Surgical Procedure And Device For Pdd
Approximately 3h before surgery, patients orally received a water-dissolved 5-ALA solution at a dose of 20mg/kg . The PDD-EBTUR will be performed by a single surgeon with substantial experience in this surgical technique , while the PDD-cTURBT will be performed by one of the following experienced urologists: M. Miyake, S. Hori, Y. Nakai, S. Anai, K. Torimoto, N. Tanaka, and K.Fujimoto. The surgical procedures and devices for PDD-EBTUR and PDD-cTURBT are described in our previous report .
Postoperative Details Of Turbt
Within the first 24 hours, a single intravesical instillation of mitomycin-C has been shown to reduce the frequency of tumor recurrence and should be considered the standard of care after TURBT or positive bladder biopsy findings. Gemcitabine has widely replaced mitomycin-C in this setting, due to its similar efficacy, lower adverse effect profile, and cost. It should be emphasized that while gemcitabine and mitomycin-C have established efficacy, there have been no studies comparing them head-to-head in this setting.
Postoperative intravesical chemotherapy is withheld if there is surgeon concern for bladder perforation extensive or deep resection or persistent hematuria, due to the possibility for systemic absorption.
Occasionally, a Foley catheter may need to be left in place for 1-3 days after TURBT. It is usually removed in the urology office.
Postoperatively, symptoms of intermittent dysuria, urinary frequency, urgency, and hematuria are anticipated.
The most common complications after TURBT are as follows :
A second TURBT should be performed 2-6 weeks after initial TURBT for several patient populations. Indications include the following:
- Incomplete initial resection
Transurethral Resection Of Bladder Tumour
1Department of Urology, Westmead Hospital, Sydney, Australia
2Discipline of Surgery, Sydney Medical School, University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia
1Department of Urology, Westmead Hospital, Sydney, Australia
2Discipline of Surgery, Sydney Medical School, University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia
Contributions:Correspondence to:Open Access Statement:
You May Like: Bladder Control Products By Mail
Turbt Recovery & Complications
After the procedure, a flexible tube may be inserted into the bladder through the urethra to assist with draining urine from the bladder. The catheter will usually stay in place for 1 to 3 days. For a few days after the catheter is removed, the patient may have difficulty controlling their urine. This should improve on its own.
Although no incision is made in the belly, TURBT is still considered a major surgery. To speed up recovery, the patient should plan on resting for a few days after the procedure. This includes avoiding stressful physical activities.
Overexertion can cause bleeding inside the bladder. Some blood in the urine, however, is normal. If this does not clear up after several days, or if urination continues to be difficult or blood clots are present in the urine, a physician should be contacted immediately. It is also normal to notice a couple of days of bloody urine again 10 to 14 days after surgery.
Antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent infections, including those of the urinary tract. If so, it is important to take them as directed in order to prevent a recurrent infection.
Other complications of TURBT are:
- Perforation of the bladder wall
What Are The Risks And Benefits Of A Turbt
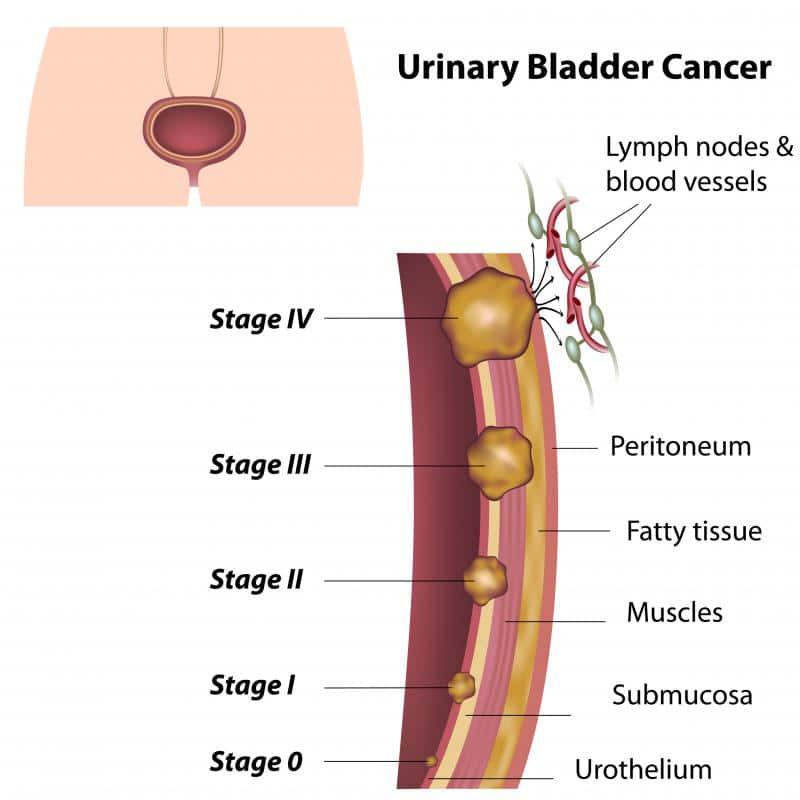
As with any type of surgery, there are both risks and benefits to a TURBT procedure. Generally, bladder tumor biopsy and resection is considered a very safe procedure. Some of the possible risks during or after surgery include:
- Anesthesia-related complications
- Infections of the urinary tract
- Bleeding after surgery
- Perforation of the bladder
Despite these risks, TURBT procedures are typically a successful treatment for early-stage cancer of the bladder. Having a TURBT can prevent cancer from spreading into the muscle wall of the bladder.
Read Also: How Do You Diagnose Overactive Bladder
How To Prepare For The Procedure
- Always ask your doctor about the steps of the treatment and any special instructions. These may differ per hospital or country, such as anaesthesia methods which include general anaesthesia and epidural anaesthesia. The latter is an anaesthetic used to numb the lower half of the body with or without sedation.
- If you are taking any medication, discuss it with your doctor. You may need to stop taking some of your medication for several days before surgery such as medications that thin your blood.
- It is important that your doctor and your other healthcare providers are informed about your treatment. It also helps that your partner, family or friends know about the procedures.
- Write down your questions or any important points you would like to discuss during appointments. Ask someone to accompany you for additional support.
You may be asked to give a urine sample to test for a urinary tract infection.
Trans Urethral Removal Of Bladder Tumour
A trans urethral resection of bladder tumour is usually the first treatment you have for early bladder cancer.
Your surgeon removes the tumour in your bladder through the urethra. The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of your body.
You might have TURBT to remove early bladder cancer:
- during a cystoscopy test if your specialist sees a tumour
- after having tests that have shown a bladder tumour
You usually have it under general anaesthetic, which means you are asleep. In some hospitals, you may have a spinal anaesthetic instead of a general anaesthetic. This is an injection into your spine so you cant feel anything from below your waist.
This treatment takes between 15 to 90 minutes.
Don’t Miss: What Causes Bladder Pain And Pressure
Procedure Of Transurethral Resection Of Bladder Tumor
TURBT is performed under general or spinal anesthesia. Your surgeon inserts a cystoscope into your bladder, through the urethral opening to locate any tumor growth or cancerous tissue in the bladder. An instrument called the resectoscope is inserted through the cystoscope. Electric current is passed through the wire loop to cut away the cancerous tissue along with a margin of healthy tissue. The complete surgical procedure takes around 15 to 40 minutes.
A catheter may be inserted into the urethra and left in place for about 24 hours to remove any blood clots formed in your bladder. You may have to stay in the hospital for 1 to 4 days after the surgery. Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to prevent infection and painkillers to provide relief from post-operative pain.
What Is Photodynamic Diagnosis
In some cases, PDD helps the surgeon to evaluate tumour cells which could have been undetected otherwise. This technique involves introducing a dye into the bladder an hour before the surgery. The dye is absorbed by cancer cells which makes these cancer cells glow red under a blue light during surgery.
PDD can also be used during follow-up cystoscopy. Your surgeon will decide whether this is necessary for you.
Recommended Reading: Can Men Get Bladder Infections
What Is Transurethral Resection Of Bladder Tumor
This surgical procedure is used in both the diagnosis and treatment of bladder cancer. Transurethral resection of bladder tumor allows your surgeon to biopsy your tumor, or remove an entire small tumor from the inside of your bladder, while leaving the bladder intact. TURBT is essential to obtain a biopsy to confirm the cancer diagnosis and determine the stage and grade of your cancer.
Sexual Effects Of Radical Cystectomy In Women
If the surgeon takes out the end of the urethra where it opens outside the body, the clitoris can lose some of its blood supply, which might affect sexual arousal. Talk with your surgeon about whether the end of the urethra can be spared.
For more on ways to cope with these and other sexual issues, see Sex and the Woman With Cancer.
Recommended Reading: Icd 10 For Metastatic Bladder Cancer
Tumours At The Ureteral Orifices
Coagulation close to the ureteral orifices should be avoided as it may cause scarring and lead to ureteric obstruction . However, tumours that involve the ureteral orifices can be resected judiciously under pure cutting settings. This would be particularly beneficial as satisfactory renal function can be facilitated if cisplatin-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy is considered for MIBC. Although it may result in vesicoureteric reflux and would be uncommon to cause stricture, a temporary ureteric stent placement between 2 and 6 weeks can further reduce the risk. A form of imaging such as renal ultrasound, CT urogram or Diethylenetriamine Pentaacetic Acid renal scan after resection is recommended.
Patient Recruitment Inclusion Criteria Exclusion Criteria And Study Design
Fig. 1
Design of the FLEBER study: inclusion criteria and endpoints. Patients should fulfill the indicated inclusion criteria to be eligible for this trial. *Hemoglobin, 9.0g/dL white blood cell count, 12,000/mm3 absolute neutrophil count, 2000 cells/mm3 platelet count, 100,000 cells/mm3 normal kidney and liver functions as determined by creatinine, total bilirubin, aspartate transaminase , and alanine transaminase 2× the upper limit of normal for the reference laboratory. Abbreviations: PDD, photodynamic diagnosis TURBT, transurethral resection of bladder tumor ECOG-PS, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group-Performance Status CIS, carcinoma in situ BCG, Bacillus Calmette-Guérin
Patients with tumors less than 6mm in diameter will be excluded from this trial because small tumors can be resected with a single cut using a standard loop electrode. In addition, patients with tumors more than 30mm in diameter will be excluded because large tumors cannot be removed en bloc from the bladder using a 28-Fr TUR resectoscope sheath. Patients who are suspected of having carcinoma in situ will be excluded because these patients will have to be treated using intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guérin postoperatively, and the carcinoma cannot be resected completely using EBTUR.
Read Also: Aggressive Bladder Cancer In Muscle
Sexual Effects Of Urostomy
Its normal people to be concerned about having a sex life with a urostomy. Having your ostomy pouch fit correctly and emptying it before sex reduces the chances of a major leak. A pouch cover or small ostomy pouch can be worn with a sash to keep the pouch out of the way. Wearing a snug fitting shirt may be more comfortable. Choose sexual positions that keep your partners weight from rubbing against the pouch. For more tips, see Urostomy Guide.
How To Prepare For Transurethral Resection
Before your surgery, your physician will ask that you end your medications that are used as blood-thinners. You will likely be given an antibiotic to prevent a urinary tract infection after the surgery. Typically, you are able to go home after the surgery, so you will need someone to drive you home. You should not work or do any strenuous activity for up to six weeks after the surgery. Your physician will be able to give you a better expectation of how much recovery time you will need.
The procedure will take between sixty to ninety minutes. You will be given general anesthesia. This means that you will be asleep for the duration of the surgery. If your physician recommends a spinal anesthesia, then you will be awake but not feel anything.
You are likely to stay in the hospital for one or two days. You will have a catheter because the swelling will block the urine flow. This will be removed within 48 hours. You may notice blood in the urine or irritating urinary symptoms. It is normal to see blood right after the surgery. If the blood becomes thick or begins to worsen, then you will want to speak to your physician. Blood clots can block the flow of urine. Painful urination will improve within eight weeks.
After surgery, your physician will likely recommend the following:
Also Check: Bladder Pacemaker For Urinary Retention
What Is A Bladder Tumour
Abnormal cell growth in the lining of your bladder can lead to the development of benign or malignant tumours.
If the tumour is cancerous, it can either be non-invasive or invasive:
- Non-invasive tumours these tend to stay in the lining of your bladder, which is the most common form of bladder cancer and usually isn’t life threatening, but there’s a small chance it could develop into an invasive tumour
- Invasive tumours these are cancers that grow into your bladder wall and can spread to other areas of your body.
What About Medications
- You can resume your usual medications
- If your blood thinning medication was stopped, your Doctor will let you know when to recommence
- You can take 1-2 paracetamol every 4-6 hours for pain and discomfort
- Ural sachets available from chemists and supermarkets, reduce acidity of the urine and provide relief from symptoms such as burning and stinging
You May Like: Can A Bladder Infection Heal Itself
How You Have It
The surgeon puts a thin rigid tube called a cystoscope into your urethra.
The cystoscope has optic fibres inside it, a light, camera and eyepiece at one end. The surgeon can look through the eyepiece or see images on a TV screen.
The surgeon passes small instruments down the cystoscope to cut any tumours out of your bladder lining.
What Can I Expect After The Procedure
- At the end of the operation, a thin tube may inserted into your bladder, which drains urine into a bag. The catheter is connected to a system that washes the blood and blood clots out of your bladder. This is known as bladder irrigation. When there is no longer a risk of clots, usually after 1-2 days, the catheter will be removed and you will be able to go home if you are passing adequate amounts of urine. If the tumour is small, you may not need a catheter and be discharged the same day.
- Bladder spasms due to the catheter. Sometimes medications are required if these are severe.
- Burning when you pass urine is common and can last up to a week. You can take Ural sachets to help with this.
- Bleeding this usually reduces over time, but can be intermittent and should stop after 4-6 weeks. You should increase your oral fluid intake to at least two to three litres of fluid per day and you can back off on your fluid intake if your urine is clear.
- Other urinarysymptoms can last for 2-4 weeks
You May Like: Bladder Infection In Older Adults
Preoperative Details Of Turbt
Patients will undergo pre-anesthesia testing in order to evaluate physical condition and medical conditions. As antithrombotic therapy has become more prevalent, the decision whether to hold anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents is a commonly discussed topic. While there are no guidelines to follow regarding the perioperative management of these medications, it is an often-debated balance between adverse cardiovascular events and persistent perioperative hematuria. While low-dose aspirin can be continued in most cases, all other antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants are almost always held perioperatively, with the duration and plan for resumption made on a case-by-case basis.
Patients scheduled for anesthetic cystoscopy with TURBT must have sterile urine documented prior to instrumentation. Sterility is usually presumed on the basis of a microscopic urinalysis showing no bacteria or white blood cells . Patients with a positive urine culture are conventionally treated with a course of culture-specific antibiotics to achieve this desired sterility.
En Bloc Resection Of Bladder Tumoris It The Way Forward
- 1Department of Urology, Luzerner Kantonsspital, Luzern, Switzerland
- 2Department of Urology, University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
- 3Department of Urology, Royal Surrey County Hospital, Guildford, United Kingdom
Transurethral resection of bladder tumors represents the cornerstone in diagnosis and treatment of bladder cancer but recurrence is observed in up to 80% and over- or understaging with TURBT is common. A more recent development to overcome these limitations represents en-bloc resection of bladder tumors which offers several advantages over TURBT. In this report, we briefly review studies assessing outcomes of bladder cancer patients undergoing ERBT. Most randomized and non-randomized trial demonstrate improvement in clinical outcomes for ERBT over TURBT, however more pathological and translational studies are warranted.
Also Check: Best Women’s Bladder Control Pads
Why Is A Turbt
Your surgeon has recommended a TUR-BT to remove a tumor from the lining of your bladder. About half, or 1 in 2 bladder cancers are found early. That means the tumor is still in the lining of the bladder and hasnt spread.
Your doctor has recommended that you have a TURBT or Transurethral Resection of a Bladder Tumor.
Before we talk about the procedure, lets review some information about your body and your medical condition.
The bladder holds urine until you release it.
It stretches like a balloon as it fills with urine. Muscle in the wall of the bladder works to push urine out of your body through your urethra.
Your surgeon has recommended a TUR-BT to remove a tumor from the lining of your bladder. About half, or 1 in 2 bladder cancers are found early.That means the tumor is still in the lining of the bladder and hasnt spread.
Bladder Cancer can be diagnosed at any age, but is most common in patients that are over 55 years old, men, and are white
Bladder Cancer is most often linked to smoking and exposure to certain chemicals in the workplace
With a TURBT, , a surgeon uses a scope to look at the bladder lining and remove the tumor.
A scope is an instrument with a light and camera. It has a loop at the tip that can cut with heat energy.
The tumor is sent to a pathology lab for examination. Further treatment may be needed in the future, after this surgery for your cancer. These plans are made if needed after the procedure and based on the final lab results.
What Is The Recovery Time From Bladder Tumor Biopsy And Resection
Following the procedure, youll have a catheter inserted into the bladder to drain urine. It is normal for there to be blood in the urine at first. Drinking liquids will help flush out your bladder and help prevent infections. Your catheter will be removed when there is no more blood visible in the urine or when you go home.
Most people can have a simple bladder tumor biopsy and resection done as an outpatient procedure. However, your provider might suggest you stay overnight if you have other medical concerns or if you have had a large amount of tissue removed.
You should be able to drink and eat the way you normally do. Youll probably be told to make sure you drink adequate amounts of fluids.
You might have some discomfort when you urinate.
You should be able to return to normal activity in a few days.
Also Check: What To Do For A Bladder Infection At Home