What Are The Stages Of Bladder Cancer
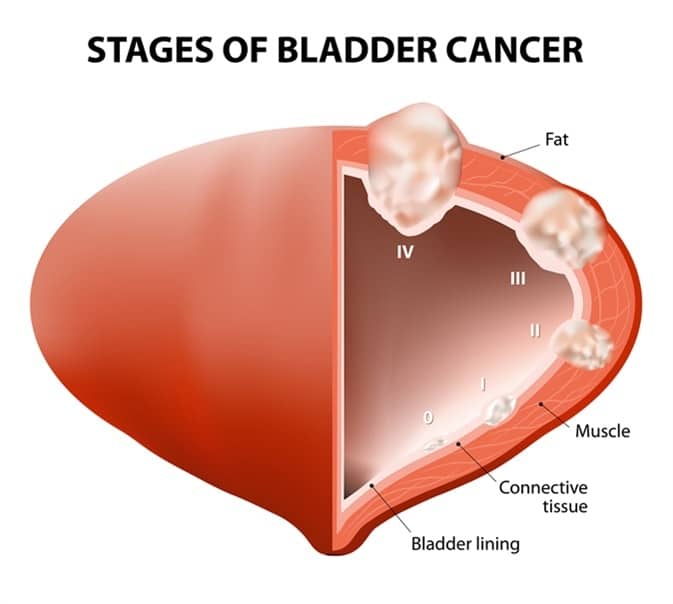
Healthcare professionals describe the cancer by assigning numbers and/or letters to each of the three staging categories. This helps to identify the best treatment options for a patients specific type of bladder cancer. The five overall stages of bladder cancer are: stage 0, stage I, stage II, stage III, and stage IV.
Rare Forms Of Bladder Cancer
Adenocarcinomas account for less than 2% of primary bladder tumors. These lesions are observed most commonly in exstrophic bladders and are often associated with malignant degeneration of a persistent urachal remnant.
Other rare forms of bladder cancer include leiomyosarcoma, rhabdosarcoma, carcinosarcoma, lymphoma, and small cell carcinoma. Leiomyosarcoma is the most common sarcoma of the bladder. Rhabdomyosarcomas most commonly occur in children. Carcinosarcomas are highly malignant tumors that contain a combination of mesenchymal and epithelial elements. Primary bladder lymphomas arise in the submucosa of the bladder. Except for lymphomas, all these rare bladder cancers carry a poor prognosis.
Small cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder is a poorly differentiated, malignant neoplasm that originates from urothelial stem cells and has variable expression of neuroendocrine markers. Morphologically, it shares features of small cell carcinoma of other organs, including the lung.
Noninvasive Vs Invasive Bladder Cancer
Doctors often use the terms noninvasive or invasive to describe whether cancer has spread into the bladder wall. Noninvasive means the cancer is in the inner cell layers. Invasive cancers are deeper in the layers of the bladder wall. If a doctor says the cancer is superficial or non-muscle invasive, that means it isnt in the bladders main muscle layerthough it may still be invasive or noninvasive and have the potential to spread to the muscle.
Different types of bladder cancer grow in different ways, so doctors may discuss a tumor in terms of the direction its growing. Papillary carcinomas grow from the bladders lining toward the hollow center, while flat carcinomas stay flush against the bladder wall.
Don’t Miss: Mitomycin 40 Mg Bladder Instillation
Bladder Cancer Survival Rate
One way to estimate life expectancy when battling cancer is to consider the five-year relative survival rate for that type of cancer. A five-year relative survival rate shows the likelihood that a patient with a specific type and stage of cancer would live for at least five years after the diagnosis, compared with people who don’t have cancer. The rate includes the life expectancy of patients who are still in treatment and those who have finished treatment and have had tests that show no evidence of disease.
The American Cancer Society reports these bladder cancer survival rates:
- Localized bladder cancer: If the cancer hasn’t spread outside the bladder, the five-year relative survival rate is 70 percent.
- Regional bladder cancer: For patients with bladder cancer that has spread to nearby lymph nodes or structures, the five-year relative survival rate is 38 percent.
- Distant bladder cancer: If the cancer has spread to distant organs or body parts , the five-year relative survival rate is 6 percent.
Expert cancer care
Patients May Want To Think About Taking Part In A Clinical Trial
For some patients, taking part in a clinical trial may be the best treatment choice. Clinical trials are part of the cancer research process. Clinical trials are done to find out if new cancer treatments are safe and effective or better than the standard treatment.
Many of today’s standard treatments for cancer are based on earlier clinical trials. Patients who take part in a clinical trial may receive the standard treatment or be among the first to receive a new treatment.
Patients who take part in clinical trials also help improve the way cancer will be treated in the future. Even when clinical trials do not lead to effective new treatments, they often answer important questions and help move research forward.
Read Also: How Is Botox Injected Into The Bladder
Other Types Of Bladder Cancer
Approximately 2% of bladder cancers are adenocarcinomas. Nonurothelial primary bladder tumors are extremely rare and may include small cell carcinoma, carcinosarcoma, primary lymphoma, and sarcoma . Small cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder accounts for only 0.3-0.7% of all bladder tumors. High-grade urothelial carcinomas can also show divergent histologic differentiation, such as squamous, glandular, neuroendocrine, and sarcomatous features.
Prognosis In Squamous Cell Carcinoma
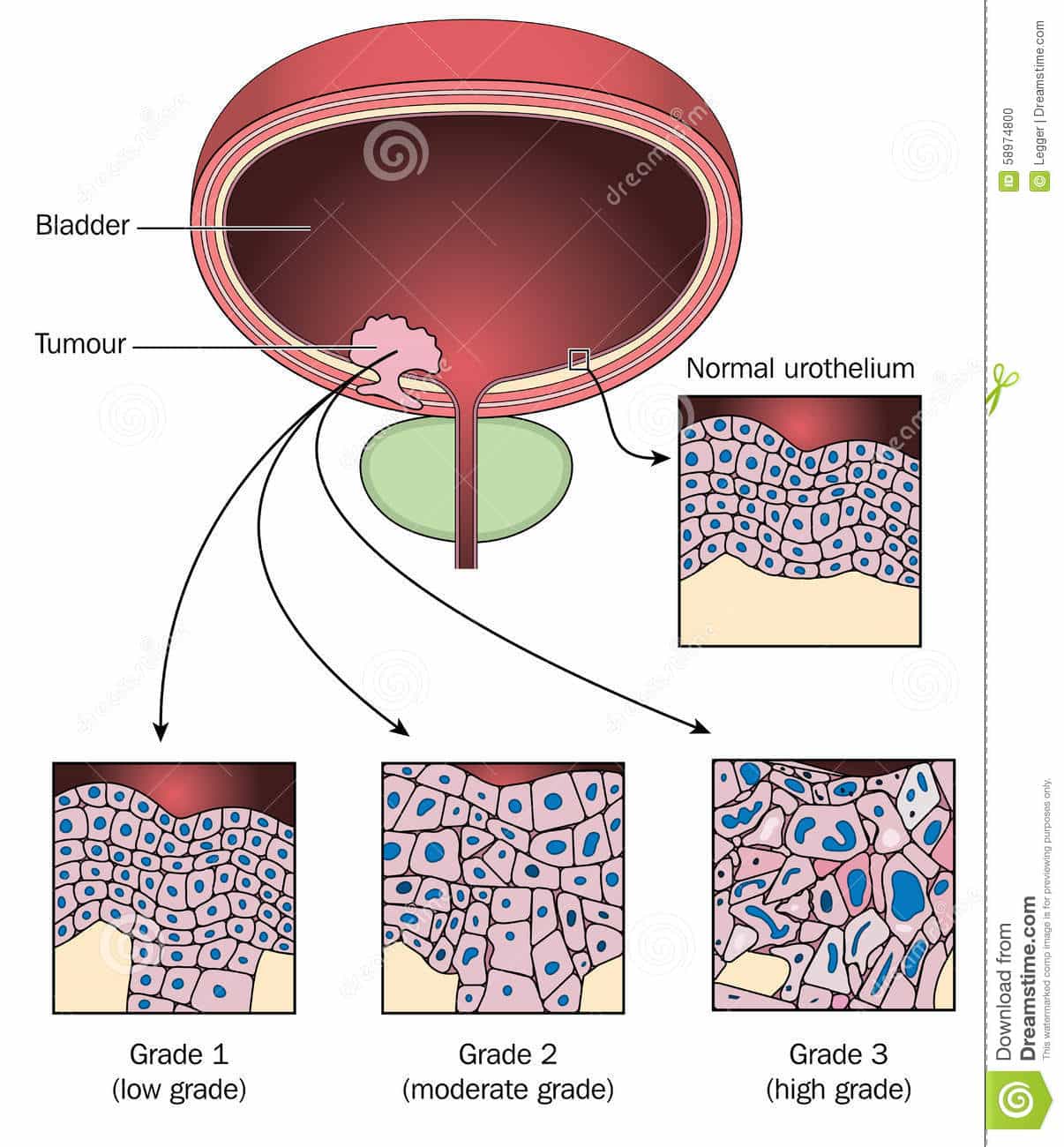
Tumor stage, lymph node involvement, and tumor grade have been shown to be of independent prognostic value in SCC. However, pathologic stage is the most important prognostic factor. In one relatively large series of 154 cases, the overall 5-year survival rate was 56% for pT1 and 68% for pT2 tumors. However, the 5-year survival rate for pT3 and pT4 tumors was only 19%.
Several studies have demonstrated grading to be a significant morphologic parameter in SCC. In one series, 5-year survival rates for grade 1, 2, and 3 SCC was 62%, 52%, and 35%, respectively. In the same study of patients undergoing cystectomy, the investigators suggested that a higher number of newly formed blood vessels predicts unfavorable disease outcome.
In SCC, the survival rate appears to be better with radical surgery than with radiation therapy and/or chemotherapy. In locally advanced tumors, however, neoadjuvant radiation improves the outcome. Sex and age have not been prognostically significant in SCC.
You May Like: Back Pain Causing Bladder Problems
How Do You Prevent Bladder Cancer
Unfortunately, there is no one way to prevent bladder cancer. Some things like age, race, gender and genetics or family history cant be controlled. However, people can take steps to reduce their risk.
Tips for bladder cancer prevention include:
- Quit or dont start smoking
- Limit chemical exposure on the job
- Drink plenty of fluids, especially water
- Eat a diet high in fruits and vegetables
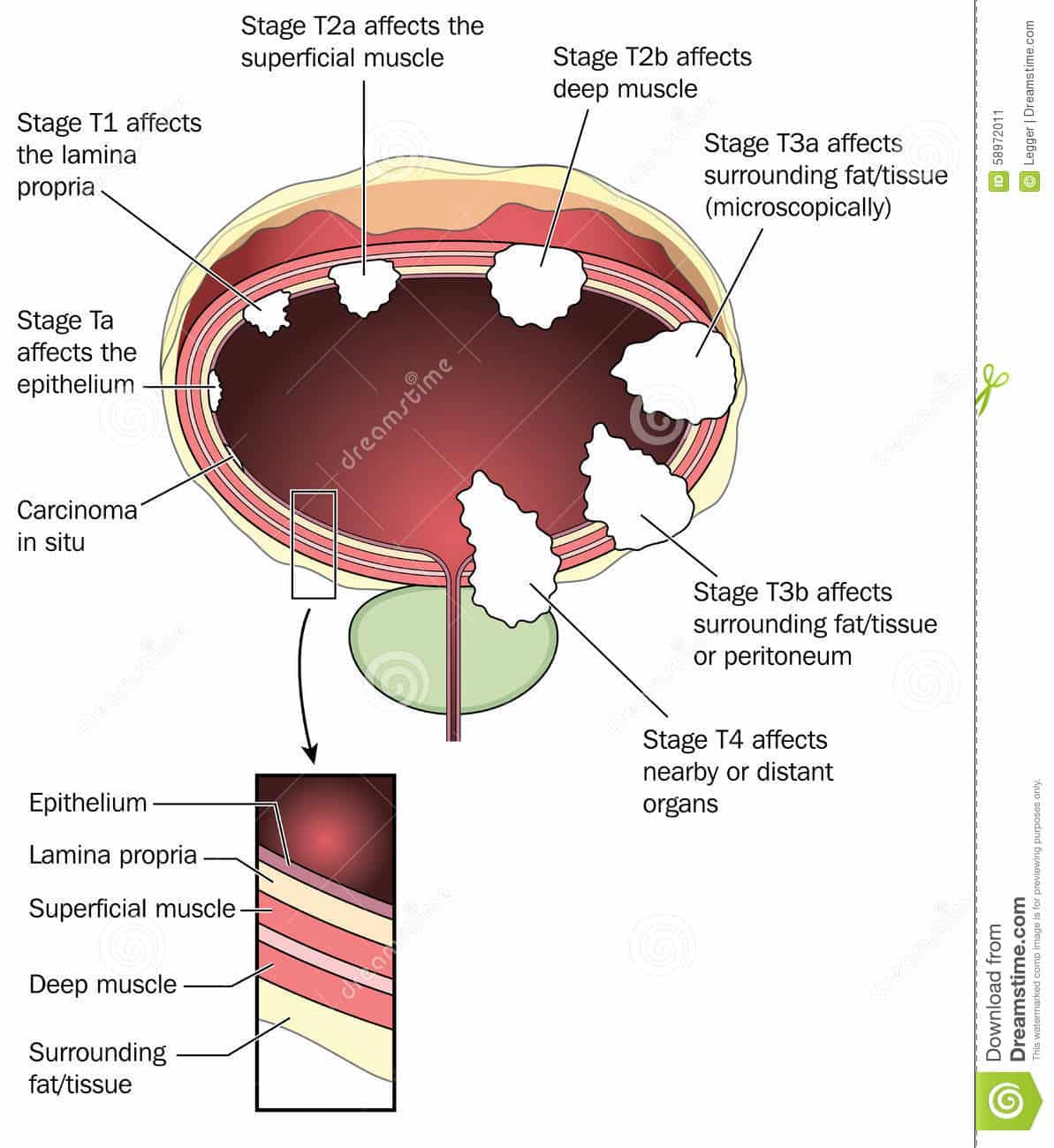
Stage 2 Bladder Cancer
A diagnosis of stage 2 bladder cancer means that the bladder cancer cells have grown into the muscle layer of the bladder wall.1,2 This is also called muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Stage 2 bladder cancer includes the following combined TNM stages:
In both of those types of stage 2 bladder cancer, the cancer cells have not grown into the nearby lymph nodes and they have not spread to other parts of the body. The muscle portion of the bladder wall has two layers. The inner half, closest to the bladder lining, is called the superficial muscle. The outer half is also called the deep muscle of the bladder. If the tumor is type T2a, it means that the cancer cells have spread into the superficial muscle, but not into the deep muscle. If the tumor is type T2b, the bladder cancer cells have grown through the superficial muscle and into the deep muscle of the bladder. However, the cancer cells have not yet spread into the layer of fatty tissue that surrounds the outer part of the bladder muscle.
Also Check: What Is The Best Medicine For Bladder Control
Symptoms In Men And Women
Bladder cancer symptoms in men and women are the same. Men are more likely to get bladder cancer, but they are also more likely to have it diagnosed earlier, according to Moffitt Cancer Center.
Women are more likely to mistake bladder cancer symptoms for urinary tract infections or menstruation.
Rarely, bladder cancer may also be misdiagnosed as interstitial cystitis in women. IC is a painful, inflammatory bladder condition that affects more women than men.
In one study, doctors found bladder cancer in about one percent out of 600 patients referred to them for IC treatment, according to an article in Urology Times.
After Bladder Cancer Has Been Diagnosed Tests Are Done To Find Out If Cancer Cells Have Spread Within The Bladder Or To Other Parts Of The Body
The process used to find out if cancer has spread within thebladder lining and muscle or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment. The following tests and procedures may be used in the staging process:
Also Check: Medicine To Treat Bladder Infection
Certain Factors Affect Prognosis And Treatment Options
The prognosis depends on the following:
- The stage of the cancer . Bladder cancer in the early stages can often be cured.
- The type of bladder cancer cells and how they look under a microscope.
- Whether there is carcinoma in situ in other parts of the bladder.
- The patients age and general health.
If the cancer is superficial, prognosis also depends on the following:
- How many tumors there are.
- The size of the tumors.
- Whether the tumor has recurred after treatment.
Treatment options depend on the stage of bladder cancer.
What Is The Prognosis For Stage 4 Bladder Cancer
As with other stage 4 cancers, the prognosis is not the most encouraging. Stage 4 bladder cancer is commonly divided into stage 4A and stage 4B. Stage 4A is considered regional spread and sees a 5-year survival rate of roughly 35%. As the disease progresses to 4B, which is known as distant disease, the 5-year survival rate falls to as low as 5%.
Don’t Miss: Bladder Medication Over The Counter
Stage Iv Bladder Cancer
Stage IV cancer has metastasized or spread to major organs in other parts of the body. This is often called metastatic cancer. About 5% of bladder cancer cases are diagnosed after theyve already spread to distant organs, according to SEER.
Stage IV bladder cancer is divided into stage IVA and IVB. IVA cancer has spread either:
- Into the wall of the abdomen or pelvis
- Into multiple lymph nodes near the major arteries of the pelvis
IVB bladder cancer has spread to other organs, which can include the lungs, bones, and liver.
What Is The Survival Rate
Metastatic bladder cancer is difficult to cure because it has already traveled to other parts of the body. The later you receive a diagnosis and the farther the cancer has traveled, the less chance it can be cured.
The 5-year survival rate is the proportion of people who survive for 5 years after a cancer diagnosis.
For bladder cancer, if the cancer has spread to the regional lymph nodes, the 5-year survival rate is
Recommended Reading: Difference Between Uti And Bladder Infection Symptoms
Diagnostic Findings Part 3
White light cystoscopy shows a single raised red flat, granular, velvety lesion in the lower part of the trigone area. Two more suspicious areas of hyperemia are seen on the posterior wall. A cold cup biopsy forceps is used to take punch biopsy samples from the lesion. Additional biopsies include the hyperemic area samples, left lateral wall, right lateral wall, base, dome, and trigone of the bladder. The prostatic urethral lining appears normal. Computed tomography urogram and abdominal CT scan shows no other lesions in the ureters, renal pelvis, and the rest of the urinary tract. No enlarged perivesicular lymph nodes or other nodes including inguinal, hypogastric, obturator, and external iliac, or presacral lymph node group are noted.
What Is The Clinical Differential Diagnosis For This Patient
The patient presents with repeated episodes of asymptomatic dark red-colored urine. There are several possibilities for cause of dark colored urine. These may be innocuous and benign such as ingestion of certain foods or prescription or over the counter medications or they may be indicative of a pathology. A careful history of comorbidities, drug audit, diet and other symptoms followed by required investigations helps to narrow the differential diagnosis and determine the cause.2
The most common abnormal color of urine seen is red or red-brown, as seen in this patient. When seen in females of reproductive age-group, it may be due to menstrual blood contamination. However, in the patient described, other causes need to be considered. The dietary causes include eating beets, rhubarb, blackberries, or foods containing certain food colorings that may be excreted in the urine. A number of medications can also result in dark red, brown, or orange colored urine. Some of these include antibiotics , analgesics and muscle relaxants , anthraquinone laxatives , purgatives , iron and chelation agents , levodopa, and anticoagulants like phenindione to name a few. Red colored urine may also be seen in porphyrias, especially congenital erythropoietic porphyria and porphyria cutanea tarda.2,3 However, lead intoxication porphyrinuria does not cause red colored urine. These can be excluded in this patient as well.
You May Like: Bladder Sling For Stress Incontinence
What Are The Survival Rates For Bladder Cancer
If the cancer is just on the inner lining of the bladder , the 5-year survival rate is about 98%.
If the cancer is growing just beyond the inner lining into the bladder wall, but is still just in the bladder , the 5-year survival rate is about 88%.
Those with bladder cancer that’s spread into the muscular wall of the bladder, but not outside the bladder, or to nearby lymph nodes or organs have a 5-year survival rate of about 63%.
If the cancer has spread through the bladder muscle into the layer of tissue around the bladder and maybe to nearby organs , but has not spread to lymph nodes or other organs , the 5-year survival rate is about 46%.
When bladder cancer has moved beyond the bladder to the pelvic or abdominal wall, to lymph nodes, or to distant parts of the body , the 5-year survival rate is about 15%.
Causes And Risk Factors
Researchers dont know exactly what causes bladder cancer, but they do know what increases the risk of getting it. These risk factors range from family history to certain types of medication.
Source: Valisure
Data published in 2021 on MedRxiv by researchers from the online pharmacy Valisure and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center showed patients who took Zantac had elevated diagnosis rates of bladder, breast, prostate and thyroid cancer.
Patients should keep in mind that this data suggests a link between ranitidine and increased risk, but it doesnt prove that all people who take ranitidine will get bladder cancer.
Recommended Reading: Over The Counter Bladder Control Meds
How Can I Prevent Bladder Cancer
You may not be able to prevent bladder cancer, but it may be helpful to know the risk factors that may increase the chance youll develop bladder cancer. Bladder cancer risk factors may include:
- Smoking cigarettes: Cigarette smoking more than doubles the risk of developing bladder cancer. Smoking pipes and cigars or being exposed to second-hand smoke also increases that risk.
- Cancer treatments: Radiation therapy is the second-most common risk factor. People who have certain chemotherapy drugs may also develop an increased risk of bladder cancer.
- Exposure to certain chemicals: People who work with chemicals, such as aromatic amines , are at an increased risk. Extensive exposure to rubber, leather, some textiles, paint and hairdressing supplies, typically related to occupational exposure, also appears to increase the risk.
- Infections: People who have frequent bladder infections, bladder stones or other urinary tract diseases may have an increased risk of developing bladder cancer.
- Past bladder cancer: People with a previous bladder cancer are at increased risk to form new or recurrent bladder tumors.
Other Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk Factors
Having bladder diverticula may increase an individuals chance of developing SCC. Rarely, bacillus Calmette-Guerin treatment for CIS has been reported to lead to development of SCC. Development of bladder cancer at a younger age has been associated with bladder exstrophy. SCC has also been described in urachal remnants.
Coffee consumption does not increase the risk of developing bladder cancer. Early studies of rodents and a minority of human studies suggested a weak connection between artificial sweeteners and bladder cancer however, most recent studies show no significant correlation.
Recommended Reading: Botox In The Bladder Procedure
Mechanistic Interactions Between Bladder Cancer And Aging
Several broad hypotheses have proposed potential mechanisms for the association between cancer and aging, whereby the biological processes of aging could influence the development and/or progression of cancer in older adults. The processes interact at multiple levels for example, tumor protein 53 a tumor suppressoris involved in both cancer and aging: alteration of the p53 gene is the most frequently encountered mutation in human cancers , and the efficiency of the response to p53 has been found to vary according to age. In a mouse study, Feng et al. reported that the efficiency of the p53 response was significantly reduced in older mice compared with their younger counterparts. The reduced response predominantly resulted from decreased transcriptional activity and p53-dependent apoptosis decreased stabilization of p53 after stress was found to be the major factor in this decline.
Recommended Reading: How To Deal With A Bladder Infection At Home
What Are The Risk Factors For Bladder Cancer
Some factors increase the risk of bladder cancer:
- Cigarette smoking is the biggest risk factor it more than doubles the risk. Pipe and cigar smoking and exposure to second-hand smoking may also increase ones risk.
- Prior radiation exposure is the next most common risk factor .
- Certain chemotherapy drugs also increase the risk of bladder cancer.
- Environmental exposures increase the risk of bladder cancer. People who work with chemicals, such as aromatic amines are at risk. Extensive exposure to rubber, leather, some textiles, paint, and hairdressing supplies, typically related to occupational exposure, also appears to increase the risk.
- Infection with a parasite known as Schistosoma haematobium, which is more common in developing countries and the Middle East.
- People who have frequent infections of the bladder, bladder stones, or other diseases of the urinary tract, or who have chronic need for a catheter in the bladder, may be at higher risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
- Patients with a previous bladder cancer are at increased risk to form new or recurrent bladder tumors.
Other risk factors include diets high in fried meats and animal fats, and older age. In addition, men have a three-fold higher risk than women.
Also Check: Bladder Prolapse Surgery Success Rate