Is Bcg Treatment Contagious
Because BCG contains live bacteria, precautions are necessary to prevent it from being passed to others.
Patients should go to the bathroom sitting down to reduce splashing and wash their hands thoroughly after urinating. Pouring bleach into the toilet after use may also prevent contamination.
Once home, a patient should drink plenty of liquids and avoid sexual contact with others for 24 hours.
Research has shown that BCG may also reduce the risk of contracting a respiratory tract infection, giving your immune system a boost. However, precautions are still necessary to stay healthy.
The care team will talk to the patient about what to expect and provide instructions to follow at home.
How Does Immunotherapy Work
Pembrolizumab is a type of immunotherapy drug called a PD-1 inhibitor, that has been approved to treat various forms of bladder cancer and other types of cancers.1,2 The bodys immune system consists of a group of organs and cells that work to protect the body from diseases and infections. In a patient with cancer, immunotherapy drugs work by affecting the way the immune system functions to help it fight cancer cells more effectively.
Side Effects Of Immunotherapy
Like all treatments, checkpoint inhibitors can cause side effects. Because these drugs act on the immune system, they can sometimes cause the immune system to attack healthy cells in any part of the body. This can lead to a variety of side effects such as skin rash, diarrhoea, breathing problems, inflammation of the liver, hormone changes and temporary arthritis. Your doctor will discuss possible side effects with you.
To learn more see Immunotherapy.
Read Also: Most Common Site Of Metastasis For Bladder Cancer
Immunotherapy For Bladder Cancer
Some people with bladder cancer have immunotherapy. Immunotherapy helps to strengthen or restore the immune systems ability to fight cancer.
You may have immunotherapy to:
- kill bladder cancer cells
- stop bladder cancer cells from growing and spreading
- lower the risk that the cancer will come back
- help keep the cancer from coming back after it has already been treated
- control symptoms of bladder cancer
Your healthcare team will consider your personal needs to plan the drugs, doses and schedules of immunotherapy. You may also receive other treatments.
-
Discover Local Ovarian Cancer resources:
SurvivorNet Fact Checking and Medical Review Standards:
The SurvivorNet News Team creates high quality medical information that complies with our industry leading standards for factual accuracy and sourcing from leading experts at academic medical institutions. Every news article is thoroughly fact-checked by our physician collaborators. We vet each piece of work for factual integrity, impartiality, and clearly label any professional conflicts.
All SurvivorNet articles adhere to the following standards:
- Save This Video
Clinical Trials Of New Treatments
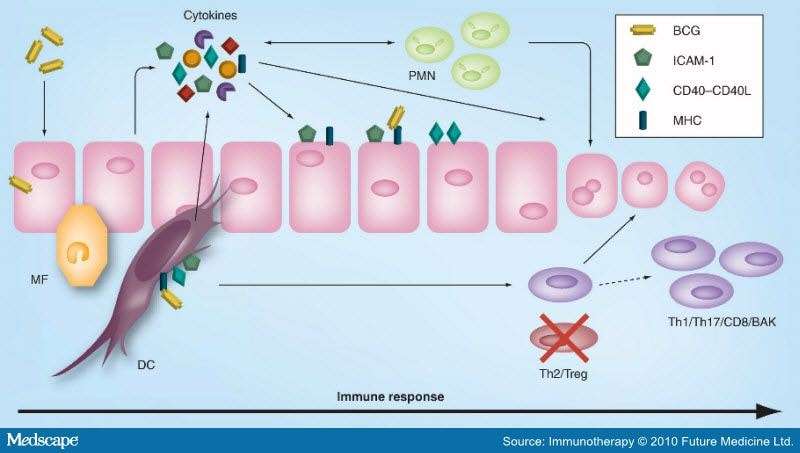
Perlmutter Cancer Center researchers are national leaders in investigating the use of new chemotherapy drugs, immunotherapies, and targeted drugs, which are designed to treat cancer cells while avoiding healthy tissue.
Clinical Trials
We are leaders in bladder cancer clinical trials that use novel combinations of immunotherapy, chemotherapy, and radiation to tailor treatment for each person.
Also Check: Why Do I Have Bladder Leakage
Is There Any Preparation Involved
Its important that you follow your doctors instructions for what to do before and after the procedure. Tell your doctor about all the medications you take. Certain immunosuppressants, antimicrobial therapies, and radiation therapies can interfere with BCG treatment.
Youll be advised to limit your fluid intake for four hours prior to the procedure. You might be told to avoid caffeine for a few hours longer than that, because its a diuretic and could make things more difficult.
Youll be asked to urinate just before the procedure so youll be able to hold the medication in your bladder for several hours.
Immunotherapy Side Effects: What To Know
If youve researched cancer treatment options, youve probably heard of immunotherapy, which trains the immune system to attack cancer, rather than attacking the cancer directly. You also might have heard that immunotherapy doesnt have side effects.
But thats not always the case. With the most common type of immunotherapy â immune checkpoint therapies â about 5-10% of patients experience side effects, and theyre life-threatening in about 1-2% of those cases, says Vivek Subbiah, M.D. Examples of immune checkpoint drugs include: pembrolizumab , nivolumab , atezolizumab , ipilimumab , avelumab and durvalumab .
Immunotherapy side effects often differ from those commonly seen with other types of cancer treatment. Heres what patients should know.
Fatigue, inflammation top common side effects
As with many cancer therapies, fatigue tends to be one of the most common, says Van Morris, M.D.
But immunotherapy drugs also can cause inflammation throughout the body. For example, patients may experience skin inflammation as pigment changes, a rash and feeling itchy, sometimes even without a rash. Inflammation in the lungs can cause a cough and chest pains. The colon may also become inflamed, causing abdominal pain and diarrhea.
Side effects often show up early in treatment or months or years later
Side effect management depends on the severity
Patients who develop diabetes may require insulin or a period of time off the immunotherapy.
Watch for changes in your body
Recommended Reading: Can A Bladder Infection Cause You To Bleed
Treating Stage Iii Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the outside of the bladder and might have grown into nearby tissues or organs and/or lymph nodes . They have not spread to distant parts of the body.
Transurethral resection is often done first to find out how far the cancer has grown into the bladder wall. Chemotherapy followed by radical cystectomy is then the standard treatment.Partial cystectomy is rarely an option for stage III cancers.
Chemotherapy before surgery can shrink the tumor, which may make surgery easier. Chemo can also kill any cancer cells that could already have spread to other areas of the body and help people live longer. It can be especially useful for T4 tumors, which have spread outside the bladder. When chemo is given first, surgery to remove the bladder is delayed. The delay is not a problem if the chemo shrinks the cancer, but it can be harmful if it continues to grow during chemo. Sometimes the chemo shrinks the tumor enough that intravesical therapy or chemo with radiation is possible instead of surgery.
Some patients get chemo after surgery to kill any cancer cells left after surgery that are too small to see. Chemo given after cystectomy may help patients stay cancer-free longer, but so far its not clear if it helps them live longer. If cancer is found in nearby lymph nodes, radiation may be needed after surgery. Another option is chemo, but only if it wasnt given before surgery.
What Is The Immune System And How Does It Work With Cancer
The immune system is a natural part of our body. Its role is to get rid of foreign or damaged material and cells before they cause trouble.
Most of the time, our immune system can find foreign invaders like bacteria and viruses, and destroy them. The immune system uses signals to attack them while leaving healthy cells alone.
Cancer is different from an illness caused by a bacteria or virus. It involves the uncontrolled growth of normal body cells. In other words, cancer cells may not be found by the immune system. Though they look different under the microscope, cancer cells can hide and grow. One way cancer cells hide is to express proteins on their surface to turn-on a âcheckpointâ to stop an immune system attack.
The National Cancer Institute studied common tumors in its Cancer Genome Atlas project. The research showed that bladder cancer, skin cancer and lung cancer have the most cellular changes . These types of cancer may be more likely to respond to treatments that help the immune system find cancer cells, called âimmunotherapiesâ.
What is Immunotherapy?
Immunotherapy is any treatment that makes the immune system stronger. For cancer, it helps the body find and attack cancer cells. The field of immuno-oncology studies how the immune system interacts with cancer. It uses that information to make new treatments.
What Happens Under Normal Conditions?
What Happens When Cancer Cells Grow and Hide?
Three things help cancers hide from the immune system:
Also Check: How To Cure Bladder Pain
When You Go Home
Some hospitals allow you to go home with the medicine in your bladder if you live close by and are okay with the treatment. Your team will let you know if you can do this. You should follow the advice on what to do when you pass urine.
You need to drink lots of fluid after this treatment for 24 hours. It helps clear your system of the BCG.
You should not have sex for 24 hours after each treatment. During your course of treatment and for a week afterwards, you should wear a condom during sex.
Having bladder cancer and its treatment can be difficult to cope with. Tell your doctor or nurse about any problems or side effects that you have. The nurse will give you telephone numbers to call if you have any problems at home.
If Your Immunotherapy Stops Working
Immunotherapy may not work for everyone who takes it. If youâve tried it and it didnât stop your cancer, you still have a few options. What kind of treatment you get next depends on what others youâve tried and what stage your cancer is in.
This treatment uses powerful drugs to kill cancer. Even if youâve already tried some drugs before or along with your immunotherapy, your doctor may try other ones or different combinations of medicines to fight your cancer. Chemo drugs for the most common form of bladder cancer include:
Youâll get chemotherapy in cycles with a few weeks in between to give your body time to recover.
Surgery
If you still have all or part of your bladder, your doctor might recommend an operation called a radical cystectomy. Your doctor will take out all of your bladder and the lymph nodes nearby. They might also remove some of your reproductive organs. For men, that could be the prostate gland and seminal vesicles. For women, it might be the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and a small part of the .
If you think you might want to join a clinical trial, your doctor will help you make the decision. They will talk about:
- How the new treatment is different from the usual treatments you could get
- What the risks are
- Any tests youâll need
- How often youâll get treatment
Youâll be able to leave the clinical trial whenever you want, for whatever reason you might have.
Also Check: Bladder Cancer In Cats Treatment
Am I Eligible For Immunotherapy
In 2018, the most common question that Emil Lou, M.D., Ph.D., heard from patients with cancer in his clinic at the University of Minnesota was: Am I eligible for immunotherapy?
Most of these patients had seen advertisements for immunotherapy on television or heard a story about a patients tumor melting away, and they wanted to know if they could get immunotherapy, said Dr. Lou, who treats patients with gastrointestinal cancers.
His patients had heard of dramatic and lasting responses to immunotherapy drugs among some patients with advanced cancers.
Although few of his patients have been candidates for immunotherapy based on the genetic features in their tumors, Dr. Lou has discussed the treatmentand possible side effectswhen it has been an option.
In these conversations, he would introduce the idea that immunotherapy drugs have side effects. In that respect, immunotherapy drugs are like all treatments for cancer, he tells his patients. They can cause rashes and joint pain and diarrhea. And in a small percentage of patients, immunotherapy can cause shortness of breath and other more serious complications.
Dr. Lou added, Immunotherapy drugs are not perfect.
What Is Bcg Treatment
Bacillus Calmette-Guerin treatment is a type of intravesical immunotherapy. This liquid drug is made from a strain of Mycobacterium bovis the same bacterium used to create the tuberculosis vaccine. When used in medicine, Mycobacterium bovis is weakened to reduce harm to your body.
BCG treatment is usually given after TURBT , which is a bladder surgery to remove any visible cancer.
Also Check: All Symptoms Of Bladder Infection
Radiotherapy With A Radiosensitiser
Radiotherapy is given by a machine that beams the radiation at the bladder . Sessions are usually given on a daily basis for 5 days a week over the course of 4 to 7 weeks. Each session lasts for about 10 to 15 minutes.
A medicine called a radiosensitiser should also be given alongside radiotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. This medicine affects the cells of a tumour, to enhance the effect of radiotherapy. It has a much smaller effect on normal tissue.
As well as destroying cancerous cells, radiotherapy can also damage healthy cells, which means it can cause a number of side effects. These include:
- erectile dysfunction
- difficulty passing urine
Most of these side effects should pass a few weeks after your treatment finishes, although there’s a small chance they’ll be permanent.
Having radiotherapy directed at your pelvis usually means you’ll be infertile .
After having radiotherapy for bladder cancer, you should be offered follow-up appointments every 3 months for the first 2 years, then every 6 months for the next 2 years, and every year after that. At these appointments, your bladder will be checked using a cystoscopy.
You may also be offered CT scans of your chest, abdomen and pelvis after 6 months, 1 year and 2 years. A CT scan of your urinary tract may be offered every year for 5 years.
Is There A Risk Of Bladder Cancer After Bcg Treatment
Like most cancers, bladder cancer can potentially return after treatment. Statistically, cancer will recur in up to 40% of people who receive BCG treatment. Its important to note, however, that even if the cancer comes back, it may not progress.
Low-grade bladder cancer usually doesnt spread to other areas of your body. But people who have low-grade bladder cancer have a higher risk of developing other low-grade cancers throughout their lifetime.
Less often, aggressive bladder cancer can develop after BCG treatment. If this happens, cystectomy is usually recommended.
Recommended Reading: Exercises To Stop Bladder Leakage
What Are Common Side Effects Of Immunotherapy
Side effects depend on the way you get immunotherapy.
Side effects of intravesical immunotherapy can include:
-
Discomfort or burning in your bladder
-
Feeling the need to urinate often
- Pain when you urinate
- Blood or clots in your urine
-
Flu-like symptoms, such as chills, fatigue, or fever
-
Serious infection if BCG spreads through your body
These side effects often go away within a few days after the treatment. Still, make sure you know what to watch for and when you need to contact your doctor.
Side effects of systemic immunotherapy can include:
- Skin changes, like itchy rashes, redness, blistering, cracking, and dryness
- Inflammation around finger and toe nails
Subtleties And Future Questions
Several factors have to be carefully considered in interpreting the trial results, explained Dr. Apolo.
A major one is that the study did not directly compare survival between people who got avelumab immediately versus when their cancer progressed. Only about half of the participants who initially received supportive care alone went on to receive immunotherapy after their cancer got worse. There could be many reasons for this, including lack of access to these drugs in different countries, Dr. Apolo said.
But it also might be that, for some people, the cancer was progressing too rapidly, she added. When these tumors start growing, they start growing very quickly. So if you wait to start at the time of progression, maybe its too late, added Dr. Apolo.
Not all patients will be caught by the second-line safety net, agreed Dr. Plimack.
So, for now, said Dr. Balar, the takeaway message from the JAVELIN study is after chemotherapy, dont wait to give immunotherapy.
But more and more, studies are looking at whether some patients should receive immunotherapy as first-line treatment, he continued. Immunotherapy is one of the most important advances weve made in the last 30 years, Dr. Balar said.
The JAVELIN results cant provide any insight into which patients benefit from first-line treatment with a platinum-based chemotherapy, he added. This trial wasnt designed to ask: Is chemotherapy necessarily the best choice for every patient? he explained.
Recommended Reading: Can Chronic Bladder Infections Lead To Cancer
Substantial Improvement In Survival
Dr. Powles and his colleagues enrolled 700 people with locally advanced or metastatic bladder cancer in the international JAVELIN Bladder 100 study, which was funded by Pfizer, the drugâs manufacturer.
All trial participants had already received chemotherapywith either cisplatin and gemcitabine or carboplatin and gemcitabine, if their health did not allow them to receive cisplatinand their disease had not worsened during chemotherapy.
Participants were then randomly assigned to receive either maintenance treatment with avelumab plus supportive care or supportive care alone. People in the maintenance group received infusions of avelumab every 2 weeks until their cancer started growing again or they left the study for other reasons. Supportive care for both groups included pain management, nutritional support, and treatment of infections.
People in the supportive care group whose cancer got worse did not receive avelumab as part of the trial. However, they could receive it or any other immunotherapy drug after leaving the study.
Maintenance treatment with avelumab after chemotherapy turned out to have substantial benefits. The median overall survival for people who received maintenance avelumab was more than 21 months, compared with about 14 months for people who received only supportive care until their cancer got worse.
Are There Any Possible Effects From The Treatment
9out of 10 people having BCG will develop some side effects these usually beginwithin 3-4 hours after treatment and may last 1-3 days.
Commontreatment effects
You should tell your doctorat your next appointment if you have any of these symptoms.
- Somebladder discomfort – an irritation rather like a urine infection.
- Flu-likesymptoms which can last for 1-3 days after each treatment.
- Wantingto pass urine more often than usual or more urgently, which can last for two tothree days.
- Failureto complete the course of treatment due to discomfort in the bladder.
- Bloodor debris in the urine.
Drinking2 litres of fluid daily, unless advised otherwise, and avoiding tea/coffee for24 hours after treatment will help flush any remaining drug out of the bladderand may ease the above symptoms.
Occasional
- Narrowing of the urethra following repeated use of a catheter.
- Inflammationwhich can affect various parts of the body .
Rare
- Persistentor severe pain after treatment, sometimes leading to removal of the bladder.
- Generalisedand possibly serious infection with the BCG bacteria needing treatment inhospital with powerful antibiotics. This is not TB and there is no risk ofcatching TB from the treatment.
Veryrarely – less than 1 person in every 100 – may experience more serious treatmenteffects.
Contact your GP/Nurse immediately if you have anyof the following:
- Urineis cloudy/offensive smelling
- HighTemperature over 38°C for 48 hours
Don’t Miss: How To Relieve Bladder Inflammation