Endometriosis And Interstitial Cystitis
A 2018 study showed that people with endometriosis often have bladder pain syndrome, also known as interstitial cystitis .1 This bladder inflammation can cause pelvic pain symptoms and bladder tenderness that can feel like a UTI.2 In my case, this led to an over prescription of antibiotics that didnt treat the underlying problem.
After a couple years of complaining that the antibiotics werent helping, my OBGYN finally sent me to a urologist. The first one told me just to pee after sex, which wasnt helpful since my pain wasnt actually from an infection. I wanted a second opinion, so I went to another urologist. After a cystoscopy when a doctor puts a terrifyingly long camera into the urethra it showed my entire bladder lining was red: a sign of chronic inflammation.
Need more info about bladder problems caused by endometriosis?
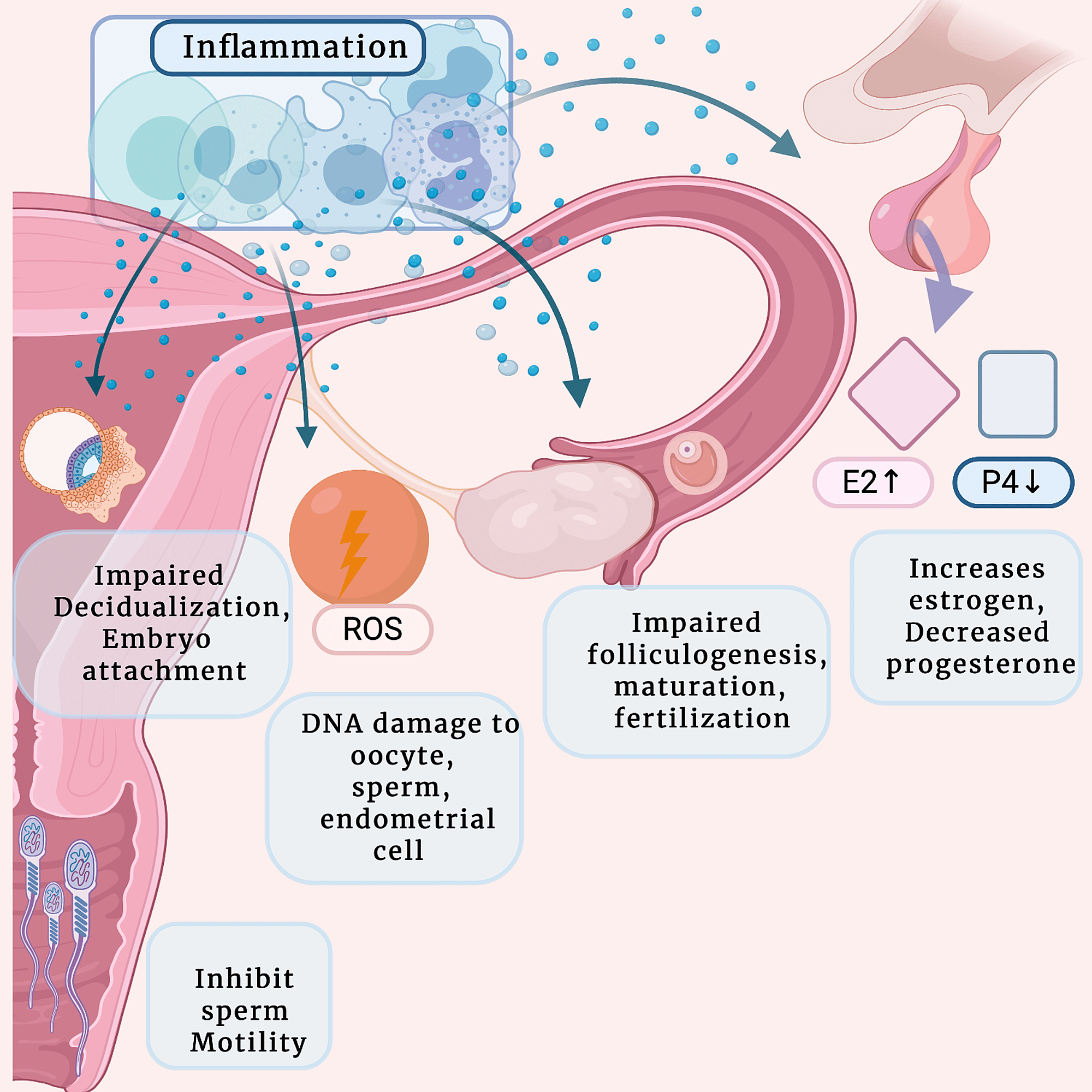
As far as I know, I dont have endometriosis on or in my bladder. However, an endometriosis specialist told me that endometriosis causes systematic inflammation, which can lead to the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines throughout the bloodstream. And if my pelvic organs are already inflamed from endo, sex can irritate my endometrial lesions even further.
IC can result from non-endo related issues, but gynecologists should be aware that the two often overlap.3,4 Its important to identify the cause of the symptoms in order to treat them effectively.
You May Like: How To Fix A Fallen Bladder
How Is Bowel Endometriosis Diagnosed
Bowel endometriosis is usually diagnosed by laparoscopy and proctoscopy . If you are having symptoms of constipation alternating with watery diarrhea, then your physician may order a CT scan of your abdomen to rule out an obstruction of the bowel that can be caused by endometriosis or another type of abnormal mass.
If you are having any rectal bleeding, then a gastrointestinal specialist should evaluate you to rule out the possibility of colon cancer. In fact, all patients age 50 years or older should be screened for colon cancer regardless of symptoms, as bowel cancer is the 3rd most common cancer in the U.S.
As mentioned, symptoms of bowel endometriosis are similar to other gastrointestinal diseases, such as irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, and even appendicitis. Sometimes patients have these diseases along with bowel endometriosis. Therefore, a thorough workup is required by both your gynecologic surgeon and a gastrointestinal specialist to make the diagnosis of these disorders.
Endometriosis And The Urinary Tract
CW: Contains surgical imagery
Endometriosis of the urinary tract involves endometrial like glands and stroma in or around the bladder, ureters or kidneys. In up to 20-50% of people with pelvic endometriosis, it is found close to the bladder and ureters. Endometriosis that grows directly into the bladder muscle or ureter occurs less commonly in only about 1-6% of cases. The symptoms associated with urinary tract endometriosis can be relatively nonspecific, making diagnosis difficult.
The urinary tract is made up of the left and right kidneys, which connect down to the bladder in the pelvis by a long tube called the ureter . Each kidney is about the size of your clenched fist. They function as our blood filtration system to remove potentially harmful substances and waste through the formation of liquid urine. The urine travels from the kidneys down through each of the tubular ureters, where it is stored in the bladder, to be expelled at your convenience through the urethra. Endometriosis can have direct and indirect effects on all the anatomical structures in the pelvis and, as a result, cause a variety of symptoms.
Image 1: The urinary tract, Kidneys, Ureters and Bladder
Image 2: Extensive superficial endometriosis over the bladder peritoneum
Image 3 -3cm Bladder deep infiltrating endometriosis nodule seen on transvaginal ultrasound
Image 4: Bladder DIE muscle lesion seen at cystoscopy
Image 6: Deep infiltrating bladder endometriosis seen from a laparoscopic view
Read Also: How Long For Bladder Infection To Go Away
Managing Pain From Endometriosis On The Ovaries
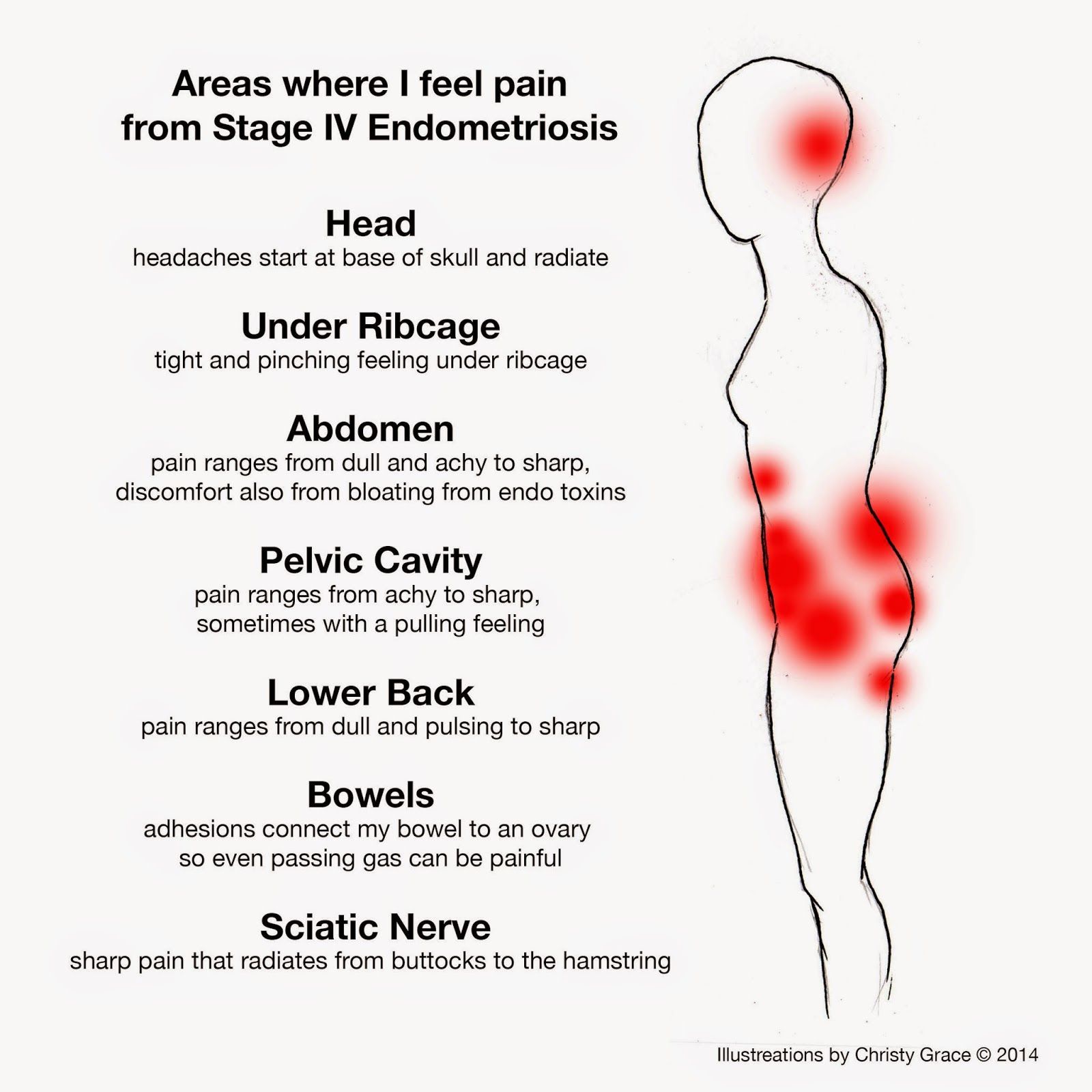
Pain from lesions, implants, scarring, adhesions, and cysts on the ovaries is common. Endometriosis pain can be severe and can have an impact on quality of life. Members of MyEndometriosisTeam report feeling varying levels of pain in and around their ovaries. My right ovary feels like its always swollen and inflamed, wrote one member. Another commented, My ovaries are killing me and Im so nauseous.
There are several approaches for managing endometriosis pain caused by endometriosis on the ovaries.
Interstitial Cystitis Is Challenging To Diagnose
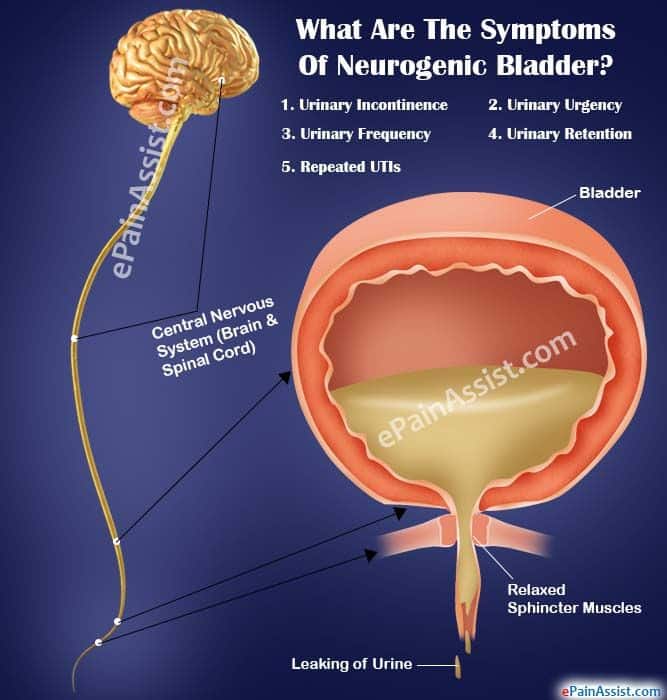
Diagnosing interstitial cystitis is a process of elimination. Your physician may use urinalysis, physical exams, and voiding diaries to evaluate your bladder health before ordering ultrasounds, cystoscopy, or urodynamic testing.
They have to rule out all other issues that could be causing your symptoms before confirming interstitial cystitis.
Also Check: Natural Remedies For Bladder Leakage
How Does Endometriosis And Exercise Fit Into All Of This
Endometriosis can hurt directly it can hurt indirectly . It will cause pelvic floor pain from spasm, which can then progress on to become its own disease, which correct exercises can help or incorrect exercises can worsen. And this pain can even continue when the endometriosis has been removed surgically. If the endo is gone, you may be tempted to ask, then why does it still hurt? While some surgeons give up at this point and proceed to hysterectomy, a trip to a pelvic floor physical therapist may make that drastic step unnecessary. This is especially poignant, since endo sufferers often have endo-related infertility, and removing the uterus is a final burning of the bridges.
This is a tragedy which happens all too often!
Treatment Of Bladder Endometriosis
Treatment of BE includes pain management and hormonal therapy. Surgery is also an option. Hormonal therapy is usually an effective treatment option for BE, but it is not a cure.
DIE that affects how the bladder or ureters function may require surgery to treat symptoms and prevent complications like bleeding or ureter blockage.
Don’t Miss: Bladder Cancer Recurrence After 5 Years
Diagnosis Of Bladder De
Bladder DE is a histologic diagnosis. The initial evaluation of suspected bladder endometriosis includes the medical history, a physical examination, and complementary tests .
4.3.1. Medical History and Physical Examination
Women with bladder endometriosis often have endometriosis at other anatomic sites therefore, the initial history and physical assessment include speculum examination , tenderness on vaginal examination, nodules in the posterior vaginal fornix, adnexal masses, and immobility or lateral displacement of the uterus.
4.3.2. Laboratory Testing
For women with clinical symptoms of bladder DE , a urinalysis test to exclude infection or hematuria should be conducted. If infection is suspected, a urinary culture should also be done. Women with hematuria and suspected bladder endometriosis should receive further testing.
4.3.3. Imaging Techniques
Ultrasound
Bladder base deep endometriosis nodule encroaching on the bladder dome.
Transvaginal ultrasound depiction of ureteral deep endometriosis nodule and hydroureter . The nodule originates from the uterosacral ligament but infiltrates the parametrium and extrinsically compresses the ureter.
A transabdominal scan of the kidneys is recommended in all women with concerns for UTE in order to exclude the presence of hydronephrosis, as this is usually asymptomatic in cases of ureteral DE .
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Supplementary Imaging
Cystourethroscopy
Clinical Symptoms Of Bladder De
Endometriosis classically causes cyclic pain and infertility. Typically, women with bladder DE present with dysuria but may also have urinary frequency, recurrent urinary tract infections and hematuria, and, more atypically, urinary incontinence . Bladder endometriosis can also be asymptomatic and incidentally diagnosed at the time of a cystoscopic or intra-abdominal procedure for a different indication. As far as we are aware, the frequency of incidental diagnoses of bladder endometriosis is still unknown.
Also Check: Regaining Bladder Control After Catheter Removal
Incontinence And Bladder Endometriosis
For many professionals, association of bladder endometriosis with urinary incontinence does not have a simple explanation. However, we do know that trapped blood in your organs can cause painful symptoms, and can often cause inflammation. This pain can make it difficult to urinate or have a bowel movement. If your bladder is affected by endometriosis, you may experience an overactive bladder.
In addition to this, women with endometriosis may also experience painful bladder or urination symptoms. These problems include:
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Incontinence is often the most embarrassing symptom to manage with bladder endometriosis. One woman with endometriosis states, because of the endometriosis on my bladder, I suffer from incontinence. It catches me completely off guard sometimes, and to be honest, Im mortified by it. I also know Im not the only one who has this. She goes on to explain how frequently problems such as stomach problems arise. She states out of nowhere, you can have an upset stomach.
How Is Bladder Endometriosis Treated
The treatment for bladder endometriosis is similar to that of pelvic endometriosis. It can be managed with hormonal regulating medications. However, for definitive treatment, the endometriosis needs to be surgically removed. Because endometriosis usually involves the full thickness of the bladder, a portion of the bladder wall usually needs to be removed.
Also Check: Natural Remedies For Uti Or Bladder Infection
And So Is Endometriosis
Here at Maiden Lane Medical, our endometriosis experts have years of experience in diagnosing and treating endometriosis, so we get to the root cause of your symptoms quickly.
However, like interstitial cystitis, there isnt a single test to confirm your diagnosis.
With endometriosis, we can use a very well-done history and physicals as well as ultrasound and MRI, but ultimately, laparoscopic surgery is the only way to be sure that any abnormal tissue and pain are due to endometriosis.
Talk To Others Who Understand
MyEndometriosisTeam is the social network for people with endometriosis. More than 123,000 members come together to ask questions, give advice, and share their stories with others who understand life with endometriosis.
Do you have endometriosis that affects your ovaries? Share your experience in the comments below, or start a conversation by posting on your Activities page.
Read Also: How To Detect Bladder Cancer Early
What Treatment Is Available For Endometriosis On The Bladder
If you are diagnosed with endometriosis on the bladder you can control the symptoms with a combination of painkillers and hormonal treatments depending on the severity of your symptoms. Should you choose not to have treatment for your bladder endometriosis, your symptoms are likely to continue and may worsen over time. Sometimes complementary treatments are useful with controlling symptoms, though these are not scientifically proven treatments.
Surgery on is the usual treatment for bladder endometriosis the surgical options vary depending on severity and the area affected. The areas affected by endometriosis can be vaporised with a laser, burned with diathermy or excised to remove them. You can expect to have a urinary catheter and, in some cases of deep endometriosis, a ureteric stent fitted during and for a few days after the operation.
To learn more about endometriosis and the bladder, download our Information Pack
A Rare Cyclic Recurrent Hematuria Case Bladder Endometriosis
Süha Akpnar1, Güliz Ylmaz1, Emre Çelebiolu2
1 Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, Near East University, Nicosia, North Cyprus, Turkey 2 Deparment of Radiology, Burhan Nalbantolu State Hospital, Nicosia, North Cyprus, Turkey
Correspondence to:
Abstract: Endometriosis is a benign gynecological disease that is characterized by the presence of functional endometrial tissue outside the uterus. Although the ovaries and uterine ligaments are the most common locations, urinary tract involvement especially the bladder endometriosis is a rare entity in women of reproductive age with clinical symptoms of cyclical urgency, hematuria and suprapubic pain. We herein present magnetic resonance imaging findings of spontaneous bladder endometriosis case with cyclical hematuria symptoms.
Keywords: Magnetic resonance imaging endometriosis bladder
Submitted Jul 21, 2014. Accepted for publication Aug 04, 2014.
doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4292.2014.08.05
Figure 1Figure 2
Endometriosis mostly presents within the ovaries and uterine ligaments which is commonly known as chocolate cyst because of the recurrent internal hemorrhage. The symptoms of the bladder endometriosis are cyclical urgency, hematuria and suprapubic pain. Cyclical menstrual hematuria is pathognomonic for bladder endometriosis however it is present in only 20% of patients .
Disclosure: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Read Also: Bcg Treatment For Bladder Cancer Procedure
Are Endometriosis And Interstitial Cystitis Related
Endometriosis and interstitial cystitis have similar symptoms. Both conditions can be challenging to diagnose, and some patients are misdiagnosed with one, the other, or both.
Additionally, studies show that women with endometriosis are up to four times more likely to develop interstitial cystitis. But what is the connection between these two painful and disruptive conditions?
First, lets review what endometriosis and interstitial cystitis are.
Endometriosis is a reproductive health issue that causes endometrial tissue to form outside of the uterus, leading to painful adhesions.
Interstitial cystitis is an immune system dysfunction that denudes the protective coating of the bladder, allowing urine to irritate the bladder.
Both conditions cause disruptive symptoms, including:
- Tenderness and trigger points in the abdomen
- Pelvic floor dysfunction
- Pain in the low back, hips, groin, and tailbone
- Painful intercourse
- Urinary urgency and incontinence
The conditions are so similar and co-occur so frequently that you might hear them referred to as the evil twins of pelvic pain.
Why is it challenging to tell the difference between endometriosis and interstitial cystitis?
There are a few reasons why endometriosis and interstitial cystitis are hard to differentiate.
History And Physical Examination
A thorough history and physical examination are critical for an evaluation of any patient who presents with CPP. During the history, it is important to ask about the onset of symptoms and the extent and location of the pain . Details on voiding symptoms, such as urgency, hesitancy, and/or frequency, should be determined as well.30
A physical examination should be performed to evaluate for tenderness and to determine whether the tenderness elicited reproduces the pain that the patient typically experiences.1 In patients with IC, a pelvic examination will often reveal tenderness of the bladder base, even upon gentle palpation.28 A commonly overlooked finding in patients with CPP is levator muscle spasm and its associated myofascial pain.38 The examination should also rule out vaginitis and other pelvic pathology.28
A urinalysis and urine culture should be performed to detect the presence of infection or hematuria. Patients with IC may also have a concurrent bladder infection that requires diagnosis and treatment.28,39 Additional tests such as a urine cytology may be helpful in excluding other potential diagnoses .28
The Pelvic Pain and Urgency/Frequency patient symptom scale is a questionnaire that screens for urinary urgency/frequency behaviors associated with IC, as well as pelvic pain and dyspareunia.40 Studies show that PUF scores correlate with the likelihood of a positive PST, which is an indicator of IC.40,41
Also Check: How Do I Cure A Bladder Infection
Diagnostic Evaluation Of Potential Ic
As noted, IC can be difficult to distinguish from disorders like endometriosis.25 Gynecologists, who see more women with CPP than other specialists, should be aware of the symptom overlap between IC and endometriosis and should screen patients with pelvic pain for IC.25 When a patient presents with symptoms typically attributed to endometriosis, or with unresolved endometriosis, the following diagnostic approach may help determine whether IC is a contributing factor.
A Case Of Bladder Endometriosis That Became Symptomatic During The Third Trimester
Endometriosis may become symptomatic during pregnancy.
-
When a mass detected in the bladder, the most appropriate tool for diagnosis is cystoscopic biopsy.
-
Cystoscopy during pregnancy may fail to detect bladder nodules.
-
With decidual changes endometriotic nodules in the bladder can mimic malignancy during pregnancy.
Also Check: Icd 10 For Metastatic Bladder Cancer
Getting The Right Diagnosis
As people with endometriosis know, getting the right diagnosis is key to treating the condition. Simply knowing my bladder was inflamed and not infected helped me treat my symptoms more appropriately, and my chronic bladder pain ultimately resolved. When I stopped the vicious cycle of antibiotics that led to yeast infections, it felt like my immune system got a break. I treated the pain with urinary analgesics or ibuprofen instead of unhelpful antibiotics.
Most importantly, I took a break from sex when it felt like my bladder was irritated. I canât tell you exactly what relieved my chronic bladder pain, but receiving the proper diagnosis helped me on the path to a resolution.
Differential Diagnosis Of Bladder De
4.4.1. Intraluminal Bladder Lesions
Angiomas and papillomas can be diagnosed by a guided tissue sampling with cystoscopy. It is especially important to rule out bladder neoplasms, as they can mimic endometriosis symptoms and a false diagnosis of endometriosis may lead to poorer outcomes .
4.4.2. Urinary Tract Infection
This can be excluded with a urine culture test.
4.4.3. Urinary Tract Calculus
The type of pelvic pain associated with urinary tract calculus is variable in severity and duration, whereas the pain associated with bladder DE is consistent. Urinary tract calculus can be identified in ultrasound studies as mobile and echogenic formations with associated acoustic shadowing. They can be associated with bladder wall thickening due to inflammation .
4.4.4. Interstitial Cystitis
Interstitial cystitis is a clinical diagnosis that involves bladder discomfort associated with bladder repletion. This is a diagnosis of exclusion that can only be reached when other etiologies, such as malignancy or bladder DE, have been ruled out.
Don’t Miss: Antimuscarinic Drugs For Overactive Bladder
Where Is The Gallbladder And What Does It Do
The Gallbladder is an organ of the hepatobiliary system. The liver, bile ducts and gallbladder compose the entire hepatobiliary system. The Gallbladder stores bile produced in the Liver. The bile is condensed after arriving in the gallbladder. Bile aids breaking down consumed fats to be absorbed for use by the body. Bile is about 95% water and 5% dissolved compounds. The number of compounds are extensive but a few important ones include: salts, amino acids, vitamins, bilirubin, phospholipids and cholesterol. The last two compounds are sensitive to female sex hormones. This hormone sensitivity plays a role in development of gallbladder disease among persons .
In addition to its role in breakdown of ingested fats, the excretion of bile also eliminates toxins, metals and drugs from our body. When a meal is consumed, the gallbladder releases bile into the small intestine via the Sphincter of Odi. The majority of digestion occurs in this first portion of the small intestine.