Monitoring For Bladder Cancer Recurrence
Those who have already been treated for bladder cancer have unique monitoring needs to protect against the threat of recurrence. Generally doctors recommend a cystoscopy to examine the inside of the bladder and urethra every 3 to 12 months, depending on your risk of recurrence, for several years after bladder cancer treatment. If several years of surveillance have gone by and no cancer recurrence has been detected, a cystoscopy once a year may be enough, though the final decision rests with the doctor and additional testing may be required depending on the nature and severity of the original cancer.
If youre recovering from treatment, ask your doctor about Cxbladder. Cxbladder is an accurate and non-invasive surveillance alternative designed to detect or rule out the return of bladder cancer. The test provides reliable results with a single urine sample, reducing the need for frequent cystoscopies in some patients, which can be both uncomfortable and inconvenient.Learn more about Cxbladder
What Are The Survival Rates For Bladder Cancer
If the cancer is just on the inner lining of the bladder , the 5-year survival rate is about 98%.
If the cancer is growing just beyond the inner lining into the bladder wall, but is still just in the bladder , the 5-year survival rate is about 88%.
Those with bladder cancer that’s spread into the muscular wall of the bladder, but not outside the bladder, or to nearby lymph nodes or organs have a 5-year survival rate of about 63%.
If the cancer has spread through the bladder muscle into the layer of tissue around the bladder and maybe to nearby organs , but has not spread to lymph nodes or other organs , the 5-year survival rate is about 46%.
When bladder cancer has moved beyond the bladder to the pelvic or abdominal wall, to lymph nodes, or to distant parts of the body , the 5-year survival rate is about 15%.
Where Do These Numbers Come From
The American Cancer Society relies on information from the SEER* database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute , to provide survival statistics for different types of cancer.
The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for bladder cancer in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread. The SEER database, however, does not group cancers by AJCC TNM stages . Instead, it groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages:
- Localized: There is no sign that the cancer has spread outside of the bladder.
- Regional: The cancer has spread from the bladder to nearby structures or lymph nodes.
- Distant: The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body such as the lungs, liver or bones.
Recommended Reading: Over The Counter Bladder Medication
Other Types Of Bladder Cancer
Approximately 2% of bladder cancers are adenocarcinomas. Nonurothelial primary bladder tumors are extremely rare and may include small cell carcinoma, carcinosarcoma, primary lymphoma, and sarcoma . Small cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder accounts for only 0.3-0.7% of all bladder tumors. High-grade urothelial carcinomas can also show divergent histologic differentiation, such as squamous, glandular, neuroendocrine, and sarcomatous features.
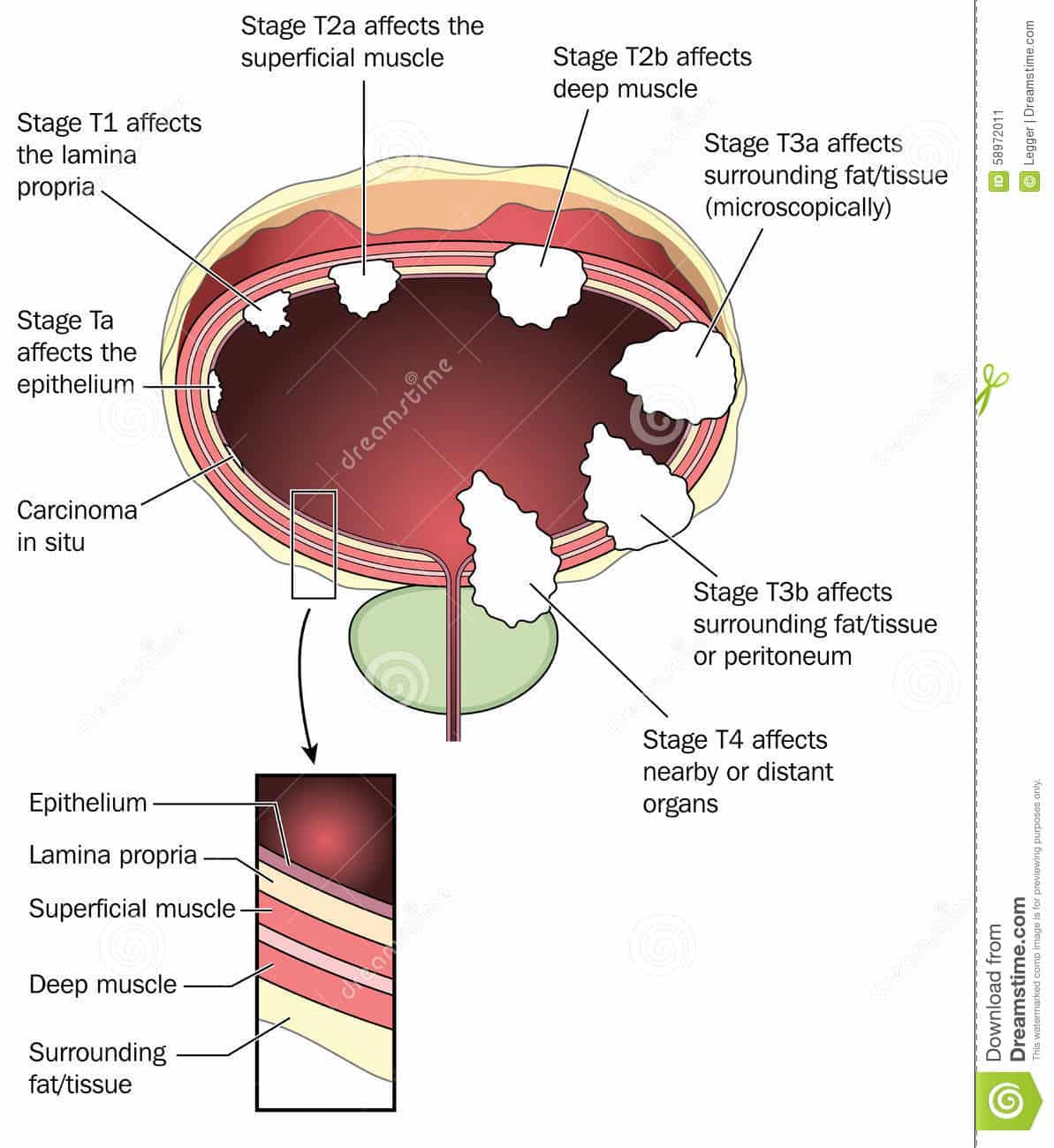
T Categories For Bladder Cancer
The T category describes how far the main tumor has grown into the wall of the bladder .
The wall of the bladder has 4 main layers.
- The innermost lining is called the urothelium or transitional epithelium.
- Beneath the urothelium is a thin layer of connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves.
- Next is a thick layer of muscle.
- Outside of this muscle, a layer of fatty connective tissue separates the bladder from other nearby organs.
Nearly all bladder cancers start in the lining or urothelium. As the cancer grows into or through the other layers in the bladder, it becomes more advanced .
The T categories are described in the table above, except for:
TX: Main tumor cannot be assessed due to lack of information
T0: No evidence of a primary tumor
Also Check: Papillary Bladder Cancer Survival Rates
How Do I Take Care Of Myself
About half of all people with bladder cancer have early-stage cancer thats relatively easy to treat. But bladder cancer often comes back . People whove had bladder cancer will need regular checkups after treatment. Being vigilant about follow-up care is one thing you can do to take care of yourself. Here are some other suggestions from the Bladder Cancer Advocacy Network include:
- Follow a heart-healthy diet: Plan menus that include skinless poultry and fish, low-fat dairy products, nuts and legumes, and a variety of fruits and vegetables.
- Focus on high-fiber foods: Bladder cancer treatment may cause digestive issues and a fiber-rich diet may help.
- Get some exercise: Gentle exercise may help manage stress.
- Connect with others: Bladder cancer often comes back. Its not easy to have a rare disease thats likely to return. Connecting with people who understand what youre going through may help.
Urinary diversion
Some people with bladder cancer need surgery that removes their bladder and their bodies natural reservoir for pee. There are three types of urinary diversion surgeries. All three types involve surgically converting part of your intestine to become a passage tube for pee or a reservoir for storing pee.
Urinary diversion may be a challenging lifestyle change. If youll need urinary diversion surgery, ask your healthcare provider to explain each surgery types advantages and disadvantages. That way, youll know what to expect and how to take care of yourself.
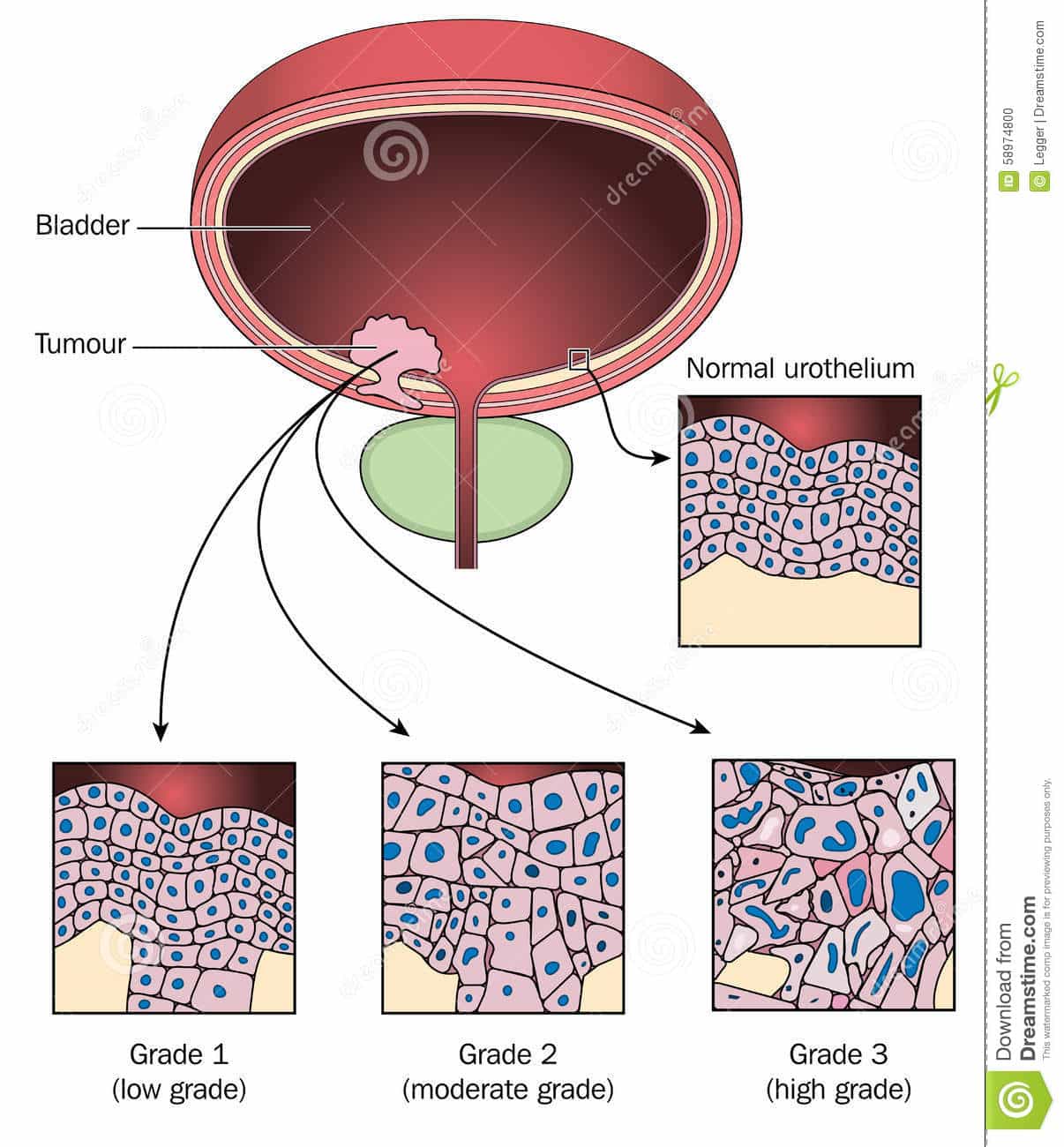
Grading Of A Bladder Cancer
Grading of a bladder cancer is assessing how aggressive it is in terms of howabnormal its cells look under a microscope. Those that are very abnormal growmore quickly. Grade can be divided into low or high orcan be scored from 1 to 3. Often this number has a G as a prefix toshow it represents the grade, e.g. G1, G2 or G3.
Recommended Reading: How Does A Drain Cleaning Bladder Work
What Is The Cure Rate For Bladder Cancer
5-year relative survival rates for bladder cancer
| SEER Stage |
|---|
| 77% |
What is the best treatment for stage 2 bladder cancer?
There are essentially two ways to treat stage II -III bladder cancers: primary surgical treatment consisting of radical cystectomy with some form of urinary diversion or combined modality treatment consisting of administration of chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy, followed by radical cystectomy only for those
What is the main cause of bladder cancer?
Smoking. Smoking is the single biggest risk factor for bladder cancer. This is because tobacco contains cancer-causing chemicals. If you smoke for many years, these chemicals pass into your bloodstream and are filtered by the kidneys into your urine.
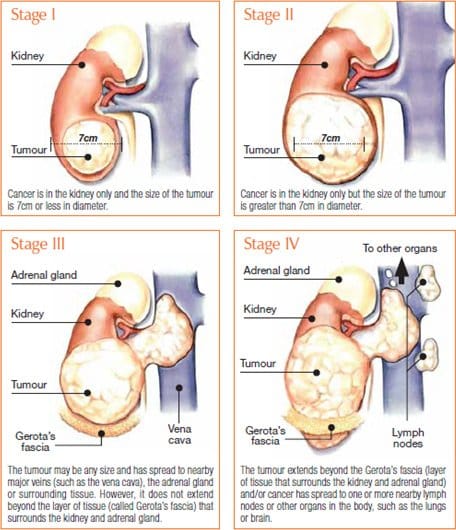
Stages Of Bladder Cancer: What You Need To Know
When you are first diagnosed with bladder cancer, your doctors will perform tests to determine the stage and grade of your disease. The bladder cancer staging and grading processes help your doctors make treatment decisions and estimate your chance of recovery.
Bladder cancer is a growth that starts in the inner wall of the bladder, the organ that collects and expels urine created by the kidneys. The bladder has three layers of muscular walls that make up its structure. A cancerous growth in the bladder can grow uncontrollably and start spreading to other parts of the body.
When doctors first diagnose a cancerous tumor of any kind, they assess how much it has grown, how far it has spread in the body, and how abnormal, or wild, the cancerous cells in the tumor look. These assessments are used to determine cancers stage and grade.
Doctors use the staging information to compare treatment options and patient outcomes. Staging and grading also important in determining your eligibility for cancer treatment clinical trials.
Don’t Miss: Why Do I Get Recurring Bladder Infections
Treating Bladder Cancer That Progresses Or Recurs
If cancer continues to grow during treatment or comes back after treatment , treatment options will depend on where and how much the cancer has spread, what treatments have already been used, and the patient’s overall health and desire for more treatment. Its important to understand the goal of any further treatment if its to try to cure the cancer, to slow its growth, or to help relieve symptoms as well as the likely benefits and risks.
For instance, non-invasive bladder cancer often comes back in the bladder. The new cancer may be found either in the same place as the original cancer or in other parts of the bladder. These tumors are often treated the same way as the first tumor. But if the cancer keeps coming back, a cystectomy may be needed. For some non-invasive tumors that keep growing even with BCG treatment, and where a cystectomy is not an option, immunotherapy with pembrolizumab might be recommended.
Cancers that recur in distant parts of the body can be harder to remove with surgery, so other treatments, such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or radiation therapy, might be needed. For more on dealing with a recurrence, see Understanding Recurrence.
Sexuality And Bladder Cancer
Having bladder cancer and treatment can change the way you feel about yourself, other people, relationships and sex. These changes can be very upsetting and hard to talk about. Doctors and nurses are very understanding and can give you support. You can ask for a referral to a counsellor or therapist who specialises in body image, sex and relationships.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Weak Bladder Control
Were Sorry The Page Youre Looking For Cant Be Found
It is possible that you used an outdated or expired MedicineNet link or you may have typed the address incorrectly.
Please try searching using the search field above. If youre not sure of the spelling, type the first few letters, followed by an asterisk.
To help you find what you are looking for, these links may help.
Browse our A-Z Lists:
Read Also: Where Is Your Bladder Woman
What Is The First Sign Of Bladder Cancer
Blood in the urine, referred to as hematuria, is usually the first sign of bladder cancer. This is because early bladder cancer commonly causes bleeding without associated pain or other symptoms.
- Depending on the amount of blood present, urine may appear pink, red, or brownish in color.
- Blood may not be present all the time there may be relatively long periods of clear urine .
If you have noticed blood in your urine it is important to speak to your doctor as soon as possible.
Other early symptoms of bladder cancer that may be experienced are urinary irritation or changes in bladder habits, such as increased urination frequency and/or urgency, pain or a burning sensation during urination, or difficulty passing urine.
You May Like: Capsaicin Pills For Overactive Bladder
Strategies To Improve Treatment
The progress that has been made in the treatment of bladder cancer has resulted from improved treatment developed in clinical trials. Future progress in the treatment of bladder cancer will result from continued participation in appropriate studies. Currently, there are several areas of active exploration aimed at improving the treatment of bladder cancer.
Supportive Care: Supportive care refers to treatments designed to prevent and control the side effects of cancer and its treatment. Side effects not only cause patients discomfort, but also may prevent the optimal delivery of therapy at its planned dose and schedule. In order to achieve optimal outcomes from treatment and improve quality of life, it is imperative that side effects resulting from cancer and its treatment are appropriately managed. For more information, go to Managing Side Effects.
Adjuvant Treatment: It is important to realize that some patients with Stage III cancer already have small amounts of cancer that spread away from the bladder. Undetectable areas of cancer are referred to as micrometastases and cannot be detected with any of the currently available tests. It is the presence of micrometastases that usually causes the relapses that follow treatment with a cystectomy alone.
Chemotherapy Combined with Biologic Agents: Combining chemotherapy with biologic agents is the focus of intensive investigation.
Treating Stage 0 Bladder Cancer
Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma and flat non-invasive carcinoma . In either case, the cancer is only in the inner lining layer of the bladder. It has not invaded the bladder wall.
This early stage of bladder cancer is most often treated with transurethral resection with fulguration followed by intravesical therapy within 24 hours.
Read Also: What Can I Do For A Bladder Infection
Understanding Your Bladder Cancer Stage
A staging system is a standard way for the cancer care team to describe how far a cancer has spread. The staging system most often used for bladder cancer is the American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM system, which is based on 3 key pieces of information:
- T describes how far the main tumor has grown through the bladder wall and whether it has grown into nearby tissues.
- N indicates any cancer spread to lymph nodes near the bladder. Lymph nodes are bean-sized collections of immune system cells, to which cancers often spread first.
- M indicates if the cancer has spread to distant sites, such as other organs, like the lungs or liver, or lymph nodes that are not near the bladder.
Numbers or letters after T, N, and M provide more details about each of these factors. Higher numbers mean the cancer is more advanced. Once a persons T, N, and M categories have been determined, usually after surgery, this information is combined in a process called stage grouping to assign an overall stage.
The earliest stage cancers are called stage 0 , and then range from stages I through IV .
As a rule, the lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. A higher number, such as stage IV, means a more advanced cancer. And within a stage, an earlier letter means a lower stage. Cancers with similar stages tend to have a similar outlook and are often treated in much the same way.
Stage Ii Bladder Cancer
Stage II cancer has invaded the muscle of the bladder wall but is still confined to the bladder. Depending on the extent and grade of the cancer, we may recommend a partial or total cystectomy. Some people may need chemotherapy before surgery. We may be able to remove the tumor with TUR followed by radiation and chemotherapy.
Don’t Miss: Best Way To Dry A Water Bladder
N Categories For Bladder Cancer
The N category describes spread only to the lymph nodes near the bladder and those along the blood vessel called the common iliac artery. These lymph nodes are called regional lymph nodes. Any other lymph nodes are considered distant lymph nodes. Spread to distant nodes is considered metastasis . Surgery is usually needed to find cancer spread to lymph nodes, since this is seldom seen on imaging tests.
The N categories are described in the table above, except for:
NX: Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed due to lack of information.
N0: There’s no regional lymph node spread.
Questions For Your Team
Asking questions will help you understand more about your bladder cancer, the treatment and how you can improve your prognosis. We have pulled together the most important common questions that you might want to ask, and we also cover what the answers might be. We always suggest taking someone with you for these appointments to help remember everything that you are told.
Read Also: Are A Bladder Infection And Uti The Same
There Are Three Ways That Cancer Spreads In The Body
Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood:
- Tissue. The cancer spreads from where it began by growing into nearby areas.
- Lymph system. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the lymph system. The cancer travels through the lymph vessels to other parts of the body.
- Blood. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through the blood vessels to other parts of the body.
Dont Miss: Overactive Bladder At Night Time Only
What Does The Grade Of A Bladder Cancer Refer To
Cancer grade refers to the appearance of the tumor cells when examined under a microscope.
- Low grade tumor cells are similar in appearance to normal cells and usually grow slowly. In general, bladder tumors made up of low grade cells tend to stay within the urothelium.
- High grade tumor cells have a very abnormal appearance and tend to grow quickly and spread to deeper layers of the bladder wall. Tumors made up of high grade cells often recur after treatment.
- Although considered superficial because they are located initially in the bladder lining, carcinoma in situ tumors are high grade. Compared to papillary carcinomas, they are more likely to lead to invasive bladder cancer and have a higher rate of recurrence.
Read Also: Can Bladder Infection Clear Up On Its Own
What Is The First Line Of Treatment For Bladder Cancer
Chemotherapy. Currently, the standard first-line treatment options include chemotherapy regimens that contain cisplatin or carboplatin. These regimens include MVAC , dose-dense MVAC, and gemcitabine-cisplatin.
What is the latest treatment for bladder cancer?
BCG : Bladder cancer may be treated with an intravesical immunotherapy called BCG. The BCG is given in a solution that is placed directly into the bladder using a catheter .
What are the 3 types of bladder cancer?
The type of bladder cancer depends on how the tumors cells look under the microscope.The 3 main types of bladder cancer are:
- Urothelial carcinoma. Urothelial carcinoma accounts for about 90% of all bladder cancers.
- Squamous cell carcinoma.
- Adenocarcinoma.
Causes And Risk Factors
Researchers dont know exactly what causes bladder cancer, but they do know what increases the risk of getting it. These risk factors range from family history to certain types of medication.
Source: Valisure
Data published in 2021 on MedRxiv by researchers from the online pharmacy Valisure and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center showed patients who took Zantac had elevated diagnosis rates of bladder, breast, prostate and thyroid cancer.
Patients should keep in mind that this data suggests a link between ranitidine and increased risk, but it doesnt prove that all people who take ranitidine will get bladder cancer.
Recommended Reading: Loss Of Bladder Control When Coughing
Read Also: Causes Of Overactive Bladder In Males