Rare Forms Of Bladder Cancer
Adenocarcinomas account for less than 2% of primary bladder tumors. These lesions are observed most commonly in exstrophic bladders and are often associated with malignant degeneration of a persistent urachal remnant.
Other rare forms of bladder cancer include leiomyosarcoma, rhabdosarcoma, carcinosarcoma, lymphoma, and small cell carcinoma. Leiomyosarcoma is the most common sarcoma of the bladder. Rhabdomyosarcomas most commonly occur in children. Carcinosarcomas are highly malignant tumors that contain a combination of mesenchymal and epithelial elements. Primary bladder lymphomas arise in the submucosa of the bladder. Except for lymphomas, all these rare bladder cancers carry a poor prognosis.
Small cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder is a poorly differentiated, malignant neoplasm that originates from urothelial stem cells and has variable expression of neuroendocrine markers. Morphologically, it shares features of small cell carcinoma of other organs, including the lung.
Monitoring For Bladder Cancer Recurrence
Those who have already been treated for bladder cancer have unique monitoring needs to protect against the threat of recurrence. Generally doctors recommend a cystoscopy to examine the inside of the bladder and urethra every 3 to 12 months, depending on your risk of recurrence, for several years after bladder cancer treatment. If several years of surveillance have gone by and no cancer recurrence has been detected, a cystoscopy once a year may be enough, though the final decision rests with the doctor and additional testing may be required depending on the nature and severity of the original cancer.
If you’re recovering from treatment, ask your doctor about Cxbladder. Cxbladder is an accurate and non-invasive surveillance alternative designed to detect or rule out the return of bladder cancer. The test provides reliable results with a single urine sample, reducing the need for frequent cystoscopies in some patients, which can be both uncomfortable and inconvenient.Learn more about Cxbladder
Signs And Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
Sometimes bladder cancer doesnt have many symptoms. Signs or symptoms can include:
- blood in your urine
- pain or burning when passing urine
- not being able to pass urine when you need to.
Not everyone with these symptoms has bladder cancer. If you have any of these symptoms or are worried, always see your doctor.
You May Like: What Antibiotic Do You Take For A Bladder Infection
Treatment For Bladder Cancer
Treatment for bladder cancer depends on how quickly the cancer is growing. Treatment is different for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer and muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
You might feel confused or unsure about your treatment options and decisions. Its okay to ask your treatment team to explain the information to you more than once. Its often okay to take some time to think about your decisions.
When deciding on treatment for bladder cancer, you may want to discuss your options with a urologist, radiation oncologist and medical oncologist. Ask your GP for referrals.
What Causes Bladder Cancer
![[Full text] Clinical and pathological implications of miRNA in bladder ... [Full text] Clinical and pathological implications of miRNA in bladder ...](https://www.healthybladderclub.com/wp-content/uploads/full-text-clinical-and-pathological-implications-of-mirna-in-bladder.png)
Bladder cancer occurs when cells within the lining of the bladder wall begin to grow in a disordered, uncontrolled way.
Exactly what prompts this disordered growth is not fully known. However, several factors associated with a higher risk of bladder cancer have been identified, including:
- Age – most people diagnosed with bladder cancer are older than 55 years.
- Sex – compared to women, men are 4 times more likely to develop bladder cancer.
- Smoking – smoking is associated with around half of all bladder cancers in men and women.
- Race – in the United States, White Americans have the highest rate of bladder cancer.
- Previous bladder cancer – people who have had bladder cancer may have a recurrence.
- Workplace exposures – certain chemicals in some workplaces may contribute to higher rates of bladder cancer in workers. For example, painters, hairdressers, and truck drivers are at increased risk.
- Arsenic in drinking water.
- Certain types of medication.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Bladder Control Problems
Can Papillary Thyroid Cancer Be Prevented
Most people with thyroid cancer have no known risk factors, so its not possible to prevent most cases of papillary thyroid cancer.
Radiation exposure, especially in childhood, is a known PTC risk factor. Because of this, healthcare providers no longer use radiation to treat less serious diseases. Imaging tests, such as X-rays and CT scans, also expose children to radiation, but at much lower doses. Its not clear how much they might increase the risk of PTC.
If you have a family history of thyroid cancer, you may want to get genetic counseling to see if you have any inherited conditions that put you at a higher risk of developing PTC. If this is the case, your healthcare provider may recommend getting preventive surgery to remove your thyroid gland before cancer develops.
Drugwatchcom Has Been Empowering Patients For More Than A Decade
Drugwatch.com has provided reliable, trusted information about medications, medical devices and general health since 2008. Weve also connected thousands of people injured by drugs and medical devices with top-ranked national law firms to take action against negligent corporations.
Our team includes experienced medical writers, award-winning journalists, researchers and certified medical and legal experts. Drugwatch.com is HONCode certified. This means the high-quality information we provide comes from credible sources, such as peer-reviewed medical journals and expert interviews.
The information on Drugwatch.com has been medically and legally reviewed by more than 30 expert contributors, including doctors, pharmacists, lawyers, patient advocates and other health care professionals. Our writers are members of professional associations, including American Medical Writers Association, American Bar Association, The Alliance of Professional Health Advocates and International Society for Medical Publication Professionals.
You May Like: Can Fluconazole Be Used For A Bladder Infection
Other Terms Often Used To Describe Bladder Cancer
Although bladder cancer types are assigned based on the cells that the cancer originates from, several other terms may be used to describe the disease.
- Advanced bladder cancer is another term that may be used to describe metastatic bladder cancer. It means that the cancer has spread to distant parts of the body such as the lungs, bones, liver, or lymph nodes outside the pelvis.
- Locally advanced bladder cancer refers to cancer that has grown through the bladder wall, and possibly into nearby lymph nodes or organs, but has not spread to distant sites in the body.
- Bladder cancer stage describes where the cancer is located within the bladder and any sites of spread. As described above, the TNM staging system assigns a patients bladder cancer to a tumor , lymph node and metastasis category. These categories may also be combined to give an overall stage number: an overall stage of 0 or 1 describes early disease, while stage 4 is the most advanced. For further information regarding staging, see Bladder Cancer Stages.
- Bladder cancer grade is based on the microscopic appearance of cancer cells and suggests how fast a cancer might grow. Low-grade cancer cells appear similar to normal cells and usually grow slowly, whereas high-grade cancer cells have a very abnormal appearance and tend to grow quickly. High-grade cancers are more likely than low-grade cancers to spread.
Also Check: Can Soda Cause Bladder Infection
What Are The Possible Side Effects And Complications Of Papillary Thyroid Cancer Treatment
Permanent hypothyroidism is an expected side effect of thyroidectomy and radioiodine therapy. Because of this, youll need to take replacement thyroid hormone medication for the rest of your life if you undergo either or both of these treatments.
Possible complications of thyroid surgery include:
- Infection.
- Accidental removal of or damage to your parathyroid glands, which help regulate your blood calcium levels.
- Damage to your recurrent laryngeal nerve, which runs behind your thyroid gland, resulting in hoarseness and a weak voice.
Potential side effects of radioactive iodine therapy include:
- Small risk of leukemia, breast or bladder cancer.
Also Check: Can A Yeast Infection Feel Like A Bladder Infection
What Is The Prognosis For Someone With Prcc
The estimate of how a disease will affect you long-term is called prognosis. Every person is different and prognosis will depend on many factors, such as
- Where the tumor is in your body
- If the cancer has spread to other parts of your body
- How much of the tumor was taken out during surgery
If you want information on your prognosis, it is important to talk to your doctor. NCI also has resources to help you understand cancer prognosis.
Doctors estimate survival rates by how groups of people with PRCC have done in the past. Because there are so few people with PRCC, these rates may not be very accurate. They also cant consider newer treatments being developed.
In general, type 2 papillary renal cell carcinoma has a poorer prognosis than type 1.
Related Resources
Prognosis And Survival Rates For Bladder Cancer
When someone is diagnosed with bladder cancer, their doctor will give them a prognosis. A prognosis is the doctors opinion of how likely the cancer will spread and the chances of getting better. A prognosis depends on the type and stage of cancer, as well as the persons age and general health.
Bladder cancer can usually be effectively treated if it is found before it spreads outside the bladder.
If you have bladder cancer, your doctor will talk to you about your individual situation when working out your prognosis. Every persons experience is different, and there is support available to you.
Recommended Reading: How To Have Better Bladder Control
Bladder Instillation Of Chemotherapy
Instillation of chemotherapy drugs into the bladder can reduce the incidence of superficial cancer recurrences, but no single drug has been confirmed to reduce progression of superficial cancer to invasive bladder cancer. This means that multiple small new cancers can be prevented, but progression to a more invasive bladder cancer may occur despite treatment.
The optimal time to administer chemotherapy is immediately after TUR, as the drugs might prevent reseeding of cancer cells that were disrupted with surgery. Mitomycin is probably the preferred drug because it produces few side effects and is not well absorbed into the system, which allows more of the drug to remain in the bladder to treat the cancer. Thiotepa is rapidly absorbed and produces low blood counts. Doxorubicin produces the most local side effects.
Prognosis In Squamous Cell Carcinoma
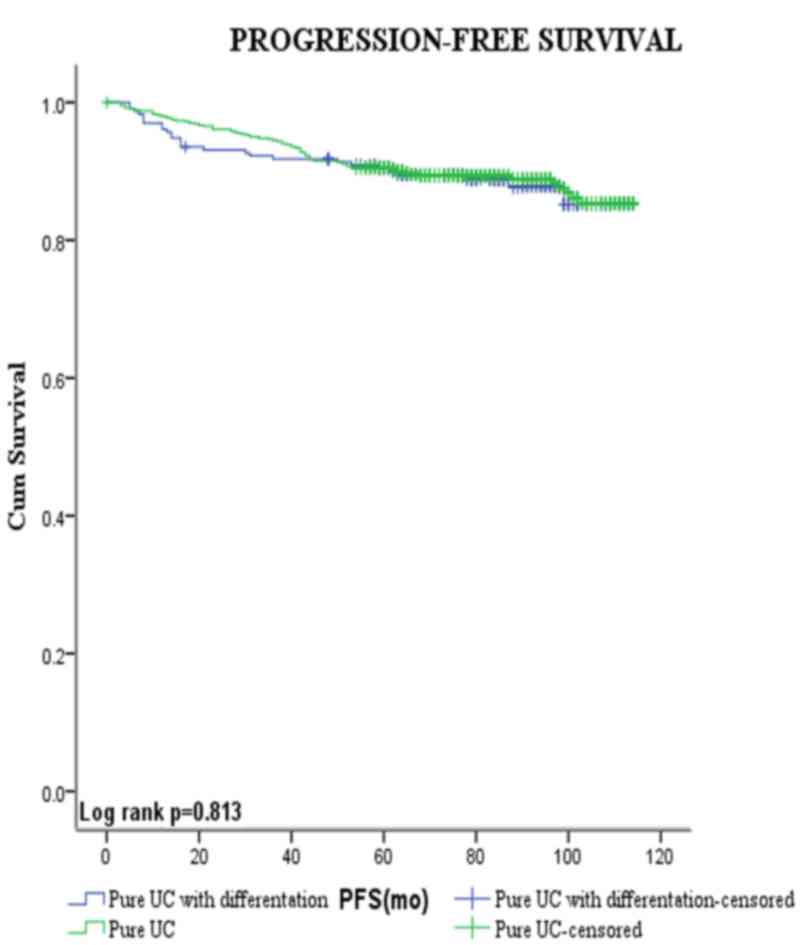
Tumor stage, lymph node involvement, and tumor grade have been shown to be of independent prognostic value in SCC. However, pathologic stage is the most important prognostic factor. In one relatively large series of 154 cases, the overall 5-year survival rate was 56% for pT1 and 68% for pT2 tumors. However, the 5-year survival rate for pT3 and pT4 tumors was only 19%.
Several studies have demonstrated grading to be a significant morphologic parameter in SCC. In one series, 5-year survival rates for grade 1, 2, and 3 SCC was 62%, 52%, and 35%, respectively. In the same study of patients undergoing cystectomy, the investigators suggested that a higher number of newly formed blood vessels predicts unfavorable disease outcome.
In SCC, the survival rate appears to be better with radical surgery than with radiation therapy and/or chemotherapy. In locally advanced tumors, however, neoadjuvant radiation improves the outcome. Sex and age have not been prognostically significant in SCC.
Read Also: Gemcitabine Bladder Instillation Side Effects
Stage Information For Bladder Cancer
In This Section
| Clinical trials |
References
What Impacts The Bladder Cancer Survival Rate
Survival rates depend on many factors, including the type and stage of bladder cancer that is diagnosed. According to the ACS, the five-year survival rate of people with bladder cancer that has not spread beyond the inner layer of the bladder wall is 96%. This is called non-muscle invasive bladder cancer . More than half of people are diagnosed at this stage.
If a tumor is invasive but has not yet spread outside the bladder, the five-year survival rate is 69%. Approximately 33% of bladders cancers are diagnosed at this stage. If the cancer extends through the bladder to the surrounding tissue or has spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs, the five-year survival rate is 37%. If the cancer has spread to distant parts of the body, the five-year survival rate is 6%. About 4% of people are diagnosed at this stage.
It is important to remember that statistics about the five-year survival rates for people with bladder cancer are estimates only and come from annual data based on the number of people with this cancer. A number of new and promising bladder cancer treatments that have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration in the last five years might not be reflected in a five-year survival rate statistic.
Just like no single treatment is appropriate for all bladder cancer patients, there is not one statistic that applies to everyone either. Talk with your doctor about your own individual situation to gain the best understanding you can.
Read Also: Tuberculosis To Treat Bladder Cancer
Side Effects Of Treatment For Bladder Cancer
All cancer treatments can have side effects. Your treatment team will discuss these with you before you start treatment. Talk to your doctor or nurse about any side effects you are experiencing. Some side effects can be upsetting and difficult, but there is help if you need it.
or email to speak with a caring cancer nurse for support.
Causes And Risk Factors
Researchers dont know exactly what causes bladder cancer, but they do know what increases the risk of getting it. These risk factors range from family history to certain types of medication.
Source: Valisure
Data published in 2021 on MedRxiv by researchers from the online pharmacy Valisure and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center showed patients who took Zantac had elevated diagnosis rates of bladder, breast, prostate and thyroid cancer.
Patients should keep in mind that this data suggests a link between ranitidine and increased risk, but it doesnt prove that all people who take ranitidine will get bladder cancer.
Don’t Miss: How Common Is Bladder Cancer In Males
Occurrence In The United States
The American Cancer Society estimates that 81,180 new cases of bladder cancer will be diagnosed in the United States in 2022 and that 17,100 people will die of the disease. The incidence of bladder cancer increases with age, with the median age at diagnosis being 73 years bladder cancer is rarely diagnosed before age 40 years.
Bladder cancer is about 4 times more common in men than in women. The male predominance in bladder cancer in the United States reflects the prevalence of transitional cell carcinoma . With small cell carcinomain contrast to TCCthe male-to-female incidence ratio is 1:2.
Bladder cancer is the fourth most common cancer in men in the United States, after prostate, lung, and colorectal cancer, but it is not among the top 10 cancers in women. Accordingly, more men than women are expected to die of bladder cancer in 2022, with 12,120 deaths in men versus 4980 in women. Nevertheless, women generally have a worse prognosis than men.
The incidence of bladder cancer is twice as high in White men as in Black men in the United States. However, Blacks have a worse prognosis than Whites.
Limited data indicate that small cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder probably has the same epidemiologic characteristics as urothelial carcinoma. Patients are more likely to be male and older than 50 years.
What Is The First Sign Of Bladder Cancer
Blood in the urine, referred to as hematuria, is usually the first sign of bladder cancer. This is because early bladder cancer commonly causes bleeding without associated pain or other symptoms.
- Depending on the amount of blood present, urine may appear pink, red, or brownish in color.
- Blood may not be present all the time – there may be relatively long periods of clear urine .
If you have noticed blood in your urine it is important to speak to your doctor as soon as possible.
Other early symptoms of bladder cancer that may be experienced are urinary irritation or changes in bladder habits, such as increased urination frequency and/or urgency, pain or a burning sensation during urination, or difficulty passing urine.
You May Like: How To Train A Weak Bladder
Latest Treatment For Bladder Cancer
Intravesical therapy is a newer treatment for people who have bladder cancer. With intravesical therapy, the doctor puts a liquid medication right into your bladder rather than administering it orally or injecting it into your blood. The medication is put in through a catheter thats placed into your bladder through the urethra. The medication stays in your bladder for up to two hours, so it can affect the cells lining the inside of the bladder without having major effects on other parts of your body. Intravesical therapy is commonly used after transurethral resection of bladder tumor . Its often performed within 24 hours of the TURBT procedure. The goal is to kill any cancer cells that may be left in the bladder.
Intravesical chemotherapy is used to treat non-invasive bladder cancer. It is used for these early-stage cancers because medication given this way mostly affects the cells lining the inside of the bladder. It has little to no effect on cells elsewhere. This means any cancer cells outside of the bladder lining are not treated by intravesical chemotherapy.