Stage 3 Bladder Cancer
Stage 3 bladder cancer means that the cancer cells have spread beyond the bladder muscle.1,2,3 Stage 3 bladder cancer includes the following combined TNM stages:
In all three types of stage 3 bladder cancer, the cancer cells have not spread to the lymph nodes near the bladder and they have not spread to other parts of the body.
In a bladder tumor that is stage T3a or stage T3b, the bladder cancer cells have grown into the layer of fatty tissue that surrounds the outside of the bladder. This layer of fatty tissue is called perivesical tissue.
In a stage T3a bladder tumor, the bladder cancer cells in the perivesical tissue are only visible through a microscope. In a stage T3b bladder tumor, the bladder cancer cells have grown into the perivesical tissue and are large enough that they are visible using an imaging test or they can be felt by a healthcare professional. A stage T4a bladder tumor is different in women and men. In women, the stage T4a tumor has grown through the perivesical tissue and into the uterus and/or vagina. In men, the stage T4a tumor has grown through the perivesical tissue and into the prostate. However, in both women and men, a stage T4a tumor has not grown into the pelvic wall or the abdominal wall.
Also Check: Loss Of Bladder Control While Coughing
What Are The 5
In 2020, approximately 17,980 deaths in the United States are predicted to be attributed to bladder cancer1. This represents the eighth most common cause of cancer deaths in men.
The general 5-year survival rate for people with bladder cancer is 77%, while the 10-year survival rate is 70% and the 15-year survival rate is 65%1. Notably, as each patient and cancer are different, it is not possible to definitely know the disease course for an individual patient.
Bladder Cancer Survival Trends Over Time
Bladder cancer survival trends are difficult to interpret because of changes to classification and coding practices affecting the definition of invasive carcinoma of the bladder.The decrease in bladder cancer survival since the 1990s is likely to be due to an increasing proportion of bladder tumours now being coded as in situ or uncertain.
One-year age-standardised net survival for bladder cancer in men has increased from 63% during 1971-1972 to 80% during 1990-1991 and then decreased to 77% during 2010-2011 in England and Wales. In women, one-year survival has increased from 53% to 70% and then decreased to 62% over the same time periods.
Bladder Cancer , Age-Standardised One-Year Net Survival, Adults , England and Wales, 1971-2011
Five-year age-standardised net survival for bladder cancer in men has increased from 41% during 1971-1972 to 63% during 1990-1991 and then decreased to a predicted survival of 57% during 2010-2011 in England and Wales. In women, five-year survival has increased from 35% to 55% and then decreased to 46% over the same time periods.
Bladder Cancer , Age-Standardised Five-Year Net Survival, Adults , England and Wales, 1971-2011
Five-year survival for 2010-2011 is predicted using an excess hazard statistical model
Bladder Cancer , Age-Standardised Ten-Year Net Survival, Adults , England and Wales, 1971-2011
Ten-year survival for 2005-2006 and 2010-2011 is predicted using an excess hazard statistical model
Also Check: How To Insert Catheter In Bladder
What Goes Into A Prognosis
When figuring out your prognosis, your healthcare provider will consider all the things that could affect the cancer and its treatment. He or she will look at risk estimates about the exact type and stage of the cancer you have. These estimates are based on what results researchers have seen over many years in thousands of people with the same type and stage of cancer.
If your cancer is likely to respond well to treatment, your healthcare provider will say you have a favorable prognosis. This means youre expected to live many years and may even be cured. If your cancer is likely to be hard to control, your prognosis may be less favorable. The cancer may shorten your life. Its important to keep in mind that a prognosis states whats likely or probable. It’s not a prediction of what will definitely happen. No healthcare provider can be fully certain about an outcome.
Your prognosis depends mainly on:
-
The type and location of the cancer
-
The stage of the cancer
-
Your overall health
-
Your treatment decisions
Statistics Of Death Due To Bladder Cancer
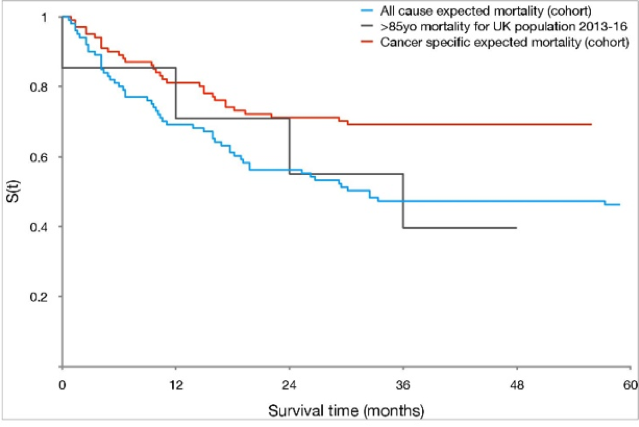
The rates of new bladder cancers and of bladder cancer deaths have slightly decreased in women in the recent years. In men, new cancer rates have been decreasing slightly and the death rates have been more or less stable, according to reports from the American Cancer Society.
- In the UK, there were about 5369 deaths from the bladder cancer, in 2014
- In the UK, 3% of the total cancer deaths were attributed to bladder cancer, in 2014
- Bladder cancer mortality rates have decreased by 21% since the early 90s in the UK
- In the US, estimated deaths in 2017 due to bladder cancer were 16,870
- Bladder cancer represents about 4.7% of all new cancer cases in the U.S.
- Bladder cancer is the 9thleading cause of cancer death in the United States. The number of deaths was about 4.4 for every 100,000 men and women per year based on 2010-2014 data.
You May Like: Cramping In Bladder Or Uterus
What Impacts The Bladder Cancer Survival Rate
Survival rates depend on many factors, including the type and stage of bladder cancer that is diagnosed. According to the ACS, the five-year survival rate of people with bladder cancer that has not spread beyond the inner layer of the bladder wall is 96%. This is called non-muscle invasive bladder cancer . More than half of people are diagnosed at this stage.
If a tumor is invasive but has not yet spread outside the bladder, the five-year survival rate is 69%. Approximately 33% of bladders cancers are diagnosed at this stage. If the cancer extends through the bladder to the surrounding tissue or has spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs, the five-year survival rate is 37%. If the cancer has spread to distant parts of the body, the five-year survival rate is 6%. About 4% of people are diagnosed at this stage.
It is important to remember that statistics about the five-year survival rates for people with bladder cancer are estimates only and come from annual data based on the number of people with this cancer. A number of new and promising bladder cancer treatments that have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration in the last five years might not be reflected in a five-year survival rate statistic.
Just like no single treatment is appropriate for all bladder cancer patients, there is not one statistic that applies to everyone either. Talk with your doctor about your own individual situation to gain the best understanding you can.
Survival Rates By Stage
The numbers listed below are based upon countless people detected with bladder cancer from 1988 to 2001. These numbers originated from the National Cancer Institutes SEER database.
- The 5-year relative survival rate for people with stage 0 bladder cancer has to do with 98%.
- The 5-year relative survival rate for individuals with stage I bladder cancer has to do with 88%.
- For stage II bladder cancer, the 5-year relative survival rate is about 63%.
- The 5-year relative survival rate for stage III bladder cancer has to do with 46%.
Bladder cancer that has spread to other parts of the body is often hard to alleviate. Phase IV bladder cancer has a relative 5-year survival rate of about 15%. Still, there are typically treatment alternatives readily available for people with this phase of cancer.
Remember, these survival rates are only approximates they cant predict exactly what will happen to any individual person. We comprehend that these data can be complicated and may lead you to have more concerns. Speak with your physician to much better comprehend your certain situation.
Being diagnosed with bladder cancer can be overwhelming and scary, especially if its phase 4.
Recommended Reading: Loss Of Bladder Control In Cancer Patients
Who Dies From Bladder Cancer
The statistics for the deaths in the U.S. are as follows :
- Among all races, the number of male deaths for every 100,000 was 7.6
- Among all races, the number of female deaths for every 100,000 was 2.2
- Among White Americans, the number of male deaths for every 100,000 was 8.1
- Among White Americans, the number of female deaths for every 100,000 was 2.2
- Among Black Americans, the number of male deaths for every 100,000 was 5.4
- Among Black Americans, the number of female deaths for every 100,000 was 2.5
- The percent of bladder cancer deaths is highest among people with age group 75-84
Survival Rates For Bladder Cancer
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time after they were diagnosed. They cant tell you how long you will live, but they may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is that your treatment will be successful.
Keep in mind that survival rates are estimates and are often based on previous outcomes of large numbers of people who had a specific cancer, but they cant predict what will happen in any particular persons case. These statistics can be confusing and may lead you to have more questions. Talk with your doctor about how these numbers may apply to you, as he or she is familiar with your situation.
Don’t Miss: What Causes Bladder Pain And Pressure
Grade And Risk Category
The biopsy results will show the grade of the cancer. This is a score that describes how quickly a cancer might grow. Knowing the grade helps your urologist predict how likely the cancer is to come back and if you will need further treatment after surgery.
| Low grade | The cancer cells look similar to normal bladder cells, are usually slow-growing and are less likely to invade and spread. Most bladder tumours are low grade. |
| High grade | The cancer cells look very abnormal and grow quickly. They are more likely to spread both into the bladder muscle and outside the bladder.
In non-muscle-invasive tumours, the grade may be low or high, while almost all muscle-invasive cancers are high grade. Carcinoma in situ is a high-grade tumour that needs prompt treatment to prevent it invading the muscle layer. |
| Risk category | Based on the stage, grade and other features, a non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer will also be classified as having a low, medium or high risk of returning after treatment. This will help your doctors work out which treatments to recommend. |
Read Also: Can Lower Back Pain Cause Bladder Problems
Types Of Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer can be described based on where it is found:
- non-muscle invasive the cancer has not spread to other layers of the bladder or muscle
- muscle-invasive the cancer has spread to other layers of the bladder, muscle or other parts of the body.
There are 3 main types of bladder cancer:
- urothelial carcinoma 80 to 90% of bladder cancers sometimes called transitional cell carcinoma
- squamous cell carcinoma 1 to 2% of all bladder cancers. It is more likely to be invasive
- adenocarcinoma 1 to 2% of all bladder cancers. It is more likely to be invasive .
There are other, less common types of bladder cancer. Treatment for these may be different. Speak to your doctor or nurse for information about these types of cancer.
You May Like: How To Train A Weak Bladder
Response Of Bladder Cancer To Nac
In metastatic breast and colon cancers, chemotherapy provides response rates of 35%60% and 17%36% , respectively. Bladder cancer is also sensitive to chemotherapy, and treatment for metastatic bladder cancer using methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, and cisplatin provides a response rate of 50%70% and complete remission in 12%40% of cases . Thus, it is possible that NAC using MVAC may be useful for treating bladder cancer. Many studies have explored the role of NAC in MIBC although most studies were underpowered to detect a significant difference in the survival rate and the surgical techniques were an important confounding factor.
Table 22.1. Randomized Clinical Trials of NAC in MIBC
| Study |
|---|
How Do Health Care Professionals Determine Bladder Cancer Staging
Bladder cancer is staged using the tumor node metastases system developed by the International Union Against Cancer in 1997 and updated and used by the American Joint Committee on Cancer . In addition, the American Urologic Association has a similar staging system that varies slightly from that used by the AJCC. The combination of both staging systems appears below. This staging gives your physician a complete picture of the extent of the personâs bladder cancer.
The T stage refers to the depth of penetration of the tumor from the innermost lining to the deeper layers of the bladder. The T stages are as follows:
- Ta â Noninvasive papillary carcinoma
- T1 â Tumor invades connective tissue under the epithelium
- T2 â Tumor invades muscle of the bladder
- T2a â Superficial muscle affected
The presence and extent of involvement of the lymph nodes in the pelvic region of the body near the urinary bladder determines the N stage. The N stages are as follows:
The metastases or the M stage signifies the presence or absence of the spread of bladder cancer to other organs of the body.
- Mx â Distant metastasis cannot be evaluated
- M0 â No distant metastasis
A health care professional then assigns a stage:
You May Like: Symptoms Of Bladder Stones In Cats
Can I Lower My Risk Of The Bladder Cancer Progressing Or Coming Back
If you have bladder cancer, you probably want to know if there are things you can do that might lower your risk of the cancer growing or coming back, such as exercising, eating a certain type of diet, or taking nutritional supplements. Unfortunately, its not yet clear if there are things you can do that will help.
Adopting healthy behaviors such as not smoking, eating well, getting regular physical activity, and staying at a healthy weight might help, but no one knows for sure. Still, we do know that these types of changes can have positive effects on your health that can extend beyond your risk of bladdercancer or other cancers.
Survival For All Stages Of Bladder Cancer
Generally, for people diagnosed with bladder cancer in England:
- around 75 out of every 100 survive their cancer for 1 year or more after diagnosis
- almost 55 out of every 100 survive their cancer for 5 years or more after they are diagnosed
- around 45 out of every 100 survive their cancer for 10 years or more after diagnosis
Cancer survival by stage at diagnosis for England, 2019Office for National Statistics
These statistics are for net survival. Net survival estimates the number of people who survive their cancer rather than calculating the number of people diagnosed with cancer who are still alive. In other words, it is the survival of cancer patients after taking into account that some people would have died from other causes if they had not had cancer.
Don’t Miss: Exercises To Help Bladder Leakage
If Youre Concerned About Bladder Cancer Talk To Your Doctor About Cxbladder
Cxbladder is a cutting-edge genomic urine test that quickly and accurately detects or rules out bladder cancer. The test combines clinical risk factor markers with genetic information, measuring five biomarker genes to detect the presence or absence of bladder cancer in hematuria patients and those being monitored for recurrence.
Cxbladder comes as a suite of tests, each optimised for a different point in the patient journey:
- Cxbladder Triage: Incorporates known bladder cancer risk factors to help quickly rule out the disease.
- Cxbladder Detect: Designed to work alongside other tests to improve overall detection accuracy.
- Cxbladder Monitor: A non-invasive surveillance alternative that can reduce the need for frequent cystoscopies.
Cxbladder gives you peace of mind and will help your physician make informed treatment decisions.
Speak to your doctor or urologist to learn more about Cxbladder and which test might be right for you. You can also contact our Customer Service Team directly.Learn more about Cxbladder Contact us for more information
Can You Have Bladder Cancer For Years And Not Know It
Even after reporting the problem to their doctors, blood in the urine may be initially misdiagnosed. It may be seen as a symptom of post-menopausal bleeding, simple cystitis or as a urinary tract infection. As a result, a bladder cancer diagnosis can be overlooked for a year or more.
Survival rates are usually given in percentages. For instance, the overall five-year survival rate for bladder cancer is 78 percent. That means that of all people who have bladder cancer, 78 of every 100 are living five years after diagnosis.
Also Check: Difference Between Bladder And Urinary Tract Infection
Where Do These Numbers Come From
The American Cancer Society relies on information from the SEER* database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute , to provide survival statistics for different types of cancer.
The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for bladder cancer in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread. The SEER database, however, does not group cancers by AJCC TNM stages . Instead, it groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages:
- Localized: There is no sign that the cancer has spread outside of the bladder.
- Regional: The cancer has spread from the bladder to nearby structures or lymph nodes.
- Distant: The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body such as the lungs, liver or bones.