Why Does Bladder Cancer Happen
Most cases of bladder cancer appear to be caused by exposure to harmful substances, which lead to abnormal changes in the bladder’s cells over many years.
Tobacco smoke is a common cause and it’s estimated that half of all cases of bladder cancer are caused by smoking.
Contact with certain chemicals previously used in manufacturing is also known to cause bladder cancer. However, these substances have since been banned.
Read more about the causes of bladder cancer and preventing bladder cancer
Signs And Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
Sometimes bladder cancer doesnt have many symptoms. Signs or symptoms can include:
- blood in your urine
- pain or burning when passing urine
- not being able to pass urine when you need to.
Not everyone with these symptoms has bladder cancer. If you have any of these symptoms or are worried, always see your doctor.
What Kind Of Treatment Will I Need
There are many ways to treat bladder cancer. You might want to get a second opinion about the best treatment plan for you.
Bladder cancer is most often treated with:
Sometimes more than one type is used. The treatment plan thats best for you depends on:
- The stage and grade of the cancer
- Whether the cancer has spread into the bladder wall
- The chance that a type of treatment will cure the cancer or help in some way
- Other health problems you have
- Your feelings about the treatment and the side effects that come with it
Don’t Miss: Galvanized Pressure Tank Vs Bladder Tank
Treatment Of Bladder Cancer By Stage
Most of the time, treatment of bladder cancer is based on the tumors clinical stage when it’s first diagnosed. This includes how deep it’s thought to have grown into the bladder wall and whether it has spread beyond the bladder. Other factors, such as the size of the tumor, how fast the cancer cells are growing , and a persons overall health and preferences, also affect treatment options.
Catheterizable Continent Diversion Pouch
This is a reservoir of bowel with a stoma that is catheterizable for emptying the bladder. The urine is siphoned out of the urinary reservoir with a small catheter every four to six hours. The catheterizable pouch may require surgical repair at some point after surgery due to the wear and tear of frequent catheterization. This type of reconstruction is not performed on patients with a history of bowel disease.
Don’t Miss: Treatment After Bladder Tumor Removal
The Following Stages Are Used For Bladder Cancer:
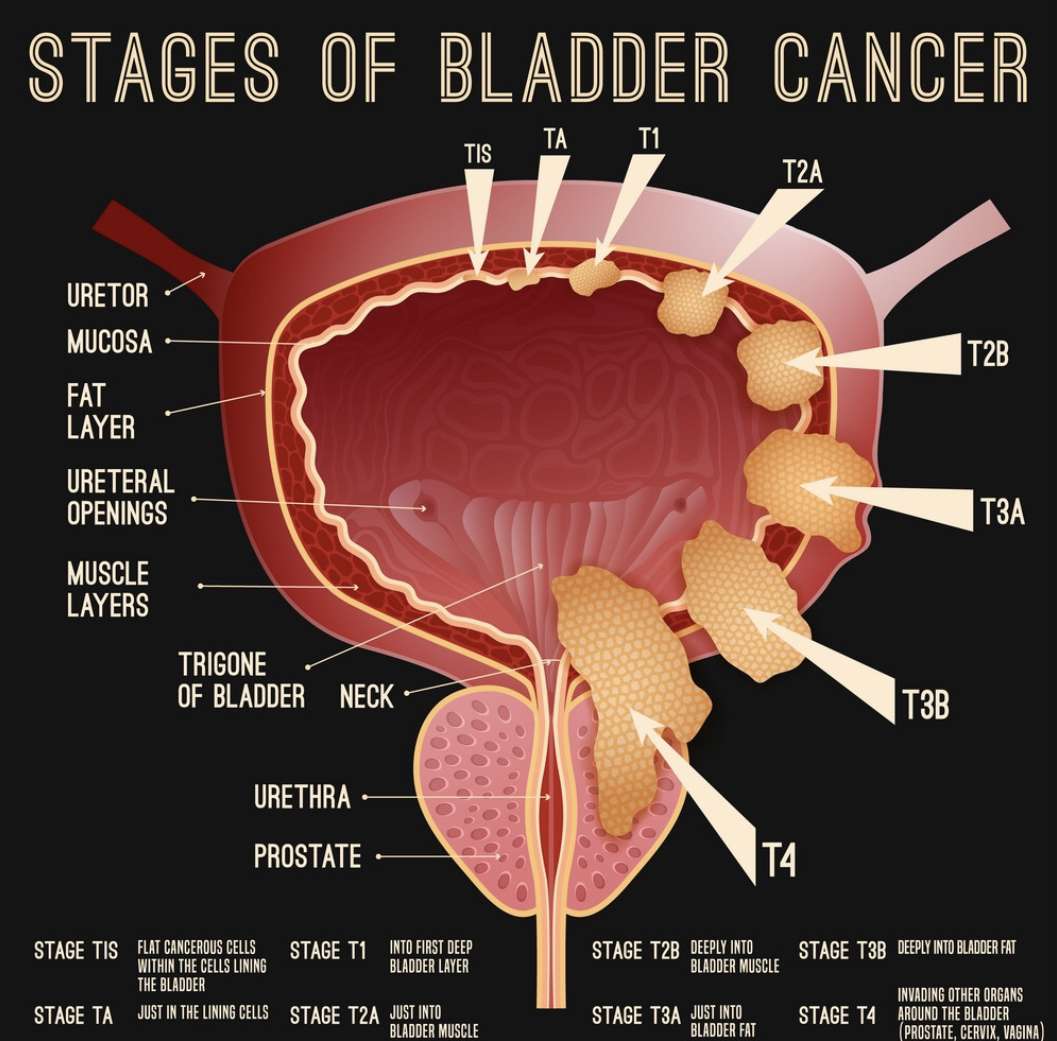
Stage 0
In stage 0, abnormalcells are found in tissue lining the inside of the bladder. These abnormal cells may become cancer and spread into nearby normal tissue. Stage 0 is divided into stages 0a and 0is, depending on the type of the tumor:
- Stage 0a is also called noninvasive papillary carcinoma, which may look like long, thin growths growing from the lining of the bladder.
- Stage 0is is also called carcinoma in situ, which is a flat tumor on the tissue lining the inside of the bladder.
Stage I
In stage I, cancer has formed and spread to the layer of connective tissue next to the inner lining of the bladder.
Stage II
In stage II, cancer has spread to the layers of muscle tissue of the bladder.
Stage III
Stage III is divided into stages IIIA and IIIB.
- cancer has spread from the bladder to the layer of fat surrounding the bladder and may have spread to the reproductive organs and cancer has not spread to lymph nodes or
- cancer has spread from the bladder to one lymph node in the pelvis that is not near the common iliac arteries .
Cancer Stages For Superficial Bladder Cancer
Ta: The most common superficial bladder cancer is stage Ta. This tumor looks like a cauliflower in the bladder, and it does not grow into any of the layers of the bladder. Further treatments for single Ta tumors are usually not needed. Patients do need to come back for regular cystoscopy to make sure the tumor does not come back. In patients with tumors that come back, or patients with many of these tumors at the initial surgery, medicine can be given inside the bladder to prevent cancer from coming back. Stage Ta cancers do come back with some regularity, but they rarely change into cancers that can grow into the bladder wall or go to other parts of the body.
Read Also: Natural Herbs For Bladder Control
Other Treatments For Bladder Cancer
For many early-stage bladder cancers, BCG is the best option for treatment. Other treatments for bladder cancer include:
- Surgery to remove the tumor: Early cancers can be removed with TURBT surgery. More advanced cancers may require more extensive surgery, like removal of part or all of the bladder .
- Intravesical chemotherapy: This treats the inside of the bladder with chemotherapy drugs. Chemotherapy drugs commonly used for bladder cancer include Mutamycin , Gemzar , or Valstar .
- Radiation therapy
- Clinical trials
Mechanistic Interactions Between Bladder Cancer And Aging
Several broad hypotheses have proposed potential mechanisms for the association between cancer and aging, whereby the biological processes of aging could influence the development and/or progression of cancer in older adults. The processes interact at multiple levels for example, tumor protein 53 a tumor suppressoris involved in both cancer and aging: alteration of the p53 gene is the most frequently encountered mutation in human cancers , and the efficiency of the response to p53 has been found to vary according to age. In a mouse study, Feng et al.28 reported that the efficiency of the p53 response was significantly reduced in older mice compared with their younger counterparts. The reduced response predominantly resulted from decreased transcriptional activity and p53-dependent apoptosis decreased stabilization of p53 after stress was found to be the major factor in this decline.
Don’t Miss: Interstitial Cystitis Or Overactive Bladder
Side Effects Of Treatment For Bladder Cancer
All cancer treatments can have side effects. Your treatment team will discuss these with you before you start treatment. Talk to your doctor or nurse about any side effects you are experiencing. Some side effects can be upsetting and difficult, but there is help if you need it.
or email to speak with a caring cancer nurse for support.
Nearly 80000 People Are Diagnosed With Bladder Cancer Each Year In The United States
While anyone at any age may be affected by bladder cancer, it’s more common in men and older adults. Since it’s often detected in the early stages, bladder cancer is also considered one of the most treatable forms of cancer that may affect the urinary system.
Even when successfully treated, however, periodic examinations by a urologist are recommended to detect signs of recurrence.
Contact Us Today
Don’t Miss: Sleep Number Bed Bladder Replacement
Treatment For Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
Surgery
Surgery for invasive bladder cancer usually involves removing the whole bladder and then constructing a new way to pass urine. There are different ways of doing this. Read more about surgery for muscle invasive bladder cancer
Radiotherapy
This involves using high energy X-rays to kill the cancer cells. Your bladder will not be removed but you may get side-effects that affect your bladder in the short or long term. Your consultant will discuss with you if you radiotherapy might be helpful for you. Read more about radiotherapy .
Chemotherapy
This is the use of drugs to kill or control the cancer cells. Chemotherapy for muscle invasive bladder cancer is given into a vein . You may have chemotherapy during radiotherapy , before radiotherapy or before or after surgery. Read more about chemotherapy .
Treatments After Or Instead Of Surgery
Sometimes, doctors will use a mix of chemotherapy and radiation therapy to avoid surgery to remove the bladder. It can be a good option if youâre not healthy enough for surgery. In this case, you will likely take the chemo drug cisplatin by itself, cisplatin and fluorouracil, or mitomycin with fluorouracil.
You may also get chemotherapy and radiation together after surgery if your cancer has grown into the muscle layer of the bladder but hasnât spread elsewhere.
If your cancer spreads after chemo, you can try other chemotherapy drugs or other types of medicine, like immunotherapy.
Read Also: Bladder Infection Spread To Kidneys
Treating Bladder Cancer That Progresses Or Recurs
If cancer continues to grow during treatment or comes back after treatment , treatment options will depend on where and how much the cancer has spread, what treatments have already been used, and the patient’s overall health and desire for more treatment. Its important to understand the goal of any further treatment if its to try to cure the cancer, to slow its growth, or to help relieve symptoms as well as the likely benefits and risks.
For instance, non-invasive bladder cancer often comes back in the bladder. The new cancer may be found either in the same place as the original cancer or in other parts of the bladder. These tumors are often treated the same way as the first tumor. But if the cancer keeps coming back, a cystectomy may be needed. For some non-invasive tumors that keep growing even with BCG treatment, and where a cystectomy is not an option, immunotherapy with pembrolizumab might be recommended.
Cancers that recur in distant parts of the body can be harder to remove with surgery, so other treatments, such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or radiation therapy, might be needed. For more on dealing with a recurrence, see Understanding Recurrence.
When To See A Doctor
There are a few side effects that can be especially dangerous, so make sure to talk to your doctor if you notice that you:
- Have a severe skin rash
- Are wheezing or having difficulty breathing
- Are finding swallowing to be difficult
- Have a high fever that isnt lowered with Tylenol or other over-the-counter fever reducers
Recommended Reading: Robotic Surgery For Prolapsed Bladder
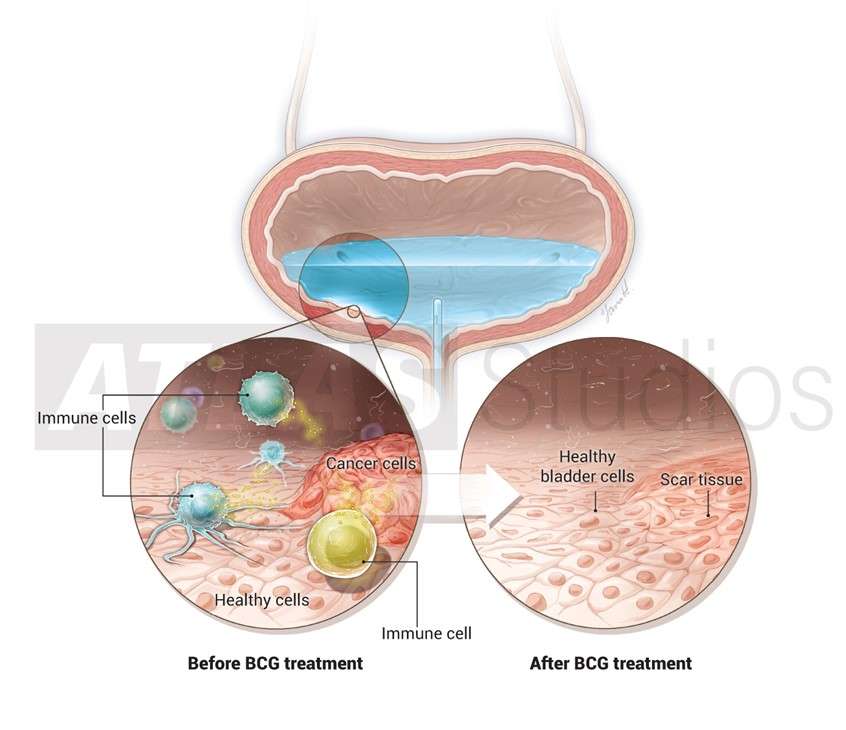
Who Can Use Bcg
BCG is a treatment for early-stage bladder cancer that has not yet invaded the muscle of the bladder wall. Called non-muscle invasive bladder cancers or in situ bladder cancers, these account for about half of all bladder cancers.
For 2021, it was estimated that about 83,730 new cases of bladder cancer would be diagnosed in the United States, and about 17,200 American bladder cancer patients would die from the disease.
Treating Stage Iv Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the pelvic or abdominal wall , may have spread to nearby lymph nodes , and/or have spread to distant parts of the body . Stage IV cancers are very hard to get rid of completely.
Chemotherapy is usually the first treatment if the cancer has not spread to distant parts of the body . The tumor is then rechecked. If it appears to be gone, chemo with or without radiation or cystectomy are options. If there are still signs of cancer in the bladder, chemo with or without radiation, changing to another kind of chemo, trying an immunotherapy drug, or cystectomy may be recommended.
Chemo is typically the first treatment when bladder cancer has spread to distant parts of the body . After this treatment the cancer is rechecked. If it looks like it’s gone, a boost of radiation to the bladder may be given or cystectomy might be done. If there are still signs of cancer, options might include chemo, radiation, both at the same time, or immunotherapy.
In most cases surgery cant remove all of the cancer, so treatment is usually aimed at slowing the cancers growth and spread to help people live longer and feel better. If surgery is a treatment option, it’s important to understand the goal of the operation whether it’s to try to cure the cancer, to help a person live longer, or to help prevent or relieve symptoms from the cancer.
Because treatment is unlikely to cure these cancers, many experts recommend taking part in a clinical trial.
Also Check: How Do You Stop Overactive Bladder
How Bladder Cancer Differs In Women And Younger Adults
Bladder cancer is one of the most commonly diagnosed forms of cancer in the U.S. About 1 in 40 Americans born today will develop this cancer at some point in their lifetime, and a majority of these people will be males over the age of 60. Bladder cancer is the fourth most common cancer in American men, representing more than 6% of all cancers in males.
But while men are three to four times more likely than women to develop bladder cancer, the disease tends to be deadlier in females. Women are also more likely to be diagnosed with larger bladder tumors. Why? These are questions that medical researchers have puzzled over for years, but answers remain elusive. We know that women are more likely than men to be diagnosed with advanced disease, but whether their cancer is biologically more active, or missed for a longer period of time, we dont know, says Dr. Janet Kukreja, an associate professor and bladder cancer specialist at the University of Colorado Cancer Center. These sex discrepancies are particularly striking because, for many other cancerssuch as cancers of the head, neck, esophagus, stomach, liver, and pancreaswomen tend to fare better than men.
Figuring out the causes of these age and sex disparities is an important area of bladder-cancer research. Finding answers could lead to improved treatments and outcomes.
Developing A Treatment Plan
In cancer care, different types of doctors often work together to create a patients overall treatment plan that combines different types of treatments. This is called a multidisciplinary team. This team is usually led by a urologist, a doctor who specializes in the genitourinary tract, or a urologic oncologist, a doctor who specializes in treating cancers of the genitourinary tract. Cancer care teams include a variety of other health care professionals, such as physician assistants, nurse practitioners, oncology nurses, social workers, pharmacists, counselors, dietitians, and others.
Treatment options and recommendations depend on several factors, including:
-
The type, stage, and grade of bladder cancer
-
Possible side effects
-
The patients preferences and overall health
Your care plan also includes treatment for symptoms and side effects, an important part of cancer care.
The first treatment a person is given for advanced urothelial cancer is called first-line therapy. If that treatment stops working, then a person receives second-line therapy. In some situations, third-line therapy may also be available.
Adjuvant systemic therapy is treatment that is given after radical surgery has been completed. In bladder cancer, adjuvant therapy is usually cisplatin-based chemotherapy or treatment in a clinical trial. Neoadjuvant therapy is treatment that is given before surgery, such as cisplatin-based chemotherapy.
Treatments by type and stage of bladder cancer:
You May Like: How To Get A Bladder Infection
Types Of Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer can be described based on where it is found:
- non-muscle invasive the cancer has not spread to other layers of the bladder or muscle
- muscle-invasive the cancer has spread to other layers of the bladder, muscle or other parts of the body.
There are 3 main types of bladder cancer:
- urothelial carcinoma 80 to 90% of bladder cancers sometimes called transitional cell carcinoma
- squamous cell carcinoma 1 to 2% of all bladder cancers. It is more likely to be invasive
- adenocarcinoma 1 to 2% of all bladder cancers. It is more likely to be invasive .
There are other, less common types of bladder cancer. Treatment for these may be different. Speak to your doctor or nurse for information about these types of cancer.
Immunotherapy For Bladder Cancer
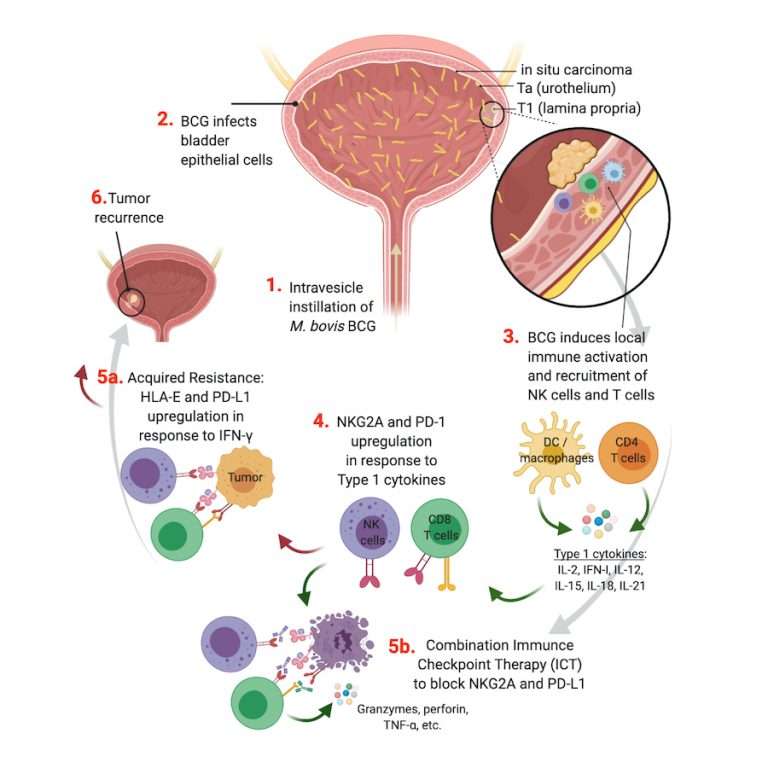
Immunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that aims to boost your immune systems response to cancer. There are a few different types of immunotherapy for bladder cancer.
In BCG immunotherapy, a type of bacteria called BCG is introduced directly to the bladder via a catheter. This helps to stimulate an immune response to the cancer. Its typically used for early stage bladder cancers that havent invaded the bladder muscle tissue.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors work by switching off one of the mechanisms that keeps the immune system from attacking cells in the body. They include drugs like nivolumab and pembrolizumab and may be used:
- to prevent cancer from coming back after surgery
- when other treatments havent been effective or arent recommended
- if cancer has come back after treatment
Monoclonal antibodies bind to certain parts of cancer cells. Those used for bladder cancer deliver chemotherapy drugs directly to cancer cells. They may be used when other treatments havent been effective or arent recommended.
Don’t Miss: Alternative Treatment For Bladder Cancer
Women And Bladder Cancer: Sharing Stories To Advance Research
BCAN was invited to share the experiences of women diagnosed with bladder cancer at the Bladder Cancer in Women: Identifying Research Needs to Improve Diagnosis and Treatment program sponsored by Johns Hopkins Greenberg Bladder Cancer Institute and the American Urological Association Translational Research Collaboration. Each of these womens stories are memorable and unique. Sadly, their stories are repeated around the country because women are not the typical bladder cancer patient. Read the the transcript of their presentation.