What Is Prostate Cancer
Cancer can start any place in the body. Prostate cancer starts in the prostate gland. It starts when cells in the prostate grow out of control.
Cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body. Cancer cells in the prostate can sometimes travel to the bones or other organs and grow there. When cancer cells do this, its called metastasis. To doctors, the cancer cells in the new place look just like the ones from the prostate.
Cancer is always named for the place where it starts. So when prostate cancer spreads to the bones , its still called prostate cancer. Its not called bone cancer unless it starts from cells in the bone.
Ask your doctor to use this picture to show you where your cancer is.
The prostate
The prostate is a gland found only in men, so only men can get prostate cancer.
The prostate is just below the bladder and in front of the rectum . The tube that carries pee goes through the prostate. The prostate makes some of the fluid that helps keep the sperm alive and healthy.
There are a few types of prostate cancer. Some are very rare. Most prostate cancers are a type called adenocarcinoma. This cancer starts from gland cells. Your doctor can tell you more about the type you have.
Testicular Cancers: How They Spread
Testicular cancer begins in your testes, the male reproductive organ. Which treatment your doctor will choose to treat it is based on the type of cancer you have and if it has spread.
The majority of testicular cancers start in germ cells. Germ cells in your testicles make sperm. When these cells begin to grow out of control, they form two main types of tumors: seminomas and non-seminomas.
They grow and spread at different rates.
Donât Miss: Yoga Exercises For Prolapsed Bladder
Bladder Incontinence In Women
Bladder incontinence is more common in women than in men. Other than the possible causes listed above, some things that may increase risk of bladder incontinence in women are:
- Changes to urinary or vaginal tissue from hormone therapy, surgery, chemotherapy, or targeted therapy
- Hormonal changes from menopause
- Pelvic prolapse the bladder, uterus, and or rectum may slip backward or downward into the vaginal canal because of weak pelvic wall muscles
- Pregnancy
- Hysterectomy
You May Like: Why Do I Have A Weak Bladder
Will Treatment Cause Erectile Dysfunction
When youre sexually excited, nerves cause tissues in your penis to relax, allowing blood to flow into the organ. The nerves that control erection are very delicate. Surgery or radiation for prostate cancer may damage them enough to cause ED. When you have ED, you cant get or keep an erection.
Radical prostatectomy is a surgery to remove the prostate gland. When your surgeon removes the gland, they may damage the nerves and blood vessels that run along it. If theyre damaged enough, you wont be able to get an erection following the procedure.
Today, doctors can do nerve-sparing surgery, which helps prevent permanent ED. Your surgeon can still touch those nerves and blood vessels, causing ED as a temporary side effect. Many men have trouble getting an erection for a few weeks, months, or even years after their procedure.
Radiation therapy also damages blood vessels and the nerves that control erection. Up to half of men who have radiation for prostate cancer experience ED afterward. In some men, this symptom will improve with time. Sometimes radiation side effects dont appear until a few months after the treatment. If ED starts late, it may not be as likely to go away.
A few treatments can help with ED until youre able to have erections on your own again.
Additional treatments include the following:
Recommended Reading: Foods Good For Bladder Control
Treating Stage Ii Bladder Cancer
These cancers have invaded the muscle layer of the bladder wall , but no farther. Transurethral resection is typically the first treatment for these cancers, but it’s done to help determine the extent of the cancer rather than to try to cure it.
When the cancer has invaded the muscle, radical cystectomy is the standard treatment. Lymph nodes near the bladder are often removed as well. If cancer is in only one part of the bladder, a partial cystectomy may be done instead. But this is possible in only a small number of patients.
Radical cystectomy may be the only treatment for people who are not well enough to get chemo. But most doctors prefer to give chemo before surgery because it’s been shown to help patients live longer than surgery alone. When chemo is given first, surgery is delayed. This is not a problem if the chemo shrinks the bladder cancer, but it might be harmful if the tumor continues to grow during chemo.
If cancer is found in nearby lymph nodes, radiation may be needed after surgery. Another option is chemo, but only if it wasn’t given before surgery.
For people who have had surgery, but the features of the tumor show it is at high risk of coming back, the immunotherapy drug, nivolumab, might be offered. When given after surgery, nivolumab is given for up to one year.
For patients who cant have surgery because of other serious health problems, TURBT, radiation, chemotherapy, or some combination of these may be options.
You May Like: Unable To Hold Urine When Bladder Is Full
Radiotherapy With A Radiosensitiser
Radiotherapy is given by a machine that beams the radiation at the bladder . Sessions are usually given on a daily basis for 5 days a week over the course of 4 to 7 weeks. Each session lasts for about 10 to 15 minutes.
A radiosensitiser should also be given alongside radiotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. This is a medicine which affects the cells of a tumour, to enhance the effect of radiotherapy. It has a much smaller effect on normal tissue.
As well as destroying cancerous cells, radiotherapy can also damage healthy cells, which means it can cause a number of side effects. These include:
- tightening of the vagina , which can make having sex painful
- erectile dysfunction
- tiredness
- difficulty passing urine
Most of these side effects should pass a few weeks after your treatment finishes, although thereâs a chance theyâll be permanent.
Having radiation directed at your pelvis usually means youâll be infertile for the rest of your life. However, most people treated for bladder cancer are too old to have children, so this isnât usually a problem.
After having radiotherapy for bladder cancer, you should be offered follow-up appointments every 3 months for the first 2 years, then every 6 months for the next 2 years, and every year after that. At these appointments, your bladder will be checked using a cystoscopy.
Read Also: The Most Frequent Initial Symptom Of Bladder Cancer Is
What Can I Do
First, work with your doctor to figure out how to best treat it. Even if it canât be cured, you may be able to slow it down and manage your symptoms with surgery, medicine, and other treatments.
You can also do a lot on your own to feel better physically and emotionally:
Pace yourself. Cancer, and even some of its treatments, can wipe you out. Try to keep your days simple and save your energy for the important activities. And donât be shy about resting when you need to.
Speak your symptoms. Your doctor can help with all kinds of common problems from cancer and its treatments, like constipation, upset stomach, and pain. But only if you say something about them. Check in with your doctor often to get the care you need.
Stay active. Exercise lifts your energy and helps you fight off anxiety, depression, and stress. Ask your doctor whatâs safe for you to do.
Tend to your body. Along with regular exercise, try to stick to a healthy diet and get the rest you need. If you donât feel like eating much, a dietitian might be able to help.
Find ways to relax. Itâll keep your mood and energy up. Take time to read a book, go for a walk, call a friend, get a massage, or try some meditation. Or all of the above. Go with works best for you.
Work with your doctor, and try to stay positive. There are more ways to treat the condition than ever before. Your doctor can help you think about which ones are best for you.
Show Sources
You May Like: Will Bladder Infections Go Away By Themselves
Don’t Miss: How Do They Inject Botox Into The Bladder
Management Of Bladder Cancer Brain Metastases
Systemic chemotherapy forms the backbone of mUC treatment as established in several randomized Phase III trials, with combination gemcitabine/cisplatin non-inferior and less toxic compared to MVAC . The expected OS for unresectable mUC is poor, with median survival < 12 months . Of note, there is little information to guide optimal treatment of mUC patients with intracranial failure since they were typically excluded from randomized systemic therapy trials, likely due to poor performance status and concern regarding brain penetration by systemic therapy . ICB using pembrolizumab is now second-line therapy for mUC following first-line platinum-based regimens, yet the Phase II/III trials of ICB excluded active brain metastases so ICB efficacy for intracranial involvement is not defined . Patients who develop UC brain metastases typically have either already received cisplatin-based chemotherapy or cannot tolerate it only about 50% of mUC patients are eligible for cisplatin-based therapy . Thus, treatment of UC intracranial failure is extrapolated from management of brain metastases from more common histologies such as non-small cell lung cancer and melanoma.
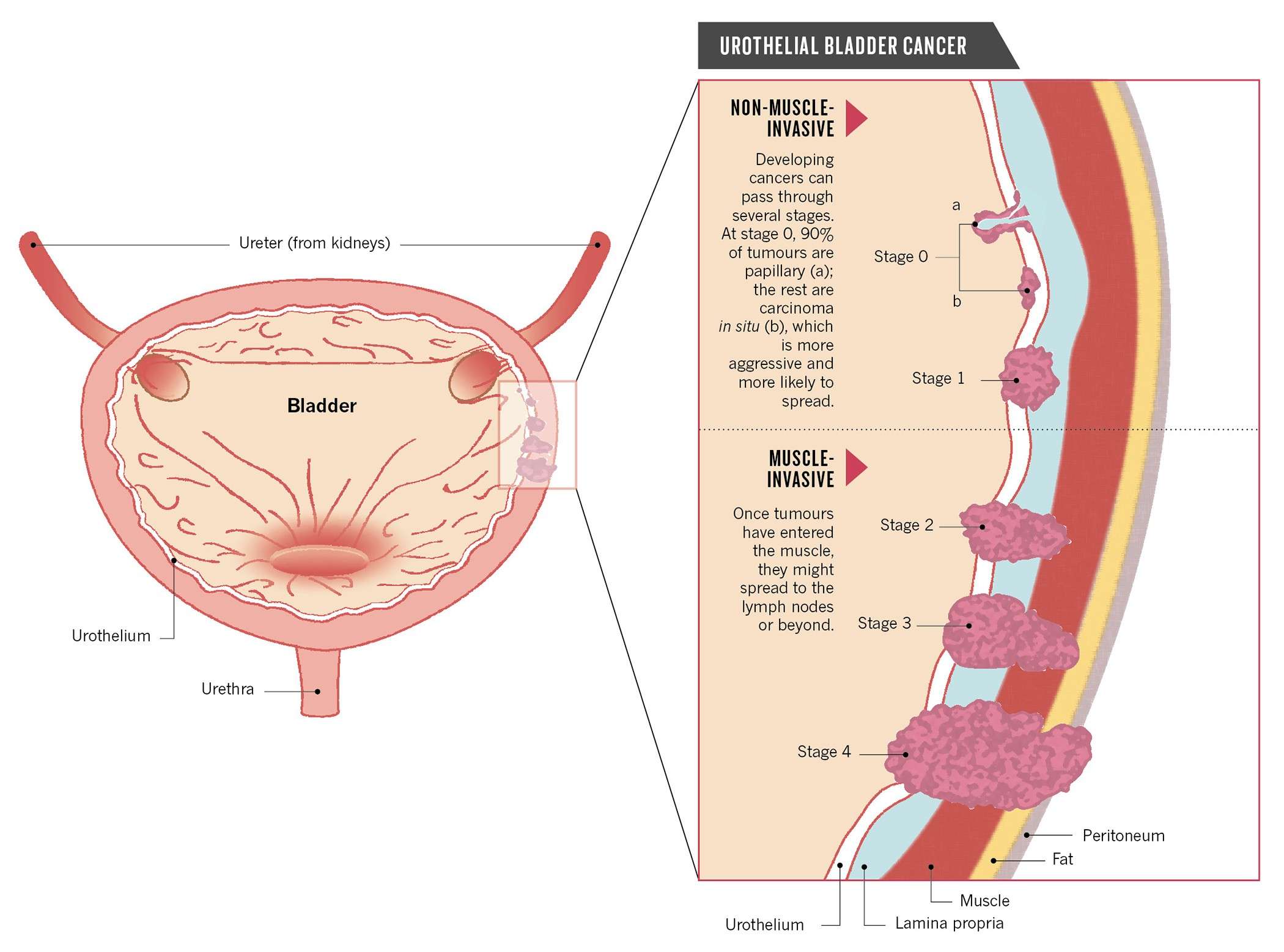
Types Of Bladder Cancer
Once diagnosed, bladder cancer can be classified by how far it has spread.
If the cancerous cells are contained inside the lining of the bladder, doctors describe it as non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer . This is the most common type of bladder cancer.
When the cancerous cells spread beyond the lining, into the surrounding bladder muscle, it’s referred to as muscle-invasive bladder cancer . This is less common, but has a higher chance of spreading to other parts of the body.
If bladder cancer has spread to other parts of the body, it’s known as advanced or metastatic bladder cancer.
Read more about diagnosing bladder cancer.
You May Like: How Do I Cure A Bladder Infection
Tests Used To Check The Prostate
This first step lets your doctor hear and understand the story of your prostate concerns. Youll be asked whether you have symptoms, how long youve had them, and how much they affect your lifestyle. Your personal medical history also includes any risk factors, pain, fever, or trouble passing urine. You may be asked to give a urine sample for testing.
Risk Factor: Chemical Exposure
Research suggests that certain jobs may increase your risk for bladder cancer. Metal workers, mechanics, and hairdressers are among those who may be exposed to cancer-causing chemicals. If you work with dyes, or in the making of rubber, textiles, leather, or paints, be sure to follow safety procedures to reduce contact with dangerous chemicals. Smoking further increases risk from chemical exposure.
Anyone can get bladder cancer, but these factors put you at greater risk:
- Gender: Men are three times more likely to get bladder cancer.
- Age: Nine out of 10 cases occur over age 55.
- Race: Whites have twice the risk of African-Americans.
Other factors at play include a family history of bladder cancer, previous cancer treatment, certain birth defects of the bladder, and chronic bladder irritation.
Read Also: Natural Ways To Control Overactive Bladder
Don’t Miss: Harbor Freight Drain Cleaning Bladder
Early Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
The following are some of the early-stage bladder cancer symptoms you might experience:
1. Blood in the Urine
Blood in urine, often referred to as hematuria, is the most common symptom or sign of bladder cancer. With this symptom:
- You might have enough blood to change your urine color to pink, orange or, less often, dark red.
- Your urine color is sometimes normal, but a urine test , which the doctor performs during a general medical checkup or if you have other symptoms, can still detect small traces of blood.
- You may have blood one day and not the next, with your urine staying clear for weeks or maybe even months at a time.
Generally, the earlier stages of bladder cancer when the cancer is small and confined to your bladder only cause bleeding with either no pain or little pain.
Itâs important to note that blood in your urine doesnât necessarily indicate bladder cancer. The cause of blood may be due to another factor. In fact, many healthy individuals may have some unseen blood in their urine at some stage . And, for most individuals, the cause isnât cancer.
In many situations, the cause is due to other things like benign tumors, medications or foods, infection, bladder or kidney stones or another benign kidney disease. Still, you should have your doctor check it out.
If youâre concerned about cancer, ask them about Cxbladder, a non-invasive genomic urine test that quickly and accurately detects or rules out bladder cancer.
Treatment Of Bone Metastases
When bladder cancer has spread to the bone, skeletal complications can occur, such as weakening of the bones or pathological fractures from minor incidents or everyday activity. This causes pain and can have a detrimental effect on your quality of life. Your doctor may suggest radiotherapy, or drug treatment to help strengthen your bones and control the pain.
Don’t Miss: Galvanized Pressure Tank Vs Bladder Tank
Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
Blood in your urine is the most common symptom of bladder cancer.
The medical name for this is haematuria and it’s usually painless. You may notice streaks of blood in your urine or the blood may turn your urine brown. The blood isn’t always noticeable and it may come and go.
Less common symptoms of bladder cancer include:
- a need to urinate on a more frequent basis
- sudden urges to urinate
- a burning sensation when passing urine
If bladder cancer reaches an advanced stage and begins to spread, symptoms can include:
- pelvic pain
- swelling of the legs
Catheterizable Continent Diversion Pouch
This is a reservoir of bowel with a stoma that is catheterizable for emptying the bladder. The urine is siphoned out of the urinary reservoir with a small catheter every four to six hours. The catheterizable pouch may require surgical repair at some point after surgery due to the wear and tear of frequent catheterization. This type of reconstruction is not performed on patients with a history of bowel disease.
You May Like: Apple Cider Vinegar And Bladder Infection
Risk Factors For Kidney Cancer
There are some things that can make you more likely to develop kidney cancer. These are called risk factors and they include:
- smoking chemicals in cigarettes can cause kidney cancer. Around one in three cases of kidney cancer may be due to smoking
- obesity excess body fat may cause changes in certain hormones that can lead to kidney cancer
- high blood pressure
- kidney failure people with end-stage kidney disease
- family history people who have family members with kidney cancer, especially a sister or brother
- exposure to toxic substances at work the risk may be higher after regular exposure to some chemicals, such as some metal degreasers, arsenic or cadmium.
Having these risk factors doesnt mean you will develop kidney cancer. Often there is no clear reason for getting kidney cancer. If you are worried about your risk factors, ask your doctor for advice.
Questions For Your Team
Asking questions will help you understand more about your bladder cancer, the treatment and how you can improve your prognosis. We have pulled together the most important common questions that you might want to ask, and we also cover what the answers might be. We always suggest taking someone with you for these appointments to help remember everything that you are told.
Don’t Miss: Loss Of Bladder Control In Men
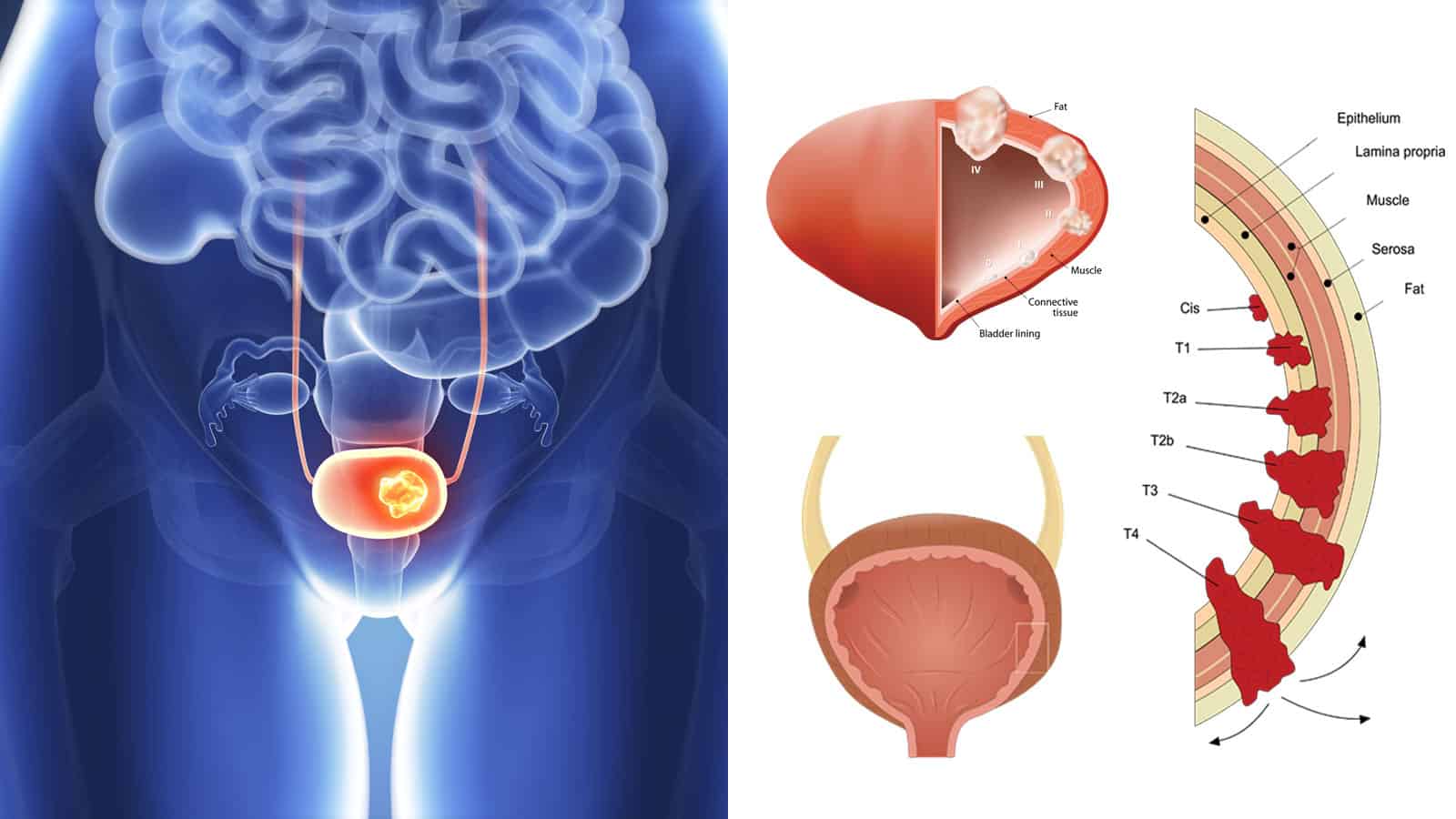
What Are The Stages Of Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer can be either early stage or invasive .
The stages range from TA to IV . In the earliest stages , the cancer is confined to the lining of the bladder or in the connective tissue just below the lining, but has not invaded into the main muscle wall of the bladder.
Stages II to IV denote invasive cancer:
- In Stage II, cancer has spread to the muscle wall of the bladder.
- In Stage III, the cancer has spread to the fatty tissue outside the bladder muscle.
- In Stage IV, the cancer has metastasized from the bladder to the lymph nodes or to other organs or bones.
A more sophisticated and preferred staging system is known as TNM, which stands for tumor, node involvement and metastases. In this system:
- Invasive bladder tumors can range from T2 all the way to T4 .
- Lymph node involvement ranges from N0 to N3 .
- M0 means that there is no metastasis outside of the pelvis. M1 means that it has metastasized outside of the pelvis.
Sexuality Fertility And Bladder Cancer
Having bladder cancer and treatment can change the way you feel about yourself, other people, relationships and sex. These changes can be very upsetting and hard to talk about. Doctors and nurses are very understanding and can give you support. You can ask for a referral to a counsellor or therapist who specialises in body image, sex and relationships.
Changes for men after a cystectomy may include damaged nerves to the penis, orgasm changes and fertility changes.
Changes for women after a cystectomy may include vaginal changes such as narrowing, shortening or dryness, changes to sexual arousal and the ability to orgasm, menopause and fertility changes.
If you may want to have children in the future, talk to your treatment team.
Read Also: What Medicine For Bladder Infection
Treating Stage 0 Bladder Cancer
Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma and flat non-invasive carcinoma . In either case, the cancer is only in the inner lining layer of the bladder. It has not invaded the bladder wall.
This early stage of bladder cancer is most often treated with transurethral resection with fulguration followed by intravesical therapy within 24 hours.