablets to take every day
- cranberry products available as juice, tablets or capsules to take every day
Be aware that D-mannose and cranberry products can contain a lot of sugar. If you’re taking warfarin, you should avoid cranberry products.
Page last reviewed: 11 February 2022 Next review due: 11 February 2025
You May Like: How To Ease Bladder Discomfort
Uti Or Something Else
Although burning during urination is a telltale sign of a UTI, it can also be a symptom of a number of other problems such as a vaginal yeast infection or certain sexually transmitted diseases . These include chlamydia, gonorrhea, and trichomoniasis. Simple lab tests are available to distinguish a UTI from an STD. Interstitial cystitis also has many of the same symptoms as a urinary tract infection. It can happen in both men and women and can start after a UTI. A cystoscopy, a thin tube and camera that is inserted into the bladder, can not diagnosis interstitial cystitis, but it can help identify abnormalities in the badder that cause cystitis.
How Are Utis Treated And Prevented
UTIs are usually treated with antibiotics. The specific antibiotic used and how long treatment lasts depend on the type of bacteria causing the infection and if there are any other health complications.
Some common antibiotics used to treat UTIs include:
- Amoxicillin
- Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
There are also some steps you can take that may help prevent UTIs. These include:
- Practicing good hygiene, including wiping from front to back for women, which helps prevent the spread of bacteria from stool.
- Drinking plenty of water, which increases urination and can help flush out bacteria.
- Avoiding some types of birth control, like spermicide, which in some women may increase the risk of UTIs.
Some studies suggest that cranberry juice and probiotics can help prevent UTIs in women, but more research needs to be done to see how helpful they really are.
If you develop symptoms of a UTI, its important to let your healthcare provider know right away so that you get the right diagnosis and treatment.
Read Also: Antibiotics For Bladder Infection While Pregnant
Women With Similar Symptoms But No Uti
The women with ongoing symptoms but no proven UTI is the group that baffles gynecologists and urologists most. This is in part due to the fact that women have a difficult time explaining exactly what they are experiencing most will start by saying that they have pain down there. This then requires a series of investigations and tests to find out exactly whats causing these symptoms.
Other medical problems that mimic the signs of a UTI are: