How Do You Know If Youre Dealing With A Standard Uti Or Severe Kidney Infection
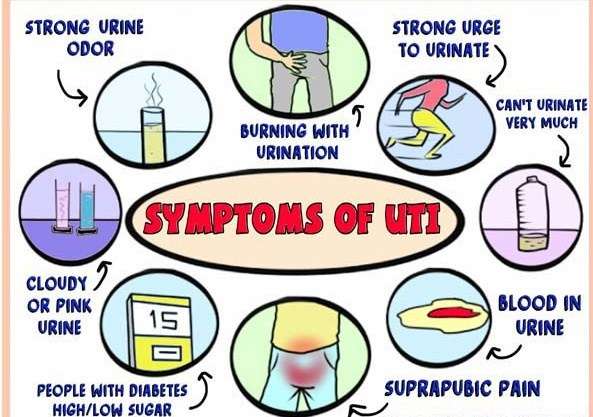
Both are technically forms of UTIs. A standard UTI, though, typically just means youre dealing with cystitis, or inflammation of the bladder. That inflammation causes those typical UTI symptoms like painful or burning urination and urgent or frequent urination, explains Dr. Mueller.
But a kidney infection, also known as pyelonephritis, is caused by the same bacteria and oftentimes results from an untreated bladder infection. These symptoms are typically much more severe.
What Do I Do If I Have One
If you notice any signs of a UTI or kidney infection, visit your doctor ASAP. He or she will probably take a urine sample, and possibly a blood test, and give you a prescription for antibiotics. Although over-the-counter pain-relievers like AZO can make you more comfortable while you wait for the drugs to kick in, they will not treat the infection.
Usually, antibiotics plus plenty of liquids will get you better in no time. And as with most things, the earlier its caught, the easier its treated and the faster youll recover.
While its true that some women do get UTIs more often than othersand some even get them chronicallyno one is immune. And unfortunately, infections dont care whether or not theres room for them on your calendar. As I learned, not everything gets better with time, tea, and wishful thinking. So keep a lookout for the symptoms, keep an open mind when self-diagnosing, and remember: if you dont take care of it now, youll pay for it later.
Also Check: Swelling Mouth From Tooth Infection
Who Gets Urinary Tract Infections
Anyone can get a urinary tract infection, but they are more common in women. This is because the urethra in females is shorter and closer to the anus, where E. coli bacteria are common. Older adults also are at higher risk for developing cystitis. This increased risk may be due to incomplete emptying of the bladder. There are several medical conditions that can be related to this, including an enlarged prostate or a bladder prolapse .
If you get frequent urinary tract infections, your healthcare provider may do tests to check for other health problems such as diabetes or an abnormal urinary systemthat may be contributing to your infections. People with frequent UTIs are occasionally given low-dose antibiotics for a period of time to prevent the infection from coming back. This cautious approach to treating frequent UTIs is because your body can develop a resistance to the antibiotic and you can get other types of infections, such as C. diff colitis. This practice is used very infrequently.
Don’t Miss: Herbal Remedies For Bladder Problems
When To See A Doctor
Contact your doctor if you have pain or discomfort when you urinate or other symptoms of a bladder infection, especially if the symptoms have been present for two days or more. If an infection lingers for too long, you risk the bacterial infection traveling to other parts of your body, including your kidneys. Therefore, you should seek treatment if you notice symptoms.
Your doctor will complete a physical examination and collect a urine sample to send for lab analysis to determine if an infection is present. Complications from an uncomplicated bladder infection are typically rare with antibiotic treatment. However, if you develop fever, chills, nausea, or confusion, you should immediately contact your doctor. These symptoms suggest a more serious infection that has spread to your kidneys. If you have a kidney infection, you may need an IV treatment of high-dose antibiotics, which may require hospitalization.
Show Sources
Ask The Doctor: What Can I Do About Bladder Infections
Q.Now that I am postmenopausal, I have been getting bladder infections more frequently. Why is that, and is there anything I can do to prevent them?
A. You’re said to have recurrent urinary tract infections if you get two or more infections in a six-month period. Postmenopausal women may be more susceptible to these infections for a few reasons. The cells in the urinary tract that help prevent infection depend on estrogen, so they don’t work as effectively when less estrogen is being produced. Also, as you get older, the function of your urinary tract can change in ways that increase your risk for infection. For example, bladder contractions can be weaker, which means some urine tends to pool in the bladder. That leftover urine provides a good environment for bacteria to grow. Women with urinary incontinence, as well as those with bladder prolapse, are also at greater risk for infection.
If you do get frequent infections, don’t try to treat yourself! It’s important to report any urinary symptoms to your doctor and get checked to see if you do have an infection. Sometimes women think they have a bladder infection when they actually don’t. Your doctor should take a focused medical history and do a thorough physical exam to determine whether you have changes in your urinary tract function. That information can help determine what treatment you need.
Anne Fabiny, MD
Read Also: Scar Tissue In Bladder Treatment
How To Treat Utis
If you think you have a UTI, the first thing you should do is schedule an appointment with your OBGYN or primary care physician. Many women will try to self-treat it, or worse, just hope it goes away on its own. And while some minor UTIs do go away on their own, its best to see a doctor and have them diagnose and treat it as the infection can spread to other parts of your body and be dangerous.
Your doctor will take a urine sample which will allow them to diagnose it right then and there, meaning youll leave the office with an answer and a solution! Well choose an antibiotic based on the type of bacteria you have, taking into account other factors like pregnancy, allergies, other medications, and medical history. Now all you have to do is take the full cycle of treatment to make sure the infection is completely gone.
Why Some Women Get Recurrent Utis
The infections are usually caused by Escherichia coli, a bacterium that lives in the intestinal system. If E. coli are carried from the rectum to the vagina, they can enter the urethra and infect the bladder.
Risk factors for UTI vary with age. Before menopause, the most common risk factors are sexual intercourse and use of spermicides. It’s thought that sex increases the number of bacteria in the bladder, and many experts advise women to urinate after sex to flush them out. Spermicides may kill off Lactobacilli, beneficial bacteria in the vagina, making it easier for E. coli to move in.
After menopause, certain physical changes help set the stage for UTIs. The numbers of Lactobacilli in the vagina naturally decline. The bladder also contracts less strongly than it once did, making it more difficult to empty it completely.
In both premenopausal and postmenopausal women, genes play a role as well. Having a mother or sister who has frequent UTIs is also a risk factor.
You May Like: Home Care For Bladder Infection
Urinary Tract Infection Diagnosis
Bladder infections are sometimes difficult to diagnose in elders because of uncommon symptoms that might occur. If a bladder infection is suspected, the easiest way to get a diagnosis is to go to the doctors and have a urinalysis done.
With a simple urine culture a doctor is able to tell whether you have an infection or not, what kind of bacteria caused your UTI and what antibiotic should be used to treat it.
Cystitis In Men And Older People
Men tend to get cystitis later in life. Where trouble with urine flow is a symptom, this may indicate that the underlying cause is a problem with their prostate gland.
Cystitis is common in older people, particularly if they are unwell. Bladder catheters and some urinary-tract operations may also increase the risk of cystitis.
Recommended Reading: Stage 3 Bladder Cancer Life Expectancy
Urinary Tract Infections : More Common In Women
Urinary tract infections, sometimes called bladder infections, strike women more often than men, and simple anatomy is the cause.
The female urethra is closer to areas that have natural bacteria, such as the anus and vagina. Its also shorter than a mans urethra, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases .
Bladder pain from UTIs can happen at any age. In young women, it is a common symptom of urinary tract infections, along with frequent and painful urination. Symptoms in older women can vary but typically include muscle aches, abdominal pain, fatigue, and weakness.
Its important to see your doctor because treatment with antibiotics like Macrobid or Bactrim can usually clear up a urinary tract infection, the NIDDK notes.
And though the infection may go away without treatment, antibiotics can speed healing and quickly eliminate uncomfortable symptoms. Drinking extra fluids and urinating frequently will also help treat the infection and your discomfort.
The Pain Has Become Unbearable What Can You Do
If you either have started taking the antibiotic and it hasnt kicked in yet or you havent gotten to the doctor yet, the pain may still be causing you a lot of discomfort. There are plenty of over-the-counter medications that you can take to relieve the symptoms while youre waiting for your antibiotic to work its magic. Simply consult with your doctor on which option they recommend and pick it up at your nearest drugstore.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Constant Bladder Infections
How Is This Condition Diagnosed
If you think you have a bladder infection you should talk with your healthcare provider. To help diagnose a bladder inflammation , you will typically be asked for a urine sample. Your urine will be collected in a sterile cup in a restroom at your providers office. You may want to avoid peeing right before your appointment so that youll be able to provide a sample during your office visit. Your provider will most likely do two tests on your urine: a urinalysis and a urine culture.
- Urinalysis: This test involves checking the appearance, concentration and content of urine.
- Urine culture: This test determines the type of bacteria causing the infection and to which antibiotics the bacteria is sensitive.
Your healthcare provider may also order additional testing if you continue to get bladder infections including an imaging test to look at your kidneys and a cystoscopy, which uses a special scope to look inside the bladder.
What To Do If You Have A Uti

DO drink lots of water. Drinking water is one of the best ways to help your body to get rid of your UTI. Keep hydrated with at least six to eight glasses of water a day to flush out the bacteria in your urethra.
DO take a cranberry supplement. Cranberry has been proven to help with UTIs. Either a cranberry supplement or cranberry juice is effective in curing and preventing UTIs. However, if you go with the juice, make sure you get the bottle marked 100% juice. Any added sugar can worsen your symptoms.
DO empty your bladder. If you have to pee, then pee. Even if it is only a small amount, every time you urinate bacteria is flushed out.
DO take probiotics. Beat the bad bacteria with good bacteria. Probiotics will help fight off the infection by getting rid of the bad bacteria and replacing it with your bodys natural, healthy bacteria. Yogurt is a natural source of probiotics, so its essential to eat it when dealing with a UTI.
DO see your physician. While natural home remedies can help, seeing a physician is the best way to deal with your UTI. Theyll be able to prescribe you with antibiotics to prevent the infection from spreading.
Also Check: Blood In Urine Female Bladder Infection
Can Utis Be Prevented
A few things can help prevent UTIs. After peeing, girls should wipe from front to back with toilet paper. After BMs, wipe from front to back to avoid spreading bacteria from the rectal area to the urethra.
Also, go to the bathroom when needed and don’t hold the pee in. Pee that stays in the bladder gives bacteria a good place to grow.
Keep the genital area clean and dry. Girls should change their tampons and pads regularly during their periods. Bubble baths can irritate the vaginal area, so girls should take showers or plain baths. Avoid long exposure to moisture in the genital area by not wearing nylon underwear or wet swimsuits. Wearing underwear with cotton crotches is also helpful. Skip using feminine hygiene sprays or douches, as these can irritate the urethra.
If you are sexually active, go to the bathroom both before and within 15 minutes after sex. After sex, gently wash the genital area to remove any bacteria. Avoid sexual positions that irritate or hurt the urethra or bladder. Couples who use lubrication during sex should use a water-soluble lubricant such as K-Y Jelly.
Finally, drinking lots of water each day keeps the bladder active and bacteria-free.
UTIs are uncomfortable and often painful, but they’re common and easily treated. The sooner you contact your doctor, the sooner you’ll be able to get rid of the problem.
What Is The Bladder
The bladder is a hollow muscular organ that is located in the pelvis. The bladder has two functions: one is to store urine and the other is to release/expel urine. Urine drains from the kidneys , down the ureters , and into the bladder. The urine is stored in the bladder where it remains until urination. When it is time to urinate, the bladder muscle contracts, and the outlet of the bladder and sphincter muscles relax to allow urine to pass through the urethra to leave the body. The bladder and urethra are part of the lower urinary tract, whereas the kidneys and ureters are part of the upper urinary tract.
Also Check: What Are The Chances Of Surviving Bladder Cancer
How Do Health Care Professionals Diagnose A Bladder Infection
A urinalysis is the initial evaluation for a bladder infection. In most cases, health care professionals use a voided urine specimen, however, there is a risk of contamination by skin bacteria. A “clean-catch” voided urine specimen involves voiding and collecting a urine sample “mid-stream” as opposed to at the very start or end of voiding. A catheterized urine sample is more accurate but has the risk of introducing bacteria into the bladder and may be uncomfortable in children. In infants, medical professionals can perform a suprapubic aspiration.
The definitive test to determine if there is a bladder infection is the urine culture. The urine culture identifies the number and type of bacteria in the urine as well as determines the sensitivity of the bacteria to several different antibiotics. The usual cutoff for a urinary tract infection is the presence of greater than 100,000 bacteria, however, in the presence of symptoms, a positive leukocyte esterase or > 10 white blood cells on urinalysis, even fewer bacteria in the urine is supportive of a urinary tract infection.
Physicians sometimes recommend prophylactic antibiotics for individuals who develop frequent symptomatic UTIs. Similarly, women who develop UTIs related to sexual activity may take a single dose of antibiotic around the time of intercourse.
From A Lower Uti To An Upper Uti
The most common type of UTI occurs in the lower urinary tract, infecting the urethra and bladder. Highly virulent strains, if left untreated, can spread further up to the ureters and the kidneys, in the upper urinary tract. Kidney infection symptoms in women are considerably worse than lower UTI symptoms, and may include back pain, nausea and fever. Kidney infections are potentially serious since they can cause damage to the kidneys and even kidney failure if left untreated. Eventually, they can also lead to urosepsis, an infection of the bloodstream that requires intensive care.
You May Like: Electrical Stimulation For Bladder Control
Urinary Tract Infections During Pregnancy: Symptoms Treatment And Common Questions
In addition, as the uterus grows throughout pregnancy, it can put pressure on the bladder, making it more difficult to empty completely.
Pregnancy can also make a UTI more difficult to treat, which can have serious consequences, including pyelonephritis preterm labor low birth weight and .
A urinalysis and a urine culture are routinely performed at an initial prenatal visit to screen for UTIs, but if you’re pregnant and suspect you may have an infection, seek medical attention quickly.
What Is My Risk For Uti
Anyone can get UTI. However, people with SCI have a higher risk than normal.
- People with SCI who use an indwelling Foley or suprapubic catheter may be at higher risk for UTI than those who use a clean intermittent catheterization technique or have an external sheath or condom catheter.
- Talk to your health professional about lowering your risk for UTI if you average more than one UTI per year. Your health professional may suggest another method of bladder management that works better for you.
Recommended Reading: How To Flush Bladder Infection
Practice Good Sexual Hygiene
The also says that sexual intercourse introduces bacteria and other microbes from outside the body to the urinary tract. Practicing good sexual hygiene can help to reduce the number of bacteria that people can transfer during intercourse and other sexual acts.
Examples of good sexual hygiene include:
- urinating before and immediately after sex
- using barrier contraception, such as a condom
- washing the genitals, especially the foreskin, before and after engaging in sexual acts or intercourse
- washing the genitals or changing condoms if switching from anal sex to vaginal sex
- ensuring that sexual partners are aware of any current or previous UTIs