What Is A Rectocele
A rectocele is a bulging of the front wall of the rectum into the back of the vagina. The bulge occurs as a result of thinning and weakening of the band of tissue that separates the vagina from the rectum. This thinning has a number of causes, including:
- Advanced age.
- Multiple vaginal childbirths or trauma during childbirth .
- Repeated surgeries in the area of the pelvic floor or rectum.
- Chronic straining during bowel movements due to long-term constipation.
Normal anatomy of rectum
Rectum with rectocele
What Symptoms Would I Have With A Rectocele
Many women with a rectocele have no symptoms, and the condition is only seen in a pelvic examination. In general, if a rectocele isnt causing you symptoms or discomfort, it can be left alone.
When symptoms are present, you may have:
- Difficulty having bowel movements.
- The need to manually reduce the bulge in your vagina to have a bowel movement.
A rectocele should be treated only if your symptoms interfere with your quality of life.
What Happens After A Post
After an ultrasound, you can wipe any remaining gel off your skin, get dressed and go home.
After bladder catheterization, your provider gently removes the catheter from your urethra. You can go home after the procedure. You may feel slight discomfort as the anesthesia wears off. Drinking lots of water, and urinating several times, can help. Your provider may prescribe an antibiotic to prevent urinary tract infection.
If you have signs of urinary retention meaning high residual urine volume your provider will discuss ways to address this. Options could include a catheter , medications and/or surgery.
You May Like: What Do Bladder Spasms Feel Like
What Is An Inability To Urinate
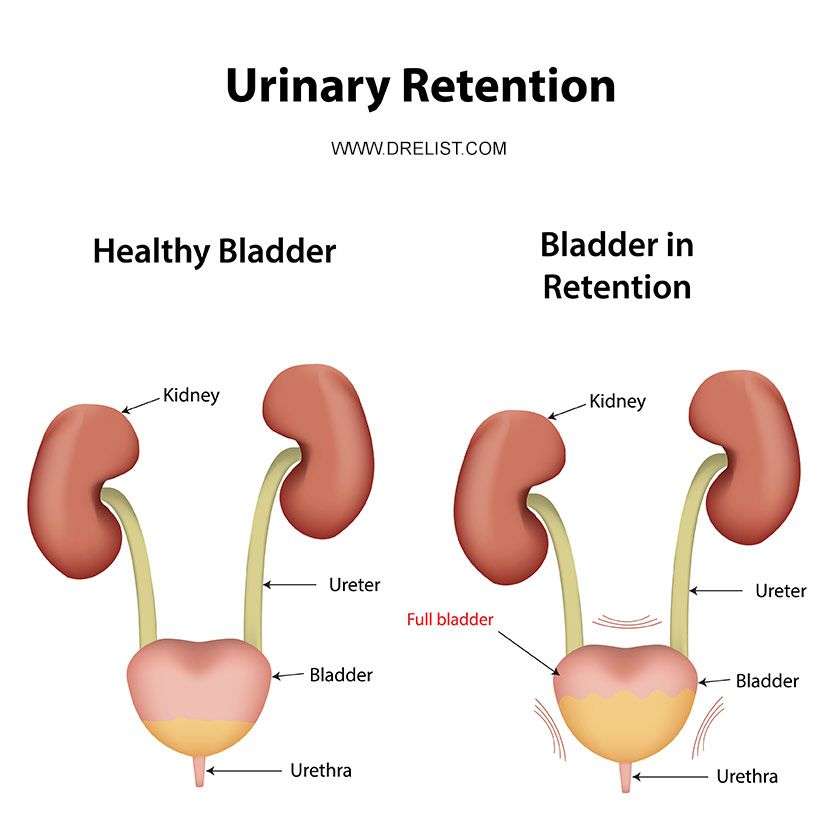
Urinary retention is the inability to completely empty your bladder. Urinary retention may be sudden in onset or gradual in onset and chronic . When you cannot empty your bladder completely, or at all, despite an urge to urinate, you have urinary retention. To understand how urinary retention occurs, it is important to understand the basics of how urine is stored in and released from the body.
The bladder is a hollow balloon-like organ in the lower part of the belly that stores and eliminates urine.
Urinary retention may cause harm to the function of the bladder and the kidneys, incontinence, and may increase the risk of urinary tract infections. Thus, it requires urgent medical attention for evaluation and management. In some cases, hospitalization is required.
Urinary retention is not an unusual medical condition, and it is more common in men than in women.
What Are The Complications Of Urinary Retention And Its Treatments

- urinary incontinence after prostate, tumor, or cancer surgery
UTIs. Urine is normally sterile, and the normal flow of urine usually prevents bacteria from infecting the urinary tract. With urinary retention, the abnormal urine flow gives bacteria at the opening of the urethra a chance to infect the urinary tract.
Bladder damage. If the bladder becomes stretched too far or for long periods, the muscles may be permanently damaged and lose their ability to contract.
Kidney damage. In some people, urinary retention causes urine to flow backward into the kidneys. This backward flow, called reflux, may damage or scar the kidneys.
Urinary incontinence after prostate, tumor, or cancer surgery. Transurethral surgery to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia may result in urinary incontinence in some men. This problem is often temporary. Most men recover their bladder control in a few weeks or months after surgery. Surgery to remove tumors or cancerous tissue in the bladder, prostate, or urethra may also result in urinary incontinence.
Also Check: How To Find Out If You Have Bladder Cancer
Empty Your Bladder Before And After Sexual Intercourse
There is nothing worse than frequent urination to put a damper on your sex life.
Even worse is if you get a UTI shortly after having sexyou might blame it on your partner and think you “picked up” something from them.
That might not be so. It might just be a case of poor planning. Use the method in this article before having sex and you will be much more comfortable both right after sex and the morning after.
- Always empty your bladder before sex and, just as importantly, again after sex. Make this a habit! Once you do the method a few times, you will be able to do it in about two minutes total. The first few times, it will take you about 6 to 8 minutes until you get the hang of it.
- Urinating before and after sex helps to eliminate the re-occurrence of that “Oh, I think I’m getting a UTI” feeling the morning after sex. Everyone has experienced this at least once.
- There is no sense in treating what you think is a UTI when, in fact, it is just an irritated bladder from sexual intercourse.
- Follow this method, as noted above, drink more water throughout the day after sex, and you should be fine.
Guarding Reflexes Against Stress Urinary Incontinence
There is an important bladder-to-urethra reflex that is mediated by sympathetic efferent pathways to the urethra. This is an excitatory reflex that contracts the urethral smooth muscle and, thus, is called a guarding reflex. The positive reflex is not activated during micturition but activates when bladder pressure is increased, such as during a cough or exercise.
A second guarding reflex is triggered by activation of sacral motoneurons that, in turn, activate urethral external sphincter efferent neurons, which send axons into the pudendal nerves and the nerves innervating the pelvic floor. This somatic guarding reflex is activated by bladder afferents and/or directly by stress such as sneezing. The activation of somatic urethral and pelvic floor efferent pathways contracts the external urinary sphincter and the pelvic floor muscle, thus preventing stress urinary incontinence. The brain inhibits the guarding reflexes during micturition.
You May Like: Bladder Control Problems At Night
Causes Of Urinary Retention
Selected Causes of Urinary Retention
Obstructive
| Cause | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Benign prostatic hyperplasia meatal stenosis paraphimosis penile constricting bands phimosis prostate cancer |
Organ prolapse pelvic mass retroverted impacted gravid uterus |
Aneurysmal dilation bladder calculi bladder neoplasm fecal impaction gastrointestinal or retroperitoneal malignancy/mass urethral strictures, foreign bodies, stones, edema |
|
|
Infectious and inflammatory |
Balanitis prostatic abscess prostatitis |
Acute vulvovaginitis vaginal lichen planus vaginal lichen sclerosis vaginal pemphigus |
Bilharziasis cystitis echinococcosis Guillain-Barré syndrome herpes simplex virus Lyme disease periurethral abscess transverses myelitis tubercular cystitis urethritis varicella-zoster virus |
|
Other |
Penile trauma, fracture, or laceration |
Postpartum complication urethral sphincter dysfunction |
Disruption of posterior urethra and bladder neck in pelvic trauma postoperative complication psychogenic |
note:For pharmacologic and neurologic causes of urinary retention, see Tables 2 and 3, respectively.
Information from references 1 and 5 through 7.
Selected Causes of Urinary Retention
Obstructive
note:For pharmacologic and neurologic causes of urinary retention, see Tables 2 and 3, respectively.
Information from references 1 and 5 through 7.
Urinary Retention At A Glance
- Urinary retention, either acute or chronic, is the problem of being unable to empty the bladder properly.
- Urinary retention occurs most frequently in older men, but it can affect women and men of any age.
- Chronic urinary retention may cause few symptoms and sometimes people dont know they have it until urinary incontinence causes them to seek treatment.
- Acute urinary retention is a medical emergency and may involve complete inability to urinate and painful, urgent need to urinate.
- Surgical and other treatments are available to resolve urinary retention.
Read Also: How Long Can You Live With Aggressive Bladder Cancer
Urinary Retention In Adults: Diagnosis And Initial Management
BRIAN A. SELIUS, DO, and RAJESH SUBEDI, MD, Northeastern Ohio Universities College of Medicine, St. Elizabeth Health Center, Youngstown, Ohio
Am Fam Physician. 2008 Mar 1 77:643-650.
Urinary retention is the inability to voluntarily urinate. Acute urinary retention is the sudden and often painful inability to void despite having a full bladder.1 Chronic urinary retention is painless retention associated with an increased volume of residual urine.2 Patients with urinary retention can present with complete lack of voiding, incomplete bladder emptying, or overflow incontinence. Complications include infection and renal failure.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
In men with benign prostatic hyperplasia, initiation of treatment with alpha blockers at the time of catheter insertion improves the success rate of trial of voiding without catheter.
A = consistent, good-quality patient-oriented evidence B = inconsistent or limited quality patient-oriented evidence C = consensus, disease-oriented evidence, usual practice, expert opinion, or case series. For information about the SORT evidence rating system, see page 579 or .
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
In men with benign prostatic hyperplasia, initiation of treatment with alpha blockers at the time of catheter insertion improves the success rate of trial of voiding without catheter.
What Is Urinary Retention
Urinary retention is a condition where your bladder doesnt empty all the way or at all when you urinate. Your bladder is like a storage tank for urine. Urine is made up of waste thats filtered out of your blood by your kidneys. Once filtered, the urine moves to your bladder where it waits till its time to move through the urethra and out of the body.
When you have urinary retention, it can be acute or chronic . Acute means that it comes on quickly and it could be severe. Chronic urinary retention means that youve had the condition for a longer period of time.
The acute form of urinary retention is an emergency. In this case, youll need to see a healthcare provider right away. The chronic form happens most of the time in older men, but it can also occur in women.
You May Like: Difference Uti And Bladder Infection
Don’t Hover Above The Toilet Seat
As stated in this article, hovering can lead to incomplete bladder evacuation due to tense pelvic muscles. If your muscles are unable to relax then they won’t allow the bladder to fully release. SO SIT DOWN AND RELAX!!! Don’t hover. Unless you’re in a really icky outhouse… Then maybe you can hover.
Initial Management Of Urinary Retention
Acute urinary retention should be managed by immediate and complete decompression of the bladder through catheterization. Standard transurethral catheters are readily available and can usually be easily inserted. If urethral catheterization is unsuccessful or contraindicated, the patient should be referred immediately to a physician trained in advanced catheterization techniques, such as placement of a firm, angulated Coude catheter or a suprapubic catheter.5 Hematuria, hypotension, and postobstructive diuresis are potential complications of rapid decompression however, there is no evidence that gradual bladder decompression will decrease these complications. Rapid and complete emptying of the bladder is therefore recommended.34
If possible, the use of chronic urethral indwelling catheters should be avoided. Complications include UTI, sepsis, trauma, stones, urethral strictures or erosions, prostatitis, and potential development of squamous cell carcinoma.44,45 In a one-year prospective study of nursing home patients, catheter use was independently associated with increased mortality.46
Read the full article.
- Get immediate access, anytime, anywhere.
- Choose a single article, issue, or full-access subscription.
- Earn up to 6 CME credits per issue.
Read Also: Bladder Exercises For Overactive Bladder
How Is A Cystocele Treated
If it is not bothersome, a mild cystocele may not require any treatment other than avoiding heavy lifting or straining that could cause the problem to get worse.
Other potential treatment options include the following:
- Weight loss.
- Estrogen replacement therapy.
- Kegel exercises to strengthen the openings of the urethra, vagina and rectum. These exercises involve tightening the muscles that are used to stop the flow of urine, holding for 10 seconds, and then releasing.
- If symptoms are modest, a device called a pessary may be placed in the vagina to hold the bladder in place. Pessaries are available in a number of shapes and sizes to ensure a proper fit. A pessary has to be removed and cleaned on a regular basis in order to avoid infection or ulcers.
Urination Difficulty At A Glance:
- Having trouble urinating also referred to as voiding difficulty is caused by an underlying mechanical problem with the coordination between the urethra and the bladder muscle that allows urine to freely pass.
- Urination problems include difficulty initiating urination and impaired bladder emptying, as well as urinary incontinence.
- Urine voiding problems in women can be caused by a variety of conditions, including urinary retention, prolapsed bladder, urinary tract infections, and the effects of menopause and pregnancy.
- Symptoms are painful urination, difficulty starting the urine stream, a sense of incomplete bladder voiding, and sometimes an inability to urinatean emergency situation known as acute urinary retention that requires immediate treatment.
- Treatments for voiding problems depend upon the underlying cause, but may include bladder muscle conditioning, medications, implant devices and surgery.
Also Check: New Drug For Overactive Bladder
Recommended Reading: Bowel And Bladder Problems After Back Surgery
Help My Bladder Doesn’t Empty Completely
Do you have a bladder the size of an acorn? Do you feel like you’ve always gotta go? As soon as you’re done urinating, do you have to go again? Do you feel like your bladder doesn’t empty completely? If so, sisters, you’re not alone!Feeling like your bladder doesn’t empty completely is a fairly common condition, and something I’ll discuss below.But first, a mini-soapbox. Please know that if you try the suggestions below and they don’t help, or if you have questions BEYOND what I’ll share below, then please seek help from a medical professional. Often, people are embarrassed to bring up questions about pee, poo, or any other “strange” bodily functions. But know that your doctor is TRAINED TO DEAL WITH STRANGE.When I was in clinical practice as a physical therapist, I saw strange EVERY DAY. And did I go home and laugh at those patients? Absolutely not!Do I remember them today? NO!!! So don’t worry about sharing your crazy or “gross” or embarrassing stories, and don’t blow them off as “not mattering.” Because if they impact you even a little then they matter.
Don’t Do Kegels While Urinating
At some point in the history of kegeling, word got out that a good time to do kegels is while urinating . The logic behind this theory is that you use your pelvic floor muscles to voluntarily stop the flow of urine, hence if you can stop the flow while urinating, you will know whether or not you can successfully contract and relax your pelvic floor muscles. Heres the deal: its okay to try a kegel or two while you urinate in order to check in to see if you are doing kegels correctly . But this is not something you should do on a regular basis.
Regularly doing kegels while urinating can lead to incomplete bladder evacuation, which can make your bladder feel like its always full.
You might think your bladder is the size of an acorn But really, its simply the fact that its never fully empty! To fully empty your bladder, practice your kegel exercises when you are OFF the toilet.
Also Check: What Is Prescribed For Bladder Infection
Approach To The Patient With Urinary Retention
Possible Etiology of Urinary Retention Based on History and Physical Examination Findings
*Most patients will present with one or more lower urinary tract symptoms. Symptoms include frequency, urgency, nocturia, straining to void, weak urinary stream, hesitancy, sensation of incomplete bladder emptying, and stopping and starting of urinary stream.
Patients with 150 to 200 mL of retained urine may have a percussible or palpable bladder
Information from references 5, 6, 28, and 29.
Possible Etiology of Urinary Retention Based on History and Physical Examination Findings
*Most patients will present with one or more lower urinary tract symptoms. Symptoms include frequency, urgency, nocturia, straining to void, weak urinary stream, hesitancy, sensation of incomplete bladder emptying, and stopping and starting of urinary stream.
Patients with 150 to 200 mL of retained urine may have a percussible or palpable bladder
Diagnostic Testing in Patients with Urinary Retention
note:Imaging studies and diagnostic procedures are guided by the clinical context and suspected diagnoses.
CT = computed tomography MRI = magnetic resonance imaging.
Information from references 5, 6, and 28 through 30.
Diagnostic Testing in Patients with Urinary Retention
note:Imaging studies and diagnostic procedures are guided by the clinical context and suspected diagnoses.
CT = computed tomography MRI = magnetic resonance imaging.
You May Like: What Do Bladder Spasms Feel Like
Blockage Or Narrowing In The Urethra Or Bladder Neck
For you to be able to urinate normally, all parts of your urinary tract need to work together in the correct order. Urine normally flows from your kidneys, through the ureters to your bladder, and out the urethra. If a blockage or narrowing occurs somewhere along the urinary tract, you may have difficulty urinating, and if the blockage is severe, you may not be able to urinate at all.
Medical problems that may narrow the urethra and block urine flow include
Read Also: Botox Procedure For Overactive Bladder
Problems With The Nerves Supplying The Bladder
Urinary retention can result from problems with the nerves that control the bladder and the valves that control the flow of urine from the bladder.
Even when the bladder is full, the bladder muscles that squeeze urine out may not receive the signal to push. The sphincters may not receive the signal to relax and allow the bladder to empty. Possible causes of nerve problems that may cause urinary retention include diabetes, a stroke, multiple sclerosis or after an injury to the pelvis.
Some children are born with conditions that may affect the nerve signals to the bladder. For example spina bifida may cause urinary retention in newborn babies.
Chronic Urinary Retention Treated At Home
If youre experiencing chronic urinary retention symptoms, its normal to feel anxious about leaving home to seek medical attention. After all, you likely want to be close to a bathroom in case you need to urinate suddenly. At DispatchHealth, we specialize in delivering high-quality healthcare in the comfort of our patients homes. All you have to do is request a visit and well send a team to your homeits as easy as that. Our medical teams are fully equipped to handle a wide range of health concerns and arrive with a stocked medical kit that has many of the same tools and diagnostics as found in an emergency room.
Request a visit by contacting us via our website, the phone, or our app!
For life-threatening and time-sensitive injuries and illnesses, call 911 or go to the nearest emergency room. DispatchHealth shouldnt be used in a life-threatening emergency and doesnt replace a primary care provider.
You May Like: Can A Bladder Infection Cause Incontinence