Living With Bladder Cancer
Cancer is a life-changing experience. And although there’s no surefire way of preventing a recurrence, you can take steps to feel and stay healthy. Eating plenty of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and keeping to modest portions of lean meat is a great start. If you smoke, stop. Limit alcohol to one drink a day for women and up to two drinks a day for men. Daily exercise and regular checkups will also support your health and give you peace of mind.
Safe Handling In Health Care Settings
As of 2018, there were no set for antineoplastic drugs, i.e., OSHA or the have not set workplace safety guidelines.
Preparation
NIOSH recommends using a that is designed to decrease worker exposure. Additionally, it recommends training of all staff, the use of cabinets, implementing an initial evaluation of the technique of the safety program, and wearing protective gloves and gowns when opening drug packaging, handling vials, or labeling. When wearing , one should inspect gloves for physical defects before use and always wear double gloves and protective gowns. Health care workers are also required to wash their hands with water and soap before and after working with antineoplastic drugs, change gloves every 30 minutes or whenever punctured, and discard them immediately in a chemotherapy waste container.
The gowns used should be disposable gowns made of polyethylene-coated polypropylene. When wearing gowns, individuals should make sure that the gowns are closed and have long sleeves. When preparation is done, the final product should be completely sealed in a plastic bag.
The health care worker should also wipe all waste containers inside the ventilated cabinet before removing them from the cabinet. Finally, workers should remove all protective wear and put them in a bag for their disposal inside the ventilated cabinet.
Administration
Employee training
Housekeeping and waste disposal
Spill control
What Tests Will I Have If My Doctor Suspects Bladder Cancer Or Another Urinary Problem
Your doctor will want to analyze your urine to determine if an infection could be a cause of your symptoms. A microscopic examination of the urine, called cytology, will look for cancer cells.
A cystoscopy is the main procedure to identify and diagnose bladder cancer. In this procedure, a lighted telescope is inserted into your bladder from the urethra to view the inside of the bladder and, when done under anesthesia, take tissue samples , which are later examined under a microscope for signs of cancer. When this procedure is done in the doctors office, local anesthesia gel is placed into the urethra prior to the procedure to minimize the discomfort.
If the diagnosis of bladder cancer is made, then the next step is to remove the tumor for detailed staging and diagnosis.
Transurethral resection is a procedure done under general or spinal anesthesia in the operating room. A telescope is inserted into the bladder and the tumor is removed by scraping it from the bladder wall , using a special cystoscope . This procedure is diagnostic as well as therapeutic.
This often can be done as an outpatient procedure, with patients discharged from hospital the same day. After removal, the tumor is analyzed by a pathologist, who will determine the type of tumor, the tumor grade and the depth of invasion. The purpose of the procedure is to remove the tumor and obtain important staging information .
Also Check: Sulfa Medication For Bladder Infection
Treatment Of Stage Iv Bladder Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage IV bladder cancer that has not spread to other parts of the body may include the following:
- Urinary diversion or cystectomy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
Treatment of stage IV bladder cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, such as the lung, bone, or liver, may include the following:
- External radiation therapy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Urinary diversion or cystectomy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- A clinical trial of new anticancer drugs.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Signs And Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
Sometimes bladder cancer doesnt have many symptoms. Signs or symptoms can include:
- blood in your urine
- pain or burning when passing urine
- not being able to pass urine when you need to.
Not everyone with these symptoms has bladder cancer. If you have any of these symptoms or are worried, always see your doctor.
Don’t Miss: New Drug For Overactive Bladder
Treatment Of Recurrent Bladder Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of recurrentbladder cancer depends on previous treatmentand where the cancer has recurred. Treatment for recurrent bladder cancer mayinclude the following:
- Radiation therapy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- A clinical trial of a new treatment.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Treating Bladder Cancer That Progresses Or Recurs
If cancer continues to grow during treatment or comes back after treatment , treatment options will depend on where and how much the cancer has spread, what treatments have already been used, and the patient’s overall health and desire for more treatment. Its important to understand the goal of any further treatment if its to try to cure the cancer, to slow its growth, or to help relieve symptoms as well as the likely benefits and risks.
For instance, non-invasive bladder cancer often comes back in the bladder. The new cancer may be found either in the same place as the original cancer or in other parts of the bladder. These tumors are often treated the same way as the first tumor. But if the cancer keeps coming back, a cystectomy may be needed. For some non-invasive tumors that keep growing even with BCG treatment, and where a cystectomy is not an option, immunotherapy with pembrolizumab might be recommended.
Cancers that recur in distant parts of the body can be harder to remove with surgery, so other treatments, such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or radiation therapy, might be needed. For more on dealing with a recurrence, see Understanding Recurrence.
You May Like: Tuberculosis Virus To Treat Bladder Cancer
Cancer That Has Spread To The Bladder
Sometimes cancer that has started elsewhere in the body can spread to the bladder. This can happen with prostate, rectum, ovary, cervix and womb cancer for example.
Cancers that have spread from somewhere else in the body are called secondary cancers. The cancer cells are the same type as the first cancer. So is the treatment.
If you have cancer that has spread to the bladder, you need to go to the section about your primary cancer.
-
Cancer and Its Management J Tobias and D HochhauserWiley Blackwell, 2015
-
A M Kamat and othersThe Lancet, 2016. Volume 388, Pages 276 -2810
-
AJCC Cancer Staging Manuel American Joint Committee on CancerSpringer, 2017
-
Bladder cancer: diagnosis and management of bladder cancerNational Institute of Health and Clinical Excellence, 2015
-
Bladder Cancer
Evaluation Of Upper Urinary Tract
Additional workup for all patients with bladder cancer includes evaluation of the upper urinary tract with intravenous urography , renal ultrasonography, computed tomography urography, or magnetic resonance urography.21,22 Renal ultrasonography alone is insufficient to complete the evaluation of hematuria in a patient with bladder cancer because it cannot delineate details of the urinary collecting system. Traditional IVU has been largely replaced by CT urography because of increased detail and data combined in the CT .
For patients unable to undergo contrast injection , magnetic resonance urography may be used to evaluate the upper urinary tract. These tests are useful for disease staging and excluding other causes of hematuria. Pelvic imaging should be performed before transurethral resection to improve staging accuracy because postoperative inflammation mimics the appearance of tumor infiltration.21 Pelvic imaging also may detect synchronous upper tract urothelial cancer, which can occur in 5 percent of patients with bladder cancer.22
Also Check: Best Over The Counter Bladder Control Medication
What Is The Most Aggressive Form Of Bladder Cancer
In general, bladder cancers that are muscle invasive and/or have high-grade cells are the most serious and aggressive. The less common types of bladder cancer such as squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, and small cell carcinoma have a greater tendency to be muscle invasive compared to urothelial carcinoma. However, if left untreated, initially low-grade, non-muscle invasive urothelial carcinoma can progress into the bladder wall and spread to other parts of the body.
The prognosis for bladder cancer is very favorable when the disease is detected early, so it is important to see your doctor if you are experiencing symptoms that could be due to bladder cancer. The most common early sign of bladder cancer is the presence of blood in the urine . Other symptoms that may be experienced include urinary irritation and changes in bladder habits. For further information regarding the signs and symptoms of bladder cancer, see Bladder Cancer Symptoms.
Ial Or Radical Cystectomy
Some people with stage 2 or stage 3 bladder cancer will need to undergo surgery to remove part of the bladder or surgery to remove the entire bladder . If you need to have a radical cystectomy, the surgeon will often create another way for urine to be stored and removed from the body. Some people who have a radical or partial cystectomy may also have chemotherapy treatment.
Recommended Reading: Malignant Neoplasm Of Trigone Of Bladder Icd 10
Stage 3 Bladder Cancer
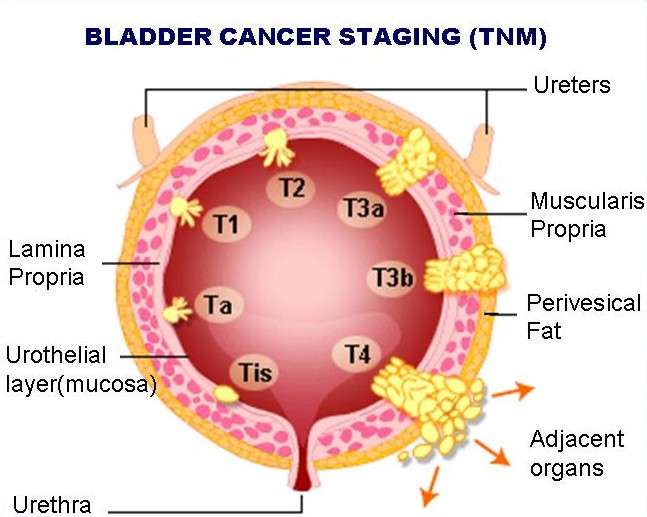
Stage 3 bladder cancer means that the cancer cells have spread beyond the bladder muscle.1,2,3 Stage 3 bladder cancer includes the following combined TNM stages:
In all three types of stage 3 bladder cancer, the cancer cells have not spread to the lymph nodes near the bladder and they have not spread to other parts of the body.
In a bladder tumor that is stage T3a or stage T3b, the bladder cancer cells have grown into the layer of fatty tissue that surrounds the outside of the bladder. This layer of fatty tissue is called perivesical tissue.
In a stage T3a bladder tumor, the bladder cancer cells in the perivesical tissue are only visible through a microscope. In a stage T3b bladder tumor, the bladder cancer cells have grown into the perivesical tissue and are large enough that they are visible using an imaging test or they can be felt by a healthcare professional. A stage T4a bladder tumor is different in women and men. In women, the stage T4a tumor has grown through the perivesical tissue and into the uterus and/or vagina. In men, the stage T4a tumor has grown through the perivesical tissue and into the prostate. However, in both women and men, a stage T4a tumor has not grown into the pelvic wall or the abdominal wall.
Sexual Effects Of Radical Cystectomy In Women
This surgery often removes the front part of the vagina. This can make sex less comfortable for some women, though most of the time it’s still possible. One option is to have the vagina rebuilt . There’s more than one way to do this, so talk with your surgeon about the pros and cons of each method. Whether or not you have reconstruction, there are many ways to make sex more comfortable.
Radical cystectomy can also affect a womans ability to have an orgasm if the nerve bundles that run along each side of the vagina are damaged. Talk with your doctor about whether these nerves can be left in place during surgery.
If the surgeon takes out the end of the urethra where it opens outside the body, the clitoris can lose some of its blood supply, which might affect sexual arousal. Talk with your surgeon about whether the end of the urethra can be spared.
For more on ways to cope with these and other sexual issues, see Sex and the Woman With Cancer.
Read Also: Homeopathic Medicine For Bladder Infection
Stage 2 Bladder Cancer
A diagnosis of stage 2 bladder cancer means that the bladder cancer cells have grown into the muscle layer of the bladder wall.1,2 This is also called muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Stage 2 bladder cancer includes the following combined TNM stages:
In both of those types of stage 2 bladder cancer, the cancer cells have not grown into the nearby lymph nodes and they have not spread to other parts of the body. The muscle portion of the bladder wall has two layers. The inner half, closest to the bladder lining, is called the superficial muscle. The outer half is also called the deep muscle of the bladder. If the tumor is type T2a, it means that the cancer cells have spread into the superficial muscle, but not into the deep muscle. If the tumor is type T2b, the bladder cancer cells have grown through the superficial muscle and into the deep muscle of the bladder. However, the cancer cells have not yet spread into the layer of fatty tissue that surrounds the outer part of the bladder muscle.
Cancerous Tumours Of The Bladder
A cancerous tumour of the bladder can grow into nearby tissue and destroy it. It can also spread to other parts of the body. Cancerous tumours are also called malignant tumours.
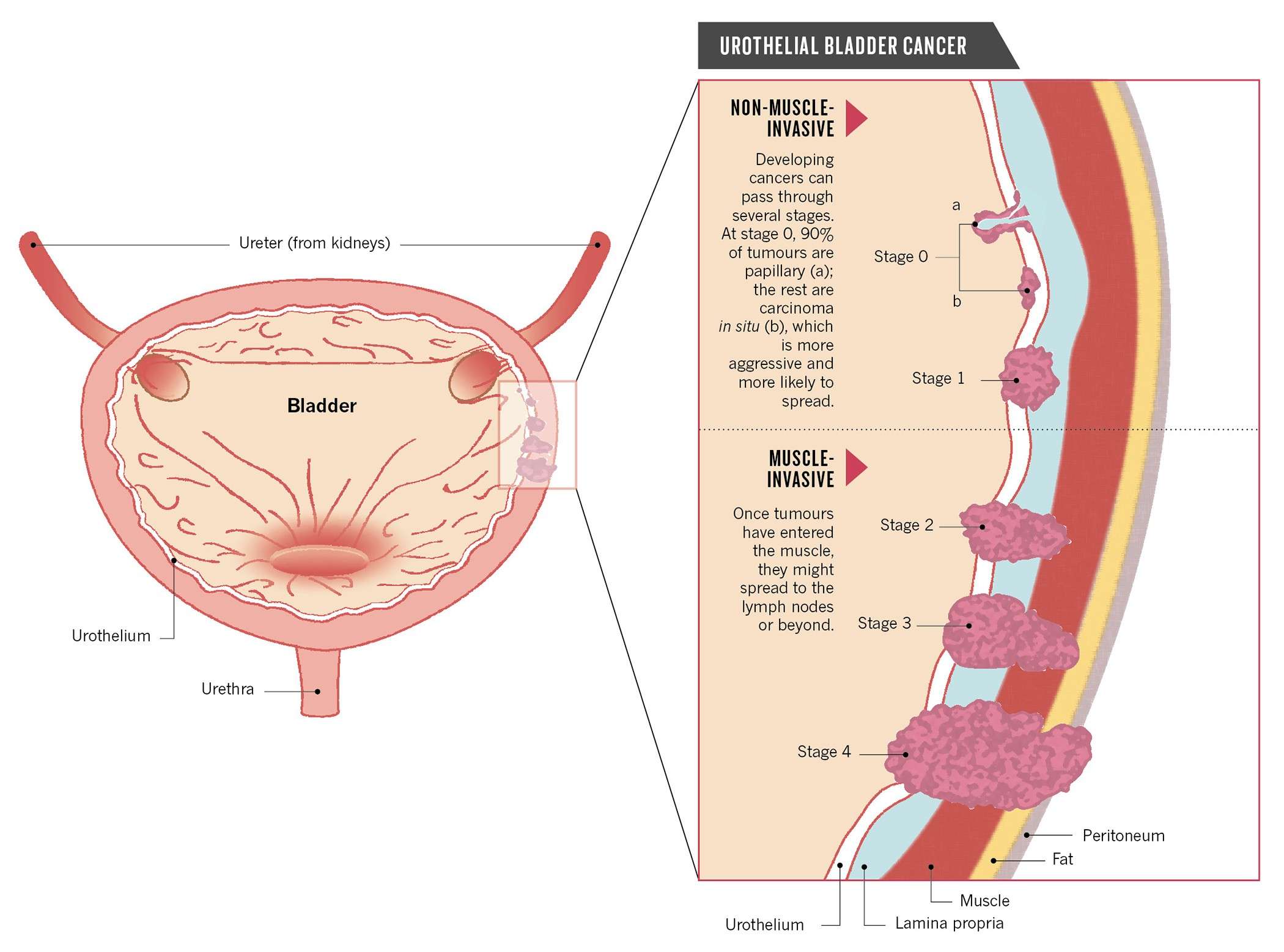
Bladder cancer is often divided into 3 groups based on how much it has grown into the bladder wall.
- Non-invasive bladder cancer is only in the inner lining of the bladder .
- Non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer has only grown into the connective tissue layer .
- Muscle-invasive bladder cancer has grown into the muscles deep within the bladder wall and sometimes into the fat that surrounds the bladder.
Also Check: How To Fix Bladder Leakage Naturally
There Are Three Ways That Cancer Spreads In The Body
Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood:
- Tissue. The cancer spreads from where it began by growing into nearby areas.
- Lymph system. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the lymph system. The cancer travels through the lymph vessels to other parts of the body.
- Blood. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through the blood vessels to other parts of the body.
Treating Stage Iv Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the pelvic or abdominal wall , may have spread to nearby lymph nodes , and/or have spread to distant parts of the body . Stage IV cancers are very hard to get rid of completely.
Chemotherapy is usually the first treatment if the cancer has not spread to distant parts of the body . The tumor is then rechecked. If it appears to be gone, chemo with or without radiation or cystectomy are options. If there are still signs of cancer in the bladder, chemo with or without radiation, changing to another kind of chemo, trying an immunotherapy drug, or cystectomy may be recommended.
Chemo is typically the first treatment when bladder cancer has spread to distant parts of the body . After this treatment the cancer is rechecked. If it looks like it’s gone, a boost of radiation to the bladder may be given or cystectomy might be done. If there are still signs of cancer, options might include chemo, radiation, both at the same time, or immunotherapy.
In most cases surgery cant remove all of the cancer, so treatment is usually aimed at slowing the cancers growth and spread to help people live longer and feel better. If surgery is a treatment option, it’s important to understand the goal of the operation whether it’s to try to cure the cancer, to help a person live longer, or to help prevent or relieve symptoms from the cancer.
Because treatment is unlikely to cure these cancers, many experts recommend taking part in a clinical trial.
Also Check: Overactive Bladder And Back Pain
Five Types Of Standard Treatment Are Used:
Surgery
One of the following types of surgery may be done:
- Transurethral resection with fulguration: Surgery in which a cystoscope is inserted into the bladder through the urethra.A tool with a small wire loop on the end is then used to remove thecancer or to burn the tumor away with high-energy electricity. This is known as fulguration.
- Radical cystectomy: Surgery to remove the bladder and anylymph nodes and nearby organs that contain cancer. This surgery may bedone when the bladder cancer invades the muscle wall, or when superficialcancer involves a large part of the bladder. In men, the nearby organs that areremoved are the prostate and the seminal vesicles. In women, the uterus, theovaries, and part of the vagina are removed. Sometimes, when the cancer hasspread outside the bladder and cannot be completely removed, surgery to removeonly the bladder may be done to reduce urinarysymptoms caused by the cancer.When the bladder must be removed, the surgeon creates another way for urine toleave the body.
- Partial cystectomy: Surgery to remove part of thebladder. This surgery may be done for patients who have a low-grade tumor thathas invaded the wall of the bladder but is limited to one area of the bladder.Because only a part of the bladder is removed, patients are able to urinate normally afterrecovering from this surgery. This is also called segmental cystectomy.
- Urinary diversion: Surgery to make a new way forthe body to store and pass urine.
Radiation therapy
Chemotherapy