What Are Different Types Of Bladder Cancer
There are three main types of bladder cancer:
- Urothelial cell or transitional cell carcinoma: Urothelial cells are responsible for the tissue that lines the interior of the bladder. Urothelial carcinoma or transitional cell carcinoma is the most common type of bladder cancer.
- Squamous cell carcinoma:Squamous cell carcinoma is a rare type of bladder cancer that generally occurs as a result of chronic irritation or inflammation of the bladder lining due to infections or urinary catheter placement.
- Adenocarcinoma: Adenocarcinoma is also a rare type of bladder cancer that originates from the glands in the urinary bladder.
Other Treatments For Bladder Cancer
For many early-stage bladder cancers, BCG is the best option for treatment. Other treatments for bladder cancer include:
- Surgery to remove the tumor: Early cancers can be removed with TURBT surgery. More advanced cancers may require more extensive surgery, like removal of part or all of the bladder .
- Intravesical chemotherapy: This treats the inside of the bladder with chemotherapy drugs. Chemotherapy drugs commonly used for bladder cancer include Mutamycin , Gemzar , or Valstar .
- Radiation therapy
- Clinical trials
There Are Different Types Of Treatment For Patients With Bladder Cancer
Different types of treatment are available for patients with bladder cancer. Some treatments are standard , and some are being tested in clinical trials. A treatment clinical trial is a research study meant to help improve current treatments or obtain information on new treatments for patients with cancer. When clinical trials show that a new treatment is better than the standard treatment, the new treatment may become the standard treatment. Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial. Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment.
Don’t Miss: Can A Yeast Infection Feel Like A Bladder Infection
Intraoperative Details Of Turbt
In most cases, general or regional anesthesia must be used to establish nerve paralysis, to minimize risk of obturator nerve reflex and subsequently, bladder perforation.
Complete eradication of tumor is the first step in TURBT. Most tumors are papillary and are easily removed by endoscopically transecting their narrow stalk or base. Following this, biopsy of the base or deeper resection is performed to ensure complete removal and the absence of invasion. The goal is that muscle tissue must is present in the base biopsy specimen to ensure accurate staging.
Medium and large tumors are resected in a controlled serial fashion prior to transection of the stalk. This ensures that large segments do not remain that might be too large to evacuate through the resectoscope.
Smaller and more friable tumors may be removed at least partially by knocking off fragments with the cutting loop of the resectoscope without the electricity turned on. This sometimes allows partial removal with less risk of bladder perforation.
Pulling the cutting loop away from the tumor is generally much safer than pushing it toward the tumor. Lifting the tumor away from the surrounding normal bladder tissue using the cutting loop is also advisable.
Transurethral resection syndrome, which results from absorption of electrolyte-free irrigating fluid, has become uncommon since the advent of bipolar resectoscopes, which utilize normal saline irrigation.
What Is The Prognosis For People Who Have Cystectomy
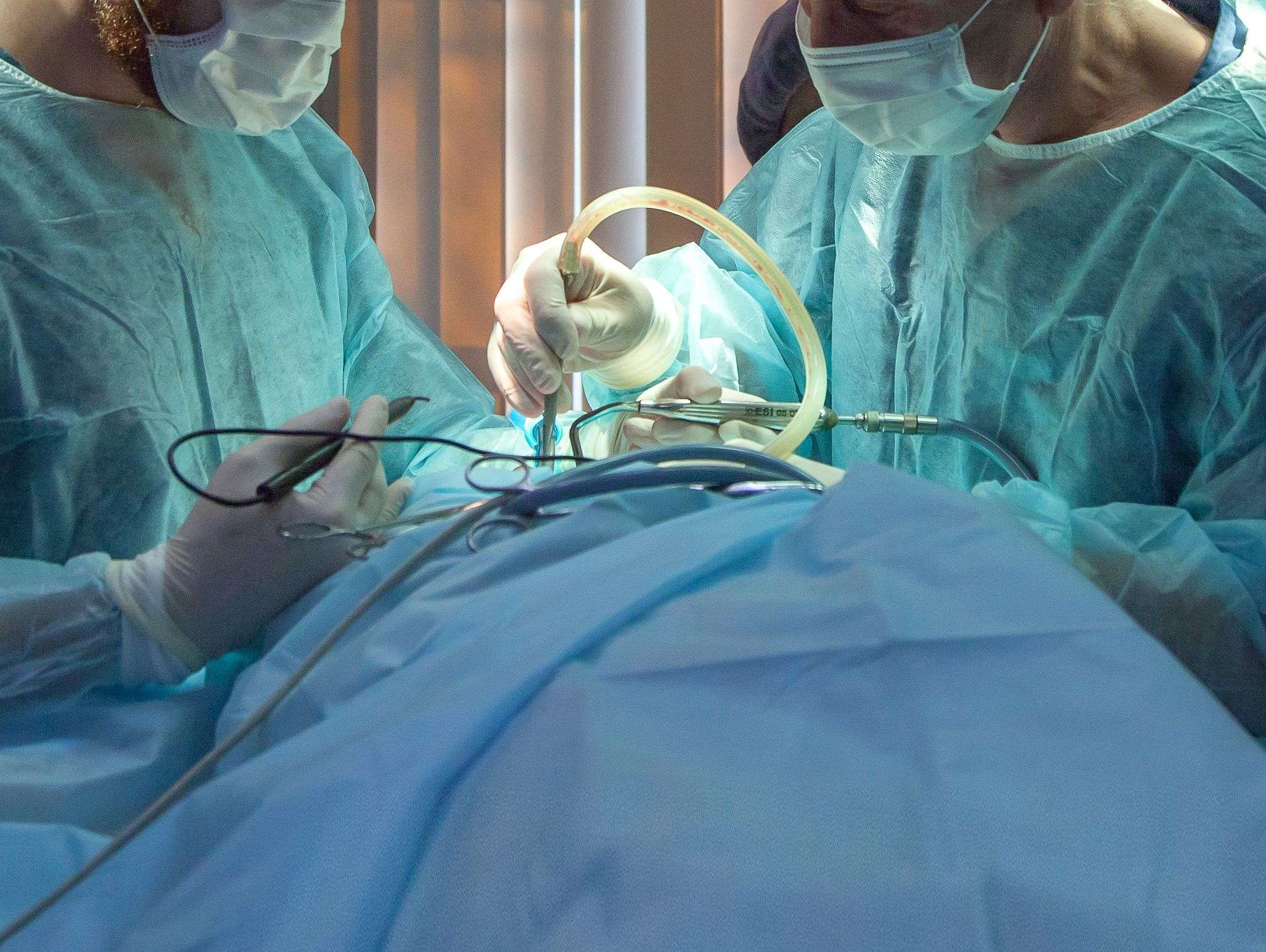
Your recovery depends on the type of bladder removal surgery you have. Typically, patients who undergo a partial cystectomy will have a shorter recovery period compared with patients who undergo a radical cystectomy. Many patients will have poor appetite and abnormal bowel function immediately after radical cystectomy, and complete recovery may take several weeks to months.
Dont Miss: Terry Naturally Sagapro Bladder Health
Recommended Reading: Is Heat Good For Bladder Infection
Treating Bladder Cancer That Progresses Or Recurs
If cancer continues to grow during treatment or comes back after treatment , treatment options will depend on where and how much the cancer has spread, what treatments have already been used, and the patient’s overall health and desire for more treatment. Its important to understand the goal of any further treatment if its to try to cure the cancer, to slow its growth, or to help relieve symptoms as well as the likely benefits and risks.
For instance, non-invasive bladder cancer often comes back in the bladder. The new cancer may be found either in the same place as the original cancer or in other parts of the bladder. These tumors are often treated the same way as the first tumor. But if the cancer keeps coming back, a cystectomy may be needed. For some non-invasive tumors that keep growing even with BCG treatment, and where a cystectomy is not an option, immunotherapy with pembrolizumab might be recommended.
Cancers that recur in distant parts of the body can be harder to remove with surgery, so other treatments, such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or radiation therapy, might be needed. For more on dealing with a recurrence, see Understanding Recurrence.
Transurethral Resection Of The Bladder Cancer Tumor
This is when the tumor is removed from the urinary tract through the urethra using an electrical force. Transurethral resection is an endoscopic or scope procedure that does not involve making an incision in the body.
Drug therapy after TUR is commonly prescribed for patients with large, multiple or high-grade tumors.
You May Like: Do You Bleed With A Bladder Infection
What To Expect On The Day Of Surgery
Before surgery:When you arrive at the hospital on the day of your surgery, you will meet with your surgical nurse as well as your doctor and anesthesiologist . They will ask if you have any questions before proceeding with the surgery and ask you to sign a consent form
Your nurse will then check your weight, temperature, breathing rate, and pulse. You may also have blood tests or an ECG on the day of surgery. You will be given a hospital gown and socks to wear and given a bag for your clothing. It’s best to leave all valuables at home and have a friend or family member take care of any articles you bring with you.
During surgery: You will then be taken to the operating room and your anesthesiologist will talk to you about the anesthetic. An intravenous line will be inserted to put you to sleep, and a dose of antibiotics is given.
Next, the surgical team will clean and prepare the site of surgery, and place sterile surgical drapes over your body. The full preparation and surgical steps will depend upon the exact type of procedure being completed.
After surgery: You will be taken to recovery until you begin to wake up, then you’ll be moved to your hospital room, where you will be reunited with any friend or family member present. You will likely have a PCA device so that you can self-administer intravenous medication to manage your pain.
What Is A Partial Or Radical Cystectomy
The most common type of cystectomy is a radical cystectomy, in which the surgeon removes the patients entire bladder, lymph nodes in the pelvis, and potentially additional tissues and organs. Male patients may have the prostate and seminal vesicles removed in female patients, surgeons may remove the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, cervix, and part of the vagina. Partial cystectomies, in which only part of the bladder is removed, are less commonly used to treat muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
Don’t Miss: Stage 4 Bladder Cancer Symptoms
Continent Diversion With A Continent Diversion You Control Urination The Surgeon Makes A Pouch To Hold The Urine You Drain The Urine From This New Pouch Either With A Tube Or Through The Ureter A Continent Cutaneous Reservoir Is Also Called A Continent Diversion With Catheterizable Cutaneous Stoma The Surgeon Creates A Pouch Using The Right Side Of The Colon And A Piece Of The Small Intestine The Pouch Is Attached To An Opening Made In The Abdominal Wall And Skin You Drain Urine From The Pouch By Inserting A Tube Into The Opening Several Times Throughout The Day
An orthotopic neobladder is when the surgeon makes a pouch usually from part of the small intestine. The ureters are attached to the pouch, which is then attached to the urethra. You empty the pouch by urinating normally. An orthotopic neobladder is a more difficult type of surgery than other urinary diversions and there is more chance of problems . So it is usually done in younger people without serious medical problems.
Find out more about .
What Is The Outlook For Someone Who Has Had Bladder Tumor Biopsy And Resection
Bladder tumor biopsy and resection is a successful treatment for early stage bladder cancer. It can prevent cancer from spreading into the bladder muscle wall. Invasive bladder cancers that spread require more extensive treatment.
However, bladder cancer often comes back . More TURBT procedures may be needed. Your doctor will do frequent follow-up checkups with you to look for signs that the cancer has returned. The risks of repeated TURBT procedures is small.
Some providers might choose to burn off smaller tumors rather than remove them.
If the TURBT shows that you have a more advanced bladder cancer, youll probably need further treatment. This could include:
- A more extensive TURBT.
- Surgery to remove the tumor.
- Surgery to remove the bladder.
- Chemotherapy.
- Radiation.
- Bacillus Calmette-Guerin therapy or BCG. This is a type of therapy that uses the bodys own immune system to fight the cancer.
Your urologist and pathologist will determine the best course of treatment based on the staging of the tumor and your personal medical history. TURBT can help in staging the cancer by determining if the cancer has invaded the bladder wall. Staging refers to determining how serious the cancer is.
Don’t Miss: Panty Liners For Bladder Leakage
What Type Of Bladder Cancer Surgery Do I Need
The type of bladder cancer surgery you need depends on many factors, including whether the cancer is located only on the bladders surface layers or has invaded the bladder muscle .
- Superficial bladder cancer: Most patients are diagnosed with non-invasive bladder cancer. If you have superficial bladder cancer, we can surgically remove just the tumor and leave the rest of the bladder intact, using an endoscopy technique. With no incision involved.
- Transurethral Resection : In this surgery, your doctor used an endoscope to scrape the cancer off the surface layer of your bladder. Your doctor might also fulgurate off the cancer as well. TUR can be part of a treatment plan that includes one or more of the following: chemotherapy, immunotherapy and/or radiation therapy.
What Are The Risks Of Bladder Tumor Biopsy And Resection
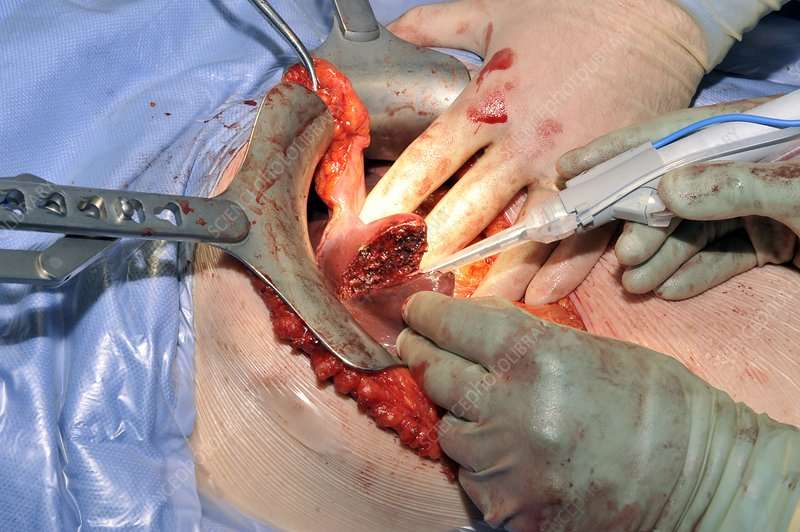
Bladder tumor biopsy and resection is a very safe procedure. However, like any surgery, it has some risks. These include:
- Risks related to anesthesia.
- Excessive or prolonged bleeding.
- Perforation in the bladder.
If you have any symptoms such as fever, feeling cold and shivery, or heavy bleeding following bladder tumor biopsy and resection, you should seek medical help right away.
Don’t Miss: Does A Bladder Infection Cause Bloating
What Are The Risks Of Cystectomy
Like any major surgical procedure, bladder removal surgery poses some risks, including:
- Bleeding
- Organ damage
- Reactions to anesthesia
You may also have changes in how you urinate after any bladder surgery. Your bladder is smaller after partial cystectomy, so you may need to go to the bathroom more often. If you have a radical cystectomy, your ability to urinate depends on the type of reconstructive surgery you have.
For some men, bladder removal surgery causes sexual side effects. Men may have difficulty getting and maintaining erections. Because doctors remove the seminal vesicles along with the bladder, men will no longer produce semen.
Women may also experience sexual side effects. While intercourse is still possible, it may cause discomfort if doctors remove part of the vagina. Some people have nerve damage. This damage may limit a womans ability to become aroused and achieve orgasm.
Treating Stage Ii Bladder Cancer
These cancers have invaded the muscle layer of the bladder wall , but no farther. Transurethral resection is typically the first treatment for these cancers, but it’s done to help determine the extent of the cancer rather than to try to cure it.
When the cancer has invaded the muscle, radical cystectomy is the standard treatment. Lymph nodes near the bladder are often removed as well. If cancer is in only one part of the bladder, a partial cystectomy may be done instead. But this is possible in only a small number of patients.
Radical cystectomy may be the only treatment for people who are not well enough to get chemo. But most doctors prefer to give chemo before surgery because it’s been shown to help patients live longer than surgery alone. When chemo is given first, surgery is delayed. This is not a problem if the chemo shrinks the bladder cancer, but it might be harmful if the tumor continues to grow during chemo.
If cancer is found in nearby lymph nodes, radiation may be needed after surgery. Another option is chemo, but only if it wasn’t given before surgery.
For people who have had surgery, but the features of the tumor show it is at high risk of coming back, the immunotherapy drug, nivolumab, might be offered. When given after surgery, nivolumab is given for up to one year.
For patients who cant have surgery because of other serious health problems, TURBT, radiation, chemotherapy, or some combination of these may be options.
You May Like: Bladder Cancer Chemo Treatment Side Effects
Palliative Or Supportive Care
If your cancer is at an advanced stage and can’t be cured, your medical team should discuss how the cancer will progress and which treatments are available to ease the symptoms.
You can be referred to a palliative care team, who can provide support and practical help, including pain relief.
Page last reviewed: 01 July 2021 Next review due: 01 July 2024
Treatments After Or Instead Of Surgery
Sometimes, doctors will use a mix of chemotherapy and radiation therapy to avoid surgery to remove the bladder. It can be a good option if youâre not healthy enough for surgery. In this case, you will likely take the chemo drug cisplatin by itself, cisplatin and fluorouracil, or mitomycin with fluorouracil.
You may also get chemotherapy and radiation together after surgery if your cancer has grown into the muscle layer of the bladder but hasnât spread elsewhere.
If your cancer spreads after chemo, you can try other chemotherapy drugs or other types of medicine, like immunotherapy.
Read Also: Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy In Bladder Cancer
Bladder Cancer Stages And Survival Rates
Cancer survival rates are also categorized according to the stage of the cancer when it was diagnosed. The stage of cancer generally refers to how far it has progressed, and whether it has spread to other parts of the body. For bladder cancer, the 5-year survival rate for people with:2,3
- Bladder cancer in situ is around 96 percent
- Localized bladder cancer is around 70 percent
- Bladder cancer that has spread to the regional lymph nodes is 35 percent
- Distant or metastasized bladder cancer is 5 percent
If you would like to learn more about bladder cancer statistics, consider speaking with someone on your health care team. They will be able to explain more about how these statistics apply to your cancer. Tell us about your experience in the comments below, or with the community.
When Should I Call My Doctor
Let your doctor know if you think you may have an infection. Also tell them if:
- You have bleeding from the stoma that doesnât stop with a little pressure.
- You have pain, cramping, or swelling in your belly.
- Your pouch leaks regularly or doesnât stay in place.
- Your skin around the stoma keeps getting red or sore.
- The stoma turns dark purple, brown, or black.
You May Like: What Is The Best Medicine For Bladder Control
Clinical Trials To Improve Treatment
Your doctor might ask if youd like to take part in a clinical trial. Doctors and researchers do trials to make existing treatments better and develop new treatments.
-
BMJ Best Practice. Bladder CancerD Lamm and others
-
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence , February 2015
-
EAU Guidelines on Muscle-invasive and Metastatic Bladder CancerJ A Witjes and othersEuropean Association of Urology, 2017
-
Bladder cancer: ESMO Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up J Bellmunt and others
Cystoscopy With Cautery Destruction Of The Bladder Tumor
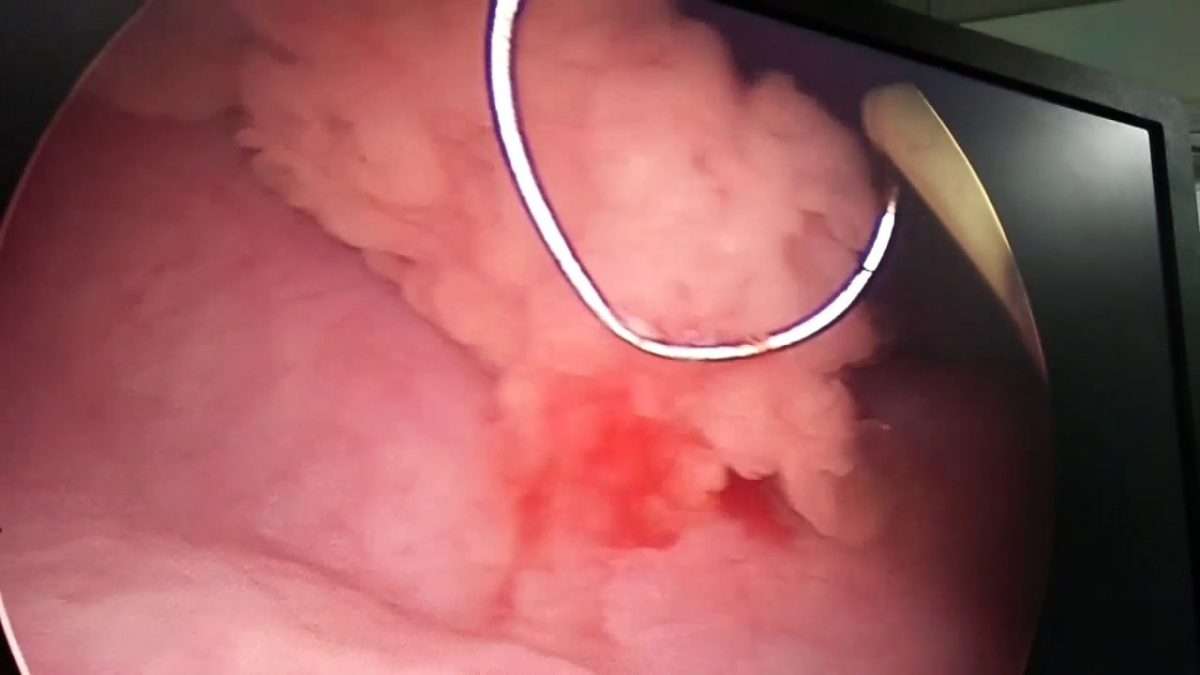
Cystoscopy is an outpatient procedure during which a thin, lighted tube with a camera is passed through the urethra into the bladder, allowing your doctor to see the inside of the bladder.
Most modern cystoscopes are also equipped with channels that permit small instruments to be passed into the bladder. During a cystoscopy, your doctor may use these instruments to remove tissue, stop bleeding with a special electrical device called an electrocautery or even perform laser treatment. If the bladder cancer tumor is small enough, this cautery may be used to remove the cancer.
Recommended Reading: Does Azo Bladder Control Cause Weight Gain
When Bladder Removal Is Recommended Patients Have Options
Bladder cancer is considered advanced when the cancer invades the muscle.
In these cases, patients may face removal of the bladder in order to treat the cancer.
If you dont do something aggressive, such as remove the bladder, most of the time the cancer will spread, explains urologic oncologist Joseph Jacob, MD. Almost 100 percent of the time, the cancer will spread into the bloodstream and the lymph nodes. And then at that point, theres no cure for the patient.
It may sound extreme, but removing the bladder can be lifesaving. The procedure is called a cystectomy.
The kidneys lter blood and create urine. Tubes called ureters carry the urine to the bladder. If that organ is removed, Jacob says, most patients have three options:
— A urinary conduit, called a urostomy. In this procedure, surgeons turn a small segment of the patients small bowel into a pipe that carries urine from the kidneys out through a new opening in the skin, into a bag. The patient would periodically empty the bag.
This is the most common approach because its the most straightforward, Jacob says. But it may not be the most appealing to patients.
— A neobladder, or bladder replacement. This makes use of a slightly longer segment of small bowel.
I tell patients we do some origami work. Basically, we fold this into a sphere, and then you connect that bladder back to the urethra. Then the patient would learn how to urinate like theyre used to urinating.