Symptoms In Men And Women
Bladder cancer symptoms in men and women are the same. Men are more likely to get bladder cancer, but they are also more likely to have it diagnosed earlier, according to Moffitt Cancer Center.
Women are more likely to mistake bladder cancer symptoms for urinary tract infections or menstruation.
Rarely, bladder cancer may also be misdiagnosed as interstitial cystitis in women. IC is a painful, inflammatory bladder condition that affects more women than men.
In one study, doctors found bladder cancer in about one percent out of 600 patients referred to them for IC treatment, according to an article in Urology Times.
You May Like: How Do I Treat A Bladder Infection At Home
Survival Rates By Stage
The numbers listed below are based upon countless people detected with bladder cancer from 1988 to 2001. These numbers originated from the National Cancer Institutes SEER database.
- The 5-year relative survival rate for people with stage 0 bladder cancer has to do with 98%.
- The 5-year relative survival rate for individuals with stage I bladder cancer has to do with 88%.
- For stage II bladder cancer, the 5-year relative survival rate is about 63%.
- The 5-year relative survival rate for stage III bladder cancer has to do with 46%.
Bladder cancer that has spread to other parts of the body is often hard to alleviate. Phase IV bladder cancer has a relative 5-year survival rate of about 15%. Still, there are typically treatment alternatives readily available for people with this phase of cancer.
Remember, these survival rates are only approximates they cant predict exactly what will happen to any individual person. We comprehend that these data can be complicated and may lead you to have more concerns. Speak with your physician to much better comprehend your certain situation.
Being diagnosed with bladder cancer can be overwhelming and scary, especially if its phase 4.
Read Also: What Is Prescribed For Bladder Infection
Case Authors Lament Scant Information On Treatments Or Outcomes
byKate Kneisel, Contributing Writer, MedPage Today April 26, 2021
A 59-year-old man presents to a hospital in Yokohama, Japan, after being referred by his local medical provider for further workup regarding gross hematuria. He has no other symptoms.
Clinicians perform cystoscopy, followed by CT and MRI scans, which identify a nodular tumor that occupies the patients bladder it is 8 cm in diameter.
Aside from being a tobacco smoker, the patients medical history is unremarkable. Laboratory tests are performed but fail to identify any abnormalities. The patient undergoes transurethral resection of the bladder tumor, which is sent to histology for analysis.
The pathology report reveals the tumor as the sarcomatoid variant of urothelial carcinoma with a heterologous osteosarcomatous element of osteosarcoma and high-grade spindle cells. The patient refuses to undergo the radical cystectomy proposed by clinicians, opting instead to undergo another transurethral resection of the tumor.
The specimen from the second surgery reveals the same elements, with evidence of invasion to the muscle. Based on these findings, clinicians schedule the patient for two courses of neoadjuvant chemotherapy with gemcitabine and cisplatin they recommend that this be followed by a radical cystectomy.
At that point, the patient is unable to undergo radical cystectomy. Six months after his initial consultation, the patient succumbs to cancer of the bladder.
Discussion
Also Check: Best Dog Food For Dogs With Bladder Stones
How The Study Was Performed
During the study, scientists randomized 1,071 men with intermediate- or high-risk localized prostate cancer into four groups. One group received radiation and six months of an anti-testosterone drug called leuporelin, and the second group received radiation plus 18 months of leuporelin therapy. Two other groups were treated with the same regimens of either radiation plus six or 18 months of leuporelin therapy, along with another drug called zoledronic acid, which helps to limit skeletal pain and related complications should cancer spread to the bones. Study enrollment occurred between 2003 and 2007 at 23 treatment centers across New Zealand and Australia.
Read Also: Is Fatigue A Sign Of Prostate Cancer
What Are The 5
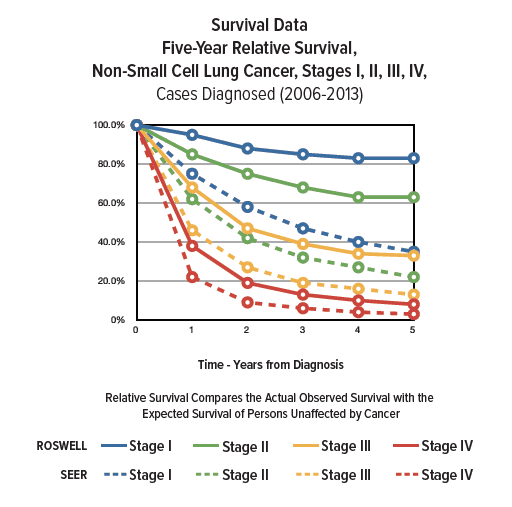
In 2020, approximately 17,980 deaths in the United States are predicted to be attributed to bladder cancer1. This represents the eighth most common cause of cancer deaths in men.
The general 5-year survival rate for people with bladder cancer is 77%, while the 10-year survival rate is 70% and the 15-year survival rate is 65%1. Notably, as each patient and cancer are different, it is not possible to definitely know the disease course for an individual patient.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Best Medicine For Overactive Bladder
Radiotherapy With A Radiosensitiser
Radiotherapy is given by a machine that beams the radiation at the bladder . Sessions are usually given on a daily basis for 5 days a week over the course of 4 to 7 weeks. Each session lasts for about 10 to 15 minutes.
A medicine called a radiosensitiser should also be given alongside radiotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. This medicine affects the cells of a tumour, to enhance the effect of radiotherapy. It has a much smaller effect on normal tissue.
As well as destroying cancerous cells, radiotherapy can also damage healthy cells, which means it can cause a number of side effects. These include:
- difficulty passing urine
Most of these side effects should pass a few weeks after your treatment finishes, although theres a small chance theyll be permanent.
Having radiotherapy directed at your pelvis usually means youll be infertile .
After having radiotherapy for bladder cancer, you should be offered follow-up appointments every 3 months for the first 2 years, then every 6 months for the next 2 years, and every year after that. At these appointments, your bladder will be checked using a cystoscopy.
You may also be offered CT scans of your chest, abdomen and pelvis after 6 months, 1 year and 2 years. A CT scan of your urinary tract may be offered every year for 5 years.
You May Like: Can A Ct Urogram Detect Bladder Cancer
Survival For All Stages Of Bladder Cancer
Generally, for people diagnosed with bladder cancer in England:
- around 75 out of every 100 survive their cancer for 1 year or more after diagnosis
- almost 55 out of every 100 survive their cancer for 5 years or more after they are diagnosed
- around 45 out of every 100 survive their cancer for 10 years or more after diagnosis
Cancer survival by stage at diagnosis for England, 2019Office for National Statistics
These statistics are for net survival. Net survival estimates the number of people who survive their cancer rather than calculating the number of people diagnosed with cancer who are still alive. In other words, it is the survival of cancer patients after taking into account that some people would have died from other causes if they had not had cancer.
Also Check: Where Is Your Bladder Woman
Can A Tumour Grow After A Cystoscopy
Yes, its the interval between cystoscopies that concerns me. In simple terms, if a tumour started growing immediately after a clear cystoscopy, how much larger/more invasive could it become 6 months down the road as opposed to 3 months. The cystoscopy itself seems such a quick and straightforward procedure that it would be no great strain on the Health System to do it more frequently if there was a value to this.
Transurethral Resection Of Bladder Tumour
Transurethral resection of bladder tumour alone in MIBC patients is onlypossible as a therapeutic option if tumour growth is limited to the superficial muscle layerand if re-staging biopsies are negative for residual tumour . In general, approximately 50% of patients will still have toundergo RC for recurrent MIBC with a disease-specific mortality rate of up to 47% withinthis group . A disease-free status at re-staging TURB appearsto be crucial in making the decision not to perform RC . A prospective study by Solsona et al. including 133 patients with radical TURB andre-staging negative biopsies, reported a 15-year follow-up .Thirty per cent of patients had recurrent NMIBC and went on to intravesical therapy, and 30% progressed, of which 27 died of BC. After five, ten, and fifteen years, the resultsshowed CSS rates of 81.9%, 79.5%, and 76.7%, respectively and PFS rates with an intactbladder of 75.5%, 64.9%, and 57.8%, respectively.
In conclusion, TURB alone should only be considered as atherapeutic option for muscle-invasive disease after radical TURB, when the patient is unfitfor cystectomy, or refuses open surgery, or as part of a multimodality bladder-preservingapproach.
7.5.1.1.Guideline for transurethralresection of bladder tumour
|
Recommendation |
Strength rating |
|
Do not offer transurethral resection of bladdertumour alone as a curative treatment option as most patients will not benefit. |
Strong |
Recommended Reading: How Common Is Bladder Cancer In Males
Hormonal Therapy For Aggressive Prostate Cancer: How Long Is Enough
- By Charlie Schmidt, Editor, Harvard Medical School Annual Report on Prostate Diseases
Men weighing treatment options for intermediate- or high-risk cancer that is still localized to the prostate can face a tricky question. A standard approach in these cases is to give radiation to the prostate along with drugs that block testosterone, a hormone that makes the cancer cells grow faster. For how long should this hormone therapy last? Thats not entirely clear. The drugs have side effects, such as fatigue, impotence, and a loss of muscle mass. But radiation doesnt control prostate cancer effectively without them. Doctors therefore aim to give hormone therapy only for as long as it takes to help their patients, without causing any undue harm.
Now, newly published results from a phase 3 clinical trial are providing some needed guidance.
Read Also: Whatâs The Difference Between Colon Cancer And Prostate Cancer
How Is Adenocarcinoma Treated
Treatment of adenocarcinoma depends on the anatomical site and its manifestations. Below are treatment options for adenocarcinoma.
- Surgery: The primary treatment after diagnosis is usually to remove the tumor and the tissue around it. Usually, the tissue is sent to pathology lab to determine the aggressiveness of the cancer. Depending on the pathology result, an individual might need to combine other treatments with surgery.
- Chemotherapy: Drugs used in chemotherapy can kill adenocarcinoma cells, slow their growth, or even cure the disease.
- Radiation: Generally, high-energy X-rays or other types of rays are exposed to the cancerous site to kill the cancer cells.
Cancer treatment can have side effects which include vomiting and weakness doctors usually treat these side effects with medications.
Also Check: Overactive Bladder Medication Side Effects
What Is Bladder Tumor
Bladder tumors: Are usually found in middle and older age pateint, presenting with gross or microscopic blood in the urine. Some are superficial not penetrating into muscle, and penetrate later into muscle. Not all progress, but some do. Instilled treatments are used first, but if muscle invasive, bladder removal is treatment of choice.
Causes And Risk Factors

Researchers dont know exactly what causes bladder cancer, but they do know what increases the risk of getting it. These risk factors range from family history to certain types of medication.
Source: Valisure
Data published in 2021 on MedRxiv by researchers from the online pharmacy Valisure and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center showed patients who took Zantac had elevated diagnosis rates of bladder, breast, prostate and thyroid cancer.
Patients should keep in mind that this data suggests a link between ranitidine and increased risk, but it doesnt prove that all people who take ranitidine will get bladder cancer.
Read Also: Icd 10 Code For Neurogenic Bladder
Is Bladder Cancer Treatable
Many types of therapy are used to treat bladder cancer. In general, the treatment pathway chosen depends on the type and stage of bladder cancer present and a patients overall health and individual preferences. Common treatment options include:
- Surgery: to remove tumor cells and surrounding tissue. The type of surgery used depends on factors such as the size and progression of the tumor.
- Chemotherapy: which refers to the use of drugs to destroy cancer cells. Chemotherapy may be local or systemic .
- Immunotherapy: which uses naturally occurring or man-made substances to improve or bolster the bodys immune system function. Like with chemotherapy, immunotherapy may be delivered locally or systemically.
- Radiation therapy: which uses x-rays or other high-energy waves or particles to kill cancer cells.
Recommended Reading: Oregano Oil For Bladder Infection
How Do You Prevent Bladder Cancer
Unfortunately, there is no one way to prevent bladder cancer. Some things like age, race, gender and genetics or family history cant be controlled. However, people can take steps to reduce their risk.
Tips for bladder cancer prevention include:
- Quit or dont start smoking
- Limit chemical exposure on the job
- Drink plenty of fluids, especially water
- Eat a diet high in fruits and vegetables
Also Check: Early Symptoms Bladder Cancer Woman
Signs And Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
Sometimes bladder cancer doesnt have many symptoms. Signs or symptoms can include:
- blood in your urine
- pain or burning when passing urine
- not being able to pass urine when you need to.
Not everyone with these symptoms has bladder cancer. If you have any of these symptoms or are worried, always see your doctor.
Treatmentof Patients With Bone Metastases
The prevalence of metastatic bone disease in patients withadvanced/metastatic UC is 3040% . Skeletal complicationsdue to MBD have a detrimental effect on pain and QoL and are also associated with increasedmortality . Bisphosphonates such as zoledronic acid reduce anddelay skeletal-related events due to bone metastases by inhibiting bone resorption,as shown in a small pilot study . Denosumab, a fully humanmonoclonal antibody that binds to and neutralises RANKL , was shown to be non-inferior to zoledronic acid in preventing ordelaying SREs in patients with solid tumours and advanced MBD, including patients with UC. Patients with MBD, irrespective of the cancer type, should beconsidered for bone-targeted treatment .
Patients treated with zoledronic acid or denosumab should be informed aboutpossible side effects including osteonecrosis of the jaw and hypocalcaemia. Supplementationwith calcium and vitamin D is mandatory. Dosing regimens of zoledronic acid should followregulatory recommendations and have to be adjusted according to pre-existing medicalconditions, especially renal function . For denosumab, no doseadjustments are required for variations in renal function.
You May Like: Where Do You Feel Bladder Pain
Read Also: Botox For Bladder Control Reviews
How Fast Does Aggressive Bladder Cancer Spread
As many as 50% of patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer may have occult metastases that become clinically apparent within 5 years of initial diagnosis and around 5% will have distant metastasis at the time of initial diagnosis. Most patients with overt metastatic disease die within 2 years despite chemotherapy.
Can The Gleason Score On My Biopsy Really Tell What The Cancer Grade Is In The Entire Prostate
Because prostate biopsies are tissue samples from different areas of the prostate, the Gleason score on biopsy usually reflects your cancers true grade. However, in about 1 out of 5 cases the biopsy grade is lower than the true grade because the biopsy misses a higher grade area of the cancer. It can work the other way, too, with the true grade of the tumor being lower than what is seen on the biopsy.
Recommended Reading: What Should I Do If I Have A Bladder Infection
What Causes Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer occurs when cells within the lining of the bladder wall begin to grow in a disordered, uncontrolled way.
Exactly what prompts this disordered growth is not fully known. However, several factors associated with a higher risk of bladder cancer have been identified, including:
- Age – most people diagnosed with bladder cancer are older than 55 years.
- Sex – compared to women, men are 4 times more likely to develop bladder cancer.
- Smoking – smoking is associated with around half of all bladder cancers in men and women.
- Race – in the United States, White Americans have the highest rate of bladder cancer.
- Previous bladder cancer – people who have had bladder cancer may have a recurrence.
- Workplace exposures – certain chemicals in some workplaces may contribute to higher rates of bladder cancer in workers. For example, painters, hairdressers, and truck drivers are at increased risk.
- Arsenic in drinking water.
- Certain types of medication.
How Is Gallbladder Cancer Usually Treated

Treatment for gallbladder cancer may include
- Surgery: It can be used to remove the gallbladder. If cancer has spread, then surgery can also be used to remove the surrounding tissue, lymph nodes and parts of other organs.
- Cancer found in the wall of the gallbladder can be completely removed by surgery.
- Unresectable cancer cannot be removed completely by surgery. Most patients with gallbladder cancer have unresectable cancer.
- Recurrent cancer is cancer that has recurred after it has been treated. GBC may come back in the gallbladder or in other parts of the body.
You May Like: How Do You Calm An Irritated Bladder
Where Do These Numbers Come From
The American Cancer Society relies on information from the SEER* database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute , to provide survival statistics for different types of cancer.
The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for bladder cancer in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread. The SEER database, however, does not group cancers by AJCC TNM stages . Instead, it groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages:
- Localized: There is no sign that the cancer has spread outside of the bladder.
- Regional: The cancer has spread from the bladder to nearby structures or lymph nodes.
- Distant: The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body such as the lungs, liver or bones.