Lnmat1 Directly Interacts With Hnrnpl
We subsequently performed an RNA pull down assay using in vitro transcribed biotinylated LNMAT1 and an antisense control to identify LNMAT1-interacting proteins in UM-UC-3 cells. An obvious band at between 50 and 75kDa was specifically enriched in the LNMAT1 pull down proteins . hnRNPL was identified as the most abundant LNMAT1-interacting proteins via mass spectrometry . To validate the physical interaction between LNMAT1 and hnRNPL, we performed RNA pull down followed by western blot using hnRNPL antibody. The results showed that LNMAT1 specifically interacted with hnRNPL but not with hnRNPQ or hnRNPA1 . Consistently, RIP assays using nuclear extract or RNA pull down assay with purified recombinant hnRNPL protein demonstrated that LNMAT1 directly interacted with hnRNPL . Serial deletion analysis demonstrated that 5-terminal region of the LNMAT1 were required for direct interaction with hnRNPL , which was further confirmed by RNA pull down with truncated LNMAT1 . Moreover, overexpression of the truncated LNMAT1 in LNMAT1-silenced bladder cancer cells restored the CCL2 upregulation function of LNMAT1 . These data suggest that, in bladder cancer cells, LNMAT1 regulates CCL2 expression through direct interaction with hnRNPL.
Fig. 6
Bladder And Urinary Troubles
A prostate tumor that has grown significantly in size may start to press on your bladder and urethra. The urethra is the passage the carries urine from your bladder out of your body. If the tumor is pressing on your urethra, you might have trouble passing urine.
One of the common areas for prostate cancer to spread to is the bladder, because the two organs are close. This can cause additional problems with urination and bladder function.
Some symptoms your bladder and urethra are being affected by cancer include:
- urinating more frequently
- getting up in the middle of the night to pee
- having blood in your urine or semen
- feeling like you have to urinate often and not actually passing anything
Its not as common, but prostate cancer can also spread to your bowel. The cancer first spreads to the rectum, which is the part of your bowel closest to the prostate gland.
Symptoms of cancer thats spread to the bowels include:
- stomach pain
Stage Iv Bladder Cancer
Stage IV cancer is the most advanced form of bladder cancer. It is called metastatic. This means the cancer has spread to distant lymph nodes or organs. Cancers that have spread beyond the bladder into the wall of the abdomen or pelvis are also considered Stage IV. Stage IV cancer is usually treated with chemotherapy and, more recently, with immunotherapy as well.
People with bladder cancer of all stages may be able to participate in a clinical trial. Clinical trials are research studies that test new treatments to see how well they work.
Recommended Reading: Can Sugar Cause Bladder Infection
Setting Your Browser To Accept Cookies
There are many reasons why a cookie could not be set correctly. Below are the most common reasons:
- You have cookies disabled in your browser. You need to reset your browser to accept cookies or to ask you if you want to accept cookies.
- Your browser asks you whether you want to accept cookies and you declined. To accept cookies from this site, use the Back button and accept the cookie.
- Your browser does not support cookies. Try a different browser if you suspect this.
- The date on your computer is in the past. If your computer’s clock shows a date before 1 Jan 1970, the browser will automatically forget the cookie. To fix this, set the correct time and date on your computer.
- You have installed an application that monitors or blocks cookies from being set. You must disable the application while logging in or check with your system administrator.
Stage Ii Bladder Cancer
Stage II cancer has invaded the muscle of the bladder wall but is still confined to the bladder. Depending on the extent and grade of the cancer, we may recommend a partial or total cystectomy. Some people may need chemotherapy before surgery. We may be able to remove the tumor with TUR followed by radiation and chemotherapy.
You May Like: Get Rid Of Bladder Infection Naturally
How Is Bladder Cancer Treated
Treatment for bladder cancer will depend on the stage and type of cancer you have. Your provider will talk to you about treatment options and which plan of care is best for you.
Superficial Bladder Cancer
Superficial bladder cancer is bladder cancer that has not invaded into the muscle. It is often treated with surgery and intravesicular therapy.
Surgery
A TURBT is a surgical treatment in which a surgeon removes the bladder tumor using a tool placed into the body through the urethra. The extent of the disease is based mainly on findings during this test. TURBT is the main treatment for superficial disease since all of the tumor is often able to be removed. After a TURBT, you may have intravesicular therapy to prevent the cancer from coming back.
Intravesicular Therapy
Intravesicular therapy is when chemotherapy or immune therapy is injected directly into the bladder. This treatment destroys any remaining cancer cells. Both immunotherapy and chemotherapy medications can be used in intravesicular therapy.
Bacillus Calmette-Guerin is an immunotherapy medication that is used. BCG is a type of virus that works to stimulate the immune system to destroy any cancer cells in the area. You will likely be given this medication multiple times. After treatment, you will have regular cystoscopies to monitor for any reoccurrence or new tumor development.
Muscle Invading Bladder Cancer
Surgery
Chemotherapy
Bladder Preservation Therapy
Radiation and Chemoradiation
Immunotherapy
When Does Cancer Spread To The Lymph Nodes
The rate that cancer spreads to a persons lymph nodes may depend on the cancer they have.
Some cancers can spread more quickly to the lymph nodes. Other cancers are slow to develop, and may spread at a slower rate.
Certain cancers may only spread to lymph nodes on rare occasions. Research indicates that osteosarcomas, a form of bone cancer, only spread to the lymph nodes in 411% of cases.
Cancer can affect people in different ways, so it can be hard to predict how it may spread.
When a doctor discusses a persons cancer with them, they may refer to the stage it is at. Different stages of cancer indicate how far it has spread from its original location.
The National Cancer Institute states that the stages of cancer are:
- Stage 0: Stage 0 cancer, also called carcinoma in situ , is when abnormal cells are present, but have not spread.
- Stage 1, 2, and 3: Stages 1 to 3 indicate that there is cancer present. The higher the stage, the larger and more spread out the cancer is.
- Stave 4: Stage 4 cancer is when the cancer has spread to areas that are distant from the original tumor.
Healthcare professionals also break stage 3 into multiple categories, including 3a, b, and c. The stage at which cancer has spread to the lymph nodes varies. According to the United Kingdoms National Health Service, the cancer may have spread to the lymph nodes at stage 3.
| Number beside the N |
- for melanoma
Discovering and treating cancer early can
You May Like: Foods To Prevent Bladder Cancer Recurrence
Survival For All Stages Of Bladder Cancer
Generally, for people diagnosed with bladder cancer in England:
- around 75 out of every 100 survive their cancer for 1 year or more after diagnosis
- almost 55 out of every 100 survive their cancer for 5 years or more after they are diagnosed
- around 45 out of every 100 survive their cancer for 10 years or more after diagnosis
Cancer survival by stage at diagnosis for England, 2019Office for National Statistics
These statistics are for net survival. Net survival estimates the number of people who survive their cancer rather than calculating the number of people diagnosed with cancer who are still alive. In other words, it is the survival of cancer patients after taking into account that some people would have died from other causes if they had not had cancer.
Will Treatment Cause Erectile Dysfunction
When youre sexually excited, nerves cause tissues in your penis to relax, allowing blood to flow into the organ. The nerves that control erection are very delicate. Surgery or radiation for prostate cancer may damage them enough to cause ED. When you have ED, you cant get or keep an erection.
Radical prostatectomy is a surgery to remove the prostate gland. When your surgeon removes the gland, they may damage the nerves and blood vessels that run along it. If theyre damaged enough, you wont be able to get an erection following the procedure.
Today, doctors can do nerve-sparing surgery, which helps prevent permanent ED. Your surgeon can still touch those nerves and blood vessels, causing ED as a temporary side effect. Many men have trouble getting an erection for a few weeks, months, or even years after their procedure.
Radiation therapy also damages blood vessels and the nerves that control erection. Up to half of men who have radiation for prostate cancer experience ED afterward. In some men, this symptom will improve with time. Sometimes radiation side effects dont appear until a few months after the treatment. If ED starts late, it may not be as likely to go away.
A few treatments can help with ED until youre able to have erections on your own again.
Additional treatments include the following:
Recommended Reading: Foods Good For Bladder Control
Remission And The Chance Of Recurrence
A remission is when cancer cannot be detected in the body and there are no symptoms. This may also be called having no evidence of disease or NED.
A remission may be temporary or permanent. This uncertainty causes many people to worry that the cancer will come back. While many remissions are permanent, it is important to talk with your doctor about the possibility of the cancer returning. Understanding your risk of recurrence and the treatment options may help you feel more prepared if the cancer does return. Learn more about coping with the fear of recurrence.
If the cancer returns after the original treatment, it is called recurrent cancer. It may come back in the same place , nearby , or in another place .
When this occurs, a new cycle of testing will begin again to learn as much as possible about the recurrence. After this testing is done, you and your doctor will talk about the treatment options.
People with recurrent cancer often experience emotions such as disbelief or fear. You are encouraged to talk with the health care team about these feelings and ask about support services to help you cope. Learn more about dealing with cancer recurrence.
Demographics And Pathological Characteristics
A total of 10,653 patients with BCA from the SEER database who met the criteria were registered in the present study. A total of 5,327 patients, including 2,757 patients with positive lymph nodes and 2,570 patients with negative lymph nodes, were randomly assigned to a training set, and the remaining 5,326 patients, including 2,768 patients with positive lymph nodes and 2,558 patients with negative lymph nodes, were assigned to the verification set. The characteristics of these patients are presented in Table 1.
Table 1 Clinicopathological characteristics of the cohort by lymph node status.
You May Like: How To Take Care Of A Bladder Infection At Home
When To Contact A Doctor
If a person notices any signs of cancer having spread to their lymph nodes, they should speak with a doctor immediately.
Additionally, if a person with cancer notices any unusual new symptoms, they should contact a doctor. The sooner a person receives treatment for cancer that has spread, the better their chances of survival.
What Causes Bladder Cancer And Am I At Risk
Each year, about 83,730 new cases of bladder cancer will be diagnosed in the United States. It affects more men than women and the average age at diagnosis is 73.
Cigarette smoking is the biggest risk factor for bladder cancer. About half of all bladder cancers are caused by cigarette smoking. Other risk factors for developing bladder cancer include: family history, occupational exposure to chemicals , previous cancer treatment with cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide, or pelvic radiation, the medication pioglitazone, exposure to arsenic , aristolochic , bladder infections caused by schistosoma haematobium, not drinking enough fluids, a genetic condition called Lynch Syndrome, a mutation of the retinoblastoma gene or the PTEN gene. and neurogenic bladder and the overuse of indwelling catheters.
Don’t Miss: Will A Bladder Infection Go Away On Its Own
Find The Best Treatment For An Enlarged Prostate You Have Options
There are various treatment options available, depending on the severity of symptoms. The options range from medication to shrink the prostate, to removal of prostate tissue in surgery.
At any stage, or as a long-time solution, your doctor might recommend symptom relief with the use of a catheter. This is a good option as it empties the bladder completely every time. Resulting in that you wont have to go to the toilet in the middle of the night or have to worry about embarrassing leaks.
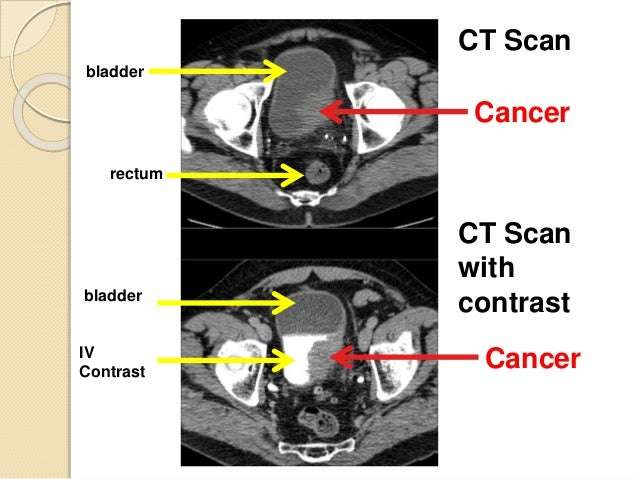
The Stages Of Invasive Bladder Cancer
Your doctor diagnoses invasive bladder cancer by looking at how far cancer tumours have grown into the bladder. This is called the T stage . There are three T stages of invasive bladder cancer:
- T2 means cancer has grown into the muscle layer of the bladder
- T3 means cancer has grown through the muscle layer into the fatty tissue layer
- T4 means cancer has grown outside the bladder OR into the prostate, womb or vagina, OR into the wall of the pelvis or tummy
Your doctor also looks at:
- whether cancer has spread to any lymph nodes
- whether or not it has spread to other parts of the body like the bones, lungs or liver
Don’t Miss: Treatment Of Overactive Bladder In Males
How Is Bladder Cancer Staged
Cancer staging describes how much the cancer has grown and invaded the area, explaining the extent of the disease. Bladder cancer is often found at an early stage, as hematuria starts early in the course of the disease. Sometimes bladder cancer can advance to invasive disease before causing symptoms. To best understand staging, you need to know how cancer spreads and advances in stage.
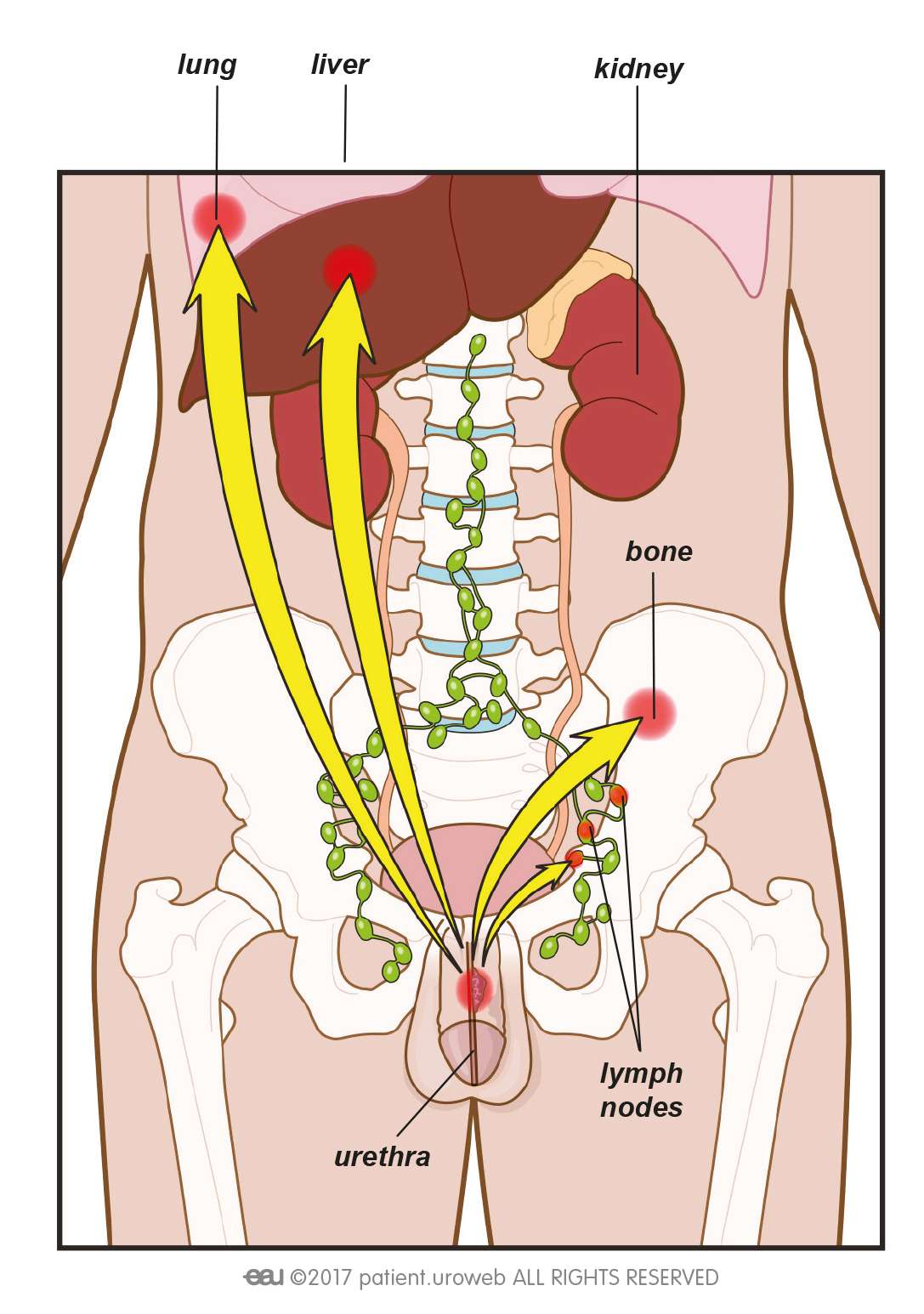
Cancers can spread and disrupt how normal organs work. Bladder cancers often begin very superficially, involving only the lining of the bladder. Bladder cancers can invade the bladder wall, involving the muscular layers of the wall. As bladder cancer grows it can invade the entire way through the wall and into the fat surrounding the bladder or even into other organs . This local extension is the most common way bladder cancer spreads.
When cancer spreads to another area in the body, that area is called metastasis. Cancer can also spread through the lymph system and the bloodstream. Bladder cancer often spreads locally or to lymph nodes before spreading distantly, though this is not always the case. The lungs and bones are the most common areas for metastases to develop. When bladder cancer spreads to another area, it is still bladder cancer. For instance, if it spreads to the lung, it is not called lung cancer, but bladder cancer that has metastasized to the lung. If we look at the affected lung tissue under a microscope, it will look like bladder cancer cells.
Swollen Lymph Nodes: What Do They Mean
Swollen lymph nodes, or swollen glands, are a symptom of many illnessesfrom the common cold to some forms of cancerand a sign that something is wrong in the body. The swelling or enlargement, called lymphadenopathy, occurs in the lymph nodes when theyre filtering cells affected by a condition, such as an infection, injury or cancer. The most common reason lymph nodes swell is because of an infection, particularly viral infections such as a cold. Its much rarer for swollen lymph nodes to be a symptom of a more serious condition such as cancer.
The lymph nodes are likely to swell in one specific region depending on the illness. This will usually occur in the neck, armpits or groin. Less common is when lymph nodes swell in several regions at the same time. That condition may be brought on by infections such as strep throat or mononucleosis, a reaction to certain medicines, an immune system disorder such as rheumatoid arthritis, and forms of cancer such as lymphoma and leukemia.
When lymph node swelling persists and is accompanied by other symptoms, such as fever or night sweats, or when theres no obvious infection, it may be time to seek medical advice or evaluation from a doctor.
You May Like: Botox Dose For Overactive Bladder
A Pictorial Review Of Bladder Cancer Nodal Metastases
Prasad R. Shankar, Daniel Barkmeier, Lubomir Hadjiiski, Richard H. Cohan
Department of Radiology, Michigan Medicine, Ann Arbor, MI , USA
Contributions: Conception and design: PR Shankar, RH Cohan Administrative support: PR Shankar Provision of study materials or patients: PR Shankar, D Barkmeier, RH Cohan Collection and assembly of data: PR Shankar, D Barkmeier, RH Cohan Data analysis and interpretation: PR Shankar Manuscript writing: All authors Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
Correspondence to:
Abstract: Lymph node involvement in bladder cancer is common and has prognostic implications. Early and accurate identification of metastatic lymph nodes is, therefore, important in ensuring appropriate patient triage and management. The purpose of this review is to provide a pictorial and educational overview of the staging and imaging appearance of metastatic lymph nodes in bladder cancer. Additionally, a secondary aim of this manuscript is to provide a review of the diagnostic accuracy of common imaging modalities available for detecting metastatic lymph nodes in affected patients.
Keywords: Bladder cancer lymph node metastasis nodal metastasis nodal staging urothelial cancer
Submitted Jun 16, 2018. Accepted for publication Aug 20, 2018.
doi: 10.21037/tau.2018.08.25
The Lymphatic System And Bladder Cancer
The lymphatic system helps protect us from infection and disease. It is part of the bodys immune system.
The lymphatic system helps protect us from infection and disease. It is part of the bodys immune system.
It also drains lymph fluid from the tissues of the body before returning it to the blood. The lymphatic system is made up of fine tubes called lymphatic vessels that connect to groups of lymph nodes throughout the body.
Lymph nodes are small and bean-shaped. They filter bacteria and disease from the lymph fluid. When you have an infection, lymph nodes often swell as they fight the infection.
Sometimes, cancer can spread through the lymphatic system. If bladder cancer cells spread outside the bladder, they can go to the lymph nodes near the bladder. These are called pelvic lymph nodes.
Recommended Reading: How To Help Overactive Bladder