Managing Bladder Or Urinary Incontinence
Sometimes urinary incontinence can last a short time, depending on what’s causing it. But sometimes incontinence can be long-term and uncomfortable, making some everyday activities difficult to manage.
Your health care team will ask you questions to determine the type of bladder incontinence you might have. Then, you might need tests to verify the type and learn the cause of it which will help them know the best way to manage it.
- Pelvic floor muscle strengthening may be recommended. A physical therapist that specializes in pelvic floor muscle exercises can help. This might help muscle strength and bladder control get better by doing exercises that tighten and relax muscles that control the flow of urine.
- Bladder training canhelp manage how often you need to urinate throughout the day, by assigning certain time intervals to empty your bladder.
When You Should See A Health Care Professional
You shouldnt have to wear a pad to soak up urine every day. Also ask yourself these questions:
-
Is the urge to urinate interfering with your work because of leaking or frequent bathroom breaks?
-
Do you map out where bathrooms are when you run errands?
-
Is incontinence interfering with your sex life or intimacy with your partner?
These are all signs of a problem, and that it may be time for you to talk with a gynecologist.
You Have An Enlarged Prostate
The urethra connects the bladder to the outside world. In women, its that simple. But in men, the tube goes through the prostate, which expands with age. As it expands, it can put undue pressure on the bladder and urethra. The bladder responds by becoming overactive and sensitive to even small amounts of urine, making you feel like you have to go even when your tank is relatively empty, explains Brahmbhatt.
Read More: What All Men Should Know About Taking Care Of Their Prostate
This is typically an issue in men over the age of 50, Brahmbhatt says. Still, strictures and chronic prostatitis can have similar side effects in younger guys.
Recommended Reading: Treatment After Bladder Tumor Removal
What Specialists Treat Urinary Retention
Urologists are most often involved in the care of patients with urinary retention. However, urogynecologists also treat women with urinary retention. Internists, family physicians, and emergency-room physicians also frequently treat urinary retention and will refer you to a urologist or urogynecologist if it is not improving.
Causes Of Urinary Incontinence
Stress incontinence is usually the result of the weakening of or damage to the muscles used to prevent urination, such as the pelvic floor muscles and the urethral sphincter.
Urge incontinence is usually the result of overactivity of the detrusor muscles, which control the bladder.
Overflow incontinence is often caused by an obstruction or blockage in your bladder, which prevents it from emptying fully.
Total incontinence may be caused by a problem with the bladder from birth, a spinal injury, or a small, tunnel like hole that can form between the bladder and a nearby area .
Certain things can increase the chances of urinary incontinence, including:
- pregnancy and vaginal birth
Find out more about the causes of urinary incontinence.
Recommended Reading: Is It Normal To Lose Bladder Control When You Faint
Not Sure What To Do Next
If you are still concerned about your urinary retention, why not use healthdirects online Symptom Checker to get advice on when to seek medical attention.
The Symptom Checker guides you to the next appropriate healthcare steps, whether its self care, talking to a health professional, going to a hospital or calling triple zero .
Problems With The Nerves Supplying The Bladder
Urinary retention can result from problems with the nerves that control the bladder and the valves that control the flow of urine from the bladder.
Even when the bladder is full, the bladder muscles that squeeze urine out may not receive the signal to push. The sphincters may not receive the signal to relax and allow the bladder to empty. Possible causes of nerve problems that may cause urinary retention include diabetes, a stroke, multiple sclerosis or after an injury to the pelvis.
Some children are born with conditions that may affect the nerve signals to the bladder. For example spina bifida may cause urinary retention in newborn babies.
Also Check: Intravesical Chemotherapy For Bladder Cancer
Why Does Pregnancy Cause Incontinence
During pregnancy, your body goes through a lot of physical changes. As your uterus stretches to hold the growing baby, a few things happen. Your bladder can be squished by the expanding baby, making your bladder hold less than before. You might experience an increased urgency to pee during pregnancy because your bladder cannot hold as much as before. This might become even more challenging towards the end of pregnancy when the baby is at its largest.
Another reason for incontinence during pregnancy is the weakening of your pelvic floor muscles. These muscles are the support structures for all of the organs in your pelvis. During pregnancy, they can be stretched and weakened as your uterus expands.
Am I At A Higher Risk Of Incontinence At An Older Age
Your body constantly changes throughout your life. As you age, the muscles that support your pelvic organs can weaken. This means that your bladder and urethra have less support often leading to urine leakage. Your risk for developing incontinence as you age might be higher if you have a chronic health condition, have given birth to children, went through menopause, have an enlarged prostate or have had prostate cancer surgery. Its important to talk to your healthcare provider over time about the risks of incontinence and ways you can manage it without interference to your daily life.
You May Like: Bladder Cancer And Lung Cancer
Free Just Cant Wait Toilet Card
The most common cause of difficult urination in men is a blockage due to an enlarged prostate restricting the outlet from the bladder. For women one of the common causes of difficulty in urination is an anterior prolapse/bladder prolapse which can distort the urethra and restrict the flow of urine.
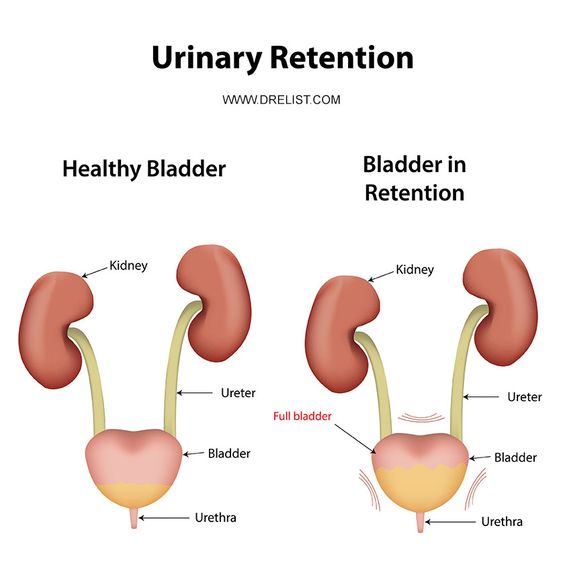
What Is Urinary Retention
Urinary retention is a condition where your bladder doesnt empty all the way or at all when you urinate. Your bladder is like a storage tank for urine. Urine is made up of waste thats filtered out of your blood by your kidneys. Once filtered, the urine moves to your bladder where it waits till its time to move through the urethra and out of the body.
When you have urinary retention, it can be acute or chronic . Acute means that it comes on quickly and it could be severe. Chronic urinary retention means that youve had the condition for a longer period of time.
The acute form of urinary retention is an emergency. In this case, youll need to see a healthcare provider right away. The chronic form happens most of the time in older men, but it can also occur in women.
Read Also: How To Know If You Have Bladder Problems
What Is Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence is the accidental loss of urine. According to the National Association for Continence, over 25 million adult Americans experience temporary or chronic urinary incontinence. UI can occur at any age, but it is more common among women over 50. Urinary incontinence may be a temporary condition that results from an underlying medical condition. It can range from the discomfort of slight losses of urine to severe, frequent wetting.
Can Incontinence Be Prevented
Different events throughout your life can lead to many of the things that cause incontinence. The muscles that support your pelvic organs can weaken over time. For women, these muscles can also be weakened by big life events like pregnancy and childbirth. However, in the same way you work out to build strength in your legs or arms, you can do exercises to strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. Doing exercises to strengthen your pelvic muscles may not prevent you from having any issues with incontinence, but it can help you regain control of your bladder. Maintaining a healthy body weight can also help with bladder control. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best ways to maintain strong pelvic floor muscles throughout your life.
Recommended Reading: Can Cervical Cancer Spread To The Bladder
Doctor’s Notes On Inability To Urinate
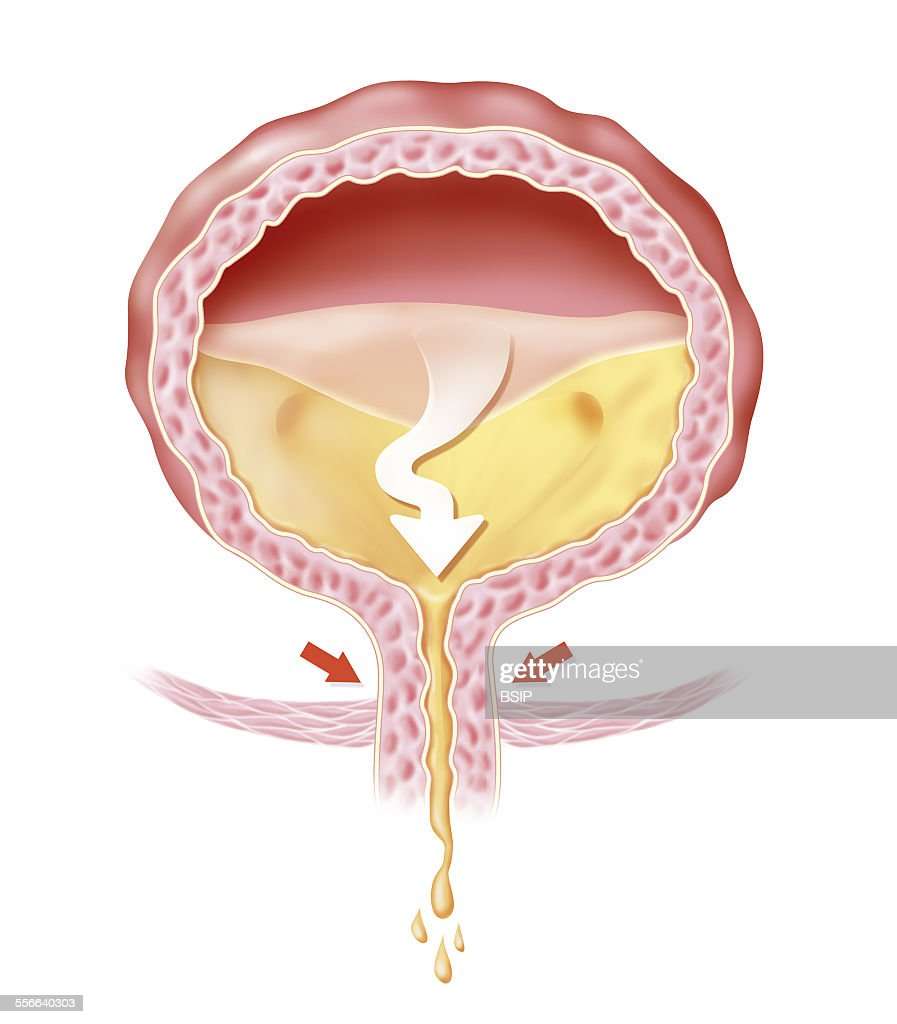
An inability to urinate means that a person cannot pass urine out of the body through the urethra. Another broad term for inability to urinate is urinary retention, although urinary retention may be considered as either partial or complete. This is different from anuria, which means the person’s body is not producing urine in the kidneys, because people who cannot acutely urinate still produce urine.
There are two types of urinary retention: acute and chronic. Acute may occur suddenly, and chronic may occur over a longer time span. Acute obstruction is a medical emergency and can be life-threatening. The causes of the inability to urinate can be either obstruction of the urethra or non-obstruction of the urethra but are due to muscle and/or nerve problems that interfere with normal signals between your brain and your bladder. The inability to urinate is a symptom itself of underlying medical problems that may affect the urinary tract.
Obstructive urinary retention or the inability to urinate are due to underlying causes. The causes include the following and frequently involve putting pressure on the urethra or obstruction of the urethral lumen that results in little or no ability for urine to pass out of the body.
- nerve disease, and
- vaginal childbirth.
- An acute inability to urinate
- Urgent and painful feeling or need to urinate
- Severe pain in the lower abdomen
Chronic urinary retention symptoms and signs may include
- Bladder damage
How Is Loss Of Bladder Control Treated
Non-surgical treatments are often recommended to help treat bladder control issues. These include:
- Physical therapy and exercise
- Reducing intake of alcohol and caffeine
- Electrical stimulation of the nerves that control the bladder
- Bladder retraining by going to the bathroom at set times
- Kegel exercises to strengthen pelvic muscles
- Bladder control device inserted into vagina that repositions urethra to reduce leakage
- Biofeedback to help patients learn to control the bladder muscles
Depending on the type of leakage and how bothersome it isand if patients do not respond to the non-surgical treatmentssurgery and other interventions can be very successful. In most cases, they can be done as an outpatient procedure.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 08/26/2015.
References
Read Also: Can A Bladder Infection Go Away
Living With Bowel Or Bladder Incontinence
There is no single, right way to cope with bladder or bowel incontinence. The challenge is to find what is best for your situation, so you can get the help you need and return to a normal daily life. Talk with your health care team if you notice a change in bowel or bladder habits, and about the best ways to manage incontinence, if it is a problem. You might find it helpful to talk with other people who are dealing with incontinence, too. Ask a member of your cancer care team about support groups in your area.
Here are some things you can do that may help make incontinence less of a problem:
- Empty your bladder every 3 to 4 hours while awake, to avoid accidents.
- Empty your bladder before bedtime or before strenuous activity.
- Limit drinks with caffeine, or and avoid alcohol and citrus juices, which can irritate the bladder and make you have to go more often.
- Avoid hygiene products that may irritate you Women should avoid feminine spray or over-the-counter vaginal suppositories.
- Because belly fat can push on the bladder, avoiding weight gain or losing needed weight sometimes helps improve bladder control.
- Avoid tobacco use which can cause coughing and bladder irritation due to harmful substances in tobacco products.
- Talk to your doctor about all medicines, vitamins, herbs, and supplements youre taking. Some may affect urine control.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes
According to the Urology Care Foundation, women are at greater risk for UI than men because they have a shorter urethra than men. As a result, any weakness or damage to the urethra in a woman is more likely to cause urinary incontinence. This is because there is less muscle keeping the urine in your bladder until you are ready to urinate.
Recommended Reading: Over The Counter Bladder Numbing Medicine
Dangers Of Holding Your Pee
The dangers of holding your pee are mostly cumulative. Holding in your pee for six hours during that one memorable road trip probably wont hurt you long-term.
But if youre constantly ignoring the urge to pee, you may develop complications. In general, you should go when you feel the need to go!
Here are some of the dangers of holding your pee:
- If you dont empty your bladder often enough, or go a couple of days without emptying it all the way, it can result in a urinary tract infection .
- If you hold your pee as a matter of habit, your bladder can start to atrophy. Over time, you may develop incontinence.
- When you hold your pee for 10 hours or more, you may develop urinary retention, meaning the muscles in your bladder cant relax and let you relieve yourself, even when you want to.
- In very rare cases, holding your pee can cause your bladder to burst.
Conditions That Cause Urinary Incontinence
There are several health and lifestyle issues that can make you start to leak urine. They can include:
Problems with your prostate. Itâs common for prostate issues to cause urinary incontinence. Your prostate may be larger due to a non-cancerous condition called benign prostatic hyperplasia . Your prostate may also be bigger than usual because of cancer. An enlarged prostate can block your urethra. When your urethra is blocked, your bladder has to work harder to squeeze pee out. This makes its walls thicker and weaker. That makes it hard for your bladder to empty all the urine in it.
You can also struggle with urinary incontinence with prostate cancer or after having certain treatments for it — such as radiation treatment or surgery to remove your prostate. The surgery may cause problems with the nerves that control your bladder.
Certain diseases. Multiple sclerosis is a disease that can damage the nerves that tell the bladder when to empty and can also lead to bladder spasms. Some other conditions that can damage your nerves and keep your bladder from sending or receiving the signals it needs to work correctly are:
- Diabetes
- Stroke
- Parkinsonâs disease
Surgery. Major bowel surgery, lower back surgery, and prostate surgery can all cause problems with your bladder. This is usually because some of the nerves in your urinary tract have been damaged during surgery.
You May Like: Bladder Cancer Drugs In Development
How To Solve Bladder Control Problems
ByFred Cicettipublished 22 July 09
This Week’s Question:This is embarrassing to discuss with anyone so I thought I’d write to you about it. I’m having bladder-control problems. What can I do?
About 10 percent of men and women over the age of 65 have trouble with bladder control, also know officially as urinary incontinence. Women suffer from this more than men.
During urination, muscles in the bladder contract, forcing urine into the urethra, a tube that carries urine out of the body. At the same time, muscles surrounding the urethra relax and let the urine pass. If the bladder muscles contract or the muscles surrounding the urethra relax without warning, the result is incontinence.
Short-term incontinence is caused by infections, constipation, and some medicines. If the problem persists, it might be caused by weak bladder muscles, overactive bladder muscles, blockage from an enlarged prostate, damage to nerves that control the bladder from diseases such as multiple sclerosis or Parkinson’s.
Treatable condition
In most cases urinary incontinence can be treated and controlled, if not cured. If you are having bladder control problems, go to your doctor. Doctors see this problem all the time, so there is no need to be embarrassed.
Your doctor may do a number of tests on your urine, blood and bladder. You may be asked to keep a daily chart about your urination.
There are several different types of urinary incontinence:
Plugs, medicines and surgery
Urinary Incontinence In Older Adults
Urinary incontinence means a person leaks urine by accident. While it may happen to anyone, urinary incontinence is more common in older people, especially women. Incontinence can often be cured or controlled. Talk to your healthcare provider about what you can do.
What happens in the body to cause bladder control problems? The body stores urine in the bladder. During urination, muscles in the bladder tighten to move urine into a tube called the urethra. At the same time, the muscles around the urethra relax and let the urine pass out of the body. When the muscles in and around the bladder dont work the way they should, urine can leak. Incontinence typically occurs if the muscles relax without warning.
You May Like: Is There Over The Counter Medicine For Overactive Bladder
What Are The Symptoms Of Urinary Retention
The signs can vary. Some people with the chronic form have a hard time starting the flow of urine. Some have a weak flow once they start. Others may feel the need to go but cant start. Others have to go a lot, while others still feel the need to go right after going. You may leak urine when you arent going because the bladder is full.
With the acute form, youre all of a sudden not able to go at all, or only able to go very small amounts. This occurs even though you have a full bladder. See a healthcare provider right away if this happens to you.