How Is Overactive Bladder Diagnosed
In most cases OAB can be diagnosed by history and physical exam and a urine analysis to rule out infection or blood in the urine. An abnormal urine analysis may prompt treatment or further testing . Sometime you doctor will check to see if your bladder is emptying well. This can be done with a small ultrasound or with a catheter). Many times, treatment can be recommended based on the information obtained from these simple things.
In some cases, a bladder diary may be recommended to help understand the severity of the condition. A bladder diary is a record kept by the patient that includes fluid intake, number or urinations, and the amount of urine with each urination.
In more complex cases further testing may be done to get a better understanding of the function and anatomy of the lower urinary tract. These tests may include:
What Can Be Done For Overactive Bladder
When doctors do a full examination, only about 8 percent of patients are diagnosed with overactive bladder, but that still means that the condition is a problem for tens of millions of people. It’s relatively easy just to pop a pill so you won’t go to the bathroom as often, but medication is just one of several options.
Surgery Is A Last Resort For Restoring Proper Bladder Function
If lifestyle measures, drug treatments, Botox, and neuromodulation therapy are all ineffective at relieving your symptoms, your doctor may consider more drastic surgical treatments for overactive bladder.
These surgical treatments are usually reserved for people with severe symptoms. At this point, two main surgical options are available:
Surgery to increase bladder capacity Surgically increasing the size of your bladder may help relieve pressure and improve its ability to store urine.
In this procedure, your doctor removes pieces of your bowel and uses them to replace a portion of your bladder.
If you have this surgery, you may need to use a catheter intermittently to urinate for the rest of your life.
Bladder removal As a last resort, your doctor may remove your bladder. A replacement bladder, called a neobladder, may be surgically constructed, or your urine may be routed to the outside of your body through a hole in your skin called a stoma.
If you have a stoma following this surgery, youll wear a bag or pouch on your skin to collect your urine.
Don’t Miss: Unable To Control Bowels And Bladder
Pelvic Floor Exercises Can Help Immensely
You cant see your pelvic floor muscles however, just like other muscles in your body they lose their strength if they are not put to use.
Pelvic floor exercises help strengthen the pelvic floor when done consistently at least twice a day. How are they done?
- Imagine you are holding back gas or urine.
- Squeeze and lift the rectal area without tightening your buttocks or belly. Try and hold it for a count of three before relaxing. Repeat this cycle 10 times. Do 10 sets of Kegel exercises, at least 3 times a day.
- Increase your contractions as your doctor recommends.
- Do not hold your breath when you do Kegel exercises. Keep your stomach, back, and leg muscles relaxed.
- Don’t use Kegel exercises to start and stop your urine stream which can lead to incomplete emptying of the bladder and an increased risk of a urinary tract infection.
Review our information about Kegel exercises for both women and men to learn more about the techniques.
What To Expect From Your Doctor
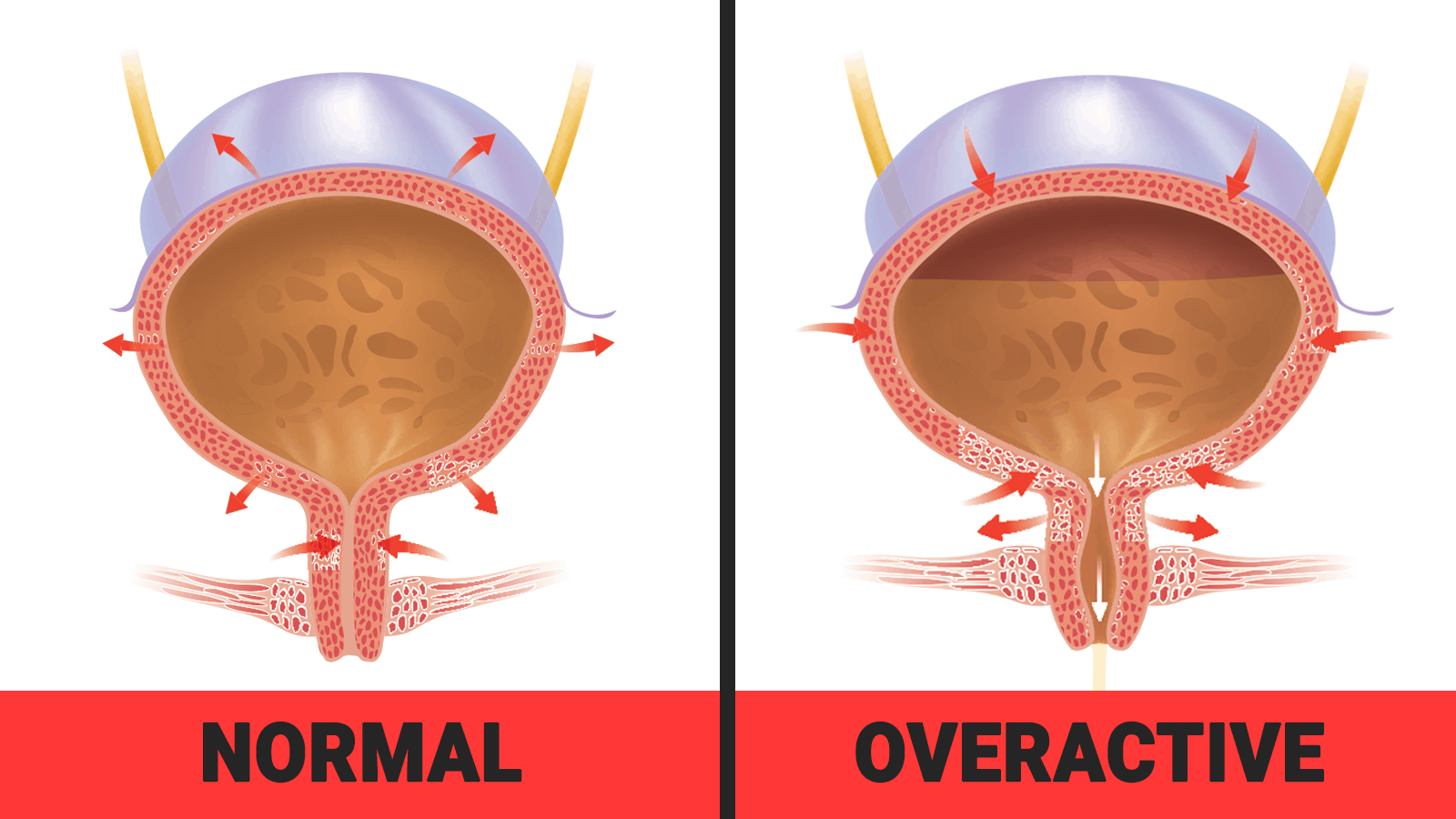
In terms of an assessment, your nurse or doctor will ask you about your general health and in particular, about your OAB problem. You may be examined orally and internally, and you might be asked to give a urine sample to see if you have any obvious problems.
As part of your treatment programme, you may be asked to keep a bladder diary for roughly 3 days, which typically involves making a record of the time of each time you pass urine and how much urine was passed.
You may also be asked to take a flow test, and in some cases a post-flow ultrasound test. This involves using a special machine which checks whether you completely empty your bladder and also measures how strong your flow is.
Here is a short list of possible questions your doctor may ask and the tests they may ask you to complete:
- An overview of your medical history.
- A physical examination, which could include a rectal exam and a pelvic exam in women.
Also Check: What Were Your Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
Try To Avoid Caffeine Carbonated Drinks Sugar Alcohol And Spicy Or Acidic Foods
- Caffeine is a diuretic which makes you need to use the bathroom more often.
- Carbonated drinks and sugar are thought to stimulate the bladder.
- Alcohol switches off the ability of your body to concentrate urine. This means you tend to urinate more dilute, watery urine, which dehydrates you. Since you are dehydrated, you may drink more.
- Acidic or spicy food may aggravate your overactive bladder and worsen your symptoms. Certain acidic fruit and juices like orange, grapefruit, lemon and lime can aggravate your bladder, too.
Overactive Bladder Vs Urinary Incontinence
Overactive Bladder
- Condition in which the bladder can no longer hold urine normally.
- Often feel a sudden urge to urinate or experience an accident.
- Defining symptom is urgency, or the inability to postpone urination.
- OAB is typically a chronic problem
- Often requires strengthening of pelvic floor muscles to get rid of symptoms like urinary incontinence.
- Symptoms including urinary incontinence are ongoing.
- Bladder muscle problems at the root of it.
- Can result from regularly consuming alcohol and caffeine in large quantities.
- Serious health conditions can lead to OAB including a stroke, diabetes, kidney disease, multiple sclerosis , or Parkinsons disease.
Urinary Incontinence
- Is when you lose control of your bladder.
- Isnt a condition its a symptom.
- Is a symptom of OAB.
- Can be caused by a loss or weakening of control over the urinary sphincter.
- Can be a sign of something simple like a singular occasion of too much fluid consumption, a temporary problem.
- Is a common symptom of a UTI along with a burning sensation during urination and/or blood in the urine.
Read Also: My Bladder Does Not Empty All The Way
What Are The Symptoms Of Overactive Bladder Syndrome
The symptoms of OAB syndrome include:
- Urgency:
- This means that you have a sudden urgent desire to pass urine. You are not able to put off going to the toilet.
- Latch key urgency is the name given to the urgent need you might feel to pass urine as soon as you get home and put your key in the door.
- Frequency:
- This means going to the toilet more often than normal – usually more than eight times a day. In many cases it is a lot more than eight times a day.
- Nocturia:
You can read more about other urinary symptoms and their causes in the two separate leaflets called Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Men and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Women .
Filling out a bladder diary will help your doctor work out which treatments would be best for you. Ideally, this should include details of your symptoms, what you ate and drank and your activities. It is best to complete the diary for at least three days and cover variations in your usual activities, such as both working and leisure days.
Seven Effective Treatments For Overactive Bladder
Overactive bladder occurs when sudden or frequent urges to urinate become hard to control, and can often lead to leakage .
In order to best treat overactive bladder, a urologist must pinpoint the underlying cause. Treatment will depend on symptom severity and the degree to which they impact someone’s quality of life. In general, there are three approaches to treatment: medication, behavioral interventions, and surgery.
Read Also: Is Epsom Salt Good For Bladder Infections
Absorbency Products Can Help
No matter how fast you can run, sometimes that bathroom is just a little bit too far in the distance. Dont let yourself get caught in an embarrassing situation There is a wide range of products available that are discreet and comfortable.
Incontinence products excel in their absorbency and wont leak or become lumpy when they get wet. They help control odor and minimize contact between urine and your skin, preventing the development of a rash or other irritation.
Many incontinence products are available, from discrete pads with little bulk that can be slipped into underwear, to disposable adult-sized underwear with in-built absorbency and easy-tear sides. Gender-specific products account for the different requirements of men and women, and there are many reusable and washable options available.
Common brands include Attends, Because, Tena, Tranquility, Depend, Prevail and Poise.
Losing Weight May Help To Improve Your Bladder Control
Excess weight puts extra stress on your pelvic floor muscles and contributes to an overactive bladder and loss of bladder control. If you can lose even a small amount of weight, it will help with bladder control.
The best weight loss plans are always those that set realistic goals combined with healthy eating habits and physical activity. Fad diets, although often successful short-term, rarely achieve sustainable weight loss, because once you tire of the diet, you often revert to ingrained unhealthy eating habits.
Check out our Obesity and Weight Loss guide for more information.
Also Check: How Do You Know If You Have Bladder Leakage
Pelvic Floor Muscle Training
Your pelvic floor muscles surround the bladder and urethra and control the flow of urine as you pee.
Weak or damaged pelvic floor muscles can cause urinary incontinence, so exercising these muscles is often recommended.
A GP may refer you to a specialist to start a programme of pelvic floor muscle training.
The specialist will assess whether you’re able to squeeze your pelvic floor muscles and by how much.
If you can contract your pelvic floor muscles, you’ll be given an exercise programme based on your assessment.
Your programme should include a minimum of 8 muscle contractions at least 3 times a day and last for at least 3 months. If the exercises are helping after this time, you can keep on doing them.
Research has shown that pelvic floor muscle training can benefit everyone with urinary incontinence.
Find out more about pelvic floor exercises.
Surgery For Overactive Bladder
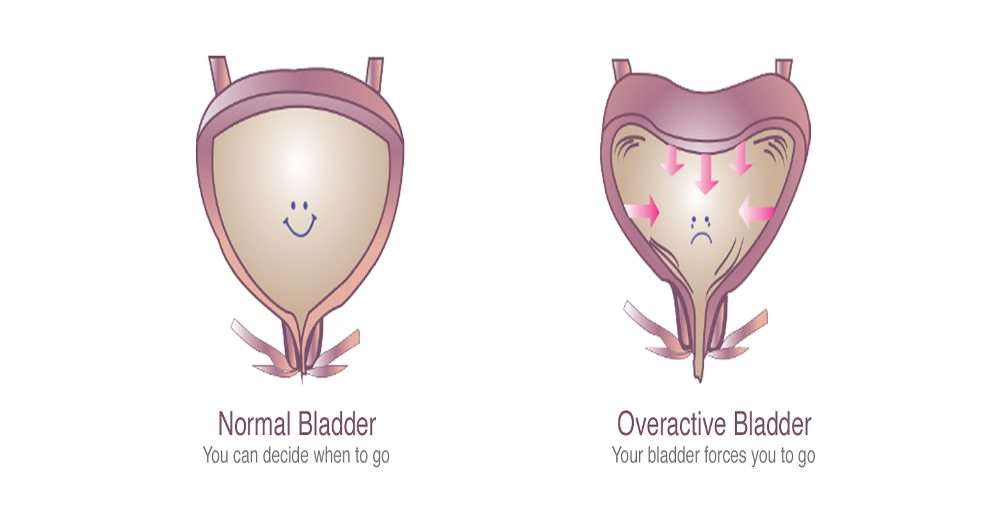
Overactive Bladder at its best can be annoying. The constant running to the bathroom can be frustrating to say the least. But at its worst, OAB can be debilitating. Those with severe OAB make multiple trips to the bathroom a day and even night, and many times may have embarrassing accidents too. It can cause anxiety in social situations, limit interaction with friends and family, and can even negatively affect a persons work. If you think youve tried everything and it hasnt worked for you, surgery may be an option.
Surgery is typically a last resort for most people and should be considered only after more conservative options, such as behavioral modifications, medication or even advanced therapies like Sacral Neuromodulation have failed. The surgeries listed below are often done on women who no longer wish to have children, as childbirth can often remove many of the benefits of surgery.
Read Also: Does Bladder Cancer Feel Like A Uti
What Is Overactive Bladder
Overactive Bladder, or OAB, is the frequent and urgent need to empty your bladder. Also sometimes called spastic bladder or irritable bladder, OAB affects an estimated 33 million people in the USA alone. And half of the people with Overactive Bladder are struggling with Urgency Urinary Incontinence , when leakage actually occurs.
Overactive bladder can be a nuisance at best, and debilitating at worst. Its frustrating to constantly be running to the bathroom, and can cause anxiety, shame and even depression when its is also accompanied by urinary incontinence.
Contrary to what many people think, overactive bladder is NOT a normal part of getting older, and isnt something you should think you have to live with. Its a real medical condition that deserves treatment.
Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises And Biofeedback
Pelvic floor muscle exercises , originally described by Kegel in 1948 for stress incontinence, may also reduce urge incontinence episodes. In a study by Burgio et al. 197 women with urge incontinence were randomized in to three groups. Patients on PFME with biofeedback had an 80.7% reduction in incontinent episodes compared to a 68.5% and a 39.4% reduction in patients on medical therapy and placebo. Three studies randomized patients with mixed incontinence to PFME, PFME with bladder training and control groups. The two groups utilizing PFME had improvement ranging from 54 to 74% in comparison to the control group. Though most of the trials are on patients with mixed and stress incontinence, a Cochrane Meta-analysis concluded that PFME is valid first line therapy for urinary incontinence.
Biofeedback ensures that with PFME, the right muscle groups are being exercised and can vary from verbal feedback to vaginal or anal electromyography. A randomized study showed a 69.4, 63.1 and 58.5% reduction in incontinence with verbal feedback, anal myometry feedback and in controls, with the difference between the three groups not reaching statistical significance.
Also Check: Does Oxybutynin Cure Overactive Bladder
Uti And Other Symptoms
Urinary incontinence is a common sign of a UTI. Other symptoms typically occur along with the frequent urge to urinate. Someone with a UTI may also experience a burning sensation during urination or notice blood in their urine. Urine may also have a strong odor or a dark color.
Men with UTIs may experience rectal pain, while women with UTIs may have back or pelvic pain.
If you have any of these symptoms, you should be evaluated by a doctor. If youre diagnosed with a UTI, your doctor will prescribe a course of antibiotics.
Precautions And Proper Diagnosis
The main symptoms of OAB can also occur in other health conditions like bladder cancer, urinary tract infection and enlarged prostate. Seeing blood in your urine is not a symptom of OAB.
A sudden and frequent need to urinate is common in both OAB and a UTI. How can you tell the difference between these two urinary health issues? Unlike OAB, a UTI also comes with other symptoms such as discomfort while urinating. In addition, OAB symptoms are continuous while UTI symptoms are sudden and may also include a fever.
Overflow incontinence is characterized by the involuntary release of urine from an overfull urinary bladder, often in the absence of any urge to urinate. This condition is not associated with OAB. It typically occurs in people who have a blockage of the bladder outlet, which can occur with benign prostatic hyperplasia, prostate cancer or a narrowing of the urethra. Overflow incontinence can also occur when the muscle responsible for removing urine from the bladder is too weak to empty the bladder in a normal way.
It is very important to see a doctor to ensure a proper diagnosis if you experience any changes in your urine and/or urination habits.
Read Also: Why My Bladder Is Weak
Antimuscarinics In Neuropathic Bladder
Propiverine hydrochloride is one of the few drugs recommended for the treatment of detrusor overactivity by the International Consultation on Incontinence. It comprises a neurotropic and a musculotropic mode of action, thus inducing antimuscarinic effects as well as effects on the calcium influx and calcium-homeostasis. In a dosage-optimizing study of spinal cord injured adults, Mazur and coworkers recommended 15 mg propiverine thrice daily dose as being adequate in most patients. Subsequently, Stohrer et al. proved the efficacy of propiverine compared to placebo over a treatment period of 14 days by documenting urodynamic improvements.
In a multicenter placebo-controlled double-blind study 61 patients with spinal cord injuries and detrusor hyperreflexia were treated with 20 mg trospium chloride twice daily over a period of 3 weeks. Pre- and post treatment urodynamic measurements demonstrated large improvements in maximum cystometric capacity , decreased maximum detrusor pressure and an increase in compliance in the treatment group. Significant difference for these parameters was reported with, no effect on maximum flow rate and residual urine.
Keeping A Bladder Diary May Help Identify Triggers
Keeping a diary may sound time consuming, but it will help both you and your doctor identify any triggers for your overactive bladder and establish just how often you visit the bathroom each day.
How should you keep a diary for your overactive bladder?
- Document exactly what kind of fluids you drink and their volume.
- Write down the type and quantity of food you eat.
- Record the number of trips to the bathroom and rate your trips as successful or not.
- Indicate what you were doing when leakage or the urge to urinate occurred
Also Check: How To Train A Weak Bladder
Types Of Urinary Incontinence
There are different types of incontinence:
- Stress incontinence occurs when urine leaks as pressure is put on the bladder, for example, during exercise, coughing, sneezing, laughing, or lifting heavy objects. Its the most common type of bladder control problem in younger and middle-age women. It may begin around the time of menopause.
- Urge incontinence happens when people have a sudden need to urinate and cannot hold their urine long enough to get to the toilet. It may be a problem for people who have diabetes, Alzheimers disease, Parkinsons disease, multiple sclerosis, or stroke.
- Overflow incontinence happens when small amounts of urine leak from a bladder that is always full. A man can have trouble emptying his bladder if an enlarged prostate is blocking the urethra. Diabetes and spinal cord injuries can also cause this type of incontinence.
- Functional incontinence occurs in many older people who have normal bladder control. They just have a problem getting to the toilet because of arthritis or other disorders that make it hard to move quickly.