How Is Bladder Cancer Treated
Treatment for bladder cancer will depend on the stage and type of cancer you have. Your provider will talk to you about treatment options and which plan of care is best for you.
Superficial Bladder Cancer
Superficial bladder cancer is bladder cancer that has not invaded into the muscle. It is often treated with surgery and intravesicular therapy.
Surgery
A TURBT is a surgical treatment in which a surgeon removes the bladder tumor using a tool placed into the body through the urethra. The extent of the disease is based mainly on findings during this test. TURBT is the main treatment for superficial disease since all of the tumor is often able to be removed. After a TURBT, you may have intravesicular therapy to prevent the cancer from coming back.
Intravesicular Therapy
Intravesicular therapy is when chemotherapy or immune therapy is injected directly into the bladder. This treatment destroys any remaining cancer cells. Both immunotherapy and chemotherapy medications can be used in intravesicular therapy.
Bacillus Calmette-Guerin is an immunotherapy medication that is used. BCG is a type of virus that works to stimulate the immune system to destroy any cancer cells in the area. You will likely be given this medication multiple times. After treatment, you will have regular cystoscopies to monitor for any reoccurrence or new tumor development.
Muscle Invading Bladder Cancer
Surgery
Chemotherapy
Bladder Preservation Therapy
Radiation and Chemoradiation
Immunotherapy
Survival Rates For Bladder Cancer
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time after they were diagnosed. They cant tell you how long you will live, but they may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is that your treatment will be successful.
Keep in mind that survival rates are estimates and are often based on previous outcomes of large numbers of people who had a specific cancer, but they cant predict what will happen in any particular persons case. These statistics can be confusing and may lead you to have more questions. Talk with your doctor about how these numbers may apply to you, as he or she is familiar with your situation.
What Are Lung Metastases
When cancer develops, it typically forms in one area or organ of the body. This area is known as the primary site. Unlike other cells in the body, cancer cells can break away from the primary site and travel to other parts of the body.
Cancer cells can move in the body through the bloodstream or the lymph system. The lymph system is made up of vessels that carry fluids and support the immune system. When cancer cells travel to other organs in the body, its called metastasis.
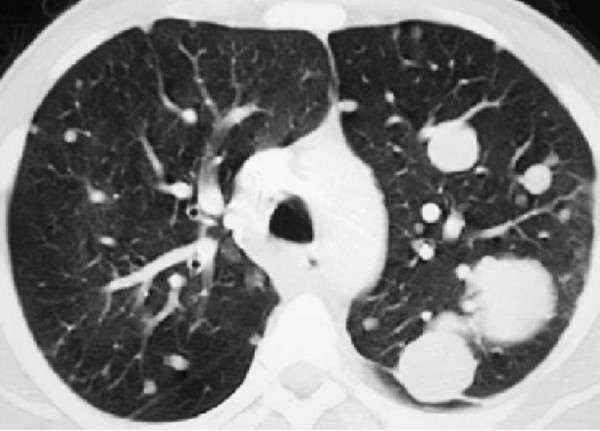
Cancer that metastasizes to the lungs from other areas is a life-threatening condition that develops when cancer in another area of the body spreads to the lung. Cancer that develops at any primary site can form metastatic tumors.
These tumors are capable of spreading to the lungs. Primary tumors that commonly spread to the lungs include:
Don’t Miss: Prostate And Bladder Cancer Together
What Is The Likelihood Of Bladder Cancer Metastasis
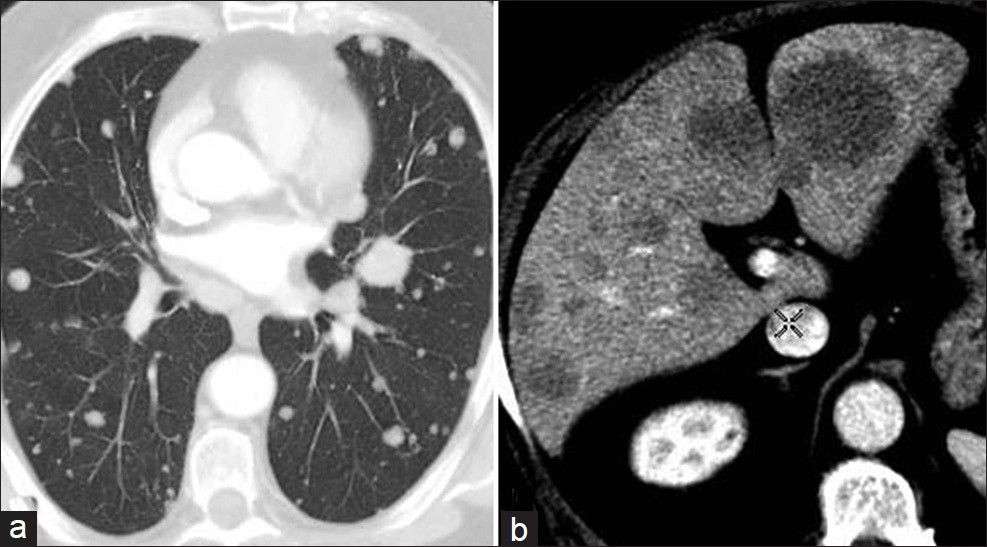
As many as 50% of patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer may have occult metastases that become clinically apparent within 5 years of initial diagnosis and around 5% will have distant metastasis at the time of initial diagnosis. Most patients with overt metastatic disease die within 2 years despite chemotherapy. Approximately 25-30% of patients with only limited regional lymph node metastasis discovered during cystectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection may survive beyond 5 years. Metastasis can occur through lymphatic spread, most commonly affecting the pelvic lymph nodes, or through hematogenous spread to the liver, lung, or bone.
What Is Stage 4 Bladder Cancer
Being diagnosed with bladder cancer can be overwhelming, especially if its stage 4.
Stage 4 bladder cancer is the most advanced stage and carries the worst prognosis. Many cancer treatments will be both difficult and challenging.
However, treatment can reduce or even eliminate your symptoms and help you live a longer, more comfortable life.
Its important to consider the pros and cons of treating stage 4 bladder cancer because treatments come with side effects and risks.
Symptoms of bladder cancer can include:
- blood or blood clots in your urine
- pain or burning during urination
- frequent urination
- needing to urinate at night
- needing to urinate but not being able to
- lower back pain on one side of the body
These symptoms commonly lead to a diagnosis, but they arent unique to stage 4 bladder cancer.
Stage 4 bladder cancer is also called metastatic bladder cancer. This means the cancer has spread outside of the bladder into other parts of the body.
People with metastatic cancer may experience symptoms relating to where the cancer has spread. For example, if a persons bladder cancer has spread to their lungs, they may experience chest pain or increased coughing.
Metastatic bladder cancer is difficult to cure because it has already traveled to other parts of the body. The later youre diagnosed and the farther the cancer has traveled, the less chance that your cancer will be cured.
The 5-year survival rate is the rate of surviving for 5 years after a cancer diagnosis.
You May Like: Uti Or Bladder Infection Treatment
Treating Metastatic Bladder Cancer
Treatment for metastatic bladder cancer is different for each person, depending on your specific situation. Your doctor and care team will discuss different options with you, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of each type of treatment option.
The goals of most types of treatment are to slow down how fast the cancer cells are growing and to shrink the tumor as much as possible. Other important goals of treatment are to help people with bladder cancer live as long as possible and to make sure they have the best possible quality of life. Palliative care can also help relieve symptoms and treatment side effects.4
Changes In Bladder Habits Or Symptoms Of Irritation
Bladder cancer can sometimes cause changes in urination, such as:
- Having to urinate more often than usual
- Pain or burning during urination
- Feeling as if you need to go right away, even when your bladder isn’t full
- Having trouble urinating or having a weak urine stream
- Having to get up to urinate many times during the night
These symptoms are more likely to be caused by a urinary tract infection , bladder stones, an overactive bladder, or an enlarged prostate . Still, its important to have them checked by a doctor so that the cause can be found and treated, if needed.
Read Also: Can You Have A Fever With A Bladder Infection
Case : Pulmonary Tumor Thromboemboli
A 47-year-old male with morbid obesity and hypertension was transferred from an outside institution for elective surgical management of UBC diagnosed through transurethral resection of bladder tumor. His initial course was complicated by hypoxia to 94% with an increased arterial-alveolar gradient, prompting CT angiography of the chest which demonstrated filling defects in multiple left- and right-sided segmental arteries . Anticoagulation was started and an inferior vena cava filter was placed. One week later, the patient underwent radical cystoprostatectomy with neobladder reconstruction and rectosigmoid colon resection as tumor was attached to the descending colon. Pathologic examination of the tumor revealed UBC with sarcomatoid features. His postoperative course was complicated by failure to wean from the ventilator due to persistent hypoxemia despite anticoagulation. The patient and his family eventually elected for comfort measures only and he died shortly thereafter. Major findings at autopsy included extensive tumor within the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneum, diffuse pulmonary metastases, and intravascular tumor thrombi. The IVC filter was also plugged with tumor thrombus, and microscopic examination revealed the tumor to be identical to the previously resected high-grade UBC with sarcomatoid features.
Figure 6:
How Is Metastatic Bladder Cancer Treated
The way that metastatic bladder cancer is treated depends primarily on where the cancer has spread and the type of cells that make up the primary tumor. Its important to remember that when bladder cancer spreads, the secondary tumors are still considered to be bladder cancer not lung cancer, liver cancer or any other type of malignancy. Potential treatment options may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy and clinical trials.
At Moffitt Cancer Center, weve treated many patients with metastatic bladder cancer, creating tailored treatment plans for every single one. To help ease the burdens of treatment, we also offer comprehensive supportive care services for patients and their caregivers.
Read Also: Clear A Bladder Infection Without Antibiotics
What Is The Prognosis For Metastatic Bladder Cancer
Most people with metastatic bladder cancer cannot be cured. The 5-year relative survival rates for people with distant bladder cancer, meaning the cancer has spread to distant parts of the body such as the lungs, liver, or bones, is about 5 percent. This means that people with metastatic bladder cancer are, on average, about 5 percent as likely as people who do not have this form of cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.1,5
However, there are treatments available that can help some people with metastatic bladder cancer to live longer and improve their quality of life.1
How Does Transitional Cell Carcinoma Of The Bladder Spread
Transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder tends to remain superficial however, in 5% to 20% of cases, it progresses to muscle invasion and, more rarely, can metastasize. TCC of the bladder primarily spreads via regional lymphatics. The most common sites of distant metastases of TCC are the liver, lung, mediastinum and bone.
Recommended Reading: Is Pumpkin Seed Oil Good For Overactive Bladder
Causes Of Bladder Cancer
Most cases of bladder cancer appear to be caused by exposure to harmful substances, which lead to abnormal changes in the bladder’s cells over many years.
Tobacco smoke is a common cause and it’s estimated that more than 1 in 3 cases of bladder cancer are caused by smoking.
Contact with certain chemicals previously used in manufacturing is also known to cause bladder cancer. However, these substances have since been banned.
Read more about the causes of bladder cancer.
Treatment For Metastatic Cancer
There are treatments for most types of metastatic cancer. Often, the goal of treating metastatic cancer is to control it by stopping or slowing its growth. Some people can live for years with metastatic cancer that is well controlled. Other treatments may improve the quality of life by relieving symptoms. This type of care is called palliative care. It can be given at any point during treatment for cancer.
The treatment that you may have depends on your type of primary cancer, where it has spread, treatments youve had in the past, and your general health. To learn about treatment options, including clinical trials, find your type of cancer among the PDQ® Cancer Information Summaries for Adult Treatment and Pediatric Treatment.
Don’t Miss: Will Cranberry Pills Help An Overactive Bladder
Types Of Bladder Cancer
Once diagnosed, bladder cancer can be classified by how far it has spread.
If the cancerous cells are contained inside the lining of the bladder, doctors describe it as non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer . This is the most common type of bladder cancer.
When the cancerous cells spread beyond the lining, into the surrounding bladder muscle, it’s referred to as muscle-invasive bladder cancer . This is less common, but has a higher chance of spreading to other parts of the body.
If bladder cancer has spread to other parts of the body, it’s known as advanced or metastatic bladder cancer.
Read more about diagnosing bladder cancer.
Second Cancers After Bladder Cancer
Cancer survivors can be affected by a number of health problems, but often a major concern is facing cancer again. If a cancer comes back after treatment it’s called a recurrence. But some cancer survivors may develop a new, unrelated cancer later. This is called a second cancer.
Being treated for bladder cancer doesnt mean you cant get another cancer. Survivors of bladder cancer can get any type of second cancer, but they have an increased risk these cancers compared to the general population:
- A second bladder cancer
- Cancer of the renal pelvis/ureter
Many of these cancers have been clearly linked to smoking, which is also a major risk factor for bladder cancer. Talk to your doctor if you need help to quit smoking.
Also Check: Best Supplements For Bladder Infection
Prognosis And Survival Rates For Bladder Cancer
When someone is diagnosed with bladder cancer, their doctor will give them a prognosis. A prognosis is the doctors opinion of how likely the cancer will spread and the chances of getting better. A prognosis depends on the type and stage of cancer, as well as the persons age and general health.
Bladder cancer can usually be effectively treated if it is found before it spreads outside the bladder.
If you have bladder cancer, your doctor will talk to you about your individual situation when working out your prognosis. Every persons experience is different, and there is support available to you.
What Is Bladder Cancer
The bladder, a hollow organ in the lower part of the abdomen, serves as a reservoir for urine until it is discharged out of the body through the urethra.
There are different types of bladder cancer. The cancer cell type can be transitional cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma or adenocarcinomaeach named for the types of cells that line the wall of the bladder where the cancer originates.
- Most bladder cancers start from the transitional cells, which occupy the innermost lining of the bladder wall. The cancers, which originate in these cells lining the bladder can, in some instances, invade into the deeper layers of the bladder , the thick muscle layer of the bladder, or through the bladder wall into the fatty tissues that surround the bladder.
- Squamous cells are thin flat cells that line the urethra and can form in the bladder after long bouts of bladder inflammation or irritation. Squamous cell carcinoma makes up about 5 percent of bladder cancers.
- Adenocarcinoma is a very rare type of bladder cancer that begins in glandular cells in the lining of the bladder. Only 1 percent to 2 percent of bladder cancers are adenocarcinoma.
You May Like: Can Clindamycin Treat Bladder Infection
What Tests Will I Have If My Doctor Suspects Bladder Cancer Or Another Urinary Problem
Your doctor will want to analyze your urine to determine if an infection could be a cause of your symptoms. A microscopic examination of the urine, called cytology, will look for cancer cells.
A cystoscopy is the main procedure to identify and diagnose bladder cancer. In this procedure, a lighted telescope is inserted into your bladder from the urethra to view the inside of the bladder and, when done under anesthesia, take tissue samples , which are later examined under a microscope for signs of cancer. When this procedure is done in the doctors office, local anesthesia gel is placed into the urethra prior to the procedure to minimize the discomfort.
If the diagnosis of bladder cancer is made, then the next step is to remove the tumor for detailed staging and diagnosis.
Transurethral resection is a procedure done under general or spinal anesthesia in the operating room. A telescope is inserted into the bladder and the tumor is removed by scraping it from the bladder wall , using a special cystoscope . This procedure is diagnostic as well as therapeutic.
This often can be done as an outpatient procedure, with patients discharged from hospital the same day. After removal, the tumor is analyzed by a pathologist, who will determine the type of tumor, the tumor grade and the depth of invasion. The purpose of the procedure is to remove the tumor and obtain important staging information .
How Cancer Spreads
While normal cells can be thought of as being “sticky,” since they have adhesion molecules that keep them in together in place, cancer cells are different. They do not make these adhesion molecules, allowing them to break free and travel as they please.
When traveling, cancer cells may extend directly to the lungs, such as cancers that begin in the esophagus or chest wall. But most cancer cells travel indirectly, through three possible ways:
- Bloodstream : Cancer cells may “leak” into small blood vessels near the tumors and then be carried to the lungs via the pulmonary arteries.
- Lymphatics: Tumor cells may leak into the small lymphatic vessels and travel along the lymph pathways .
- Pleural spread and airway spread: The pleura refers to the membranes surrounding the lung. This type of spread is often limited to lung tumors and is much less common.
You May Like: Can You Die From Bladder Cancer
What Is A 5
A relative survival rate compares people with the same type and stage of bladder cancer to people in the overall population. For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for a specific stage of bladder cancer is 90%, it means that people who have that cancer are, on average, about 90% as likely as people who dont have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
Living With Advanced Cancer
Advanced cancer usually means cancer that is unlikely to be cured. Some people can live for many months or years with advanced cancer. During this time palliative care services can help.
Most people continue to have treatment for advanced cancer as part of palliative care, as it helps manage the cancer and improve their day-to-day lives. Many people think that palliative care is for people who are dying but palliative care is for any stage of advanced cancer. There are doctors, nurses and other people who specialise in palliative care.
Treatment may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy or another type of treatment. It can help in these ways:
- slow down how fast the cancer is growing
- shrink the cancer
- help you to live more comfortably by managing symptoms, like pain.
Treatment depends on:
- how far it has spread
- your general health
Read Also: What Medication Is Good For Overactive Bladder