Bladder Cancer Clinical Trials
What about Clinical Trials?
You may hear about clinical trials for your bladder cancer. Clinical trials are research studies that test if a new treatment or procedure is safe and effective.
Through clinical trials, doctors find new ways to improve treatments and the quality of life for people with disease. Trials are available for all stages of cancer. The results of a clinical trial can make a major difference to patients and their families. Please visit our clinical trials research webpage to learn more.
Recommended Reading: Causes Of Weak Bladder Control
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
Bladder cancer is relatively rare, so you may not know as much as youd like about the condition. Here are some questions that may be helpful:
- What stage of bladder cancer do I have?
- What are possible treatments?
- What are treatment side effects?
- Will I need surgery?
- How will surgery affect my daily life?
- How often does bladder cancer come back?
- How do you treat recurrent bladder cancer?
- Are there any cutting-edge clinical trials available?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
If you have bladder cancer, it may help to know about half of all people with the condition receive treatment when their tumors are limited to the inner layer of their bladder wall. For them, surgery to remove tumors means theyre cancer-free. But bladder cancer often comes back . If youre worried about recurring cancer, talk to your healthcare provider. Theyre your best resource for information on risk factors that increase the chance youll have another bout of bladder cancer. Theyll help you stay vigilant about symptoms that may be signs of recurring bladder cancer and be there for you if you need more bladder cancer treatment.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 08/26/2022.
References
Bladder Cancer Diagnosis: Imaging
Intravenous Pyelogram
An intravenous pyelogram is an X-ray test with contrast material to show the uterus, kidneys, and bladder. When testing for bladder cancer, the dye highlights the organs of the urinary tract allowing physicians to spot potential cancer-specific abnormalities.
CT Scans and MRI
CT scans and MRI are often used to identify tumors and trace metastasized cancers as they spread to other organ systems. A CT scan provides a three-dimensional view of the bladder, the rest of the urinary tract, and the pelvis to look for masses and other abnormalities. CT scans are often used in conjunction with Positron emission tomography to highlight cells with high metabolic rates. âHot spotsâ of cells with abnormally high metabolism may indicate the presence of cancer and require further investigation.
Bone Scan
If a tumor is found in the bladder a bone scan may be performed to determine whether the cancer has spread to the bones. A bone scan involves having a small dose of a radioactive substance injected into the veins. A full body scan will show any areas where the cancer may have affected the skeletal system.
Recommended Reading: Can Candida Cause Bladder Infection
Recommended Reading: Difference Between Uti And Overactive Bladder
What Are Bladder Tumors
Bladder tumors are abnormal growths that occur in the bladder. If the tumor is benign, its noncancerous and wont spread to other parts of your body. This is in contrast to a tumor thats malignant, which means its cancerous.
There are several types of benign tumors that can develop within the bladder.
Understanding The Statistics: Cancer Survival
It is important to remember that all cancer survival numbers are based on averages across huge numbers of people. These numbers cannot predict what will happen in your individual case.
Survival rates will not tell you how long you will live after you have been diagnosed with bladder cancer. But, these numbers can give you an idea of how likely your treatment will be successful. Also, survival rates take into account your age at diagnosis but not whether you have other health conditions too.
Recommended Reading: Fastest Way To Cure Bladder Infection
Treatment Of Bladder Cancer By Stage
Most of the time, treatment of bladder cancer is based on the tumors clinical stage when itâs first diagnosed. This includes how deep itâs thought to have grown into the bladder wall and whether it has spread beyond the bladder. Other factors, such as the size of the tumor, how fast the cancer cells are growing , and a persons overall health and preferences, also affect treatment options.
Tests For Bladder Cancer
Your doctor may do some tests to check for bladder cancer:
- urine tests your urine will be checked for signs of bladder cancer
- blood tests to check your general health
- ultrasound a scan on the outside of your abdomen to check for cancer
- cystoscopy the doctor puts a small camera into your bladder to see inside
- biopsy the doctor takes a small sample of the cells from the bladder to check for signs of cancer.
Your doctor might ask you to have further tests. These can include:
- CT scan and x-rays scans that take pictures of the inside of the body, sometimes also called a CT-IVP or a triple phase abdominal-pelvic CT scan
- MRI scan a scan that uses magnetism and radio waves to take pictures of the inside of the body
- bone scan a scan that uses dye to show changes in your bones
- FDG-PET scan a scan that uses an injection of liquid to show cancer cells.
Also Check: Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation For Overactive Bladder
What Are The Layers Of The Bladder
The bladder consists of three layers of tissue. The innermost layer of the bladder, which comes in contact with the urine stored inside the bladder, is called the mucosa and consists of several layers of specialized cells called transitional cells, which are almost exclusively found in the urinary system of the body. These same cells also form the inner lining of the ureters, kidneys, and a part of the urethra. These cells form a waterproof lining within these organs to prevent the urine from going into the deeper tissue layers. These cells are also termed urothelial cells, and the mucosa is termed the urothelium.
The middle layer is a thin lining known as the lamina propria and forms the boundary between the inner mucosa and the outer muscular layer. This layer has a network of blood vessels and nerves and is an important landmark in terms of the staging of bladder cancer .
The outer layer of the bladder comprises of the detrusor muscle. This is the thickest layer of the bladder wall. Its main function is to relax slowly as the bladder fills up to provide low-pressure urine storage and then to contract to compress the bladder and expel the urine out during the act of passing urine. Outside these three layers is a variable amount of fat that lines and protects the bladder like a soft cushion and separates it from the surrounding organs such as the rectum and the muscles and bones of the pelvis.
Evaluating A Bladder Mass
To assess a bladder mass, urologists perform a physical examination, and blood and urine tests to evaluate for the presence of blood in the urine. You may also have a bladder wash to obtain cells from your bladder for a pathologist to analyze. But ultimately, the urologist needs to look inside your bladder via a procedure called cystoscopy.
Cystoscopy involves passing a cystoscope through the urethra and into the bladder, allowing the urologist to see what is there.
If your cystoscopy or imaging scans reveal a suspicious mass or any irregularity, such as a lesion, we will obtain a biopsy or tissue sample through an incisionless surgical procedure called Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor . During a TURBT, the surgeon inserts a tool called a resectoscope through the urethra to reach the inside of your bladder and remove a piece of tumor tissue or the entire tumor from your bladder.
A pathologist will then examine the tissue to determine whether it is benign or cancerous.
At Roswell Park, our pathologists are fully trained for all disease sites, but also specialize in diagnosing tumors of specific sites, such as the urinary tract, says Dr. Guru. As a high-volume cancer center, Roswell Park has pathologists who examine bladder mass tissue samples every day.
Don’t Miss: Sure Care Bladder Control Pads
Patients Can Enter Clinical Trials Before During Or After Starting Their Cancer Treatment
Some clinical trials only include patients who have not yet received treatment. Other trials test treatments for patients whose cancer has not gotten better. There are also clinical trials that test new ways to stop cancer from recurring or reduce the side effects of cancer treatment.
Clinical trials are taking place in many parts of the country. Information about clinical trials supported by NCI can be found on NCIs clinical trials search webpage. Clinical trials supported by other organizations can be found on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
Occurrence In The United States
The American Cancer Society estimates that 81,180 new cases of bladder cancer will be diagnosed in the United States in 2022 and that 17,100 people will die of the disease. The incidence of bladder cancer increases with age, with the median age at diagnosis being 73 years bladder cancer is rarely diagnosed before age 40 years.
Bladder cancer is about 4 times more common in men than in women. The male predominance in bladder cancer in the United States reflects the prevalence of transitional cell carcinoma . With small cell carcinomain contrast to TCCthe male-to-female incidence ratio is 1:2.
Bladder cancer is the fourth most common cancer in men in the United States, after prostate, lung, and colorectal cancer, but it is not among the top 10 cancers in women. Accordingly, more men than women are expected to die of bladder cancer in 2022, with 12,120 deaths in men versus 4980 in women. Nevertheless, women generally have a worse prognosis than men.
The incidence of bladder cancer is twice as high in White men as in Black men in the United States. However, Blacks have a worse prognosis than Whites.
Limited data indicate that small cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder probably has the same epidemiologic characteristics as urothelial carcinoma. Patients are more likely to be male and older than 50 years.
Also Check: Lack Of Bladder Control Uti
There Are Different Types Of Treatment For Patients With Bladder Cancer
Different types of treatment are available for patients with bladder cancer. Some treatments are standard , and some are being tested in clinical trials. A treatment clinical trial is a research study meant to help improve current treatments or obtain information on new treatments for patients with cancer. When clinical trials show that a new treatment is better than the standard treatment, the new treatment may become the standard treatment. Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial. Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment.
Dont Miss: How Do You Get Rid Of Overactive Bladder
Who Gets Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer is four times more common in men than women. This form of cancer is also associated with older individuals. More than 90 percent of people diagnosed with bladder cancer are over the age of 55, and the average age of diagnosis is 73.
The most common risk factor associated with this form of cancer is smoking, which is seen in about 50 percent of cases.
You May Like: Why Do You Get Bladder Infections
Who Is At Risk For Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer can affect anyone, but certain groups are at greater risk. Men are three times more likely than women to get bladder cancer. Around 90% of cases occur in people over age 55, and whites are twice as likely as African Americans to develop the condition.
Other factors that increase the risk of getting bladder cancer include a family history of the condition and previous cancer treatment. Birth defects involving the bladder increase the risk of bladder cancer. When people are born with a visible or invisible defect that connects their bladder with another organ in the abdomen, this leaves the bladder prone to frequent infection. This increases the bladders susceptibility to cellular abnormalities that can lead to cancer. Chronic bladder inflammation increase the risk of developing bladder cancer.
Transurethral Resection Of Bladder Tumor
TURBT is a conservative approach in which localized tumors are excised through transurethral approach followed by limited rounds of adjuvant intravesical therapies to allow preservation of bladder structure and function. It has been shown to correlate with improved patient quality of life . Low-risk NMIBC is characterized by < 3 cm solitary tumor, low grade with little epithelial involvement , and lack of carcinoma in situ . These patients usually undergo TURBT plus a single dose of perioperative intravesical chemotherapy within a few hours of tumor removal followed by regular follow-up and tumor surveillance . High-risk NMIBC patients with tumors larger than > 3 cm, and greater than T1 tumor grade, presence of CIS, lymphovascular invasion and/or multiple or recurrent tumors, receive TURBT combined with intravesical therapy. Alternatively, partial or radical cystectomy is considered .
D. Cao, in, 2014
Recommended Reading: Overactive Bladder Pills Over The Counter
Recommended Reading: How To Treat A Bladder Infection At Home Naturally
Bladder Cancer Is A Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In The Tissues Of The Bladder
The bladder is a hollow organ in the lower part of the abdomen. It is shaped like a small balloon and has a muscular wall that allows it to get larger or smaller to store urine made by the kidneys. There are two kidneys, one on each side of the backbone, above the waist. Tiny tubules in the kidneys filter and clean the blood. They take out waste products and make urine. The urine passes from each kidney through a long tube called a ureter into the bladder. The bladder holds the urine until it passes through the urethra and leaves the body.
There are three types of bladder cancer that begin in cells in the lining of the bladder. These cancers are named for the type of cells that become malignant :
- Transitional cell carcinoma: Cancer that begins in cells in the innermost tissue layer of the bladder. These cells are able to stretch when the bladder is full and shrink when it is emptied. Most bladder cancers begin in the transitional cells. Transitional cell carcinoma can be low-grade or high-grade:
- Low-grade transitional cell carcinoma often recurs after treatment, but rarely spreads into the muscle layer of the bladder or to other parts of the body.
- High-grade transitional cell carcinoma often recurs after treatment and often spreads into the muscle layer of the bladder, to other parts of the body, and to lymph nodes. Almost all deaths from bladder cancer are due to high-grade disease.
See the following PDQ summaries for more information:
Living With Advanced Cancer
Advanced cancer usually means cancer that is unlikely to be cured. Some people can live for many months or years with advanced cancer. During this time palliative care services can help.
Most people continue to have treatment for advanced cancer as part of palliative care, as it helps manage the cancer and improve their day-to-day lives. Many people think that palliative care is for people who are dying but palliative care is for any stage of advanced cancer. There are doctors, nurses and other people who specialise in palliative care.
Treatment may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy or another type of treatment. It can help in these ways:
- slow down how fast the cancer is growing
- shrink the cancer
- help you to live more comfortably by managing symptoms, like pain.
Treatment depends on:
- how far it has spread
- your general health
Read Also: Bladder Cancer Spread To Lymph Nodes
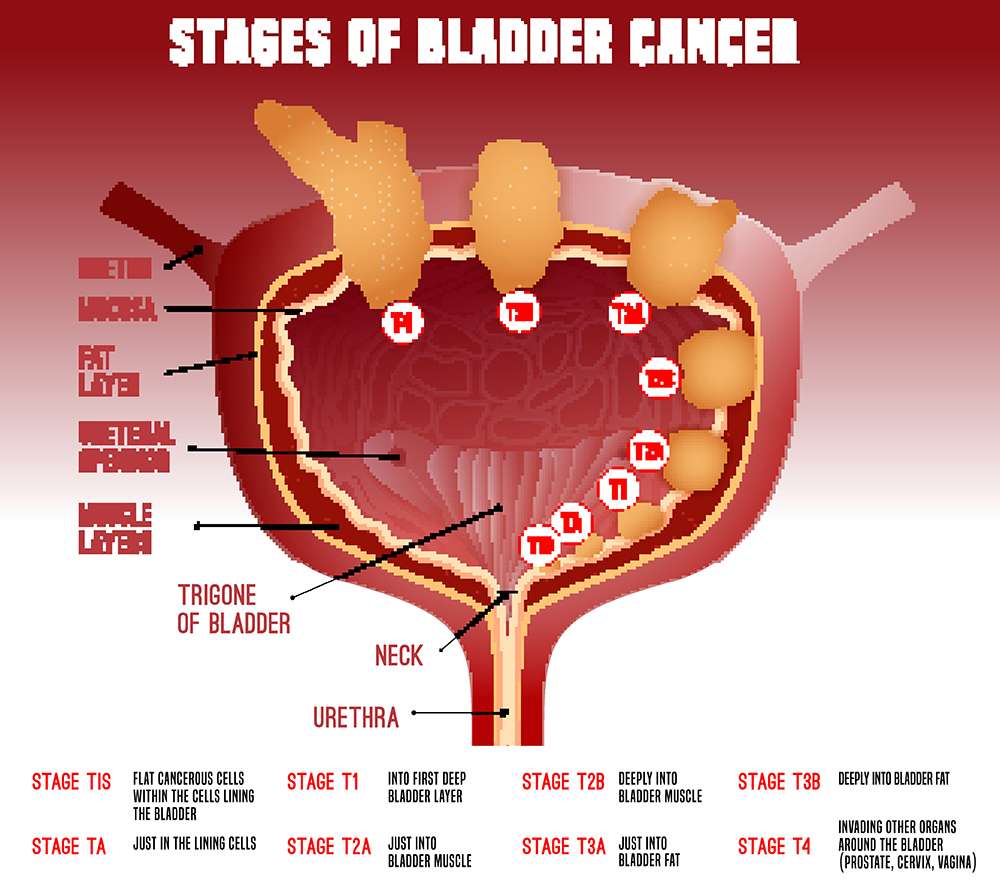
What Are The Stages Of Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer can be either early stage or invasive .
The stages range from TA to IV . In the earliest stages , the cancer is confined to the lining of the bladder or in the connective tissue just below the lining, but has not invaded into the main muscle wall of the bladder.
Stages II to IV denote invasive cancer:
- In Stage II, cancer has spread to the muscle wall of the bladder.
- In Stage III, the cancer has spread to the fatty tissue outside the bladder muscle.
- In Stage IV, the cancer has metastasized from the bladder to the lymph nodes or to other organs or bones.
A more sophisticated and preferred staging system is known as TNM, which stands for tumor, node involvement and metastases. In this system:
- Invasive bladder tumors can range from T2 all the way to T4 .
- Lymph node involvement ranges from N0 to N3 .
- M0 means that there is no metastasis outside of the pelvis. M1 means that it has metastasized outside of the pelvis.
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- What treatment do you think is best for me?
- Whats the goal of this treatment? Do you think it could cure the cancer?
- Will treatment include surgery? If so, who will do the surgery?
- What will the surgery be like?
- How will I pee after surgery?
- Will I have other types of treatment, too?
- Whats the goal of these treatments?
- What side effects could I have from these treatments?
- Is there a clinical trial that might be right for me?
- What about treatments like special vitamins or diets that friends tell me about? How will I know if they are safe?
- What should I do to be ready for treatment?
- Is there anything I can do to help the treatment work better?
- Whats the next step?
Also Check: Best Medicine For Bladder Leakage
What About Other Treatments That I Hear About
When you have cancer you might hear about other ways to treat cancer or treat your symptoms. These may not always be standard medical treatments. These treatments can be vitamins, herbs, special diets, and other things. You may be curious about these treatments.
Some of these are known to help, but many have not been tested. Some have been shown not to be helpful. A few have even been found to be harmful. Talk to your doctor about anything youre thinking about using, whether its a vitamin, a diet, or anything else.
Dont Miss: Harmony Urinary Tract And Bladder Support