Prevention Of Urinary Tract Infection
There are several steps you can take to reduce your risk of getting a UTI:
- Drink plenty of water and other liquids to help flush out bacteria.
- Urinate frequently, or about every two to three hours.
- For women: Wipe from front to back after urinating or having a bowel movement.
- Urinate before and soon after having sexual intercourse.
- Avoid synthetic underwear, tight pants, and lingering in wet gym clothes or a bathing suit. Though none of this can cause a UTI, these habits can increase the spread of bacteria.
- Avoid vaginal deodorants, douches, powders, and other potentially irritating feminine products.
- Use a method of birth control other than a diaphragm, spermicide, or unlubricated condoms.
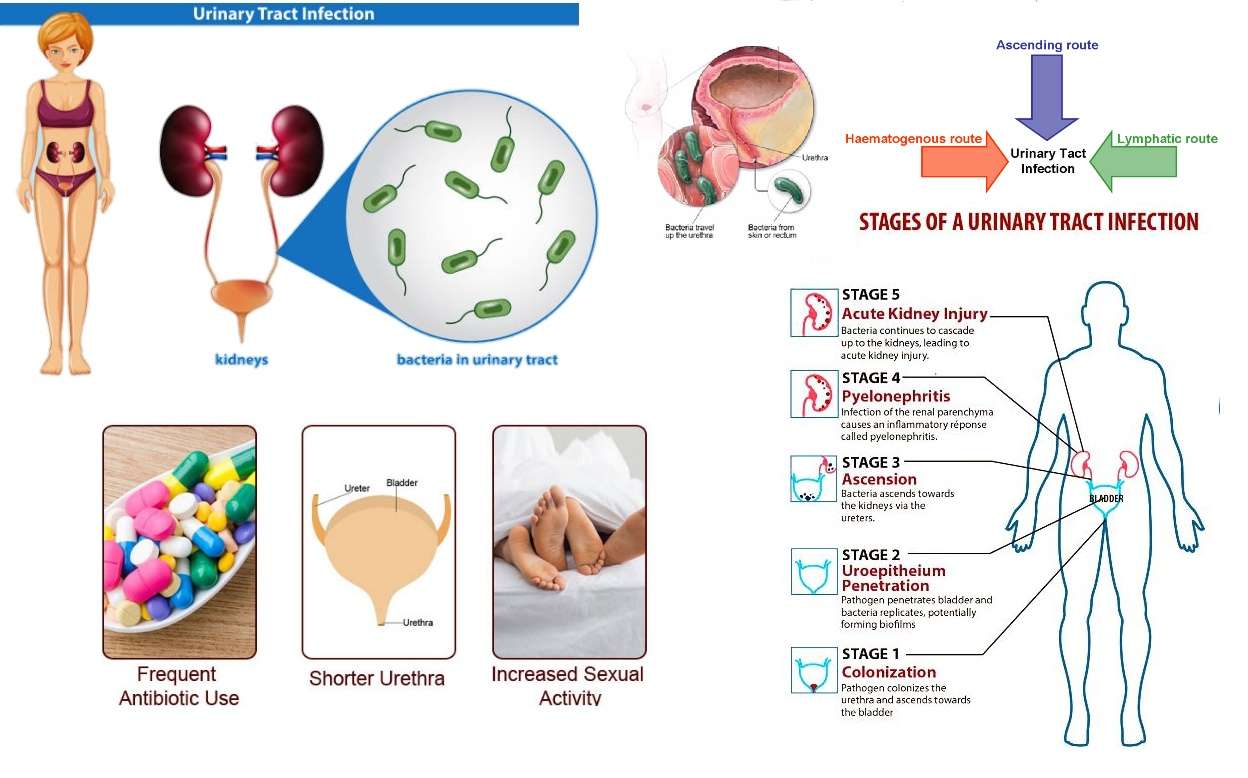
What Causes A Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infections are caused by microorganisms usually bacteria that enter the urethra and bladder, causing inflammation and infection. Though a UTI most commonly happens in the urethra and bladder, bacteria can also travel up the ureters and infect your kidneys.
More than 90% of bladder infection cases are caused by E. coli, a bacterium normally found in the intestines.
Favorite Sites To Find Docs
SWIU is all about supporting women urologists and the urologic issues that impact women. One of our favorite SWIU perks is their searchable database for prospective patients to find a local female urologist.
An excellent source for overall urinary health info, UCF also offers a tool to help would-be patients find a urologist near them. You can search by zip code, distance, and through eight urinary specialties, including pediatric urology.
Don’t Miss: Bladder Cancer Recurrence After 5 Years
Recommendations For Uti Prevention
To prevent urinary tract infection, some research suggests that the following may be helpful:
- Increasing fluid intake: The doctor may recommend increased fluid intake to help flush bacteria out of the urinary system.
- Drinking cranberry juice: Drinking 8 ounces of cranberry juice a day may help prevent recurrent UTIs. People who take blood thinners such as warfarin or are prone to kidney stones should check with a physician before trying this approach.
- Proper hygiene: Regular bathing keeps the genital area bacteria free, and women should wipe front-to-back after using the bathroom so as to avoid introducing bacteria into the urethra.
Other Ways To Prevent Recurring Utis
If you have more than 3 UTIs in 1 year, or 2 UTIs in 6 months, there are other things that may help prevent UTIs.
There is some evidence that women under 65 years old who keep getting UTIs may find it helpful to take:
- a supplement called D-mannose this is not recommended for pregnant women
- cranberry products, such as juice or tablets
Speak to your doctor before taking any of these during pregnancy.
Be aware that D-mannose and cranberry products can contain a lot of sugar.
Page last reviewed: 18 November 2020 Next review due: 18 November 2023
Don’t Miss: How Do They Diagnose Bladder Cancer
Urinary Tract Infection Treatment
If you are a healthy adult man or a woman who is not pregnant, a few days of antibiotic pills will usually cure your urinary tract infection. If you are pregnant, your doctor will prescribe a medicine that is safe for you and the baby. Usually, symptoms of the infection go away 1 to 2 days after you start taking the medicine. Its important that you follow your doctors instructions for taking the medicine, even if you start to feel better. Skipping pills could make the treatment less effective.
Your doctor may also suggest a medicine to numb your urinary tract and make you feel better while the antibiotic starts to work. The medicine makes your urine turn bright orange, so dont be alarmed by the color when you urinate.
When To Get Medical Advice
It’s a good idea to see your GP if you think you might have a UTI, particularly if:
- you have symptoms of an upper UTI
- the symptoms are severe or getting worse
- the symptoms haven’t started to improve after a few days
- you get UTIs frequently
Your GP can rule out other possible causes of your symptoms by testing a sample of your urine and can prescribe antibiotics if you do have an infection.
Antibiotics are usually recommended because untreated UTIs can potentially cause serious problems if they’re allowed to spread.
Also Check: I Have A Weak Bladder Help
Prevention Of Catheter Associated Uti
Catheter associated UTI is the most common health care associated infection throughout the world and is common in long-term care facilities. Urinary catheterization should be avoided unless there is a clear clinical indication. Catheters should be avoided where possible for the management of incontinence. Staff should also be trained on indications for catheterization and written protocols should be put in place., Catheters should also be removed the moment that they are no longer required.
Alternatives to indwelling urethral catheters should be considered. Condom catheters are associated with a lower incidence of bacteriuria, however their use is sometimes difficult in confused patients. A Cochrane review on short-term urinary catheterization in adults found that suprapubic catheterization was associated with less bacteriuria than urethral catheterization. Suprapubic catheterization does carry a small risk of visceral injury on insertion through the abdominal wall. Intermittent catheterization was also associated with a lower risk of bacteriuria when compared to indwelling catheterization in this review, however studies included were mainly in an elective orthopedic setting.
Guidelines suggest that antibiotic prophylaxis should not be used to prevent catheter associated UTI in catheterized patients. Although prophylaxis may decrease the incidence of asymptomatic bacteriuria in catheterized patients, it increases the risk of antimicrobial resistance.
Urinary Tract Infections During Pregnancy: Symptoms Treatment And Common Questions
In addition, as the uterus grows throughout pregnancy, it can put pressure on the bladder, making it more difficult to empty completely.
Pregnancy can also make a UTI more difficult to treat, which can have serious consequences, including pyelonephritis preterm labor low birth weight and .
A urinalysis and a urine culture are routinely performed at an initial prenatal visit to screen for UTIs, but if you’re pregnant and suspect you may have an infection, seek medical attention quickly.
Don’t Miss: Reasons For Bladder Control Loss
Can Cranberries Prevent Or Treat Urinary Tract Infection
Amongst the different techniques used to prevent UTI, people have been increasingly harping on the importance and effectiveness of cranberries. The idea has been increasingly circulating in the medical circles that consumption of cranberry products like juices, pills, etc. can help to prevent UTI in the lower urinary tract. A lot of investigation has been done on this domain and yet a lot of research is being conducted so that something more substantial can be found. However, as of now, there are mixed reactions to the claim.
Causes Of Urinary Tract Infections
UTIs are usually caused by bacteria from poo entering the urinary tract.
The bacteria enter through the tube that carries pee out of the body .
Women have a shorter urethra than men. This means bacteria are more likely to reach the bladder or kidneys and cause an infection.
Things that increase the risk of bacteria getting into the bladder include:
- having sex
-
do not use scented soap
-
do not hold your pee in if you feel the urge to go
-
do not rush when going for a pee try to fully empty your bladder
-
do not wear tight, synthetic underwear, such as nylon
-
do not drink lots of alcoholic drinks, as they may irritate your bladder
-
do not have lots of sugary food or drinks, as they may encourage bacteria to grow
-
do not use condoms or diaphragms with spermicidal lube on them try non-spermicidal lube or a different type of contraception
Read Also: Botox Procedure For Overactive Bladder
What If The Infection Does Not Clear Up With Treatment
Most infections clear up with treatment. However, if an infection does not clear up, or if you have repeated infections, you may be given some special tests such as:
-
a type of x-ray called an intravenous pyleogram , which involves injecting a dye into a vein and taking pictures of your kidney and bladder
-
an ultrasound exam, which gives a picture of your kidneys and bladder using sound waves
-
a cytoscopic exam, which uses a hollow tube with special lenses to look inside the bladder.
The Definition Of A Positive Urine Culture
The definition of a positive urine culture depends on the presence of symptoms and the method of urinary specimen collection, as follows and as depicted in . For the diagnosis of cystitis or pyelonephritis in women, a midstream urine count 105 cfu/mL is considered diagnostic of UTI. However, in diabetic women with good metabolic control and without long-term complications who present with acute uncomplicated cystitis, quantitative counts < 105 colony-forming units /mL are isolated from 20%25% of premenopausal women and about 10% of postmenopausal women. Only 5% of patients with acute pyelonephritis have lower quantitative counts isolated. Lower bacterial counts are more often encountered in patients already on antimicrobials and are thought to result from impaired renal concentrating ability or diuresis, which limits the dwell time of urine in the bladder., Thus, in symptomatic women with pyuria and lower midstream urine counts , a diagnosis of UTI should be suspected.
Flow chart for the diagnosis of urinary tract infection in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Abbreviations: cfu, colony-forming units UTI, urinary tract infection.
For the diagnosis of UTI in men, a midstream urine colony count of 104 cfu/mL is indicative. However, when coli-form bacteria are isolated, lower colony counts might also represent significant bacteriuria.
Recommended Reading: How To Prevent Bladder Infections In The Elderly
The Best Urinary Tract Infection Treatments
Choosing urinary tract infection treatments will be easier and quicker with this article. With our guide, you can be sure to find exactly what you are looking for. You will have a seamless shopping experience!
Disclaimer: We are using Amazon affiliate Product Advertising API to fetch products from Amazon, include: price, content, image, logo, brand, feature of products which are trademarks of Amazon.com. So, when you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no extra cost to you.. Read more.
| # |
|---|
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- Do I need any tests, such as urinalysis?
- What is the likely cause of my urinary tract infection ?
- Do I need medicine? How should I take it?
- What are the possible side effects of the medicine?
- When should I expect relief from my symptoms?
- What symptoms would indicate that my infection is getting worse? What should I do if I experience these symptoms?
- I get UTIs a lot. What can I do to prevent them?
- Do I need preventive antibiotics? If so, should I be concerned about antibiotic resistance?
- My child gets UTIs a lot. Could an anatomical problem be causing his or her UTIs?
Recommended Reading: Lower Back Pain Bladder Cancer
What Are The Treatment Procedures For Male Uti
As a first-line treatment for UTI, your doctor will prescribe you a course of antibiotics to kill the bacteria and ward off other symptoms. If there are no signs of complications, the treatment process may take from three to seven days.
However, you may require more intensive treatment if your doctor suspects serious complications. This treatment aims to reduce the risk of spreading the infection from your kidneys or your upper urinary tract. Each treatment depends on the result of the diagnosis regarding the cause of your condition. The treatment duration can also vary from a minimum of seven days and can last for up to six months.
If there are positive signs of kidney or bladder infection, surgical procedures will take place. It involves either draining or complete removal of the inflamed tissues on the affected areas.
Bladder Infection Vs Other Utis
The symptoms of a bladder infection, which people may refer to as cystitis, are very similar to those of UTIs in other parts of the urinary tract. As a result, it may be difficult to tell which part of the urinary tract has an infection based on the symptoms alone.
An infection in the urethra may cause pain and burning when urinating and discharge from the urethra, but bladder pain is not a symptom.
An infection that has spread to the kidneys will cause the most severe symptoms. A person with a kidney infection may notice the same symptoms as those of a bladder infection, plus fever, chills, and back pain.
Treatment is usually the same for all types of UTI, except for kidney infections. Treating a kidney infection may require a person to stay in the hospital.
Kidney infections can cause serious health conditions, so anyone with these symptoms should seek treatment as early as possible.
UTIs occur when harmful bacteria enter the urinary tract and start spreading.
Anyone can get a urinary tract infection, but certain risk factors can elevate the chances. These include:
- Biological sex: Females have a
Also Check: Bladder Control Problems At Night
About Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are common infections that can affect the bladder, the kidneys and the tubes connected to them.
Anyone can get them, but they’re particularly common in women. Some women experience them regularly .
UTIs can be painful and uncomfortable, but usually pass within a few days and can be easily treated with antibiotics.
This page is about UTIs in adults. There is a separate article about UTIs in children.
This page covers:
I’m Contemplating Buying A Urinary Tract Infection Treatments What Do I Need To Consider
I’m buying a urinary tract infection treatments for the first time. What are the best brands and what should I consider? Thanks for providing me with the value of a first urinary tract infection treatments, too!
Considerations should be made before purchasing a urinary tract infection treatments. It’s a good idea to do some research online before choosing urinary tract infection treatmentss, even though you’re asking here. You can find reasonably detailed information about your request here.
Read Also: Best Over The Counter Medication For Bladder Infection
Research And Statistics: Who Gets Urinary Tract Infections
In the United States, UTIs result in about 10 million doctor’s office visits annually. People of any age can get a UTI, though most commonly it affects women. According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 40 to 60 percent of women develop a UTI during their lives.
Twelve percent of men will have symptoms of at least one UTI during their lives, per the American Urological Association. While UTIs are uncommon in young men, the risk of infection increases with age, especially in men over 50.
Women are at greater risk of urinary tract infections for anatomical reasons: Women have a shorter urethra than men and their urethra is closer to the anus, which means the bacteria that live there dont have to travel far to infect the bladder.
In children, UTIs are common and also occur more frequently in girls than boys. About 3 percent of girls and 1 percent of boys will have a UTI by the time they’re 11 years old.
Uncomplicated Cystitis In Nonpregnant Patients

Uncomplicated cystitis occurs in patients who have a normal, unobstructed genitourinary tract who have no history of recent instrumentation and whose symptoms are confined to the lower urinary tract. Uncomplicated cystitis is most common in young, sexually active women. Patients usually present with dysuria, urinary frequency, urinary urgency, and/or suprapubic pain. Treatment regimens for uncomplicated cystitis in nonpregnant women are provided in Table 1, below.
References
Gupta K, Hooton TM, Naber KG, et al. International clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis in women: A 2010 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Clin Infect Dis. 2011 Mar. 52:e103-20. . .
Wagenlehner FM, Schmiemann G, Hoyme U, Fünfstück R, Hummers-Pradier E, Kaase M, et al. . Urologe A. 2011 Feb. 50:153-69. . .
Abrahamian FM, Moran GJ, Talan DA. Urinary tract infections in the emergency department. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2008 Mar. 22:73-87, vi. .
Little P, Turner S, Rumsby K, Warner G, Moore M, Lowes JA, et al. Dipsticks and diagnostic algorithms in urinary tract infection: development and validation, randomised trial, economic analysis, observational cohort and qualitative study. Health Technol Assess. 2009 Mar. 13:iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-73. .
Foxman B. The epidemiology of urinary tract infection. Nat Rev Urol. 2010 Dec. 7:653-60. .
Recommended Reading: Loss Of Bladder Control When Coughing
How Can I Prevent Male Urinary Tract Infection
You cannot prevent all UTIs, but it is possible to make its development less likely. Please take note of the following preventive measures to avoid the risk of acquiring the infection.
- Do not hold your urine. It is necessary to urinate as soon as you feel the need to go to the bathroom. Holding your urine can initiate the growth of bacteria and multiply as long as you keep your urine.
- Keep your genitals clean. Carefully washing your genitals is necessary to avoid bacterial growth. If not circumcised, it is crucial to clean the area beneath the foreskin.
- Wash before and after sex. Cleaning your genitals before and after having intercourse can help remove any bacteria that is present. If possible, urinating after sex also helps to flush out any bacteria you might have acquired during the intercourse.
- Practice safe sex. Wearing condoms is also necessary to protect you against the transmission of bacteria.
- Treat prostate problems and bladder infections. These are only some of the underlying issues that may lead to the formation of UTIs. It is essential to talk to your doctor about it to prevent complications.