Overactive Bladder Syndrome Symptoms
Overactive bladder syndrome symptoms include a sudden urge to pass urine that is very difficult to delay and may be associated with leakage. Other features include:
- Frequency of micturition.
- Abdominal discomfort.
- Urge incontinence .
There are no specific physical signs and the diagnosis is usually made from the symptoms and confirmed with urodynamic testing.
Treatment For Urinary Incontinence
Today, there are more treatments for urinary incontinence than ever before. The choice of treatment depends on the type of bladder control problem you have, how serious it is, and what best fits your lifestyle. As a general rule, the simplest and safest treatments should be tried first.
Bladder control training may help you get better control of your bladder. Your doctor may suggest you try the following:
- Pelvic muscle exercises work the muscles that you use to stop urinating. Making these muscles stronger helps you hold urine in your bladder longer. Learn more about pelvic floor exercises and how to do them.
- Biofeedback uses sensors to make you aware of signals from your body. This may help you regain control over the muscles in your bladder and urethra. Biofeedback can be helpful when learning pelvic muscle exercises.
- Timed voiding may help you control your bladder. In timed voiding, you urinate on a set schedule, for example, every hour. You can slowly extend the time between bathroom trips. When timed voiding is combined with biofeedback and pelvic muscle exercises, you may find it easier to control urge and overflow incontinence.
- Lifestyle changes may help with incontinence. Losing weight, quitting smoking, saying no to alcohol, drinking less caffeine , preventing constipation and avoiding lifting heavy objects may help with incontinence. Choosing water instead of other drinks and limiting drinks before bedtime may also help.
What Causes An Overactive Bladder
The exact cause of an overactive bladder is a mystery. However, several factors are known to contribute to the involuntary contraction of the bladder muscle, improper bladder function, and other symptoms associated with an overactive bladder.
Some nervous system abnormalities that can cause an overactive bladder include:
- Spinal cord injury
Other causes of overactive bladder can include:
- Nerve damage or trauma caused by surgery or certain therapies
- Trauma to the pelvis or abdomen
- Urinary Tract Infection
- Bladder cancer/tumours
- Enlarged prostate
There are also several risk factors that can increase the chances of an overactive bladder. These include:
- Age the risk of overactive bladder increases as you age
- Gender women tend to be more susceptible than men because menstruation, pregnancy and menopause all lead to a rise in oestrogen levels and weaker pelvic floor muscles. For men, an enlarged prostate or damage from prostate surgery can cause an overactive bladder.
- Obesity increased weight puts additional pressure on the bladder.
- Diabetes can affect the nerves that control bladder function.
- Pregnancy causes excess pressure on the bladder.
- Spinal injury damage to the spinal cord can disrupt signals sent to the bladder, causing involuntary contract of bladder muscles.
Don’t Miss: Why Do I Get Frequent Bladder Infections
Types Of Male Urinary Dysfunction
At NYU Langone, our urologists treat men who have urinary dysfunction, which arises when the bladder or urethral sphincter doesnt work properly or an enlarged prostate blocks urine flow. Causes may include conditions such as benign prostatic hyperplasia and neurogenic voiding dysfunction, both of which may be accompanied by bothersome urinary symptoms, such as the inability to empty the bladder.
Causes Of Stress Incontinence
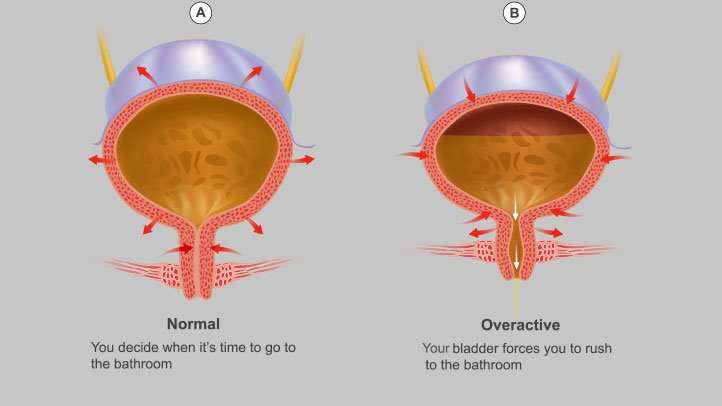
Stress incontinence is when the pressure inside your bladder as it fills with urine becomes greater than the strength of your urethra to stay closed. Your urethra is the tube that urine passes through to leave the body.
Any sudden extra pressure on your bladder, such as laughing or sneezing, can cause urine to leak out of your urethra if you have stress incontinence.
Your urethra may not be able to stay closed if the muscles in your pelvis are weak or damaged, or if your urethral sphincter the ring of muscle that keeps the urethra closed is damaged.
Problems with these muscles may be caused by:
- damage during childbirth particularly if your baby was born vaginally, rather than by caesarean section
- increased pressure on your tummy for example, because you are pregnant or obese
- damage to the bladder or nearby area during surgery such as the removal of the womb , or removal of the prostate gland
- neurological conditions that affect the brain and spinal cord, such as Parkinson’s disease or multiple sclerosis
- certain connective tissue disorders such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- certain medicines
Also Check: How To Get A Bigger Bladder
Treatment Of Bladder Spasms
How your doctor treats your bladder spasms depends on what exactly is causing your painful symptoms. But in general, therapy may involve one or more of the following treatments. A combination of treatments often works best.
Botox. Botulinum-A toxin has been shown to reduce nerve-related bladder spasms in children and adults. Botox prevents nerves from releasing chemicals that tell muscles to contract. The Botox is injected directly into the bladder muscle wall.
Change in diet. This may help prevent bladder pain if certain foods and beverages are the culprit behind your spasms. Keeping a food diary, which tracks your meals and your symptoms, can be helpful.
Timed voiding. This involves timed trips to the bathroom to urinate, usually every 1.5 to 2 hours. Timed voiding is especially helpful for children. As the bladder spasms get better and fewer wetting accidents occur, you can extend the time between trips to the bathroom.
Pelvic floor exercises . Kegels and other forms of physical therapy help strengthen the bladder and other muscles that help the body hold in urine. Kegels, combined with biofeedback, are often a good way to help reduce bladder spasms in children. To tighten your pelvic muscles, squeeze your muscles in the same way as if you were trying to stop the flow of urine or prevent yourself from passing gas. Kegel exercises take practice, and tightening the wrong muscles can put more pressure on your bladder. Ask your doctor for specific instructions.
What Causes Overactive Bladder In Men
According to latest estimates, about 11 16% men develops OAB with symptoms with advancing age. The most common factor that contributes to OAB in men is prostate enlargement which disrupts the urinary flow. Other causes of OAB in men include:
- Being on certain medications
- Infections of bladder or urinary tract
- Neurological conditions such as multiple sclerosis or Parkinsons disease.
Recommended Reading: Turbt Treatment For Bladder Cancer
Medical Treatments For Nocturia
Your doctor may prescribe medications when preventive measures and lifestyle changes fail to reduce the frequency of your nighttime urination. Doctors prescribe a class of drugs called anticholinergics to treat symptoms of OAB, if thats the cause of your nocturia. They reduce bladder spasms that create the urge to go.
Your doctor may suggest you take a diuretic for regular urine production. A diuretic can itself cause nocturia. But if you take it early enough in the day, it may help you get rid of excess fluid while youre awake. This should decrease your urine production at night.
Other drugs that may help are:
- desmopression in cases of diabetes insipidus to cause the kidneys to produce less urine
- tamsulosin , finasteride , or dutasteride to treat prostate enlargement
- antibiotics if you have a urinary tract infection
Your doctor may also adjust your diabetic medications to lower your blood sugar if theyre causing nocturia.
Understanding Overactive Bladder In Men
Many people hear the medical condition overactive bladder and associate it as a womens condition, but overactive bladder in men can happen.
OAB is more common in women. Upwards of 40% of women are affected by OAB symptoms. However, 30% of men are affected by OAB symptoms too, and this means that there are a lot of people, both women and men, suffering. OAB is stigmatized sufferers are afraid to speak to their healthcare providers, so they suffer without asking for help.
Recommended Reading: Ways To Stop Bladder Leakage
Physiotherapy Treatment Can Include
- Assessment of urinary frequency urgency and continence
- Real-Time Ultrasound pelvic floor muscle training
- Bladder management techniques for urgency and frequency management
- Guidance regarding appropriate fluid intake and voiding strategies to improve bladder capacity
With appropriate management, many men can achieve increased bladder capacity, decreased frequency of voiding and the ability to control their urge sensations effectively.
Give us a if you think a mens health physiotherapy consult may be helpful for you.
Smoking May Increase The Urge To Urinate
Smoking irritates the lining of the bladder, and also makes you cough, both of which are unhelpful if you have an overactive bladder.
It is a good decision for both general health reasons and overactive bladder reasons to stop smoking. Work with your health care provider to start a formal “Quit Smoking” program, which may involve smoking cessation medications and group support for the most successful outcome.
Learn more: Our Quit Smoking center also has some helpful advice.
Recommended Reading: How To Treat A Leaky Bladder
Emerging Options For Oab
The 3-adrenergic receptor is the most abundant of the AR subtypes in human detrusor muscle, suggesting that this subtype mediates detrusor relaxation. The mechanism by which -AR agonists induce relaxation of smooth muscles is not fully understood, but it is believed that an intracellular pathway for smooth muscle relaxation is activated by cAMP. Some animal studies of 3-adrenoceptor agonist have revealed increased bladder capacity, no change in micturition pressure and no change in residual volume . Selective 3-AR agonists should have a theoretical advantage over non-selective -AR agonists, as the latter may exhibit serious cardiovascular side effects like tachycardia or decrease of blood pressure by stimulating 1- and 2-adrenoceptors .
Who Is Most Likely To Develop Bladder Spasms
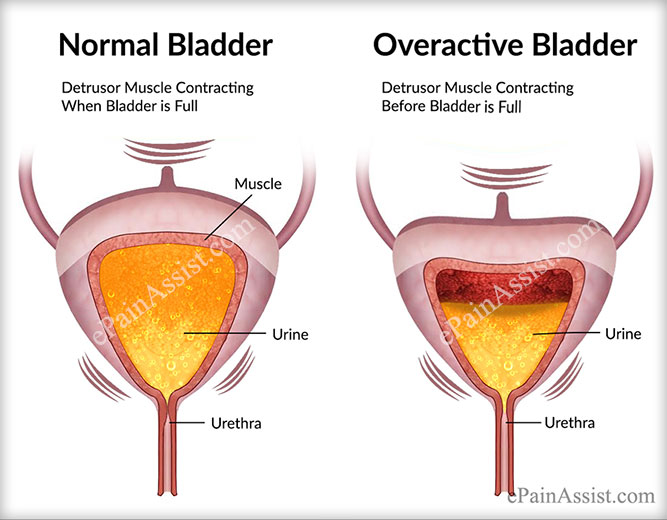
Anyone at any age can have bladder spasms. In children, bladder spasms are the leading cause of daytime incontinence.
However, you are more likely to have bladder spasms with urine leakage if you:
- Are elderly
- Have recently had lower abdominal or pelvic surgery
- Have bladder muscle damage caused by disease or injury
- Have a neurologic disease such as stroke or spinal cord injury
You May Like: Best Vitamins For Overactive Bladder
What Do Bladder Spasms Feel Like
Normally, the bladder gently fills with urine and you slowly become aware of the need to urinate. This feeling is your cue to start looking for a bathroom.
But in people who have bladder spasms, the sensation occurs suddenly and often severely. A spasm itself is the sudden, involuntary squeezing of a muscle. A bladder spasm, or “detrusor contraction,” occurs when the bladder muscle squeezes suddenly without warning, causing an urgent need to release urine. The spasm can force urine from the bladder, causing leakage. When this happens, the condition is called urge incontinence or overactive bladder.
People who have had such spasms describe them as a cramping pain and sometimes as a burning sensation. Some women with severe bladder spasms compared the muscle contractions to severe menstrual cramps and even labor pains experienced during childbirth.
Try To Avoid Caffeine Carbonated Drinks Sugar Alcohol And Spicy Or Acidic Foods
- Caffeine is a diuretic which makes you need to use the bathroom more often.
- Carbonated drinks and sugar are thought to stimulate the bladder.
- Alcohol switches off the ability of your body to concentrate urine. This means you tend to urinate more dilute, watery urine, which dehydrates you. Since you are dehydrated, you may drink more.
- Acidic or spicy food may aggravate your overactive bladder and worsen your symptoms. Certain acidic fruit and juices like orange, grapefruit, lemon and lime can aggravate your bladder, too.
Don’t Miss: What Kind Of Doctor Does Bladder Prolapse Surgery
What Works Best To Help Men With Overactive Bladder
HealthDay Reporter
TUESDAY, Jan. 14, 2020 â Learning how to control the urge to urinate may be all the therapy men need to treat an overactive bladder, a new study suggests.
A combination of drugs and behavioral therapy seems to work better than drugs alone, but behavioral therapy alone also worked better than drugs, the researchers found.
The trial of 204 men with overactive bladder suggests behavioral therapy may be a good way to start treatment, the study authors said.
âThe study provides good evidence that for the group of men with overactive bladder, symptoms without obstruction from an enlarged prostate can be successfully managed with behavioral therapy alone,â said Dr. Manish Vira, who was not involved with the study, but reviewed the findings. Heâs vice chairman of urologic research at Northwell Healthâs Arthur Smith Institute for Urology in Lake Success, N.Y.
Many medications typically prescribed for overactive bladder have significant side effects, especially in older men using multiple medications, Vira added.
For the trial, Kathryn Burgio, associate director of research at the Birmingham VA Medical Center in Alabama, and colleagues randomly assigned men to six weeks of behavioral therapy alone, drug therapy alone, or combined drug and behavioral therapy. After the initial six weeks, all of the men received combination therapy for another six weeks.
Show Sources
Also Check: Botox Injection For Bladder Incontinence
Diagnosis Of Urinary Incontinence
The first step in treating incontinence is to see a doctor. He or she will give you a physical exam and take your medical history. The doctor will ask about your symptoms and the medicines you use. He or she will want to know if you have been sick recently or had surgery. Your doctor also may do a number of tests. These might include:
- Urine and blood tests
- Tests that measure how well you empty your bladder
In addition, your doctor may ask you to keep a daily diary of when you urinate and when you leak urine. Your family doctor may also send you to a urologist, a doctor who specializes in urinary tract problems.
Read Also: How Does A Bladder Tank Work
Other Causes Of Urine Leakage
- Weakened pelvic floor muscles can allow urine to remain trapped in the urethra when you pee. As you move about afterwards, this can leak out in small amounts, known as post-micturition dribble.
- Stress urinary incontinence involuntary urine leakages when coughing, laughing, sneezing or exercising is not a common condition in men but can happen after prostate surgery if the sphincter muscle is weakened or damaged so that it is not able to fully close the urethra.
- Urinary tract infections
- Drinking large amounts of caffeine
- Taking certain medications that may affect the urinary tract
- Neurological conditions, such as Parkinsons disease and multiple sclerosis
Research And Statistics: How Many People Have Overactive Bladder
Estimates as high as 30 percent of men and 40 percent of women will develop symptoms of overactive bladder at some point in their life, according to the American Urological Association.
In addition, almost one-half of all women will leak urine at some point, and as many as one in three older men leaks urine, according to the according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
Its important to note that these numbers may underestimate the extent of overactive bladder, since many people are reluctant to report their symptoms due to embarrassment or lack of knowledge that treatments are available.
Recommended Reading: Reasons For Lack Of Bladder Control
Tips For Easing Stress And Anxiety From Overactive Bladder
Dealing with OAB? You arent alone
According to the National Association for Continence, about 17 percent of women and 16 percent of men over the age of 18 have overactive bladder . It becomes even more common with age, affecting 1 in 5 adults over the age of 40. The Urology Care Foundation emphasizes that not all people experience OAB as they age. For those that do, there is always a treatment that will help.
OAB causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge is so strong its often difficult to control. Symptoms include:
- frequent urination
- difficulty sleeping through the night
OAB can also contribute to mental health issues, including:
- stress
You May Like: How To Get Clinically Diagnosed With Anxiety
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Symptoms And Causes
What Is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia? The prostate is the male reproductive organ and is very important and sensitive. The prostate resides directly below the bladder and in front of the rectum. The primary job of the prostate is to provide fluid for the semen, which is very important for reproduction …
Don’t Miss: Bristol Myers Squibb Bladder Cancer
How Can Nerve Stimulation Help Overactive Bladder
There are several treatments that involve stimulating your nerves to help improve overactive bladder. Your nerves help communicate the message that your bladder needs to be emptied to your brain. By treating the nerves, your healthcare provider can improve your bladder control. Nerve stimulation is a reversible treatment that is considered when conservative treatments have not worked or have not been tolerated. Conservative treatments include behavioral therapies and medications.
There are several types of nerve stimulation treatments. These can include:
Initial Management In Primary Care
The following may be helpful, both for men and for women.
When to refer
- Patients on anticholinergic drugs should be reviewed four-weekly and the dosage altered or another drug in the group tried if there is no benefit from current treatment.
- A secondary care referral should be considered for patients who fail to respond to drug treatment after three months or who do not wish for drug treatment.
- Patients who are stable on drug treatment should be reviewed annually .
Don’t Miss: What Should I Do If I Have A Bladder Infection
Pelvic Floor Exercises Can Help Immensely
You cant see your pelvic floor muscles however, just like other muscles in your body they lose their strength if they are not put to use.
Pelvic floor exercises help strengthen the pelvic floor when done consistently at least twice a day. How are they done?
- Imagine you are holding back gas or urine.
- Squeeze and lift the rectal area without tightening your buttocks or belly. Try and hold it for a count of three before relaxing. Repeat this cycle 10 times. Do 10 sets of Kegel exercises, at least 3 times a day.
- Increase your contractions as your doctor recommends.
- Do not hold your breath when you do Kegel exercises. Keep your stomach, back, and leg muscles relaxed.
- Don’t use Kegel exercises to start and stop your urine stream which can lead to incomplete emptying of the bladder and an increased risk of a urinary tract infection.
Review our information about Kegel exercises for both women and men to learn more about the techniques.