Male Ic/bps Versus Chronic Prostatitis
CP/CPPS, or NIH Type III prostatitis,63 is characterized by pain in the perineum, suprapubic region, testicles or tip of the penis.64
The pain is often exacerbated by urination or ejaculation. Voiding symptoms such as sense of incomplete bladder emptying and urinary frequency are also commonly reported, but pain is the primary defining characteristic of CP/CPPS. It is clear that the clinical characteristics which define CP/CPPS are very similar to those previously described for IC/BPS. In general, the Panel believes that the diagnosis of IC/BPS should be strongly considered in men whose pain is perceived to be related to the bladder, or they have symptoms of painful bladder filling and/or painful urgency. However, it is also quite clear that certain men have symptoms which meet criteria for both conditions .
In such cases, the treatment approach can include established IC/BPS therapies as well as other therapies that are more specific to CP/ CPPS. It is interesting to note that some studies of patients with CP/CPPS have high rates of bladder glomerulation under anesthesia.65 Additionally, empiric IC/BPS strategies in those CP/CPPS patients have demonstrated clinical symptomatic improvement.62, 65, 66
How Is Interstitial Cystitis Diagnosed
No single test can diagnose IC. And symptoms of IC are a lot like those of other urinary disorders. For these reasons, a variety of tests may be needed to rule out other problems. Your healthcare provider will start by reviewing your medical history and doing a physical exam. Other tests may include:
-
Urinalysis. Lab testing of urine to look for certain cells and chemicals. This includes red and white blood cells, germs, or too much protein.
-
Urine culture and cytology. Collecting and checking urine for white blood cells and bacteria. Also, if present, what kind of bacteria there are in the urine.
-
Cystoscopy. A thin, flexible tube and viewing device, is put in through the urethra to examine the bladder and other parts of the urinary tract. This checks for structural changes or blockages.
-
Bladder wall biopsy. A test in which tissue samples are removed from the bladder and checked under a microscope to see if cancer or other abnormal cells are present.
-
Lab exam of prostate secretions . This is done to look for inflammation and/or infection of the prostate.
Overactive Bladder Vs Interstitial Cystitis: Overlapping Conditions
Posted by John Thomas Stoffel, MD | May 2022
John Thomas Stoffel, MD, presented Overactive Bladder vs. Interstitial Cystitis: Overlapping Conditions? during the 41stAnnual Ralph E. Hopkins Urology Seminar on February 3, 2022, in Jackson Hole, Wyoming.
How to cite: Stoffel, John Thomas. Overactive Bladder vs. Interstitial Cystitis: Overlapping Conditions? February 3, 2022. Accessed Aug 2022. https://grandroundsinurology.com/overactive-bladder-vs-interstitial-cystitis-overlapping-conditions/
You May Like: My Journey With Bladder Cancer
Influence Of Childhood Traumatic History Anxiety And Depression On Perceived Stress Levels
Stress levels may be influenced by psychosocial factors such as childhood traumatic events, anxiety and depression. These factors were assessed using the childhood traumatic event scale and the hospital anxiety and depression scale , respectively . OAB patients with a childhood history of sexual trauma or physical trauma reported higher stress levels on the PSS compared to OAB patients without such a history . OAB patients with higher anxiety scores had higher stress levels than those with lower anxiety scores , PSS of 23.1±1.3 versus 11.9±1.1, p< 0.0001. OAB patients with higher depression scores had higher stress levels than those with lower depression scores , PSS of 22.9±1.2 versus 15.1±1.4, p=0.014.
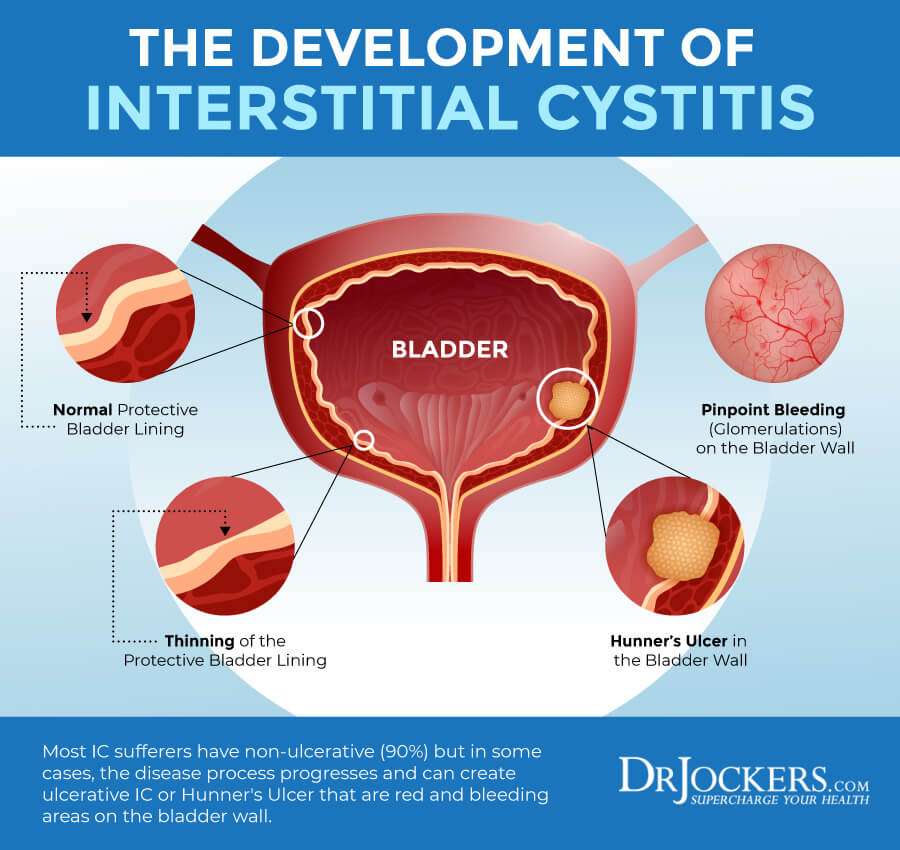
Key Points About Interstitial Cystitis
-
Interstitial cystitis is an inflamed or irritated bladder wall.
-
The cause of IC is unknown and it does not get better with antibiotics.
-
Symptoms of IC include changes in urination such as frequency and urgency pressure, pain, and tenderness around the bladder, pelvis, and the area between the anus and vagina or anus and scrotum and pain during sex.
-
There is no best way to diagnose IC. A variety of tests may be needed. Urine tests will be done and imaging tests may be used to look at the different parts of the urinary tract and make sure everything is normal. Tissue samples may be removed from the bladder and examined under a microscope to see if cancer or other abnormal cells are present.
-
Treatments are aimed at easing symptoms. A variety of procedures, medicines, and lifestyle changes may be advised.
You May Like: How Do You Treat A Bladder Infection
Oab Or Ic Symptoms In The Presence Of Blood In The Urine
- If a female has these symptoms and there is blood in the urine there is the possibility of a small ureteral stone near the bladder exists
- The blood must be proved to be benign with CT Scan and cystoscopy
Now to the issues of your bladder unrelated to an infection and requires treatment modalities that dont utilize antibiotics and require the expertise of someone in tune with what you are experiencing. You know who you are. We at the Northeast Georgia Urological Associates understand the frustration of bladder disorders and want to help. Christie Woodruff, our nurse practitioner, has a particular interest in these disorders in females. She, along with the over thirty years of experience of the NGUA physicians treating these type of conditions, is anxiously awaiting beginning the process of making things better.
Christie on the Radio Discussing Interstitial Cystitis-A Podcast.
Can Overactive Bladder Be Controlled
Overactive bladder therapy can be challenging to manage. However, many people are very satisfied with the treatment they receive and they often see a dramatic improvement in their quality of life. Your doctor will guide you to the best steps to begin with and give you options for any additional treatments you may need over time.
Also Check: Why Does My Bladder Leak
Supportive Therapies And Treatments
Some people may also find the following therapies and supportive treatments helpful:
- physiotherapy a specialist pelvic floor physiotherapist can help you relax your muscles to ease pain.
- acupuncture may help with pain relief
- talking therapies and counselling to help you cope with your symptoms and their impact on your life
- transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation where a small battery-operated device is used to relieve pain by sending electrical impulses into your body
- pain management ask the GP to refer you to a pain specialist
My Interstitial Cystitis Story
About 16 years ago I found myself having strange symptoms after a few urinary tract infections in a short period of time. I think it was something like two in one month, meaning two separate rounds of antibiotics within 30 days or so.
After the infections were “gone” my symptoms were not. For the next year I noticed an increasingly sensitive bladder, meaning I felt the urgency to urinate a lot more frequently during the day, and even more at night, which was a pretty foreign experience for a 21-year-old who was used to sleeping like a rock.
That started a long decade of chronic pain and poor sleep . While IC is bad during the day, it’s even worse at night. Eating a trigger food during the day sometime meant a sleepless night or 10+ trips to the bathroom.
The discomfort grew over time. On the worst days I’d be up all night not able to sleep because I constantly felt stinging in my bladder and that I had to pee. It made no difference if I had gone 10, 4, or even 2 minutes ago. Even the smallest amount of urine would irritate my bladder leaving me unable to fall asleep or get restful sleep, period. Occasionally I’d go into my doctor to see if I had another UTI, but they’d always come back clean, a dead giveaway of interstitial cystitis or painful bladder syndrome. A condition that according to the internet “can’t be cured”…
Also Check: Malignant Neoplasm Of Bladder Unspecified Icd 10
How Is Bps Diagnosed
There is no single test to diagnose BPS . You may have several tests to exclude other causes of your symptoms before a diagnosis can be confirmed.
The tests offered may include:
- cystoscopy a procedure to look inside your bladder using a thin camera called a cystoscope
- urine tests
Ask your doctor to explain what tests you are being offered and what they’re for.
How Is It Diagnosed
Thereâs no test for interstitial cystitis. If you go to your doctor complaining about bladder pain along with frequency and the urgency to pee, the next step is to rule out what else it could be.
Both men and women would first need to rule out urinary tract infections, bladder cancer, sexually transmitted diseases, and kidney stones.
In women, endometriosis is another possibility. For men, IC can be mistaken for an inflamed prostate or chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
These tests can rule out other conditions:
- Urinalysis and urine culture. Youâll be asked to pee in a cup. Itâll be sent to a lab to check for infection.
- Postvoid residual urine volume. Using an ultrasound, this test measures the amount of pee that remains in your bladder after you go to the bathroom.
- Cystoscopy. A thin tube with a camera is used to see the inside of the bladder and urethra. This is usually done only if there is blood in your pee or if treatment doesnât help.
- Bladder and urethra biopsy. A small piece of tissue is taken and tested. This is usually done during cystoscopy.
- Bladder stretching. Your bladder is filled with liquid or gas to stretch it out. Youâll be asleep under anesthesia. Sometimes this is also used as a treatment. This is done with a cystoscopy.
- Prostate fluid culture . Your doctor will need to press on your prostate and milk a sample to test. This is not commonly done.
You May Like: Why Does Cranberry Juice Help Bladder Infections
Oxalates And Interstitial Cystitis
Oxalates are the salt form of oxalic acid, an acid that is found in many plant foods and can also be produced in the body.
Oxalic acid can form oxalate crystals when binding to minerals such as calcium. When deposited in the body, these can cause a lot of pain, similar to tiny glass shards.
This is probably most well-known with regards to kidney stones, which can often be oxalate/calcium stones.
There is also some evidence that excess oxalates could play a role in painful bladder conditions, such as interstitial cystitis. However, this evidence is more anecdotal than based on scientific studies . Today I would like to look at some potential connections between oxalates and interstitial cystitis.
I dont believe that there is one single cause to so-called interstitial cystitis, which is why I try to look at the different possibilities. I had heard about the potential of high-oxalate foods before, but oxalates recently peaked my interest when some of my own test results showed high oxalic acid levels. Not much later, I also spoke to a client whose urinary symptoms seemed to get worse when high-oxalate foods were consumed.
What Causes Overactive Bladder
An overactive bladder can be caused by several things, or even a combination of causes. Some possible causes can include:
- Weak pelvic muscles: Pregnancy and childbirth can cause your pelvic muscles to stretch and weaken. This can cause the bladder to sag out of its normal position. All of these factors can cause leakage.
- Nerve damage: Sometimes signals are sent to the brain and bladder to empty at the wrong time. Trauma and diseases can cause this to happen. These can include:
- Pelvic or back surgery.
- Stroke.
Often, there may be no specific explanation for why this is occurring.
Also Check: Can A Prolapsed Bladder Cause Uti
How Common Is Ic/bps
BPS /IC is a chronic condition with unknown aetiology As the definition of IC/BPS has evolved it is seen now as a diagnosis of exclusion with no definitive diagnostic test hence it is difficult to estimate prevalence, which can be dependant on whether symptoms are clinician assigned or patient reported. We know from NHS Digital that in 204/15 that there were over 330,000 Patient Episodes of Urinary related problems including IC.
Having the right information about your condition is vital.
How Is Interstitial Cystitis Treated
There is no cure for IC and it can be hard to treat. Treatments are aimed at easing symptoms, and may include:
-
Bladder enlargement. This method increasing bladder capacity. It also interferes with pain signals being sent by the nerve cells in the bladder.
-
Bladder wash. The bladder is filled with a solution that is held for varying times, from a few seconds to 15 minutes. Then it is drained out through a catheter.
-
Medicine. Medicine may be taken by mouth or put right into the bladder. There are many different drugs that may be used.
-
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation . Mild, electric pulses enter the body for minutes to hours, 2 or more times a day. The pulses are sent through wires placed on the lower back, or through special devices put into the vagina in women or into the rectum in men. For some people, TENS eases bladder pain and urinary frequency and urgency.
-
Bladder training. You urinate at specific times and use relaxation techniques and distractions to help keep to the schedule. Over time, you try to lengthen the time between the scheduled voids.
-
Surgery. Surgery to remove all or part of the bladder may be done in severe cases, if other treatments do not work.
Management of IC may also include:
Talk with a healthcare provider with any questions of concerns you may have about this health problem.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Weak Bladder In Males
Comparison Of Perceived Stress Levels Between Oab Patients With Urgency Incontinence Versus Mixed Incontinence
OAB patients were recruited if they had urinary urgency, with or without urgency incontinence, in accordance with the 2002 ICS definition of OAB . Patients with concomitant stress incontinence were also eligible if they reported predominant urgency incontinence by history. Overall, 98% of OAB patients in our cohort reported incontinence symptoms on the ICIQ-UI. Among them, 45% reported urgency incontinence without stress incontinence, and 53% reported mixed incontinence on the ICIQ-UI. There was no difference in PSS between OAB patients with urgency incontinence versus those with mixed incontinence . Because the percent of OAB patients without any incontinence was too small, we were not able to compare the PSS between OAB patients with incontinence versus OAB patients without incontinence.
Oxalates And The Urinary Tract
Oxalates can form in the kidneys, as well as the bladder and ureter. If they grow big enough, they become kidney stones and can cause a lot of pain.
But even small crystals have the potential of causing pain. Some of these crystals can have very sharp ends.
The shape of oxalate crystals somewhat depends on which mineral they bind to. Calcium stones for example can look like little stars or even corals. Zinc crystals can look like little discs with very sharp edges.
Oxalate stones seem to be more common in the kidneys and therefore, there seems to be a chance of high oxalates affecting the urinary tract.
Now what would happen if smaller crystals were present in high amounts in the urinary tract, without being full-blown kidney stones? Well they might just have the potential to cause some pain and potentially damage.
You May Like: Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Survival
What Is Interstitial Cystitis
Painful bladder syndrome or bladder pain syndrome, also commonly known as interstitial cystitis, is a chronic inflammation of the bladder wall. It is not caused by bacteria and does not respond to conventional antibiotic therapy. It can affect both women and men, although it is more common in women.
It can be a long and difficult process to correctly diagnose painful bladder syndrome. The disease affects individuals in different ways. There are no generalised symptoms and day-to-day life is seriously upset. It is important to rule out any other conditions that have similar symptoms to painful bladder syndrome, such as cancer, kidney problems, vaginal infections and neurological disorders. Painful bladder syndrome is often debilitating and can cause feelings of desperation and despair.
There is no cure for this condition and there is no one individual specific treatment that works for everyone. People who suffer from painful bladder syndrome need to investigate ways to help themselves manage the condition. Unfortunately, it is a case of trial and error for the patient.
What Is Interstitial Cystitis/bladder Pain Syndrome
Interstitial cystitis /bladder pain syndrome is a chronic bladder health issue. It is a feeling of pain and pressure in the bladder area. Along with this pain are lower urinary tract symptoms which have lasted for more than 6 weeks, without having an infection or other clear causes.
Symptoms range from mild to severe. For some patients the symptoms may come and go, and for others they don’t go away. IC/BPS is not an infection, but it may feel like a bladder infection. Women with IC/BPS may feel pain when having sex. The more severe cases of IC/BPS can affect your life and your loved ones. Some people with IC/BPS have other health issues such as irritable bowel syndrome, fibromyalgia, and other pain syndromes.
The bladder and kidneys are part of the urinary system, the organs in our bodies that make, store, and pass urine. You have 2 kidneys that make urine. Then urine is stored in the bladder. The muscles in the lower part of your abdomen hold your bladder in place.
How the Urinary System Works
Also Check: Panty Liners For Bladder Leakage