What Is Oab And Who Gets It Your Browser Does Not Support Html5 Audio Playback You May Download The Audio File Directly Here
Overactive bladder is the name for a group of bladder symptoms. There are three main symptoms:
- A feeling that you have to go to the bathroom, urgently.
- Sometimes incontinence, which means that you leak urine with the “gotta go” feeling.
- Usually the need to go to the bathroom often , day and night.
With OAB, you feel that you need to empty your bladder even when it’s not full. This leads to the feeling that you need a bathroom quickly, right now. You can’t control or ignore this feeling. If you “gotta go” eight or more times each day and night, or fear that urine will leak out before youre ready, you may have OAB.
OAB affects about 33 million Americans. It’s not a normal part of aging. It’s a health problem that can last for a long time if it’s not treated. Many older men and women struggle with OAB symptoms. Often people don’t know about treatments that can help, or they don’t ask for help.
Stress urinary incontinence or SUI is a different bladder problem. People with SUI leak urine while sneezing, laughing or being active. It is not the same as that sudden “gotta go” feeling from OAB. To learn more about SUI, go to .
In this guide you will find clear information about how to manage OAB. Please ask for help, even if you feel embarrassed. Don’t wait, because there are several treatments that work well for OAB. Your health care provider should be trained to talk with you and help you manage your symptoms without embarrassment.
What Is The Urinary Tract
The urinary tract consists of the organs, tubes, and muscles that work together to make, move, store, and release urine. The upper urinary tract includes the kidneys, which filter wastes and extra fluid from the blood, and the ureters, which carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. The lower urinary tract includes the bladder, a balloon-shaped muscle that stores urine, and the urethra, a tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body during urination. If the urinary system is healthy, the bladder can hold up to 16 ounces-2 cups-of urine comfortably for 2 to 5 hours.
Muscles called sphincters squeeze shut the tubes from the bladder to help keep urine from leaking. The sphincter muscles close tightly like a rubber band around the opening of the bladder, which leads into the urethra.
Nerves in the bladder tell you when it is time to urinate. As the bladder first fills with urine, you may notice afeeling that you need to go. The sensation to urinate becomes stronger as the bladder continues to fill. As itreaches its limit, nerves from the bladder send a message to the brain that the bladder is full and the urge toempty your bladder intensifies.
When you urinate, the brain signals the bladder muscle to tighten, squeezing urine out of the bladder. At the sametime, the brain signals the sphincter muscles to relax. As these muscles relax, urine exits the bladder through theurethra. When all the signals occur in the correct order, normal urination occurs.
How Is Urinary Retention Diagnosed
First, we record a history of when the problem started and how often its been happening. Well check if your bladder feels hard or if there are any signs of constipation. Well also do an ultrasound scan of the bladder and kidneys.
We might suggest a bladder function assessment. This is a combination of tests we use to examine your childs urinary system and how its working in close detail. This is usually carried out over a period of up to five hours, using a special uroflow toilet, which takes lots of measurements as your child is weeing.
Some children may benefit from having a micturating cystourethrogram , which is a scan that shows how well the childs bladder works. We use this to diagnose why your child may have urinary tract infections, and to see any abnormalities with their urinary system.
Another test that the doctor might suggest is a cystoscopy, a test that allows us to look inside and around your childs bladder using a cystoscope .
You can find out more about all these tests here.
Don’t Miss: If I Have A Bladder Infection What Should I Do
Nerve Disease Or Spinal Cord Injury
Many events or conditions can damage nerves and nerve pathways. Some of the most common causes are
- vaginal childbirth
- infections of the brain or spinal cord
- accidents that injure the brain or spinal cord
- multiple sclerosis
- heavy metal poisoning
- pelvic injury or trauma
In addition, some children are born with nerve problems that can keep the bladder from releasing urine.
What Are Risk Factors And Causes Of An Inability To Urinate
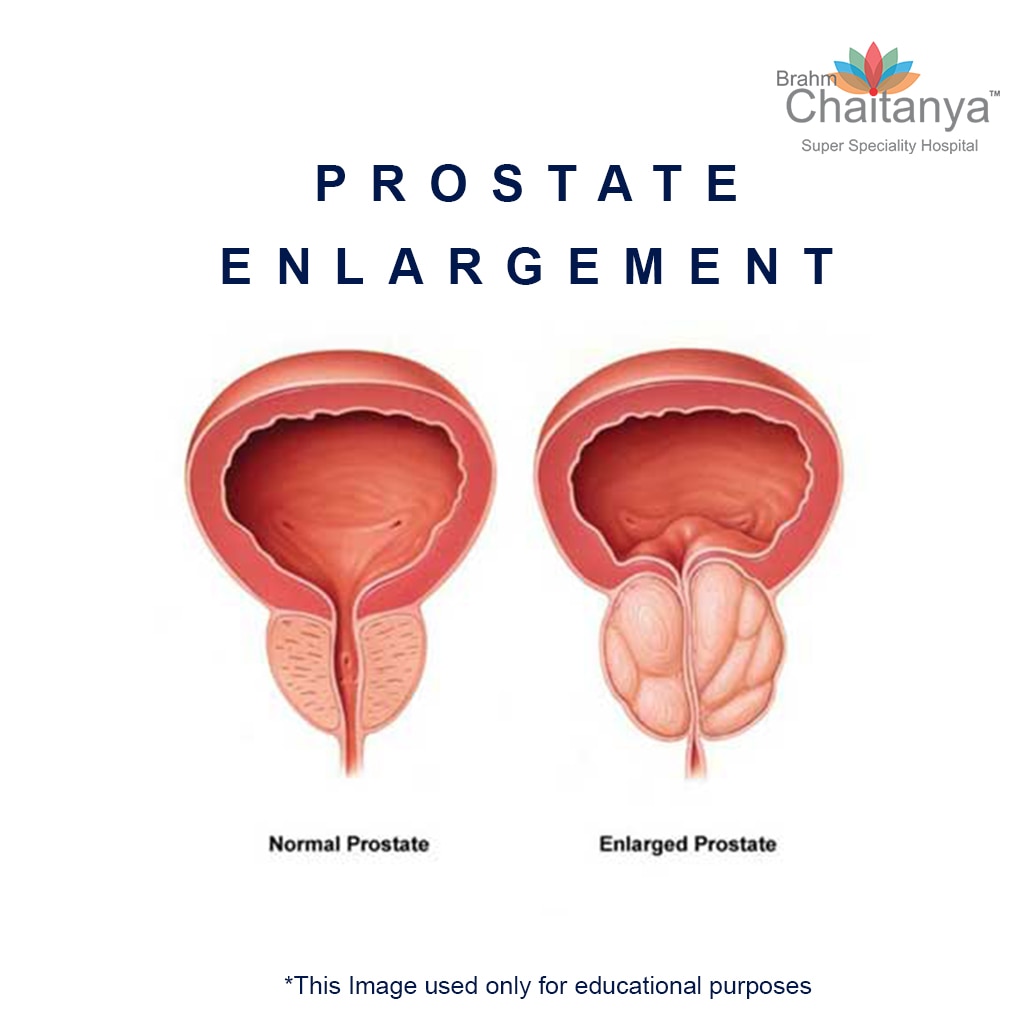
There are a number of medical conditions and medications that may cause urinary retention. These medical conditions and medications may affect the function of the bladder itself, the function of the outlet of the bladder, and/or the urethra. Obstruction may be fixed or dynamic . There are also infectious causes and surgical causes of urinary retention.
Common Causes/Risk Factors
Medication-Related Causes
Certain medications can cause urinary retention, especially in men with prostate enlargement. Many of these medications are found in over-the-counter cold and allergy preparations. These drugs include the following:
- Drugs that act to tighten the urinary channel and block the flow of urine include ephedrine , pseudoephedrine , phenylpropanolamine , phenyleprhine , and amphetamines.
- Antihistamines such as diphenhydramine and chlorpheniramine , as well as some older antidepressants, can relax the bladder too much and cause urination problems.
- Beta-adrenergic sympathomimetics, including isoproterenol , terbutaline , and metaproterenol
- Opioid-containing medications
Urinary Retention in Children
Also Check: Can Caffeine Cause Bladder Spasms
How The Urinary Tract Works And What Happens With Oab Your Browser Does Not Support Html5 Audio Playback You May Download The Audio File Directly Here
The urinary tract is the important system that removes liquid waste from our bodies:
- kidneys: two bean-shaped organs that clean waste from the blood and make urine
- ureters: two thin tubes that take urine from the kidney to the bladder
- bladder: a balloon-like sac that holds urine until its time to go to the bathroom
- urethra: the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body. The urethra has muscles called sphincters that lock in urine. The sphincters open to release urine when the bladder contracts.
When your bladder is full, your brain signals the bladder. The bladder muscles then squeeze. This forces the urine out through the urethra. The sphincters in the urethra open and urine flows out. When your bladder is not full, the bladder is relaxed.
With a healthy bladder, signals in your brain let you know that your bladder is getting full or is full, but you can wait to go to the bathroom. With OAB, you cant wait. You feel a sudden, urgent need to go. This can happen even if your bladder isnt full.
Whats The Best Way To Recover From A Gallbladder Removal
Recovery after gallbladder removal tip 1: Get out of bed and walk around Light activity after surgery, such as walking, can aid in your recovery. After a laparoscopic gallbladder removal, some of the carbon dioxide used during surgery might have remained in your abdomen, causing pain in your stomach and shoulders.
Read Also: Why My Bladder Is Weak
Free Just Cant Wait Toilet Card
The most common cause of difficult urination in men is a blockage due to an enlarged prostate restricting the outlet from the bladder. For women one of the common causes of difficulty in urination is an anterior prolapse/bladder prolapse which can distort the urethra and restrict the flow of urine.
How Is It Diagnosed
To diagnose urinary retention, a doctor will first ask about the history of your symptoms and perform a physical exam. The physical will include an examination of your genitals and rectum to look for any symptoms affecting those areas that may also affect the urinary tract.
Some other tests that may be used to confirm a diagnosis
likely be inserted to help quickly drain the urine. Local anesthesia will be used to make sure you dont feel pain or discomfort from the catheter.
If a catheter doesnt work or cant be used because of an injury or other condition, a doctor may insert a suprapubic catheter into the skin above your bladder to drain the urine.
Recommended Reading: Can A Hernia Affect Your Bladder
Causes Of Urinary Retention
There are many different causes.
Blockage In men, the urethra may be constricted by an enlarged prostate a common condition for men over 50. In women, blockage can be caused by certain types of pelvic prolapse, including Cystocele and Rectocele .
Other blockage reasons for both men and women include urethral stricture and urinary stones.
Infection / Swelling In men, prostatitis , can cause swelling that blocks the free flow of urine. Urinary Tract Infections and Sexually Transmitted Diseases can also cause swelling that leads to urinary retention.
Nerve Problems Urinary retention could be caused by a problem with the nerves that control the bladder. If the nerves are damaged, it can cause a breakdown in the signals between the brain and bladder. Some causes of nerve damage include:
Urinary Retention: Does Drinking Water Really Help
Urinary retention is a condition characterized by an inability to fully empty the bladder. The bladder serves as a storage tank for urine, a substance made by the kidneys after they have filtered out waste and extra water from your blood. Once made, the urine travels to the bladder where it will stay until a person is ready to urinate. In a healthy individual, the bladder can hold up to two cups of urine comfortably for up to five hours.
Urinary retention can occur for a variety of reasons. Among men, an enlarged prostate is the most common cause. Among women, bladder muscle dysfunction and urinary stones are the typical culprits. Individuals with this condition may experience:
- Feeling the need to urinate right after using the bathroom
Read Also: How To Reduce Bladder Infection Pain
Urinating Should Be One Of Your Bodys Most Natural Functions So Youre Bound To Be Frustrated When You Cant Go Read On To Find Out What May Be Causing The Trouble
For most of your adult life, peeing is delightfully simple. You feel the need to go, you find a place to go and then ahhh! sweet relief.
So, when you feel like you need to go only to find you cant, it naturally feels like cause for concern. The inability to empty your bladder completely, called urinary retention, can result from:
What Medications Treat Urinary Retention
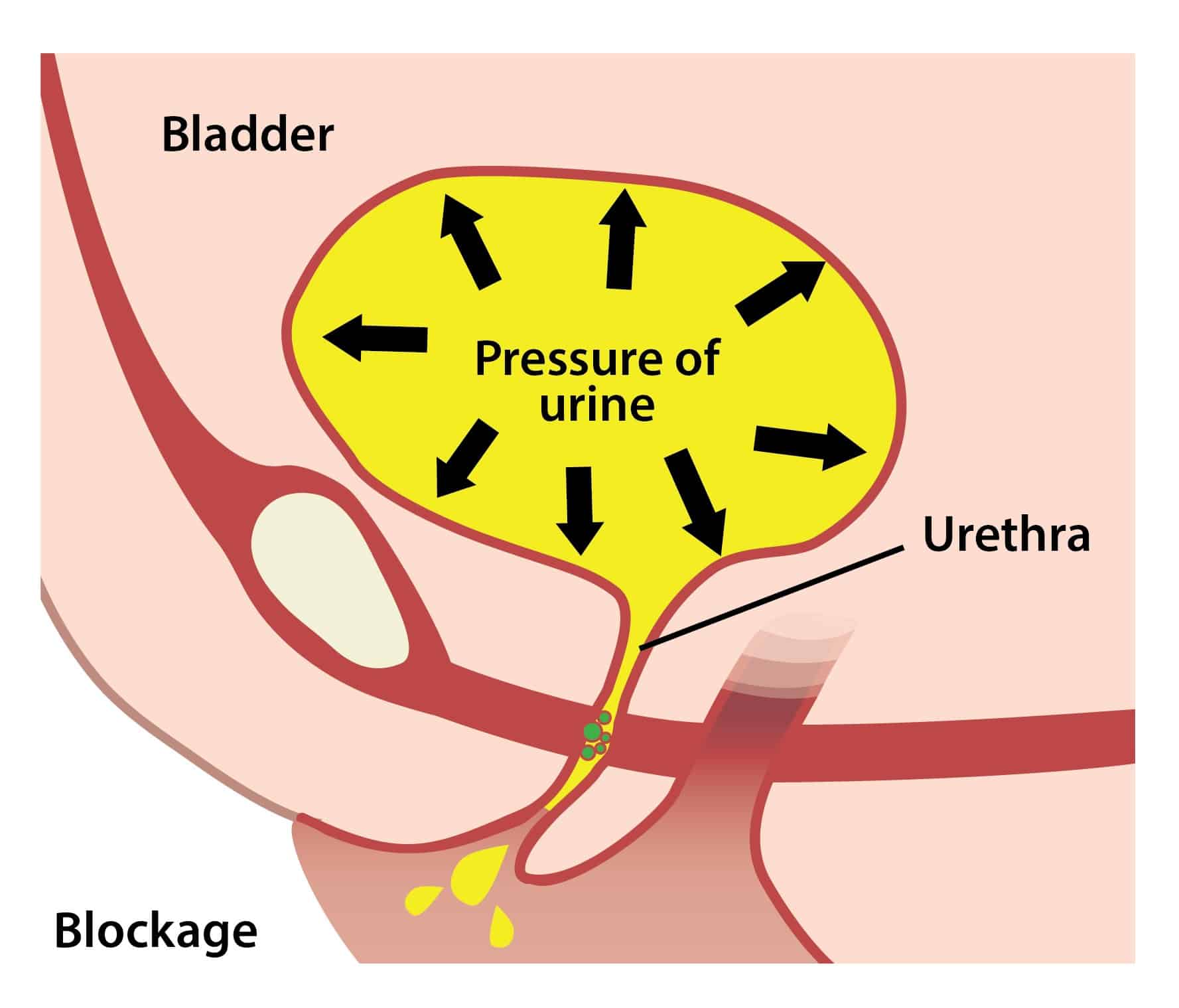
There are three types of medications available for treating urinary symptoms in men thought to be related to an enlarged prostate and may be helpful in men with urinary retention secondary to an enlarged prostate .
The first class of medications work by relaxing the muscles at the neck of the bladder, thus reducing the obstruction to the flow of urine. The common medications in this class are terazosin , tamsulosin , doxazosin , silodosin , and alfuzosin . These medications are generally used for treating long-standing obstructive symptoms due to an enlarged prostate, but they may have a role in treating acute obstruction. Some studies have suggested that early initiation of these medications may improve urinary problems upon the removal of a urinary catheter.
Alpha-blockers are also very helpful in individuals with bladder neck dysfunction, a medical condition in which the bladder outlet does not open prior to the bladder contracting. This condition typically requires long-term use of alpha-blockers.
The third class of medications for treatment of urinary symptoms related to BPH are PDE-5 inhibitors. Cialis is approved for the treatment of BPH symptoms in men. It is not fully known how this medication, which is typically used for troubles with erections, helps with symptoms related to enlargement of the prostate, but studies have shown it as effective as alpha-blockers.
Recommended Reading: Bladder Stones In Dogs Surgery
Surgical Treatment Is Necessary For Some Cases These Treatments Might Include:
- Prostate surgery. The most common surgery is transurethral resection of the prostate. In this procedure, the urologist uses a tiny tool, inserted through a catheter, to remove a section of the prostate. This treatment is used frequently for urinary retention caused by BPH.
- Internal urethrotomy. When there is a stricture that cannot be resolved by widening, a urologist can open the stricture with an incision. The procedure is performed via a special catheter inserted into the urethra.
- Cystocele or rectocele repair. Women whose bladder or rectum has fallen may need surgery to return the organs to their normal position. A urologist specializing in female reproductive surgery will repair any defects in the tissue of the vaginal wall. This repaired tissue then will be strong enough to hold the organs in their proper places, restoring normal urinary retention function.
- Removal of tumors or cancer. If the cause of the urinary retention is a tumor or cancerous tissue in the urethra, bladder or prostate, removing those tissues may reduce the problem.
History Of Complaints And Physical Examination
A physician will suspect urinary retention by your symptoms and will attempt to confirm the diagnosis with a physical examination of the lower abdomen. The physician may be able to feel the distended bladder by lightly tapping on your lower belly. Tapping or striking for diagnostic purposes is called percussing.
Don’t Miss: What Does Bladder Leakage Look Like
What The Patient Can Do
Here are some things that may help make urine retention less of a problem:
- Empty your bladder at least every 4 hours, even if you don’t feel the urge to do so.
- Empty your bowels regularly.
- If tolerated, drink 6 to 8 glasses of fluid daily, preferably water.
- Talk to your doctor about all medicines, vitamins, herbs, and supplements youre taking.
- Avoid drinks with caffeine or alcohol and citrus juices, which can irritate the bladder.
- Avoid hygiene products and chlorinated pools and hot tubs that may irritate the bladder
How Does Bladder Cancer Impact The Bladder Lining
Bladder cancer usually starts growing in the thin layer of cells that line the inside of the bladder. The cancer cells can gather together to form tumors in the bladder lining. In non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer, the tumors are only located in the bladder lining.
In muscle-invasive bladder cancer, the cancer is more advanced and the tumors may have grown deeper into the muscles of the bladder wall. If the bladder cancer has metastasized, it means that the cancer cells have spread to other parts of the body beyond the bladder. The symptom of being unable to urinate is more common among patients who have more advanced bladder cancer than in patients with early stage bladder cancer.
Also Check: Is Bladder Cancer Fast Or Slow Growing
What Symptoms Would I Have With A Rectocele
Many women with a rectocele have no symptoms, and the condition is only seen in a pelvic examination. In general, if a rectocele isnt causing you symptoms or discomfort, it can be left alone.
When symptoms are present, you may have:
- Difficulty having bowel movements.
A rectocele should be treated only if your symptoms interfere with your quality of life.
Introduction Your Browser Does Not Support Html5 Audio Playback You May Download The Audio File Directly Here
Millions of people in the United States struggle with Overactive Bladder symptoms. The most common symptom is the ongoing urgent need to go to the bathroom. Now.
OAB can interfere with work, going out with friends, exercise and sleep. It can lead you to the bathroom many times during the day or night. Some people leak urine after this urgent “gotta go” feeling. Others feel afraid they’ll leak.
Fortunately, there is help and there are treatments.
It took me nearly 5 years to talk with my doctor about this. I’m glad I finally did.
Read Also: How Long Can You Live With Bladder Cancer Without Treatment
Urinary Retention: 5 Reasons You May Have Trouble Peeing
Did you know that we spend roughly 2,208 hours on the toilet in our lifetime? Thats a lot of time on the potty! And, if youre having trouble going No. 1, it could be costing you even more time than you like. Time spent anywhere else but a bathroom stall.
If you cant get the flow going when you feel you need to, and your bladder is full, you may have urinary retention. Urinary retention is the inability to pass urine in your bladder, and it can be acutea sudden inability to urinateor chronica gradual or slow inability to empty the bladder.
The difference can be from the cause and sometimes the symptoms, said James Wolach, MD, a urologist at Banner Health Clinic in Colorado. Acute is usually painful and they have the sensation to void but cant, whereas many people with chronic retention dont have any feeling they are not able to empty their bladders. While chronic may not seem as serious, it can lead to serious problems, so its important that both receive attention from your doctor.
There are many different causes for urinary retention, and much of your treatment will depend on the underlying cause. Here are five reasons you may be stuck and ways to improve your flow.
What Is A Post
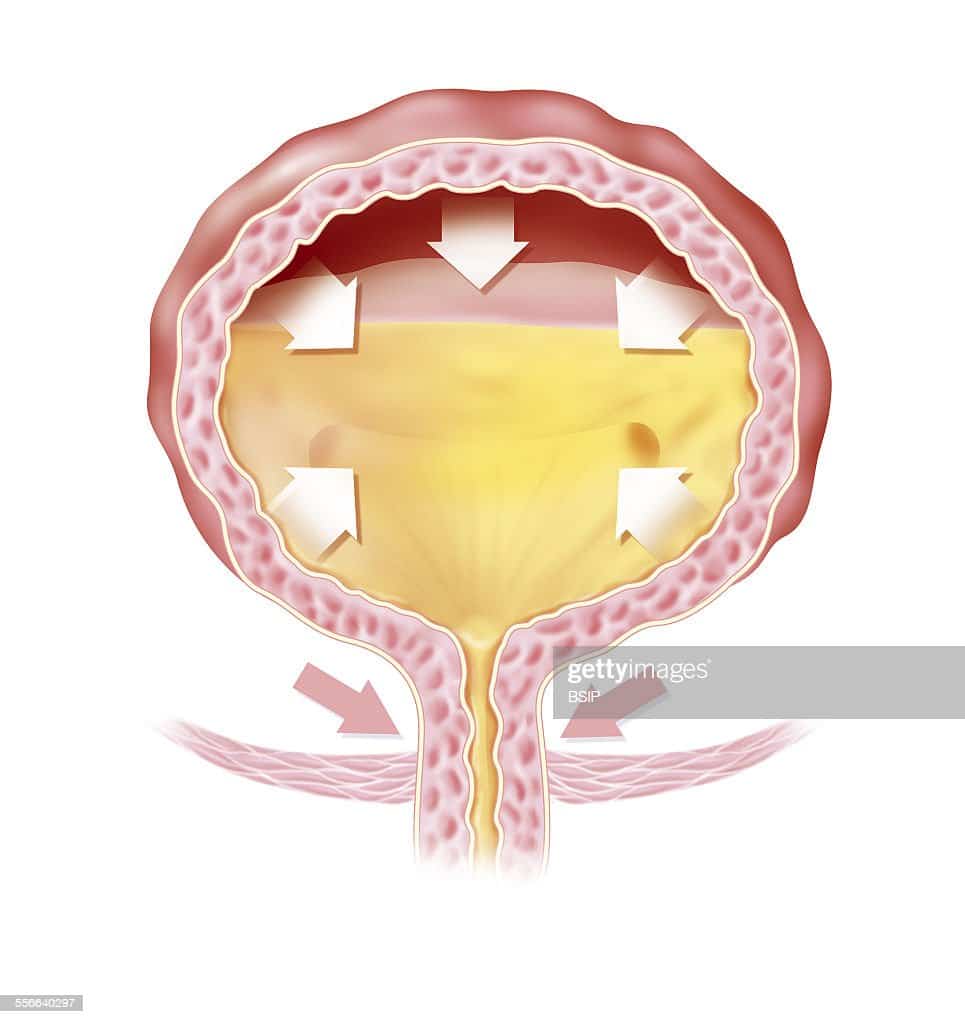
The amount of urine that remains in your bladder after you urinate is called post-void residual . A post-void residual urine test measures the amount of urine left in your bladder.
Ideally, when you go to the bathroom, your bladder should empty completely. But sometimes, urine stays in the bladder even after you think youve emptied it. The PVR test can tell your healthcare provider if youve completely emptied your bladder. A small amount of residual urine is generally ok, but large amounts can be concerning for urinary retention.
Recommended Reading: Can Bladder Infection Cause Cramps