Can Anything Be Done To Prevent Prolapse
Although no one knows for sure, it makes sense that if you do regular strengthening exercises called Kegel exercises, the muscles will maintain their strength and prolapse will be prevented. Many doctors believe that undergoing a cesarean section instead of natural childbirth will reduce the likelihood of subsequent prolapse. Beware, though, a cesarean section has its own complications and it might not be the best solution for you. Elective cesarean section is a controversial subject, which you should discuss in detail with your doctor if you are considering it.
Prolapse Of The Uterus
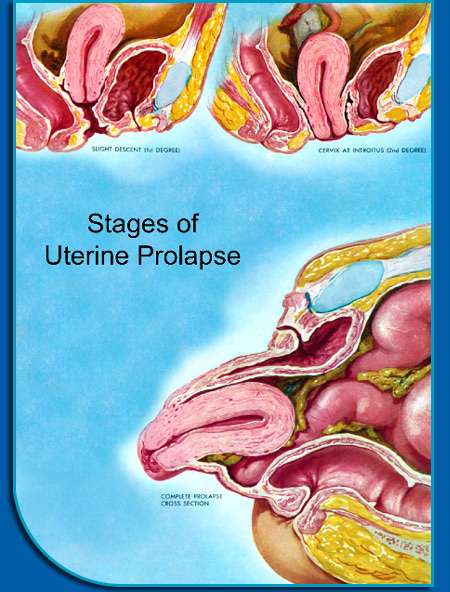
In prolapse of the uterus, the uterus drops down into the vagina. It usually results from weakening of the connective tissue and ligaments supporting the uterus. The uterus may bulge in the following ways:
-
Only into the upper part of the vagina
-
Down to the opening of the vagina
-
Partly through the opening
-
All the way through the opening, resulting in total uterine prolapse
How far down the uterus drops down determines how severe symptoms are.
At first, prolapse of the uterus may cause mild or no symptoms. When prolapses worsens, the first symptom most women report is feeling a bulge at the opening of the vagina. They may also have pain in the lower back or over the tailbone, difficulty having a bowel movement, and pain during sexual intercourse, as well as a feeling of heaviness or pressureâa feeling that pelvic organs are dropping out.
Total uterine prolapse can cause pain during walking. Sores may develop on the protruding cervix and cause bleeding, a discharge, and infection.
Constipation Constipation in Adults Constipation is difficult or infrequent bowel movements, hard stool, or a feeling that the rectum is not totally empty after a bowel movement . (See also Constipation… read more can occur.
The Major Types Of Pelvic Organ Prolapse And Their Differences
Its been reported that 23.7% of women experience some form of pelvic floor disorder. Common issues range from urinary incontinence to several kinds of pelvic organ prolapse . A prolapse is the slipping down or forward of a part or Read More
Its been reported that 23.7% of women experience some form of pelvic floor disorder. Common issues range from urinary incontinence to several kinds of pelvic organ prolapse . A prolapse is the slipping down or forward of a part or organ, often as a result of weakened or stretched connective tissue. Prolapses happen for both men and women, but women have several more types of prolapse that may affect the pelvic region of their bodies. This may cause pressure, pain during sex, incontinence, stretching sensations or lower back pain, an odd bulging sensation like sitting on a ball and in severe cases the prolapsed organ may sink so that parts are exposed outside of the body. Taking preventative measures, such as doing pelvic floor exercises, may help prevent these issues in women.
Recommended Reading: Turbt Treatment For Bladder Cancer
How Do I Know If I Need Treatment
For the overwhelming majority of patients with prolapse treatment is completely elective. That means you decide if the symptoms are bad enough to warrant treatment. However, for some patients, treatment is medically necessary because your prolapse causes a blockage to the kidneys or such a severe blockage to the bladder that you are not able to urinate at all.
Many Women Are Living With Uncomfortable Pelvic Organ Prolapse Here Are Your Next Steps If You’re One Of Them
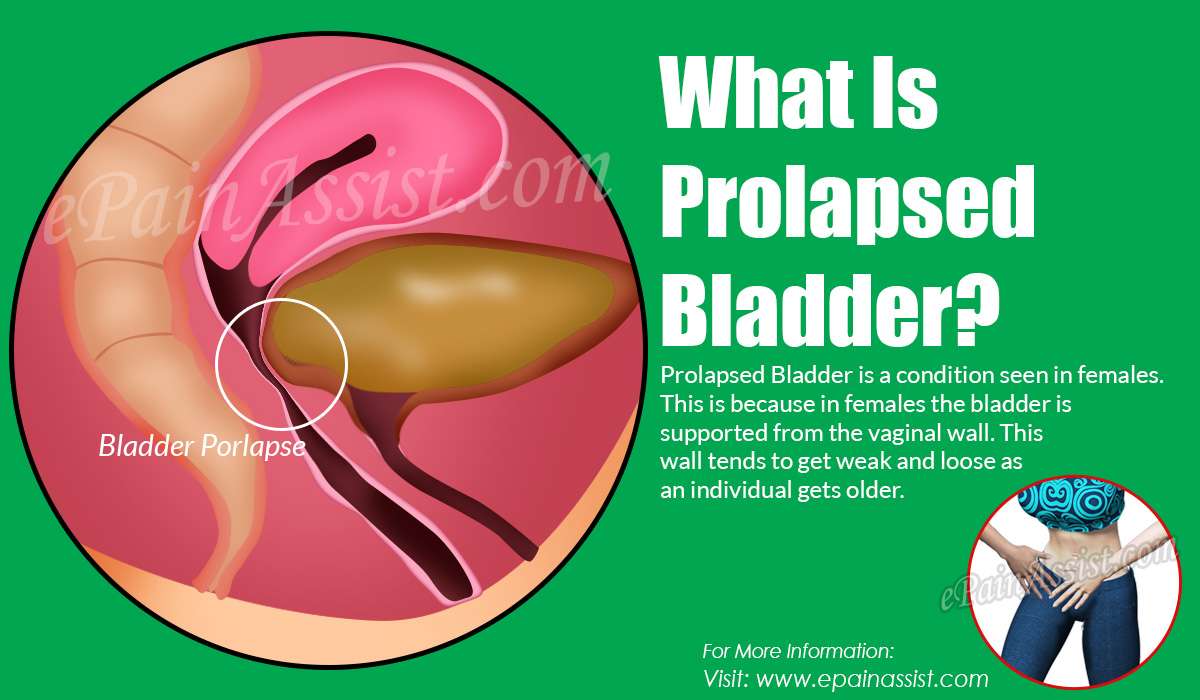
One of the most uncomfortableand awkwardconditions that afflicts women is pelvic organ prolapse. Normally, the pelvic organsthe bladder, uterus, vagina, and rectumare supported and held in place by a group of muscles and tissues called the pelvic floor. When these muscles weaken over time, the pelvic organs can droop down and bulge out of the vagina.
In addition to the sensation of feeling an uncomfortable bulge in the vagina, you can experience symptoms such as
- pain or pressure in the pelvis, the lower back, or both
- urinary problems, like urine leaking or the feeling that you need to constantly urinate
Recommended Reading: Hernia Of The Urinary Bladder
Risk Factors And Other Causes Of A Prolapsed Bladder
Prolapsed bladders in women are commonly associated with menopause. The lower levels of estrogen associated with menopause can cause the vaginal walls to weaken. If they deteriorate enough, the bladder is no longer supported and can fall into the vagina. This can cause urinary problems such as stress incontinence.
Other risk factors for bladder prolapse are:
- Childbirth
- Surgery, such as a hysterectomy
- Constipation or irregular bowel movements
- Excessive strain on the pelvic muscles from things like long-term constipation, lifting heavy objects or weight gain
- Chronic coughing
Treatment Of Pelvic Organ Prolapse
The first treatment your doctor might recommend is pelvic floor physical therapy, which may include . You squeeze and release the muscles you use to hold in gas, which strengthens the muscles that help to support the pelvic organs.
It’s important to do Kegels the right way, Dr. Wakamatsu says. A physical therapist can use techniques like biofeedback to help you find the right muscles to squeeze. Physical therapy with Kegels may be enough to relieve prolapse symptoms.
Your doctor might also recommend a device called a . Pessaries are made from silicone and come in many different shapes. The pessary is inserted into the vagina to help support the prolapsed organs. It is usually fitted to you, and it’s removable.
Surgery is an option for women who aren’t comfortable with the idea of using a pessary, or who have tried it and found it didn’t relieve their symptoms. There are several different types of surgery, based on the location and severity of the prolapse and other health issues. For women who have uterine prolapse, often a hysterectomy is recommended. Women who are at high risk for repeated prolapse may have a procedure called sacrocolpopexy, in which the surgeon works through small incisions in the abdomen to reposition the pelvic organs back where they should be.
Don’t Miss: Causes Of Weak Bladder Muscles
No Relief After Voiding The Bladder
When individuals feel no relief after voiding their bladder, it may indicate they have a prolapsed bladder. When the bladder prolapses, the malfunction causes part of the bladder to sag to an elevation underneath where the urethra meets the bladder. This bulge can be referred to as a cystocele. As a result of gravity and the impaired position of part of the bladder, patients cannot effectively fully empty their entire bladder. The reason is that urine accumulates in the cystocele, the region of the bladder that sags underneath the point where the urethra meets the bladder, and has no force to push it up to that opening.
The sensations a healthy individual experiences when the bladder contains a considerable amount of urine that needs to be voided are a result of the nerves in the bladder communicating with the brain. The brain then signals the sphincter to expel the urine, which effectively turns off the sensation individuals feel when they need to urinate. However, the brain will continue to send electrical signals to the nerves around the bladder that cause these sensations in prolapsed bladder patients because urine is still present.
Exams And Tests For A Prolapsed Bladder
An exam of the female genitalia and pelvis, known as a pelvic exam, is required in order to diagnose a prolapsed bladder. A bladder that has entered the vagina confirms the diagnosis.
For less obvious cases, the doctor may use a voiding cystourethrogram to help with the diagnosis. A voiding cystourethrogram is a series of X-rays that are taken during urination. These help the doctor determine the shape of the bladder and the cause of urinary difficulty. The doctor may also test or take X-rays of different parts of the abdomen to rule out other possible causes of discomfort or urinary difficulty.
After diagnosis, the doctor may test the nerves, muscles, and the intensity of the urine stream to help decide what type of treatment is appropriate.
A test called urodynamics or video urodynamics may be performed at the doctor’s discretion. These tests are sometimes referred to as “EKGs of the bladder”. Urodynamics measures pressure and volume relationships in the bladder and may be crucial in the decision making of the urologist.
Cystoscopy may also be performed to identify treatment options. This test is an outpatient office procedure that is sometimes performed on a television screen so the person can see what the urologist sees. Cystoscopy has little risk and is tolerable for the vast majority of people.
Read Also: 3 Types Of Bladder Cancer
What Are The Symptoms Of Prolapse
The most common symptom of Prolapse is a feeling of pressure in the lower abdomen, vaginal or rectal area a feeling like you are sitting on a ball. In severe cases you may actually see the prolapse protruding from the vagina and, if so, it may get irritated and cause a discharge or even bleeding. With more severe degrees of prolapse it may be difficult to urinate, causing you to have to push or strain. You may experience a weak urine stream and feel like you do not empty your bladder. You may be unable to urinate at all, in which case you would need to have a catheter passed into the bladder to empty the urine. Sometimes the prolapse can block the kidneys causing kidney failure. Fortunately, when the prolapse is repaired the kidneys usually return to normal, provided that the condition is caught early enough.
Prolapse may also cause constipation. If you push or strain, instead of the stool coming out, you may push the rectum down and the stool can get stuck in a pocket.
Protection For Bladder Prolapse & Incontinence
While youâre going through these treatments, it can be helpful to wear protection against little urine leaks resulting from your condition so you can feel as comfortable as possible. Always Discreet liners and pads come in a variety of different sizes and absorbencies to match urinary needs. Always Discreet liners and pads quickly turn liquid and odors into gel to keep you confident and comfortable throughout your day.
Recommended Reading: Stage 4 Bladder Cancer Symptoms
How To Prevent Pelvic Organ Prolapse
“Women should lose weight if they’re overweight. They should stop smoking because it can lead to repetitive coughing,” Dr. Wakamatsu says. “And they should protect their pelvic floor by pulling in their lower abdominal muscles and tightening their pelvic floor muscles when they lift heavy objects.”
What You Need To Know

- Vaginal prolapse, also known as vaginal vault prolapse, occurs when the top of the vagina weakens and collapses into the vaginal canal. In more serious cases of vaginal prolapse, the top of the vagina may bulge outside the vaginal opening.
- Symptoms of vaginal prolapse include the feeling of vaginal pressure or fullness like youre sitting on a small ball and the sensation that something has fallen out of your vagina.
- A cystocele or rectocele usually occurs with vaginal prolapse.
- Mild cases of vaginal prolapse do not require treatment. Moderate to severe symptoms require nonsurgical therapies or minimally invasive surgeries, such as vaginal prolapse repair.
Also Check: Bladder Cancer Ct Scan With Contrast
Prolapsed Bladder Care At Home
For mild-to-moderate cases of prolapsed bladder, the doctor may recommend activity modification such as avoiding heavy lifting or straining. The doctor may also recommend Kegel exercises. These are exercises used to tighten the muscles of the pelvic floor. Kegel exercises might be used to treat mild-to-moderate prolapses or to supplement other treatments for prolapses that are more serious.
Stages Of Bladder Prolapse
The severity of bladder prolapse can be measured in several ways. Terms such as mild, moderate and severe are not always completely accurate, as they depend on a persons opinion, but are often used in day-to-day conversations to help people understand the severity of the prolapse.A more commonly used grading is:
- Stage 1 the bladder protrudes a little way into the vagina
- Stage 2 the bladder protrudes so far into the vagina that its close to the vaginal opening
- Stage 3 the bladder protrudes out of the vagina
- Stage 4 most severe form, in which all pelvic organs including the bladder protrude out of the vagina.
Many gynaecologists now use the Pelvic Organ Prolapse Quantification system, which measures in centimetres where the prolapse is in relation to the vaginal entrance to ascertain the stage of prolapse.
Also Check: Can You Treat A Bladder Infection Without Antibiotics
What Can Be Expected After Treatment For A Cystocele
In mild cases, non-surgical treatments may be all that is needed to successfully deal with a cystocele.
When surgery is performed for more serious cases, some women will eventually need another surgery because the first surgery failed, the cystocele returned or another pelvic floor problem developed. Women who are older, who smoke, are diabetic, or who have had a hysterectomy, may be at higher risk for complications.
How Do Health Care Professionals Diagnose A Cystocele
To diagnose a cystocele, health care professionals ask about your symptoms and medical history and perform a physical exam, including a pelvic exam to check your lower abdomen. You may be asked to stand during part of the exam, which may feel awkward but allows your health care professional to determine the severity of your cystocele. Your health care professional may also order medical tests to determine how advanced the cystocele is or to help find or rule out other problems in your urinary tract or pelvis.
Read Also: Is Pumpkin Seed Oil Good For Overactive Bladder
How Can You Tell If Your Bladder Has Dropped
The urinary bladder is a hollow organ in the pelvis that stores urine. During urination, urine leaves the bladder and exits the body through the urethra. The vagina supports the front of the bladder in women. This wall can weaken with age or get damaged during vaginal childbirth. If weakness is significant, the bladder can prolapse , and this is called bladder prolapse or cystocele.
Many patients may be asymptomatic in the early stages. Signs and symptoms of a prolapsed bladder depend on the extent and grade of prolapse. Patients can usually tell if their bladder has dropped when they face difficulty urinating, pain or discomfort, and stressincontinence , which are the most common symptoms of a prolapsed bladder. One of the early symptoms of a prolapsed bladder is the presence of tissue that feels like a ball in the vagina. Some common signs and symptoms of a prolapsed bladder include:
How Is Prolapse Treated
Many women with prolapse don’t need treatment, as the problem doesn’t seriously interfere with their normal activities.
Lifestyle changes such as weight loss and pelvic floor exercises are usually recommended in mild cases.
If the symptoms require treatment, a prolapse may be treated effectively using a device inserted into the vagina, called a vaginal pessary. This helps to hold the prolapsed organ in place.
Surgery may also be an option for some women. This usually involves giving support to the prolapsed organ. In some cases, complete removal of the womb is required, especially if the womb has prolapsed out.
Most women experience a better quality of life after surgery, but there’s a risk of problems remaining or even getting worse.
Also Check: High Grade Bladder Cancer Recurrence
Anterior Vaginal Wall Prolapse
Anterior vaginal wall prolapse often occurs at the top of the vagina where the uterus used to be in women who have had a hysterectomy. This type of prolapse occurs when the bladder’s supportive tissue, called fascia, stretch or detach from the attachments securing it to the pelvic bones. With this loss of support, the bladder falls down into the vagina. As this condition worsens, the prolapsed pelvic organs may bulge outside the opening of the vagina causing pressure, discomfort or pain. Other symptoms MAY include:
- Urinary frequency, nighttime voiding, loss of bladder control and recurrent bladder infectionsusually due to the bladder not emptying well
- Stress urinary incontinence with activity such as laughing, coughing, sneezing, or exercise) cause by weakened support for the urethra
Why Does Prolapse Happen
Prolapse is caused by weakening of tissues that support the pelvic organs. Although there’s rarely a single cause, the risk of developing pelvic organ prolapse can be increased by:
- your age prolapse is more common as you get older
- childbirth, particularly if you had a long or difficult labour, or gave birth to multiple babies or a large baby up to half of all women who have had children are affected by some degree of prolapse
- changes caused by the menopause such as weakening of tissue and low levels of the hormone oestrogen
- being overweight, obese or having large fibroids or pelvic cysts which creates extra pressure in the pelvic area
- previous pelvic surgery such as a hysterectomy or bladder repair
- repeated heavy lifting and manual work
- long-term coughing or sneezing for example, if you smoke, have a lung condition or allergy
- excessive straining when going to the toilet because of long-term constipation
Certain conditions can also cause the tissues in your body to become weak, making a prolapse more likely, including:
- joint hypermobility syndrome where your joints are very loose
- an inherited condition that affects the blood vessels, eyes and skeleton
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome a group of inherited conditions that affect collagen proteins in the body
Read Also: What Does Overactive Bladder Feel Like
What Causes A Prolapsed Bladder
Factors commonly associated with causing a prolapsed bladder are those that weaken the pelvic floor muscles and ligaments that support the bladder, urethra, uterus, and rectum, which can lead to detachment from the ligaments or pelvic bone where the muscles attach:
- Pregnancy and childbirth: This is the most common cause of a prolapsed bladder. The delivery process is stressful on the vaginal tissues and muscles, which support a woman’s bladder.
- Aging can lead to weakening of the muscles.
- Menopause: Estrogen, a hormone that helps maintain the strength and health of supporting tissues in the vagina, is not produced after menopause.
- Previous pelvic surgery: such as hysterectomy
- Other risk factors that increase the pressure within the abdomen, leading to increased pressure on the pelvic floor muscles include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease , obesity, constipation, and heavy manual labor .