Not Sure What To Do Next
If you are still concerned about your urinary retention, why not use healthdirects online Symptom Checker to get advice on when to seek medical attention.
The Symptom Checker guides you to the next appropriate healthcare steps, whether its self care, talking to a health professional, going to a hospital or calling triple zero .
Common Neurologic Causes Of Impaired Bladder Emptying
Spinal cord injury. Any injury to the spinal cord, including blunt, degenerative, developmental, vascular, infectious, traumatic, and idiopathic injury, can cause voiding dysfunction. Injury to the cauda equina and peripheral sacral nerves can have devastating effects on bladder and urethral sphincter function. The true incidence of lower urinary tract dysfunction as a result of cauda equina and pelvic plexus injury is unknown, mainly because of the lack of prospective studies with preoperative and postoperative neurourologic evaluation of patients.
Pelvic surgery. The incidence of vesicourethral dysfunction has been reported to be 20% to 68% after abdominal perineal resection, 16% to 80% after radical hysterectomy, 10% to 20% after proctocolectomy, and 20% to 25% after anterior resection.
Pelvic and sacral fractures. Pelvic trauma can result in cauda equina and pelvic plexus injury. The frequency of neurologic injury after pelvic fracture is estimated to be between 0.75% and 11%. The injury most closely correlated with neurologic damage is transverse sacral fracture. Approximately two thirds of these patients will have neurogenic bladder. Because most of the injuries are incomplete, the majority of patients with neurourologic injury after pelvic and sacral fractures will improve over time.
Infectious neurologic processes. There are a number of infectious causes of incomplete emptying of the bladder:
When Should Someone Seek Medical Care For An Inability To Urinate
- This condition requires urgent bladder drainage to prevent damage to the bladder, kidneys, and ureter.
- Your doctor may advise you to go to a hospital emergency department without delay.
- If you have symptoms of chronic urinary retention, you should also let your health care provider know, since chronic urinary retention may lead to urinary tract infections, incontinence, further bladder damage, and damage to your kidneys.
Urologists are most often involved in the care of patients with urinary retention. However, women are also often treated by urogynecologists. Internists, family physicians, and emergency-room physicians also frequently treat urinary retention.
You May Like: Sjogren’s Syndrome And Bladder Problems
Urinary Retention: Does Drinking Water Really Help
Urinary retention is a condition characterized by an inability to fully empty the bladder. The bladder serves as a storage tank for urine, a substance made by the kidneys after they have filtered out waste and extra water from your blood. Once made, the urine travels to the bladder where it will stay until a person is ready to urinate. In a healthy individual, the bladder can hold up to two cups of urine comfortably for up to five hours.
Urinary retention can occur for a variety of reasons. Among men, an enlarged prostate is the most common cause. Among women, bladder muscle dysfunction and urinary stones are the typical culprits. Individuals with this condition may experience:
- Feeling the need to urinate right after using the bathroom
When To Seek Medical Care

A person who has any of the following symptoms should see a health care provider right away:
- complete inability to urinate
- electromyography
Physical Exam
A health care provider may suspect urinary retention because of a patient’s symptoms and, therefore, perform a physical exam of the lower abdomen. The health care provider may be able to feel a distended bladder by lightly tapping on the lower belly.
Postvoid Residual Measurement
This test measures the amount of urine left in the bladder after urination. The remaining urine is called the postvoid residual. A specially trained technician performs an ultrasound, which uses harmless sound waves to create a picture of the bladder, to measure the postvoid residual. The technician performs the bladder ultrasound in a health care provider’s office, a radiology center, or a hospital, and a radiologist — a doctor who specializes in medical imaging — interprets the images. The patient does not need anesthesia.
A health care provider may use a catheter — a thin, flexible tube — to measure postvoid residual. The health care provider inserts the catheter through the urethra into the bladder, a procedure called catheterization, to drain and measure the amount of remaining urine. A postvoid residual of 100 mL or more indicates the bladder does not empty completely. A health care provider performs this test during an office visit. The patient often receives local anesthesia.
Medical Tests
Read Also: Can A Ct Urogram Detect Bladder Cancer
What Is Urinary Retention
Urinary retention is a condition where your bladder doesnt empty all the way or at all when you urinate. Your bladder is like a storage tank for urine. Urine is made up of waste thats filtered out of your blood by your kidneys. Once filtered, the urine moves to your bladder where it waits till its time to move through the urethra and out of the body.
When you have urinary retention, it can be acute or chronic . Acute means that it comes on quickly and it could be severe. Chronic urinary retention means that youve had the condition for a longer period of time.
The acute form of urinary retention is an emergency. In this case, youll need to see a healthcare provider right away. The chronic form happens most of the time in older men, but it can also occur in women.
What Medications Treat Urinary Retention
There are three types of medications available for treating urinary symptoms in men thought to be related to an enlarged prostate and may be helpful in men with urinary retention secondary to an enlarged prostate .
The first class of medications work by relaxing the muscles at the neck of the bladder, thus reducing the obstruction to the flow of urine. The common medications in this class are terazosin , tamsulosin , doxazosin , silodosin , and alfuzosin . These medications are generally used for treating long-standing obstructive symptoms due to an enlarged prostate, but they may have a role in treating acute obstruction. Some studies have suggested that early initiation of these medications may improve urinary problems upon the removal of a urinary catheter.
Alpha-blockers are also very helpful in individuals with bladder neck dysfunction, a medical condition in which the bladder outlet does not open prior to the bladder contracting. This condition typically requires long-term use of alpha-blockers.
The third class of medications for treatment of urinary symptoms related to BPH are PDE-5 inhibitors. Cialis is approved for the treatment of BPH symptoms in men. It is not fully known how this medication, which is typically used for troubles with erections, helps with symptoms related to enlargement of the prostate, but studies have shown it as effective as alpha-blockers.
Also Check: Will Cranberry Juice Help A Bladder Infection
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Diagnosis and treatment of urinary retention require an interprofessional team effort. Primary care physicians, emergency department physicians, and hospitalists should be able to recognize the early signs and symptoms of urinary retention. Nurses should monitor the urine output in hospitalized patients and report to physicians if they notice a decrease or complete absence of urine output. Consultation with a urologist being obtained in advanced cases. Pharmacists also have a role in recognizing the medications, which can cause urinary retention and coordinating efforts with the prescribing clinician. Unfortunately, despite optimal treatment, the recurrence of urinary retention is frequent.
How To Empty The Bladder
This article was co-authored by Robert Dhir, MD. Dr. Robert Dhir is a board certified Urologist, Urological Surgeon, and the Founder of HTX Urology in Houston, Texas. With over 10 years of experience, Dr. Dhirs expertise includes minimally-invasive treatments for enlarged prostate , kidney stone disease, surgical management of urological cancers, and mens health . His practice has been named a Center of Excellence for the UroLift procedure, and is a pioneer in non-surgical procedures for ED using his patented Wave Therapy. He earned his undergraduate and medical degrees from Georgetown University and was awarded honors in pre-medical studies, urology, orthopedics, and ophthalmology. Dr. Dhir served as chief resident during his urological surgical residency at University of Texas at Houston / MD Anderson Cancer Center in addition to completing his internship in general surgery. Dr. Dhir was voted Top Doctor in Urology for 2018 to 2019, one of the top three Best Rated Urologists in 2019 & 2020 for Houston Texas, and Texas Monthly has named him to the 2019 & 2020 Texas Super Doctors Rising Stars list.There are 15 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 85% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 390,268 times.
Don’t Miss: Small Cell Bladder Cancer Treatment
What Are Risk Factors And Causes Of An Inability To Urinate
There are a number of medical conditions and medications that may cause urinary retention. These medical conditions and medications may affect the function of the bladder itself, the function of the outlet of the bladder, and/or the urethra. Obstruction may be fixed or dynamic . There are also infectious causes and surgical causes of urinary retention.
Common Causes/Risk Factors
Medication-Related Causes
Certain medications can cause urinary retention, especially in men with prostate enlargement. Many of these medications are found in over-the-counter cold and allergy preparations. These drugs include the following:
- Drugs that act to tighten the urinary channel and block the flow of urine include ephedrine , pseudoephedrine , phenylpropanolamine , phenyleprhine , and amphetamines.
- Antihistamines such as diphenhydramine and chlorpheniramine , as well as some older antidepressants, can relax the bladder too much and cause urination problems.
- Beta-adrenergic sympathomimetics, including isoproterenol , terbutaline , and metaproterenol
- Opioid-containing medications
Urinary Retention in Children
Approach To The Patient With Urinary Retention
Possible Etiology of Urinary Retention Based on History and Physical Examination Findings
*Most patients will present with one or more lower urinary tract symptoms. Symptoms include frequency, urgency, nocturia, straining to void, weak urinary stream, hesitancy, sensation of incomplete bladder emptying, and stopping and starting of urinary stream.
Patients with 150 to 200 mL of retained urine may have a percussible or palpable bladder
Information from references 5, 6, 28, and 29.
Possible Etiology of Urinary Retention Based on History and Physical Examination Findings
*Most patients will present with one or more lower urinary tract symptoms. Symptoms include frequency, urgency, nocturia, straining to void, weak urinary stream, hesitancy, sensation of incomplete bladder emptying, and stopping and starting of urinary stream.
Patients with 150 to 200 mL of retained urine may have a percussible or palpable bladder
Diagnostic Testing in Patients with Urinary Retention
note:Imaging studies and diagnostic procedures are guided by the clinical context and suspected diagnoses.
CT = computed tomography MRI = magnetic resonance imaging.
Information from references 5, 6, and 28 through 30.
Diagnostic Testing in Patients with Urinary Retention
note:Imaging studies and diagnostic procedures are guided by the clinical context and suspected diagnoses.
CT = computed tomography MRI = magnetic resonance imaging.
Information from references 5, 6, and 28 through 30.
You May Like: What Do Bladder Spasms Feel Like
How Is It Diagnosed
To diagnose urinary retention, a doctor will first ask about the history of your symptoms and perform a physical exam. The physical will include an examination of your genitals and rectum to look for any symptoms affecting those areas that may also affect the urinary tract.
Some other tests that may be used to confirm a diagnosis
likely be inserted to help quickly drain the urine. Local anesthesia will be used to make sure you dont feel pain or discomfort from the catheter.
If a catheter doesnt work or cant be used because of an injury or other condition, a doctor may insert a suprapubic catheter into the skin above your bladder to drain the urine.
Surgery For Women With Cystocele Or Rectocele
Women may need surgery to lift a fallen bladder or rectum. The most common procedure for cystocele and rectocele repair is for the surgeon to make an incision in the wall of the vagina to find the defect or hole in the membrane-a wall of tissue called fascia-that normally separates the vagina from the other pelvic organs. The surgeon places sutures in the fascia to close up the defect, then closes the incision in the vaginal wall with more stitches, removing any excess tissue. These suturing steps tighten the layers of tissue that separate the organs, creating more support for the pelvic organs.
Don’t Miss: Can Anxiety Cause Bladder Leakage
When A Sling Is Too Tight
Slings can be too tight. This happens around 1-2% of the time. So, not very often but it absolutely happens. If this is the case, I wait 2 weeks and then cut the sling. I wait the 2 weeks because the sling is likely to be scarred in place at that time and will still work if I cut it. So, cutting it loosens it so you can empty your bladder but it still should correct your stress incontinence.
Before surgery, I talk a lot about catheters and maybe needing to have one for 2 weeks. This may seem a little nutty to you, since it only happens 1-2% of the time. But it is an unpleasant surprise. I think it is best to know this MIGHT happen, and then be pleasantly surprised when it does not. Just sayin.
What Is The Urinary Tract
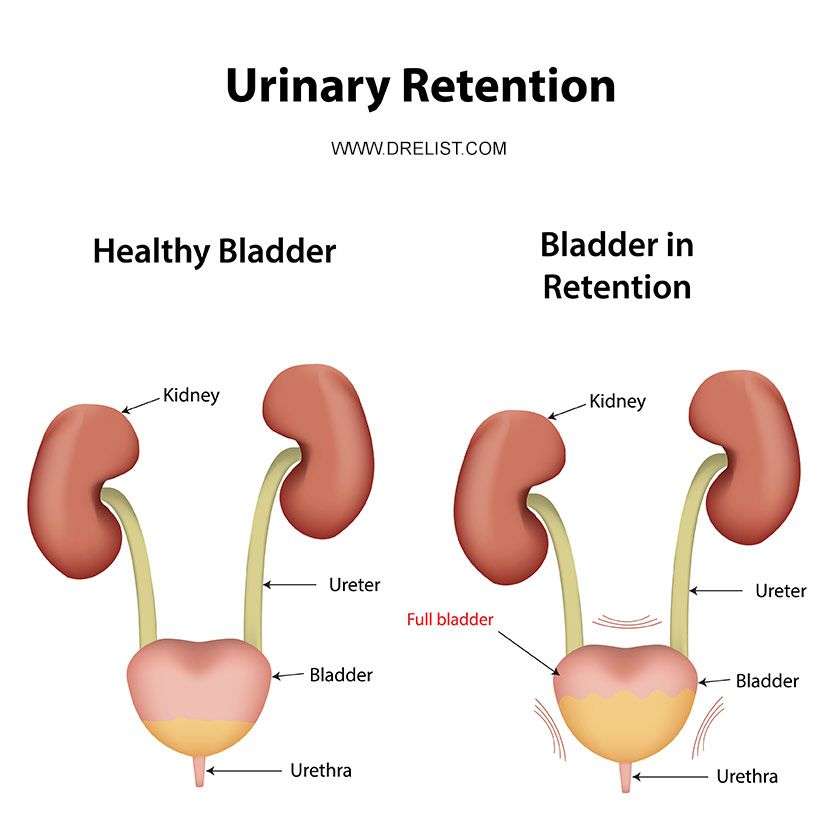
The urinary tract consists of the organs, tubes, and muscles that work together to make, move, store, and release urine. The upper urinary tract includes the kidneys, which filter wastes and extra fluid from the blood, and the ureters, which carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. The lower urinary tract includes the bladder, a balloon-shaped muscle that stores urine, and the urethra, a tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body during urination. If the urinary system is healthy, the bladder can hold up to 16 ounces2 cupsof urine comfortably for 2 to 5 hours.
Muscles called sphincters squeeze shut the tubes from the bladder to help keep urine from leaking. The sphincter muscles close tightly like a rubber band around the opening of the bladder, which leads into the urethra.
Nerves in the bladder tell you when it is time to urinate. As the bladder first fills with urine, you may notice a feeling that you need to go. The sensation to urinate becomes stronger as the bladder continues to fill. As it reaches its limit, nerves from the bladder send a message to the brain that the bladder is full and the urge to empty your bladder intensifies.
Also Check: What Is The Best Medicine For Bladder Control
What Do You Know About Hair Loss
Thirty or more years ago, when I learned to use ergonomics to go to the bathroom, it was so I wouldn’t have to self-catheterize. There was always a risk of getting more infections from self-catheterizing, not because it was unclean, but because it was invasive, often scraping the urethra and causing irritation .
This method was the answer to my prayers. All I wanted was to get a good night’s sleep.
My Own Personal Method
Urination Difficulty At A Glance:
- Having trouble urinating also referred to as voiding difficulty is caused by an underlying mechanical problem with the coordination between the urethra and the bladder muscle that allows urine to freely pass.
- Urination problems include difficulty initiating urination and impaired bladder emptying, as well as urinary incontinence.
- Urine voiding problems in women can be caused by a variety of conditions, including urinary retention, prolapsed bladder, urinary tract infections, and the effects of menopause and pregnancy.
- Symptoms are painful urination, difficulty starting the urine stream, a sense of incomplete bladder voiding, and sometimes an inability to urinatean emergency situation known as acute urinary retention that requires immediate treatment.
- Treatments for voiding problems depend upon the underlying cause, but may include bladder muscle conditioning, medications, implant devices and surgery.
Also Check: New Drug For Overactive Bladder
Catheters Vs Johnny Or Jane Bottles
At some point, many people who aren’t able to go to the bathroom on their own will find the urine just trickled out by itself, leaving them wet. You need to find ways to keep dry. Many patients resign themselves to the fact that they need a catheter in place all the time. Catheters can be intra-urethral or super-pubic .
Some people find that having a catheter in place during a long car ride, plane ride, etc. assisted by a leg or belly bag can be most comfortable and reduce bathroom stops, thus making the driver happy. A Johnny or Jane bottle is also good to keep handy.
As for sleeping, catheters connected to a bed bag , will most certainly eliminate bathroom trips and allow for a full restful night’s sleep.
I use a bed bag every time I get a UTI so that I don’t have to get up and run to the bathroom only to find a few painful drops have eeked out. A catheter is very helpful during treatment of a UTI. I usually use it for two nightsthen, I go back to my ergonomic method above.
Restful sleep is paramount when you are sick like that. You can choose to take the catheter out each morning but it’s best to leave it in for the whole two days/nights.
Put The Lid Down When You Flush
Experts say the water vapor and spray from flushing can reach as high as six feet in the air, contaminating toilet paper, towels, and everything else you are trying to keep clean. Why is that lid up anyway? You don’t need to watch your duty go down the toilet. Only children feel the need to watch. Put the lid down.
Something else to consider if you want to get well and stay well is your storage areas.
If the only storage space for your only cleaning products is in the bathroom, start looking around for another room or closet near the bathroom. Maybe you can store everything under the kitchen sink and only keep one bottle of spray bleach on the toilet tank or on the floor next to the toilet to use after each toilet use.
If you continue to store your cleaning products in the same area as your toilet paper and tissues, you will never get the full benefits of these suggestions.
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Bladder Leakage Naturally