Cervical Cancer Control: A Comprehensive Approach
The Global strategy towards eliminating cervical cancer as a public health problem,adopted by the World Health Assembly in 2020, recommends a comprehensive approach to cervical cancer prevention and control. The recommended actions include interventions across the life course.
The life-course approach for cervical cancer prevention and control
|
Primary prevention |
||
|---|---|---|
Girls 9-14 years
|
From 30 years of age for women from the general population and 25 years of age for women living with HIV | All women as needed |
Girls and boys should also be offered, as appropriate
|
|
Treatment of invasive cancer at any age
|
Cervical cancer prevention should encompass a multidisciplinary, including components from community education, social mobilization, vaccination, screening, treatment and palliative care.
HPV vaccination
Clinical trials and post-marketing surveillance have shown that HPV vaccines are safe and effective in preventing infections with HPV infections, high grade precancerous lesions and invasive cancer .
What Can I Do To Lower My Risk Of Hpv Infection
- Educate yourself about HPV and safer sexual practices.
- Get vaccinated.
- The HPV vaccine is recommended for all individuals age 12-26.
- It is approved for use up to age 45 however, insurance companies usually don’t cover the HPV vaccine for individuals over the age of 26.
- Talk to your healthcare provider about your risk factors and vaccination.
- Even if you already have HPV, you can still be vaccinated. The vaccine can protect you from other types of HPV.
- Women should have routine pap tests to screen for cervical pre-cancer even if they are vaccinated.
- Visit your dentist regularly for oral cancer screenings. Early detection of HPV-related oral cancers is important.
Does Hpv Infection Cause Symptoms
Infection with high-risk HPV does not usually cause symptoms. The precancerous cell changes caused by a persistent HPV infection at the cervix rarely cause symptoms, which is why regular cervical cancer screening is important. Precancerous lesions at other sites in the body may cause symptoms like itching or bleeding. And if an HPV infection develops into cancer, the cancer may cause symptoms like bleeding, pain, or swollen glands. Learn more about signs and symptoms of cervical, vaginal, vulvar, penile, anal, and oropharyngeal cancers.
Recommended Reading: How Do Males Get Bladder Infections
Can Hpv Infection Be Prevented
Theres no sure way to prevent infection with all the different types of HPV. But there are things you can do to lower your chances of being infected. There are also vaccines that can be used to protect young people from the HPV types most closely linked to cancer and genital warts.
HPV is passed from one person to another during contact with an infected part of the body. Although HPV can be spread during sexual contact including vaginal, anal, and oral sex sex isnt the only way for the infection to spread. All thats needed is skin-to-skin contact with an area of the body infected with HPV. There may be other ways to become infected with HPV that arent yet clear.
HPV can be present for years without causing any symptoms. It doesnt always cause warts or any other symptoms. Someone can have the virus and pass it on without knowing it.
Screening For Other Hpv
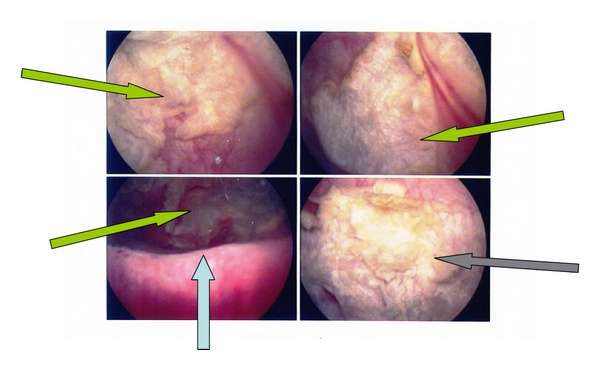
There are no Food and Drug Administration approved tests to detect HPV infections or HPV-caused cell changes in anal, vulvar, vaginal, penile, or oropharyngeal tissues. Research studies are ongoing to identify tests that can detect precancers in these areas or find cancer in an earlier, more treatable stage.
Anal cancer screening: Among populations that are at higher risk for HPV infection, such as men who have sex with men or men who are HIV positive, some research has found that an anal Pap test may help to detect early cell changes or precancerous cells. Research is ongoing to see if treating anal precancer prevents anal cancer.
Learn more about Anal Cancer Prevention .
Oral cancer screening: Currently, there are no standard screening tests for oral cancer. The United States Preventive Services Task Force has found that the current evidence is insufficient to assess the balance of benefits and harms of screening for oral cancer in asymptomatic adults. However, the American Dental Association recommends dentists check for signs of oral and oropharyngeal cancer as part of a routine dental check-up in all patients.
Learn more about Oral Cavity, Pharyngeal, and Laryngeal Cancer Screening and about symptoms in Oropharyngeal Cancer Treatment .
Also Check: Why Do You Lose Control Of Your Bladder
Sexually Transmitted Infections Linked To Cancer
Below, there are a few sexually transmitted infections that are known to be related to various forms of cancer. Is cancer an STI? In a word: no. There are still a few forms of cancer that can be related to a sexually transmitted infection.
They include:2
- Human papillomavirus . HPV is the most common sexually transmitted disease, and it has been linked with cervical cancer, anal cancer, penile cancer, vaginal cancer, and head and neck cancers. In most cases, infection with HPV goes away on its own, but when persistent, may lead to inflammation and cancer. Not all strains of HPV are linked with cancer
- Hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus. Both hepatitis B and C are associated with liver cancer, and together are the greatest cause of liver cancer worldwide.
- HIV/AIDS. There are several types of cancer associated with HIV/AIDS, related to immunosuppression
- Human herpes virus Type 8 or Kaposi sarcoma herpes virus most commonly leads to Kaposi’s sarcoma in people with HIV
What Causes Bladder Cancer
Researchers do not know exactly what causes most bladder cancers. But they have found some risk factors and are starting to understand how they cause cells in the bladder to become cancer.
Certain changes in the DNA inside normal bladder cells can make them grow abnormally and form cancers. DNA is the chemical in our cells that makes up our genes, which control how our cells function. We usually look like our parents because they are the source of our DNA, but DNA affects more than just how we look.
Some genes control when cells grow, divide into new cells, and die:
- Genes that help cells grow, divide, and stay alive are called oncogenes.
- Genes that normally help control cell division, repair mistakes in DNA, or cause cells to die at the right time are called tumor suppressor genes.
Cancers can be caused by DNA changes that turn on oncogenes or turn off tumor suppressor genes. Several different gene changes are usually needed for a cell to become cancer.
You May Like: How To Reduce Bladder Inflammation Naturally
Causes Of Cervical Cancer
In almost all cases, cervical cancer is the result of a change in cell DNA caused by the human papilloma virus .
Cancer begins with a change in the structure of the DNA that’s present in all human cells. DNA provides the cells with a basic set of instructions, including when to grow and reproduce.
A change in the DNA’s structure is known as a mutation. It can alter the instructions that control cell growth, which means the cells continue growing instead of stopping when they should. If the cells reproduce uncontrollably, they produce a lump of tissue called a tumour.
Study Identifies Crucial Characteristic Of High
HPV16-infected cells.
NCI researchers have found that for the most common high-risk type of human papillomavirus to cause cervical cancer, an important viral gene may need to have a precise DNA sequence. The findings, the researchers believe, contribute to a better understanding of HPV biology and may have implications for cervical cancer prevention and treatment.
The study investigators analyzed the genomes of HPV type 16one of the most potent human carcinogensfrom more than 5,000 infected women around the world, making it the largest genomic study of HPV16 to date. Some of the women in the study had cervical cancer while others did not.
They found that the sequence of a viral oncogene called E7 was almost identical among women with cervical cancer but had many different mutations among those without cancer.
We knew that E7 was important, but we didnt realize that its genetic conservation might be critical for HPV16 to cause cancer, said lead investigator Lisa Mirabello, Ph.D., of NCIs Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics . Conservation refers to whether the sequence of a gene remains unchanged over time.
The new findings were reported online on September 7 in Cell.
This study really nicely shows that E7 is a very important, arguably the most important, oncogene for HPV16-associated cervical cancer development, said Dohun Pyeon, Ph.D., associate professor of immunology and microbiology at the University of Colorado, who was not involved in the study.
Also Check: What Can Be Done About Bladder Leakage
What Causes Cervical Cancer
Almost all cases of cervical cancer are caused by the human papilloma virus . HPV is a very common virus that can be passed on through any type of sexual contact with a man or a woman.
There are more than 100 different types of HPV, many of which are harmless. However, some types of HPV can cause abnormal changes to the cells of the cervix, which can eventually lead to cervical cancer.
Two strains of the HPV virus are known to be responsible for 70% of all cases of cervical cancer. These types of HPV infection don’t have any symptoms, so many women won’t realise they have the infection.
However, it’s important to be aware that these infections are relatively common and most women who have them don’t develop cervical cancer.
Using condoms during sex offers some protection against HPV, but it can’t always prevent infection, because the virus is also spread through skin-to-skin contact of the wider genital area.
Since 2008, a HPV vaccine has been routinely offered to girls aged 12 and 13.
Read more about the causes of cervical cancer and preventing cervical cancer
Urethral Cancer Grades And Stages
Once your doctor confirms a cancer diagnosis, theyll give the cancer a stage and a grade. These classifications tell your doctor and other health care providers a lot about your cancer.
Cancer grade: Grades identify how quickly the tumor can grow and spread.
- A low-grade cancer is growing slowly and unlikely to spread.
- A high-grade cancer is growing quickly and may recur, spreading outside the urethra.
Cancer stage: A stage tells if the cancer has spread beyond the urethra. The higher the number, the greater the spread. For example, a stage 1 tumor is still localized to the urethra and nearby tissue, but a stage 4 tumor has spread to other organs.
Recommended Reading: How To Reduce Bladder Pain
Tips For Caring For Cervical Cancer At Home
Certain things can ease the physical and mental stresses of cervical cancer and treatment.
One of the best things you can do is get the right nutrition. You may lose your appetite or have trouble eating during treatment. But if you get enough calories and protein, youâll have more strength and energy, and youâll be able to handle treatment better. You might want to work with a nutritionist to keep up your calorie and protein intake. They may suggest you eat smaller portions more often.
Other lifestyle changes may help keep you stronger and more comfortable during treatment:
- Get mild physical activity to keep up your energy level. Make sure it doesn’t wear you out.
- Get enough rest at night, and take naps if you need.
- Don’t drink alcohol. You may not be able to drink alcohol while taking some medications.
Hpv And Sexual Health
- While HPV is referred to as a sexually transmitted infection, you do not need to have intercourse to contract HPV or give it to your partner.
- HPV can be passed on during vaginal or anal penetration, oral sex , genital skin-to-skin sexual contact, or genital touching .
- Experts do not know all the ways HPV is spread.
- Condom and/or dental dam use may decrease areas that are exposed.
- Using barrier methods cannot totally prevent exposure completely since HPV can be found on the scrotum, inner thigh, and vulva.
- Higher numbers of sexual partners and earlier age of first sexual encounter may increase your exposure to HPV and your chances of being infected.
- Studies have found that anal sex can increase the risk of anal cancers.
- Oral sex can increase the risk of oral cancers.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know If Bladder Cancer Has Spread
What Is Penile Cancer
Penile cancer remains rare in the developed world. It accounts for less than 1% of all cancers in males. Just 2,000 cases are diagnosed in the United States each year, with about 450 people dying due to metastases . When it’s diagnosed and treated early, penile cancer has a five-year survival rate of over 80%.
There are seven kinds of penile cancer, and squamous cell carcinomas account for about 95% of all cases.
Penile cancers usually begin with lesions, or sores, on the head or shaft of the penis. The lesions can be red bumps that look more like a rash, or the skin may be crusty. Sometimes the sores may look like white patches, as in the case of the early-stage Bowen’s disease, a non-invasive type of skin cancer.
It’s common for smelly fluid to be leaking from the sores, and you may have pain when urinating.
Are There Support Groups And Counseling For Cervical Cancer
Living with cervical cancer can present new challenges for you and your loved ones.
You might worry about how it will affect your everyday life. Many people feel anxious or depressed, and some are angry and resentful. Talking about your feelings and concerns can help.
Your friends and family members can be supportive. If you want to talk, let them know. They may be waiting for a cue from you.
Some people don’t want to “burden” their loved ones, or they prefer talking about their concerns with a more neutral professional. A social worker, counselor, or member of the clergy can help.
Many people get a boost from talking with others with similar experiences. Your hospital or medical center might have support groups. The American Cancer Society also has information about support groups all over the U.S.
Don’t Miss: Fastest Way To Cure Bladder Infection
Human Papillomavirus Might Cause Bladder Cancer Research Suggests
- Date:
- Universidad de Granada
- Summary:
- An analyzed of 44 articles as well as a new study lead researchers to postulate that human papillomavirus might cause bladder cancer. The HPV is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases today.
The Human Papillomavirus is considered the cause of one of the most important sexually transmitted diseases today, and it affects both men and women. HPV is so common in our society that only people who have never had sexual relations can be sure that they have not been exposed to this disease.
However, as with other microbes, people infected do not necessarily develop the disease, because, in most cases, infection only results in colonization. Only some of the people colonized will fall ill with different processes.
Nevertheless, the development of this disease might have serious consequences: It is probable that HPV is related to bladder cancer, according to a recent study carried out by the Department of Microbiology of the University of Granada, in collaboration with the Department of Biostatistics and the Urology Service of San Cecilio Hospital.
Several previous studies point out the possibility that HPV might cause, in certain subjects, some types of cancer: cervical, anus, vulva, penis, oropharyngeal and bladder cancer.
Standardization of methods
Story Source:
Genetic Alterations In Hpv16
Persistent infection with one of a dozen high-risk HPV types can lead to cervical, anal, oropharyngeal, and other cancers. HPV16, however, is the cause of half of all cervical cancers and an even larger fraction of other HPV-related cancers.
Although it is estimated that roughly 40% of women will be infected with a high-risk type of HPV at some point in their lives, most of these infections are successfully controlled by the immune system. Scientists do not fully understand why only some HPV infections persist and lead to cervical precancer or cancer.
Dr. Mirabello and her colleagues obtained cell or tissue samples from about 3,960 HPV16-infected women in the United States or Costa Rica who had benign infections, advanced cervical precancer, or cancer. Advanced cervical precancer can turn into cancer, and in the United States, it is treated to prevent progression to cancer.
They found a high amount of diversity between the HPV16 genomes of all the samples only about a quarter of the HPV16 genomes were exactly the same between two or more women in the study. When they looked at the quantity of mutations, they found that the HPV16 genomes from women with benign infections had more mutations than those from women who had precancer or cancer.
The researchers found similar patterns when they analyzed HPV16 genomes from more than 1,600 cervical cancer samples obtained from women in 39 different countries.
You May Like: Can Bladder Cancer Be Cured If Caught Early
What Cancers Are Caused By Hpv Infection
Long-lasting infections with high-risk HPVs can cause cancer in parts of the body where HPV infects cells, such as in the cervix, oropharynx , anus, penis, vagina, and vulva.
HPV infects the squamous cells that line the inner surfaces of these organs. For this reason, most HPV-related cancers are a type of cancer called squamous cell carcinoma. Some cervical cancers come from HPV infection of gland cells in the cervix and are called adenocarcinomas.
HPV-related cancers include:
In the United States, high-risk HPVs cause 3% of all cancers in women and 2% of all cancers in men. Each year, there are about 45,000 new cases of cancer in parts of the body where HPV is often found, and HPV is estimated to cause about 36,000 of these, according to the Centers for Disease Control .
Worldwide, the burden of HPV-related cancers is much greater. High-risk HPVs cause about 5% of all cancers worldwide, with an estimated 570,000 women and 60,000 men getting an HPV-related cancer each year. Cervical cancer is among the most common cancers and a leading cause of cancer-related deaths in low- and middle-income countries, where screening tests and treatment of early cervical cell changes are not readily available.