What Does It Mean For Prostate Cancer To Spread
Cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body. If this occurs, doctors say the cancer has metastasized or spread.
Areas of the body to which prostate cancer can spread include:
- the bones
- the lungs
- the lymph nodes, usually those around the pelvis
A doctor will typically recommend imaging scans and tissue samples to test for the presence of cancerous cells.
According to the Prostate Cancer Foundation, age is the biggest contributing factor to the risk for prostate cancer. An estimated 65 percent of all prostate cancers are diagnosed in men older than 65 years of age.
Additional risk factors for prostate cancer include:
- Family history: Men who have a father or brother with prostate cancer are twice as likely to get prostate cancer as men who do not.
- Race: African-American men face the greatest risk of prostate cancer.
- Smoking: A history of smoking is associated with a higher risk of aggressive prostate cancer.
Researchers are also studying a link between diet and increased prostate cancer risk. Diets low in vegetables or high in calcium have been linked to an increased risk of aggressive prostate cancer.
The prostate is very close to the point at which urine drains from the body. As a result, many prostate cancer symptoms affect the urination process. Examples of these symptoms include:
Some of these symptoms are associated with aging and an enlarged prostate. As a result, some men may ignore these symptoms instead of seeking medical attention.
Side Effects Of Treatment For Bladder Cancer
All cancer treatments can have side effects. Your treatment team will discuss these with you before you start treatment. Talk to your doctor or nurse about any side effects you are experiencing. Some side effects can be upsetting and difficult, but there is help if you need it.
or email to speak with a caring cancer nurse for support.
Differences In Nusap1 Expression Between Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Positive Lymph Nodes And Normal Bladder Tissues
Primarily, NUSAP1 was localized to the cytoplasm of the positive cells. Immunohistochemistry was performed for 47 pathological lymph node samples and the corresponding adjacent normal bladder tissue samples and compared with the correspondingly matched BUC primary foci tissues. 91.49%, 17.02%, and 82.98% of positive lymph nodes, normal bladder tissues, and BUC tissues, respectively, were positive for NUSAP1 expression the difference between these two was statistically significant .
Table 2 NUSAP1 expression in BUC and normal bladder tissues.
Read Also: Blood In Urine Female Bladder Infection
Prognosis And Survival For Bladder Cancer
If you have bladder cancer, you may have questions about your prognosis. A prognosis is the doctors best estimate of how cancer will affect someone and how it will respond to treatment. Prognosis and survival depend on many factors. Only a doctor familiar with your medical history, the type and stage and other features of the cancer, the treatments chosen and the response to treatment can put all of this information together with survival statistics to arrive at a prognosis.
A prognostic factor is an aspect of the cancer or a characteristic of the person that the doctor will consider when making a prognosis. A predictive factor influences how a cancer will respond to a certain treatment. Prognostic and predictive factors are often discussed together. They both play a part in deciding on a treatment plan and a prognosis.
The following are prognostic and predictive factors for bladder cancer.
What Are Bone Metastases With Prostate Cancer
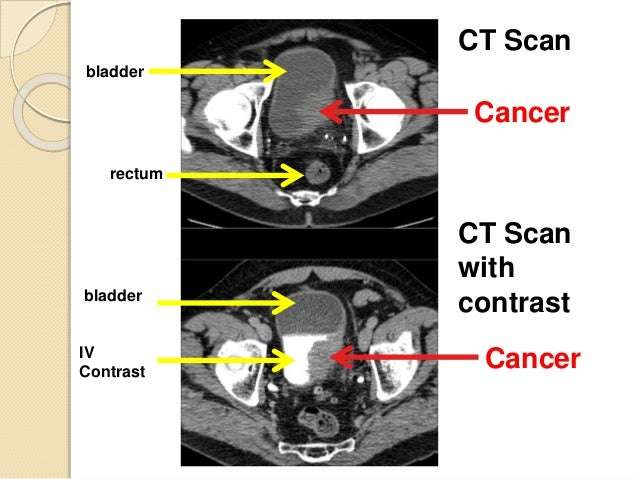
The ACS describes bone metastases as areas of bone containing cancer cells that have spread from another place in the body. In the case of prostate cancer, the cells have spread beyond the prostate gland. Since the cancer cells originated in the prostate gland, the cancer is referred to as metastatic prostate cancer.
The cancer cells spread to the bones by breaking away from the prostate gland and escaping attack from your immune system as they travel to your bones.
These cancer cells then grow new tumors in your bones. Cancer can spread to any bone in the body, but the spine is most often affected. Other areas cancer cells commonly travel to, according to the ACS, include the pelvis, upper legs and arms, and the ribs.
Dont Miss: Does Prostate Cancer Make You Tired
You May Like: How To Relax The Bladder Naturally
Where Does Metastatic Bladder Cancer Spread To
Bladder cancer spreads when cancerous cells reproduce and invade surrounding healthy tissues. This is known as metastasis. Usually, metastatic bladder cancer refers to cancer that has spread to distant organs, but metastasis can occur locally in the muscles and connective tissues that are directly adjacent to the bladder as well.
Remission And The Chance Of Recurrence
A remission is when cancer cannot be detected in the body and there are no symptoms. This may also be called having no evidence of disease or NED.
A remission may be temporary or permanent. This uncertainty causes many people to worry that the cancer will come back. While many remissions are permanent, it is important to talk with your doctor about the possibility of the cancer returning. Understanding your risk of recurrence and the treatment options may help you feel more prepared if the cancer does return. Learn more about coping with the fear of recurrence.
If the cancer returns after the original treatment, it is called recurrent cancer. It may come back in the same place , nearby , or in another place .
When this occurs, a new cycle of testing will begin again to learn as much as possible about the recurrence. After this testing is done, you and your doctor will talk about the treatment options.
People with recurrent cancer often experience emotions such as disbelief or fear. You are encouraged to talk with the health care team about these feelings and ask about support services to help you cope. Learn more about dealing with cancer recurrence.
Also Check: Not Able To Control Bladder
Multivariable Analysis Of Ln+
We used multivariate logistic regression to evaluate whether the association between age and LN+ at the time of diagnosis was independent of other known risk factors. Sex, race, year of operation, tumor grade, and LNE were used as covariates of the adjusted model. Age remained a significant predictor of LN+ in all T stages , and young MIBC patients were more likely to have LN+. Compared with the reference group , patients with T2 and T4 stages, aged < 50years, were more likely to have LN+, and the adjusted OR was 1.805 and 1.492 , respectively. The probability of LN+ was the highest in the 5059-year age group with T3, and the adjusted OR was 1.407 .
Table 4 Association of age and rate of LN+
Where Can Bladder Cancer Spread
Bladder cancer can spread through the tissue to nearby organs, such as the prostate or vagina . It can also spread through the lymph system, by traveling through lymph vessels to lymph nodes in different parts of the body. It can also spread through the bodys blood vessels and form tumors in other parts of the body, such as the bones or lungs.
Don’t Miss: Does Coffee Cause Bladder Infections
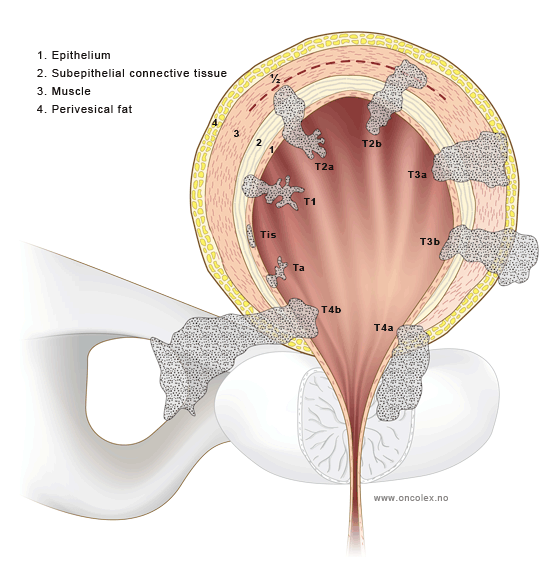
The Stages Of Invasive Bladder Cancer
Your doctor diagnoses invasive bladder cancer by looking at how far cancer tumours have grown into the bladder. This is called the T stage . There are three T stages of invasive bladder cancer:
- T2 means cancer has grown into the muscle layer of the bladder
- T3 means cancer has grown through the muscle layer into the fatty tissue layer
- T4 means cancer has grown outside the bladder OR into the prostate, womb or vagina, OR into the wall of the pelvis or tummy
Your doctor also looks at:
- whether cancer has spread to any lymph nodes
- whether or not it has spread to other parts of the body like the bones, lungs or liver
Donât Miss: Treatment Of Overactive Bladder In Males
When To Contact A Doctor
If a person notices any signs of cancer having spread to their lymph nodes, they should speak with a doctor immediately.
Additionally, if a person with cancer notices any unusual new symptoms, they should contact a doctor. The sooner a person receives treatment for cancer that has spread, the better their chances of survival.
Read Also: How To Get Rid Of A Bladder Infection Quickly
How Can I Prevent Bladder Cancer
Stopping smoking is the best way to prevent bladder cancer. You should also reduce your exposure to cancer-causing agents to help prevent bladder cancer. Other than these measures, decreasing your risk of invasive bladder cancer relies on early detection of symptoms and possibly screening if you are high-risk.
Lymph Nodes And What They Do
Lymph vessels send lymph fluid through nodes throughout the body. Lymph nodes are small structures that work as filters for foreign substances, such as cancer cells and infections. They contain immune cells that can help fight infection by attacking and destroying germs that are carried in through the lymph fluid. Lymph nodes are located in many parts of the body, including the neck, armpit, chest, abdomen , and groin. They contain immune cells that can help fight infection by attacking and destroying germs that are carried in through the lymph fluid.
There are hundreds of lymph nodes throughout the body. Each lymph node filters the fluid and substances picked up by the vessels that lead to it. Lymph fluid from the fingers, for instance, works its way toward the chest, joining fluid from the arm. This fluid may filter through lymph nodes at the elbow, or those under the arm. Fluid from the head, scalp, and face flows down through lymph nodes in the neck. Some lymph nodes are deep inside the body, such as between the lungs or around the bowel, to filter fluid in those areas.
Don’t Miss: Why Is My Bladder Not Emptying
Lymph Node Staging Of Bladder Cancer
Staging of nodal metastases from bladder cancer is based on the current TNM guidelines from the American Joint Committee on Cancer, eight edition staging manual . Definitive lymph node staging is based on post-operative histology and should only be suggested on imaging studies when lymph node involvement is obvious. Nodal staging, which is provided in Figure 1, is also summarized as follows:
Schematic of bladder cancer lymph node staging . Nodal staging of bladder cancer detailed for N1âM1a . N1 disease depicted as a single abnormal left perivesical lymph node . N2 disease depicted as multiple abnormal left regional lymph nodes . N3 disease depicted as abnormal lymph nodes involving the left common iliac distribution . M1a disease depicted as abnormal lymph nodes involving the para-aortic region above the level of the aortic bifurcation . Abnormal lymph nodes are depicted with irregular margins for illustrative purposes.
What Is Lymph Node Dissection
Lymph node dissection is a type of surgery that is commonly used to treat patients with bladder cancer.1-4 In most patients, bladder cancer starts to grow in the urothelium, which is the thin layer of cells that line the inside of the bladder. In patients with bladder cancer that is muscle-invasive, the bladder cancer cells have grown from the bladder lining and into the muscle of the bladder wall. Many patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer need to have surgery called a cystectomy. In a radical cystectomy, the surgeon removes all of the bladder and in a partial cystectomy, the surgeon removes part of the bladder.
Lymph node dissection is a procedure that is generally performed at the same time as a cystectomy for both men and women with bladder cancer. It is not usually performed as a separate surgery. After removing the patients bladder and other organs that may be affected by bladder cancer, the surgeon also removes lymph nodes in the patients pelvis. This procedure is also called a pelvic lymph node dissection .
Read Also: What Is The Best Medicine For Overactive Bladder
Treating Stage I Bladder Cancer
Stage I bladder cancers have grown into the connective tissue layer of the bladder wall , but have not reached the muscle layer.
Transurethral resection with fulguration is usually the first treatment for these cancers. But it’s done to help determine the extent of the cancer rather than to try to cure it. If no other treatment is given, many people will later get a new bladder cancer, which often will be more advanced. This is more likely to happen if the first cancer is high-grade .
Even if the cancer is found to be low grade , a second TURBT is often recommended several weeks later. If the doctor then feels that all of the cancer has been removed, intravesical BCG or intravesical chemo is usually given. If all of the cancer wasn’t removed, options are intravesical BCG or cystectomy .
If the cancer is high grade, if many tumors are present, or if the tumor is very large when it’s first found, radical cystectomy may be recommended.
For people who arent healthy enough for a cystectomy, radiation therapy might be an option, but the chances for cure are not as good.
Cancer Spreading To The Lymph Nodes
Cancer appearing in the lymph nodes is an indicator of how the cancer is spreading. If cancer cells are only found in the lymph nodes near the original tumor, it may indicate the cancer is in an earlier stage and has not spread far beyond its primary area.
On the other hand, if your doctor finds the cancer cells have traveled to lymph nodes far from the initial tumor, the cancer may be spreading at a faster rate and could be in a later stage.
Additionally, its important to know how many cancer cells have traveled to the respective lymph node. If theres visible or palpable cancer in lymph nodes, or the cancer has grown outside the lymph node walls, the cancer may have progressed further and may require a different treatment plan.
If cancer cells have spread to your lymph nodes , symptoms may include:
- lump or swelling in your neck, under your arm, or in your groin
- shortness of breath
- pain
Don’t Miss: Can Bladder Cancer Be Detected By Blood Test
Intravenous Or Retrograde Pyelograms
For example, intravenous or retrograde pyelograms are types of x-rays that use a special dye to highlight the organs of the urinary tract. This can make it possible to detect cancer that has spread to the kidneys, ureters, or other parts of the urinary tract. If healthcare providers suspect that the bladder cancer may have spread to the patients lungs, then a chest x-ray may be used.
Will Treatment Cause Erectile Dysfunction
When youre sexually excited, nerves cause tissues in your penis to relax, allowing blood to flow into the organ. The nerves that control erection are very delicate. Surgery or radiation for prostate cancer may damage them enough to cause ED. When you have ED, you cant get or keep an erection.
Radical prostatectomy is a surgery to remove the prostate gland. When your surgeon removes the gland, they may damage the nerves and blood vessels that run along it. If theyre damaged enough, you wont be able to get an erection following the procedure.
Today, doctors can do nerve-sparing surgery, which helps prevent permanent ED. Your surgeon can still touch those nerves and blood vessels, causing ED as a temporary side effect. Many men have trouble getting an erection for a few weeks, months, or even years after their procedure.
Radiation therapy also damages blood vessels and the nerves that control erection. Up to half of men who have radiation for prostate cancer experience ED afterward. In some men, this symptom will improve with time. Sometimes radiation side effects dont appear until a few months after the treatment. If ED starts late, it may not be as likely to go away.
A few treatments can help with ED until youre able to have erections on your own again.
Additional treatments include the following:
Recommended Reading: Foods Good For Bladder Control
You May Like: Will Amoxicillin Cure A Bladder Infection
Mechanisms Of Lymph Node Metastasis
Tumor-associated lymphatic vessels serve as a route for lymph node metastasis
Lymph node. Metastases of tumor cells through lymphatic vessels to lymph nodes.
Local extension of tumor cells from the primary tumor into the surrounding lymphatics through a process called permeation is one means through which tumor cells can enter into the lymphatic vessels . In addition, tumor cells can be stimulated by cytokines produced by the lymphatic vessels, which promote chemotactic diffusion of tumor cells into the lymphatics . Finally, many tumors have the ability to secrete growth factors that induce the growth of new lymphatic vessels from a precursor, a process called lymphangiogenesis .
Problems Emptying Your Bladder
If the cancer is pressing on your urethra or the opening of your bladder, you may find it difficult to empty your bladder fully. This can sometimes cause urine retention, where urine is left in your bladder when you urinate. There are several things that can help, including the following.
- Drugs called alpha-blockers. These relax the muscles around the opening of the bladder, making it easier to urinate.
- A catheter to drain urine from the bladder. This is a thin, flexible tube that is passed up your penis into your bladder, or through a small cut in your abdomen .
- An operation called a transurethral resection of the prostate to remove the parts of the prostate that are pressing on the urethra.
You May Like: Cystoscopy Transurethral Resection Of Bladder Tumor